Lecture 7 - Allosteric Control
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Ligand
Any compound that will bind to a receptor
Hyperbolic kinetics
(Most enzymes) the rate of enzyme activity increases as the ligand concentration increases until it reaches saturation
Sigmoidal kinetics
Enzymic rate modulated by the binding of multiple ligand molecules and effectors
Characteristics of proteins showing sigmoidal kinetics
Proteins which use co - operative binding
Co operative binding
When the first substrate molecule binds to its binding sit on one of the sub units, it increases the affinity of the second so it binds easier
allosteric proteins…
show co operativity and sigmoidal kinetics
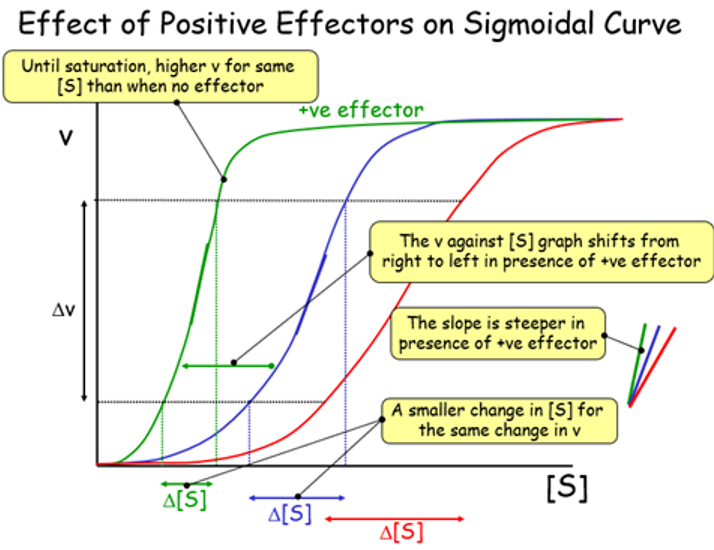
effect of positive effectors
increase affinity
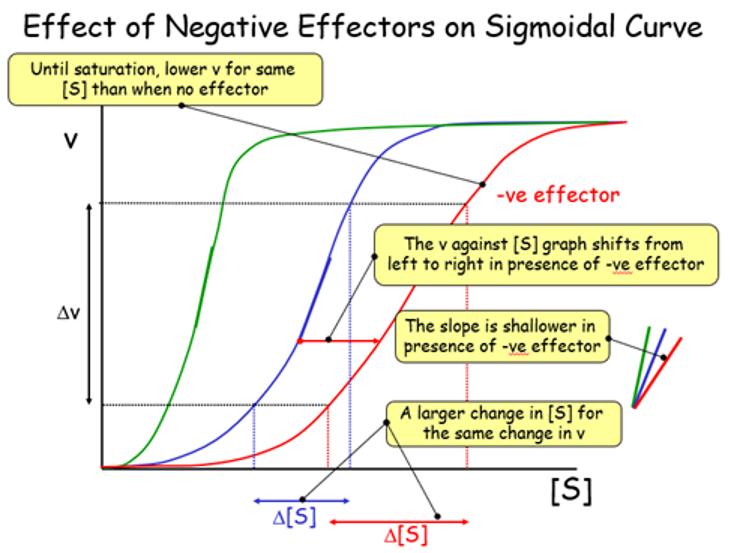
effect of negative effectors
decrease affinity
effect of positive effectors on sigmoidal curve
move s curve left
effect of negative effectors on sigmoidal curve
move s curve right, shallower slope
2 models to describe allosteric effects
Concerted model and sequential model (most enzymes follow a mix)
Concerted model of allosteric effects
One substrate binding to T form causes all sub units to convert to R form
Sequential model of allosteric effects
One substrate binding to T form converts one sub unit to R form making it easier for substrate to bind to other sub units
States which sub units exist in
T and R
What is the T state
Low affinity for the substrate
What is the R state
High affinity for the substrate
Positive effectors on the sub units
Stabilise the R state of the sub units
Negative effectors on the sub units
Stabilise the T state of the sub units
Cell with high energy stores have
High ATP, low ADP/AMP, low NAD+
Positive effector in glycogenolysis: Glycogen phosphorylase
AMP
Negative effector in glycogenolysis: glycogen phosphorylase
ATP
Positive effector in glycolysis: hexokinase, PFK, pyruvate kinase
AMP
Negative effector in glycolysis: hexokinase, PFK, pyruvate kinase
ATP
Positive effector of pyruvate deHase (TCA cycle)
AMP, NAD+
Negative effector of pyruvate deHase (TCA cycle)
NADH
Negative effector of citrate synthase (TCA cycle)
ATP
Positive effector of isocitrate deHase (TCA cycle)
ADP
Negative effector of isocitrate deHase (TCA cycle)
NADH