Human Physiology Exam 3 Quiz Questions
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Partial pressure of oxygen dissolved in blood is 50 mm Hg. That means that
It would be in equilibrium with gaseous oxygen that is at partial pressure of 50 mm Hg
Molar concentration of dissolved gas …
Is found from the Henry law
The principle that diffusion is faster in gases than in liquids is important in the pathogenesis of
Pulmonary edema
The principle that larger alveoli are less efficient than small ones in supporting gas exchange is important in the pathogenesis of
Emphysema
What causes the expansion of lungs during inspiration?
Neither surface tension or connective tissue fibers
Match the left column (form of hemoglobin) to the right column (what causes it)
Carbaminohemoglobin
Oxyhemoglobin
Deoxyhemoglobin
Methemoglobin
Carboxyhemoglobin
Carbaminohemoglobin: CO2
Oxyhemoglobin: Oxygen
Deoxyhemoglobin: Absence of oxygen
Methemoglobin: Fe3+
Carboxyhemoglobin: CO
Chloride shift is mediated by
Countertransport
Which hemoglobin would be most effective in transferring oxygen from alveoli with 120 mm Hg oxygen pressure to a tissue with 40 mm Hg oxygen?
B because at 120 mm Hg, all three types are saturated; at 40 mm Hg, type A has less oxygen bound than B or C, therefore it will release the largest amount of oxygen
Oxyhemoglobin has a higher affinity for CO2 compared to deoxyhemoglobin
False
A defect in type 2 alveolar cells would mostly affect
Inspiration
What happens to hydrogen ions produced by carbonic anhydrase in erythrocytes?
Binds hemoglobin
Oxygen diffusion from the lungs into the tissue can be described by the equation: F = P(Clung – Ctissue). Which of these parameters is most affected by convection (ventilation)?
Clung
The main reason why hemoglobin increases the blood capacity for oxygen has to do with
High concentration of oxygen-binding sites provided by hemoglobin
Why is alveolar PO2 close to 100 mm Hg?
Because alveoli are located deep in the body
Henry’s constant for nitrogen is 6∙10-4 M/atm. A diver dives to a depth where nitrogen partial pressure is 3 atm. What would be the nitrogen concentration in the diver’s blood at equilibrium in mmol/L? (Put the number without units)
1.8
Bulk flow is driven by differences in protein concentration
False
Choose the sentence that makes most sense.
If cardiac output is constant, then an increase in resistance would cause an increase in arterial pressure.
Indicate in each case, whether a given quantity is larger in veins or in arteries. Put “v” if it is larger in veins, “a” if it is larger in arteries, and “e” if it is equal for veins and arteries.
Compliance
Pressure
Velocity of blood flow (centimeters per second)
Total blood flow (liters per minute)
Compliance: v
Pressure: a
Velocity of blood flow (centimeters per second): a
Total blood flow (liters per minute): e
What can be the cause of the plateau in the middle section of this curve?
Contraction of vascular smooth muscle
The relationship between cardiac output (CO), mean arterial pressure (AP), and total peripheral resistance (PR) is
AP = CO*PR
What maintains a relatively steady arterial pressure during the entire cardiac cycle? Choose the best answer.
Tension in the artery
When proteins escape from capillaries, edema may develop. This fact can be explained by
Increase in the colloid osmotic pressure of the interstitial fluid
How is lactate production in the muscle expected to affect local circulation?
Dilate arterioles
Hydrostatic pressure of blood = 50 mm Hg
Hydrostatic pressure of interstitial space = 0
Oncotic pressure of blood = 30 mm Hg
Oncotic pressure of interstitial space = 20 mm Hg
Calculate pressure balance. Put the number in mm Hg without units. Add a minus if the total pressure is directed into the capillary.
40
Calculate blood flow rate if the vessel cross section area is 1 mm2 and blood velocity is 20 mm/s. (Keep in mind that 1 mm3 = 1 μl)
20 μl/s
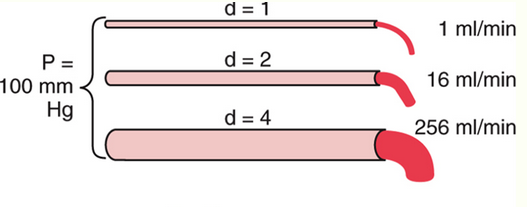
This is a picture from a lecture. What would be the blood flow rate for d = 3? Put a number without units
81
Indicate the pressure range where Korotkoff sounds can be heard
Between a and c
The blockage of lymph flow may cause edema by
An increase in the interstitial oncotic pressure
Insert yes, if you agree, or no, if you disagree
Sympathetic neurons regulate arterioles:
Capillaries regulate arterioles:
Veins regulate arterioles:
Sympathetic neurons regulate arterioles: yes
Capillaries regulate arterioles: no
Veins regulate arterioles: no
Suppose you put a clamp on the end of a horizontal blood vessel, so that blood flow in that vessel stopped. What can we say about the pressure difference along this vessel?
Equal everywhere along the vessel
The Starling forces determine primarily the exchange of
Water
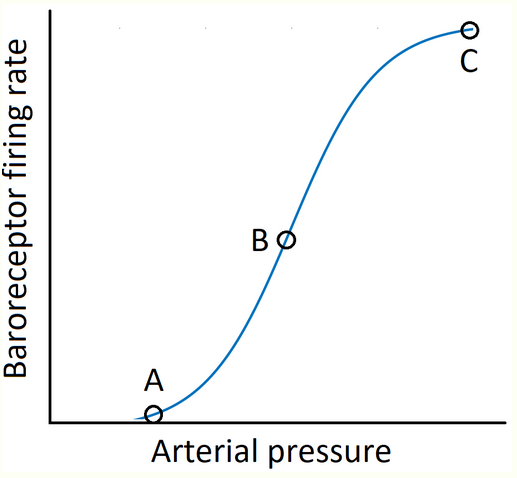
Which is the correct expression for baroreceptor sensitivity? Use Y for firing rate and X for arterial pressure.
dY/dX
At what point is baroreceptor sensitivity the highest?
B
The main reason for creating a high osmolarity in the medulla is to …
Facilitate water absorption from the collecting duct
What is the main mechanism of elimination by the kidneys of toxins contained in the blood plasma?
Toxins lack transporters in the tubules
Glomerular filtration is enhanced by the constriction of the afferent arteriole
False
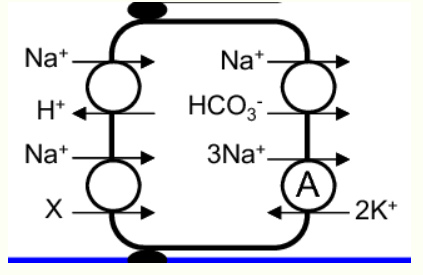
The basolateral membrane is shown on the right
True
Inhibition of P-glycoprotein may cause
Accumulation of drugs in the organism
Reabsorption of glucose takes place in
Proximal tubule
Calculate the glomerular capillary blood pressure, if the oncotic pressure, the net glomerular filtration pressure and the pressure in the Bowman’s capsule are all 15 mm Hg. (Put just the number without units)
45
Hypertension can be treated by inhibitors of sodium reabsorption because…
Sodium increases the osmolarity of the plasma
This is a table from the lecture:
Why do the flow rates decrease in the more distal parts of nephron?
Water is reabsorbed
High osmolarity of the medulla is created by
Salts removed from the ascending loop of Henle
Destruction of the special cells that cover glomerular capillaries is likely to cause
Loss of protein
In which area of the kidney (1-6) are podocytes located?
1
Arrange the steps in logical order (starting with 1 and ending with 5) as they lead to passive absorption of urea in the proximal tubule:
Osmotic absorption of water
Import of Na+ from the apical side
Increase in the luminal urea concentration
Active pumping of Na+ by the basolateral Na+-K+ pump
Passive diffusion of urea into the epithelium
42135
Factors that cause vasoconstriction often exhibit a second effect. What is it?
Stimulation of sodium reabsorption
Where does the blood flow in the left capillary along the loop of Henle: up (1) or down (2)?
2
What is the main purpose of the loop of Henle?
Conservation of water