Culture: Sterotypes, Conflict & Discrimination
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Hunger Games Controversy
When Amandla Stenberg was casted as Rue, there was negative comments regarding her being black
Patrica Arquette's Acceptance Oscar Acceptance Speech
- Speaking out on wage equally
- The pay gap over time
- 41% of wage gap remains
- Women still have 82% of man's salary
Many Forms of Identity
Institutional, Structural, Individual
Institutional Identity
official descriptions of who we are
Structural Identity
The large groups and social constructions with which a person is affiliated.
Individual Identity
The traits that make up a person's sense of individuality
Group-based biases
decisions made based on association with an individual or group
Group Based Bias Structure
Psychological Componets -> Affect(prejudice), Behavior(Discrimination) & Cognition (Stereotyping
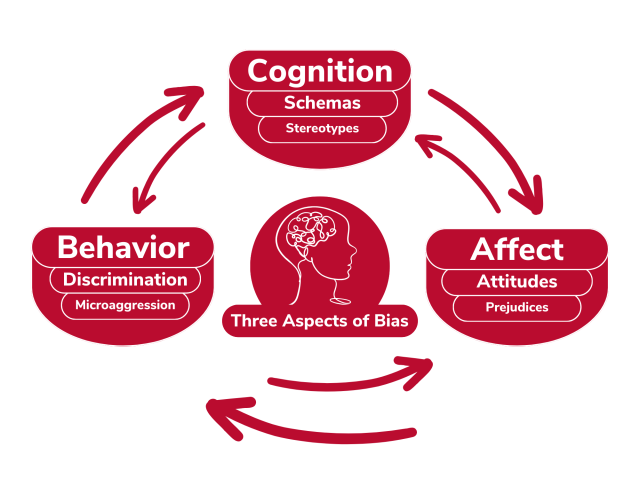
Affective Component: Prejudice
feelings associated with objects of prejudice
Old Fashion Racism Scale: Explict racism
Mordern Scale: Form of prejudice that surfaces in subtle ways when it its safe and easy to rationalize
old fashion racism scale
Antilocution: Antilocution occurs when an in-group freely purports negative images of an out-group. ...
Avoidance: Members of the in-group actively avoid people in the out-group.
Modern Racism Scale
measures "acceptable" ways to express prejudice
Explicit Racism
Prejudicial attitudes that are held in declarative memory. Always aware of your explicit prejudice
Implicit Prejudice
Auto prejudice attitudes that are the dangers to which you associate certain groups with certain traits or concepts of "good" or "bad"
Implicit vs. Explict Prejudice
Phase 1: Measuring Prejudice - Implicit & Explicit stereotyping measure
Phase 2: Interaction with In & Outgroup members - Evaluations & Eye contact Findings: Negative Correlation
- Implicit measure predicted amount of eye contact - more spontaneous auto behavior.
- Explict measure predicted evaluations - more controlled, deliberate behavior
Cognitive Component: Sterotypes
Belief or association that links a group of people with certain traits and characteristics. Can be positive, negative or neutral
Stereotype Bias Our Memory - Experiment (Method)
Participant learned wordlist of traits describing 3 Target individuals
- List either positive Sterotypes or not
Participants were asked to recall the lists later
Selective Encoding by Sterotypes (Experiment) Results
Participants recalled words by Sterotypes typically
How do you feel towards people based on stereotypes and Ingroup
Who Sterotypes?
Most people who have knowledge of cultural Sterotypes
Egalitarian Ideologies
A political philosophy that advocates for equality and fairness for all people. emphasizes social equality, advocating for equal rights, opportunities, and treatment for all, regardless of background or status.
Egalitarian Ideologies Experiment (Hypothesis)
The person is egalitarian, still activist Sterotypes automatic, but then actively surprises a prejudice response
Egalitarian Ideologies Experiment (Method)
- Participants all increase in, Except Canada: Cognitive load or not
- Rate aggressiveness of "Blk Americans" & "White Americans
Egalitarian Ideologies Experiment (Conclusion)
When egalitarian ideologies had cognitive resources to control their judgement, they didn't show a bias
Modern Racism Explanation
- Outwardly acting unprejdiced while iwardly making prejudiced attitudes
- Key is regulaly behavior
- The symbolic racism 2000 scale
Explicit Prejudice
Prejudicial attitudes that are held in declaritve memory. Always awae of your EP
Implicit Prejudice
Auto prejudice attiudes that are the degrees to which you associate certain groups with certain traits or concepts of "good" or "bad"
Stereotypes Bias our memory Experiement Method
- Participant learned wordlist of traits describing 3 target indiviuals (list either sterotype or not
- Particpant were asked to recall the lists later
Behavioral Componet: Discrimination
Action that derives from sterotyping + prejudice. Understanding the experience of targets of prejudice
Can people understand other peoples experience with prejudice
No, study shows that white people & people of color that people of other races can't truly understand the way their race sees things
Study about Discrimination Method
- White Particpants particpate in vid-chat w/ osterial other (Blk) particpants
- Particpants watch vid of Black confed talking a race-related experience vs. non-race related experience
- Need to affilate & percieved understanding
- White people desire to affilate correlated with pecieved understanding of Black partner
Reasons for Inter-group Bias
- Self-Esteem
- Need to belong
- Cognitive Misattribtuion (Snap Judgements)
- Implict Attitudes
- Evolutionary Perspective
Evolutionary Perspective
perspective that focuses on the biological bases of universal mental characteristics that all humans share
Social Identity Theory
Diffuse but interrelated set of social psychology theories about when & why indiviuals identify with, & behave as part of social groups
Assumptions of Social Idenity Theory
- Key 1: We all have a need for + self regard & how do we achieve that
- Via our own achievements
- Via identification with achievements of social groups we belong to
Main Compnets of Social Identity Theory
Categorization, Identification & Comparison
Main Compnets of Social Identity Theory: Categorization
People not grouping other social objects into groups. Creates in & out-group distinction
Reason - Cognitive Miser
Cognitive Miser
a term used to describe people's reluctance to do much extra thinking

Minimal Group Paradigm
An experimental paradigm in which researchers create groups based on arbitrary and seemingly meaningless criteria and then examine how the members of these "minimal groups" are inclined to behave toward one another
Minimal Group Paradigm Experiment: Method
- Participants came into lab in-groups
- Asked to estimate the number f dots on a page
- Random assigned to groups: "over" & "underestimators"
- Ask particpants to rate each group & allocate study payment to fellow ingroup & outgroup
Minimal Group Paradigm Experiment: Result
Doesn't matter which group you were in, you always favor you in-group
Main Compnets of Social Identity Theory: Identification
Processes of association the self with certain groups
Bolster self-esteem
Effects on social idenoty theory are dependent on identifying with the groups
Main Compnets of Social Identity Theory: Comparison
Compare In & Out groups, seeing a favoarble biase toward the grup which we belong (Ingroup favoritism & Outgroup Derogation)
In-group favoritism
the tendency to discriminate in favor of ingroups over outgroups
Out group Derogation
Belief that outgroups are bas across a variety of characterisitcs & less deserving of good things
Consequences for Target of Group Biases Experiement (What Would Mothers Say): Method
Mothers of young boys anf girls watched a video of child engaging in risky beahior on the playground
- Task: Stop the tape whenever they would say something to child
Consequences for Target of Group Biases Experiement (What Would Mothers Say): Results
Mothers of daughters stopped tape more often to express caution & mothers of sons expressed more encouragement
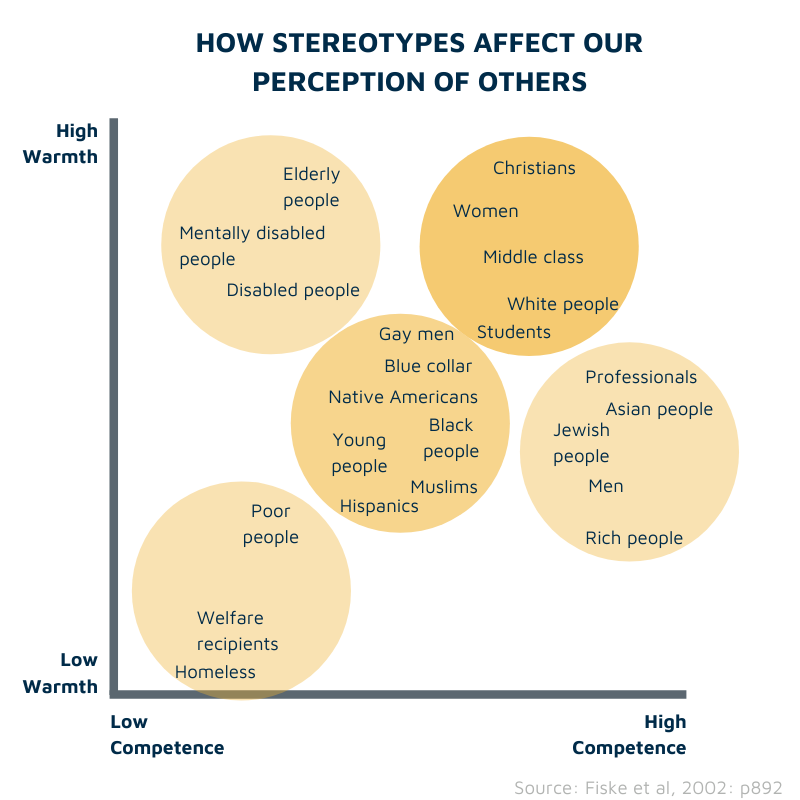
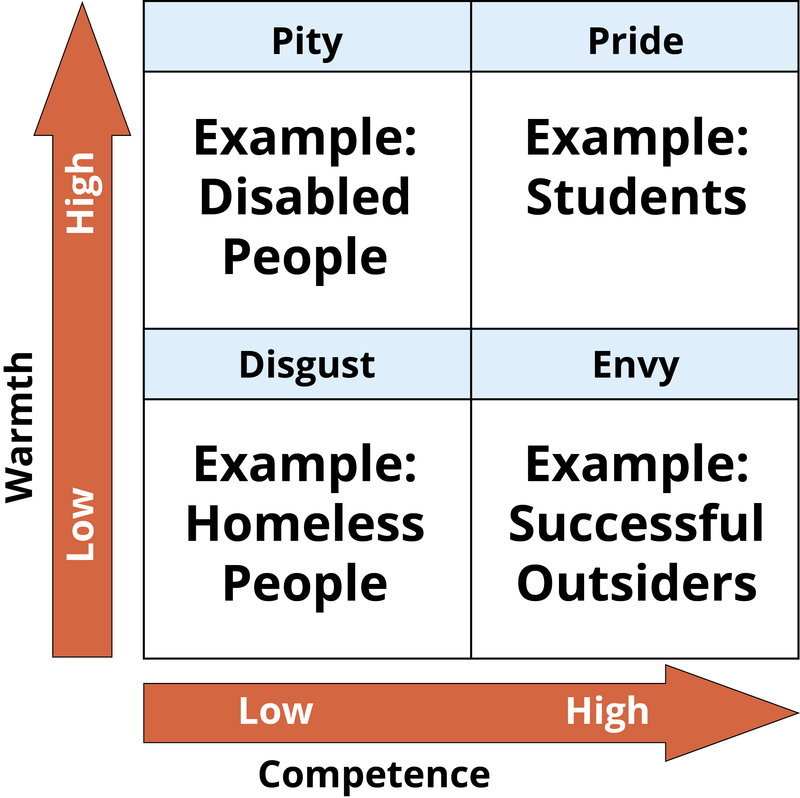
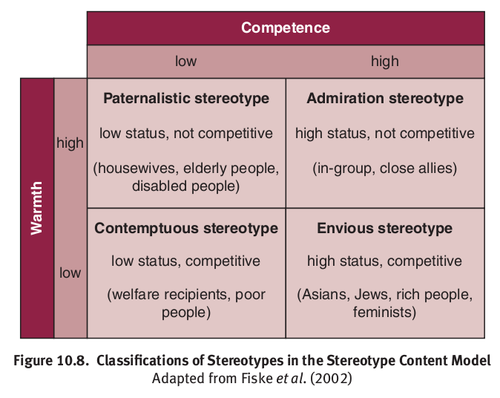
Stereotype Content Model
Warmth: + or -, emotions toward you/If they mean well
Competence: If the erson lost the ability to act on their actions
Consequences of Prejudice
self-perpetuating stereotypes, self-fulfilling prophecy, stereotype threat
Consequences of Prejudice Results of study summary
Dehumanizing Outgroups
- Percieved process faces to extreme outgroup members more like objects than fellow human beings
Shooter Bias
the tendency to mistakenly see objects in the hands of black men as guns
Shooter Bias Important Factors
- Contextual factors that signal threat increase in shooter bias
- Bias decreases in police officers with increase amounts of training
- Bias is stronger when police officers are concerned about being percieved as bias
Stereotype Threat
A self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
self-perpetuating stereotypes
Whenever a member of a group behaves as expected, we duly note the fact; our prior belief is confirmed
self-fulfilling prophecy
an expectation that causes you to act in ways that make that expectation come true.
Sterotype Threat Experiement
- When particpating through the test diagonstic of their ability, white people performed better than Black people
- When participants thought the test was not diagnostic of their ability, White & Black people performed equally well
- With sterotype threat can hamper somebodys performance
Conditions of Stereotype Threat
Knowledge of sterotype
Idenitfy causes
Strong Identification w/ sterotyped threat
Strong identification with sterotyped domain
Consequences of Prejudiced Threat How to deal with Sterotype Threat
- Refute sterotype (difficult for indiviual)
- Avoiding identity cues
- Having can incremental vs. fixed mindset
- Deidenitfy: Stop caring about the domain (remember self-esteem)
Reducing sterotype threat
- Successful intervetions against the steortype threatbeffect & the fact that indiviuals feel a sense of trust, safety in the situation
- Learning about sterotype threat (Avoiding misattribtution of Arousal)
- Make enviroment less threatening ( decrease idenity cues or introduce counter sterotypical cues)
Belongingness Intervention
Members of an decreased represetation minority may be relatively increased uncertainity about their social belonging in mainstream insutitions
Belongingness Intervention Experiement
- Particpants 92 freshman at Standford
- Recieved belongingness intervention just before starting 2nd term then graduation, controlg group didn't recieve e intervention
- Control: Watch videos of seniors describing their experience of physical campus life
Results of Belongingness Intervention Experiement
Minority students got gpas got higher
Contact Hypothesis
The idea that stereotypes and prejudice toward a group will diminish as contact with the group increases.
Requirements for Contact Hypothesis
- Equal stakes
- Common goals
- Cooperation
- Support from authoritites
Benefit of Cross-Group Friendship
Developing friendships a cross groups is one of the best ways to experience many of the optical conditions for contact
Breaking The Prejudice Habit
- Become aware of their biases & why it exists?
- Motiviated to overcome the bias
- Able to detect the subtle influence of sterotyes
- Learn & Practice strategies that help lower automatic biases
Breaking The Prejudice Habit Experiement
- Everyone takes IAT (90% showed bias)
- Recieve feedback on IAT score
- Control group dismissed (would return 2x)
- Exp Group: 45-min narrated & interactive slideshow sep into education & training sections
- Measurement of use of strategies, implict bias, explict bias at several times for next 6 weeks
Breaking The Prejudice Habit Experiement Strategies
- (Labeling, evaulating, replacing)
- Thinking of counter sterotypic examples
- Individuating instead of generalizing
- Persepctive Talking
- Increasing opportunities for contact
- Stereotype Threat
Re-categorization
an attempt to find a different social category that is more congruent with new information