Psychology Study Guide - Unit 2: The Nervous System
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Nervous System
The body’s communication network that consists of all nerve cells.
“Body’s Electrical Wiring”
Central Nervous System
Contains the brain and spinal cord, which are both encased in bone for protection.
The largest part of the nervous system.
The spinal cord is an information highway connecting the peripheral nervous system to the brain.
Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain, responsible for higher-order cognitions (thought and reasoning, language, memory, emotion, and movement)
In the upper part of the brain, divided into 2 hemispheres.
Cerebellum “Little Brain”
Attached to the rear of the brainstem; it helps coordinate voluntary movement, controls balance, and controls motor skills.
Stores motor skills that are learned (ie, sports, playing an instrument)
Brain Stem
The most primitive part of the brain, the base of the brain connected to the spinal cord.
On “automatic”
Controls survival functions like breathing, swallowing, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness, and whether one is awake or sleepy.
Frontal Lobe
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead that is involved in planning and judgment.
Makes up more than 40% of the human brain’s total volume.
Helps you choose a course of action quickly.
Self-awareness, assess dangers and risks.
Motor Cortex (within the frontal lobe)
a strip of brain tissue at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movement.
Different points control different parts of the body.
Body parts that are more capable of more intricate movements demand more brain tissue.
Prefrontal Cortex
“Executive function of the Brain”
Executive functions focus on controlling short-sighted, reflexive behaviors to take part in things like planning, decision-making, problem-solving, self-control, and acting with long-term goals in mind.
Parietal Lobe
Portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear, containing the centers for processing sensory signals and information.
pressure, touch, and pain.
Somatosensory Cortex (within the parietal lobe)
A strip of brain tissue at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body sensations.
There is more brain tissue for the parts of the body that are more sensitive to touch.
Temporal Lobe
lying roughly above the ears, includes the auditory processing of the brain.
hearing, memory, emotions, and some aspects of language.
Corpus Callosum
a thick band of neural fibers that connects the 2 hemispheres
Hemispheres
Each hemisphere has a specialization of function, known as laterization.
Left side → controls the right half of the body.
Right side → controls the left half of the body.
Lobes
Areas of the cerebral cortex.
Each has a location and a primary function/specialty.
(4 lobes in total)
Cerebral Cortex
The outer surface of the brain.
The tissue is folded in on itself, allowing for more surface area of the cortex to fit into the skull.
Associated with consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language, and memory.
Occipital Lobe
The rear bottom of each cerebral cortex, containing the visual centers of the brain.
Homunculus
“Little Man”
A visual map that represents the relative amount of brain area dedicated to controlling or sensing different body parts.
Limbic System
Involved in processing both emotion and memory.
Ring of structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral cortex.
Most influential during teenage years; active and often over-reactive.
Includes the hypothalamus, hippocampus, and amygdala
Hypothalamus
“Thermometer”
Regulates a number of homeostatic processes, including the regulation of body temp, appetite, and blood pressure.
Linked to emotion.
Controls the pituitary gland by secreting hormones.
Hippocampus
Essential structure for learning and memory.
Helps process new memories for permanent storage.
In adolescent brains, it is “super-charged” compared to adults.
Memories are easier to make and last longer when acquired in the teen years compared with adult years.
Amygdala
Controls emotional responses, such as fear and anger.
Becomes active during potentially threatening situations (fight-or-flight)
During adolescence, especially, emotions rule our lives.
Teens are driven by emotion, not reason (frontal lobe)
Peripheral Nervous System
Connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
The sensory and motor nerves that connect the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body.
2 major subdivisions: Somatic Nervous System & Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls our internal organs and the muscles of glands.
Don’t need conscious thought.
Breathing, blood pressure, and digesting processes
Subdivided: Sympathetic Nervous System & Parasympathetic Nervous System.
Somatic Nervous System
Associated with conscious and voluntary activities.
Division of PNS that controls the body’s skeletal muscles.
Sensory nerves gather information about what’s going on in your body and the outer world.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Arouses the body to deal with perceived threats.
Accelerate your heartbeat, raise blood pressure, slow digestion, etc.
“Fight, Flight, or Freeze Response”
Regulated by the Sympathetic Nervous System.
How we deal with perceived threats.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Calms the body.
Reduces body arousal, energy, and decreases blood sugar, etc.
“Rest & Digest Response”
Regulated by the Parasympathetic Nervous System.
Counteraction to stress.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that carry, boost, and balance signals between neurons, or nerve cells, and other cells in the body.
Act like a key, and the receptor sites act like a lock. It takes the right key to open specific locks.
Neuron
Basic building blocks
Receive info (chemical transmissions) from other neurons.
Passes info down its length as an electrochemical pulse.
Moves the info onto the next neurons in line.
Dendrites
“Antenna”
Branching extensions from the neuron.
receive info and conduct impulses toward cell body
Axon
“Talker”
Extension of a neuron through which neural impulses are sent.
Myelin Sheath
A fatty substance formed by glial cells that coats the axon.
Acts as an insulator, increasing the speed at which the signal travels.
Also acts as a protective layer.
Not continuous; small gaps down the length of the axon.
Cell Body
Soma
Synapse
The junction where a neuron transmits a signal to another cell.
Axon Terminal Branches
Tips as the end of a neuron, where neurotransmitters are stored.
Receptor Site
The site where neurotransmitters go/are received on the dendrite.
Synaptic Gap (Cleft)
The small gap between dendrites at a synapse.
Action Potential/Neural Impulse
A brief electrical charge that travels down the axon of a neuron.
Resting Potential
The state of a neuron when it’s at rest and capable of generating an action potential.
All-or-None Principle
If a neuron fires, then it always fires at the same intensity; all action potentials have the same strength.
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
They excite connecting neurons and cause them to fire; more action potentials are triggered.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Inhibit (prevent) the next neurons from firing.
Dopamine
The pleasure or reward neurotransmitter.
The brain releases dopamine during pleasurable activities.
Feel-good transmitter.
Repeat behaviors that lead to a release of dopamine.
Serotonin
Connected to feelings of well-being and happiness (regulation of emotion).
regulates the sleep cycle along with melatonin, and also regulates intestinal movement.
Serotonin is a major part of many popular drug treatments for depression and anxiety.
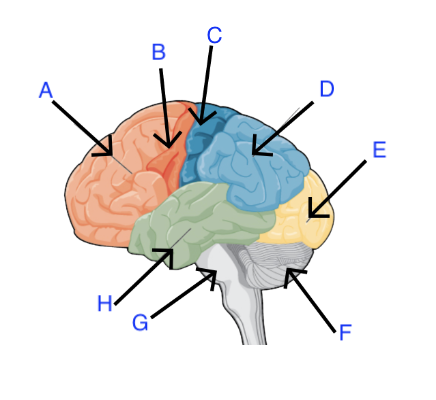
A. Prefrontal Cortex
B. Motor Cortex
A and B are both in Frontal Lobe
C. Somatosensory Cortex (within Parietal Lobe)
D. Parietal Lobe
E. Occipital Lobe
F. Cerebellum “Little Brain”
G. Brain Stem
H. Temporal Lobe
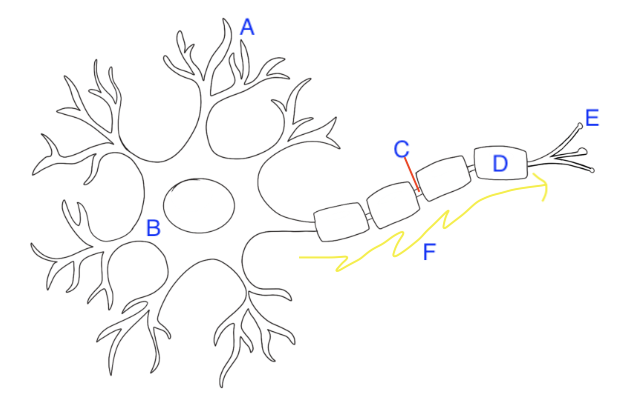
A. Dendrites
B. Cell Body “Soma”
C. Axon
D. Myelin Sheath
E. Axon Terminals
F. Neural Impulse (Action Potential)
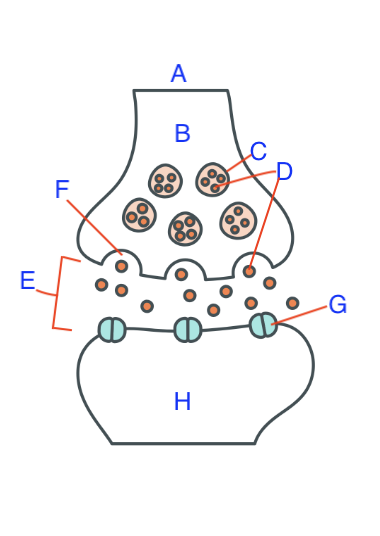
A. Pre-synaptic Cell
B. Axon Terminal
C. Synaptic Vesicle
D. Neurotransmitter
E. Synaptic cleft (gap)
F. Voltage-gated calcium channel
G. Receptor Sites for neurotransmitters
H. Post-synaptic Cell