SCL ANT100
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
169 Terms
Governmentality
The way a state is ruled by government in conjunction with other organizations.
Hegemony
A way to install self-disciplined conforming behavior that aligns with government wishes.
Surveillance
The method by which the public is monitored to maintain control for the elite.
Consent
Agreement or compliance that is essential for the maintenance of power structures, which can be voluntary and internalized.
Panopticon
A prison design featuring a central watchtower, allowing constant surveillance without prisoners knowing when they are being observed.
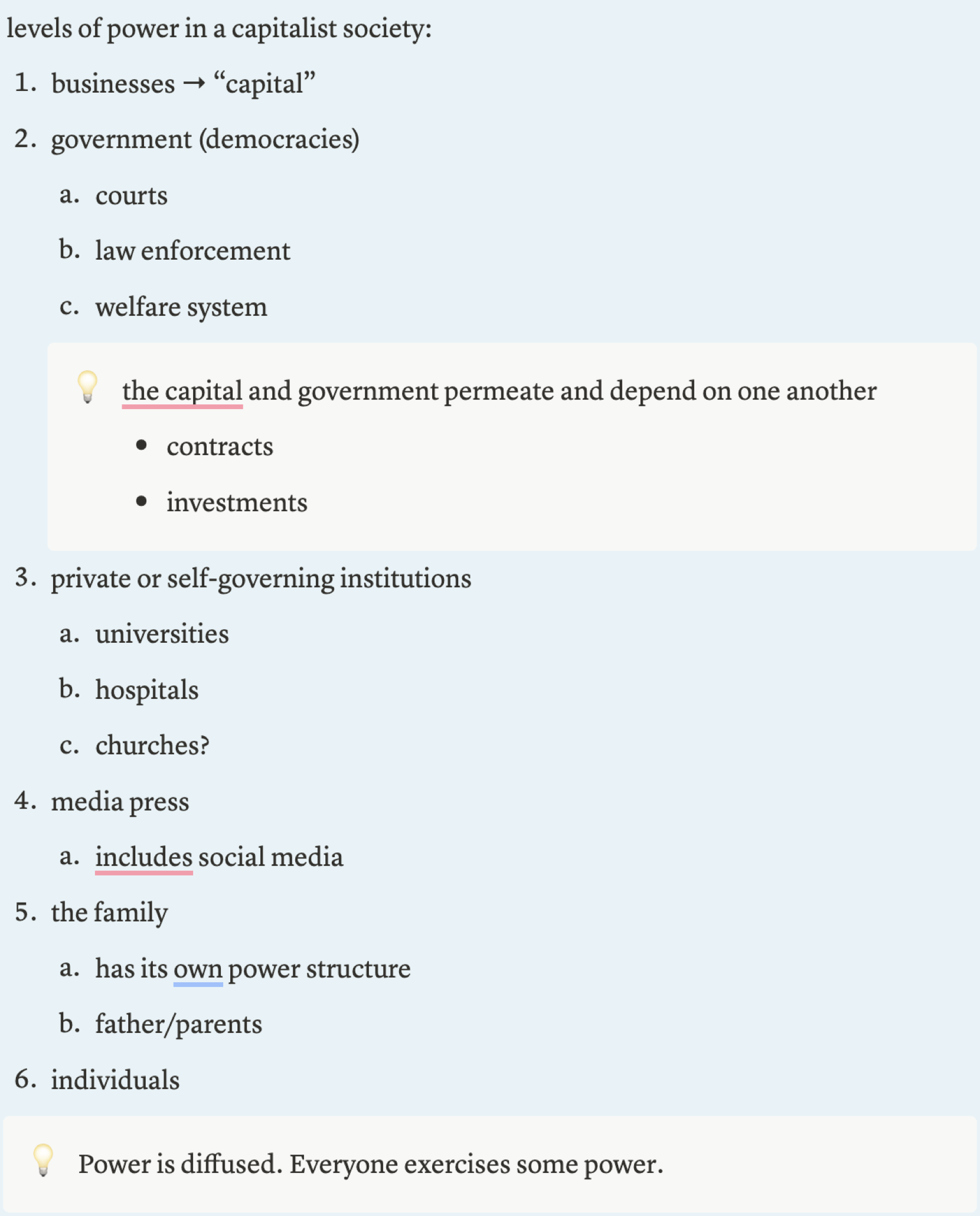
Levels of Power in a Capitalist Society
businesses
government (democracies)
private institutions
media press
family
individuals
Digital Economy
Economic activities that are conducted through digital means, often dominated by a few wealthy individuals.
Big Data
Large volumes of data analyzed to identify trends, often used by businesses and governments for surveillance.
Monopoly Capitalism
An economic system where a single entity dominates the market, often involving cooperation between the state and capital.
consent
pervades all levels of society
based on violence
violence is implied
acquired via education
Gramsci’s Hegemony
consent has to be given without thought for hegemony
consent does not always occur
if it does not occur there is a struggle
the struggle can be spontaneous
or explicitly
violent surveillance
law enforcement
war
voluntary surveillance
welfare
entertainment
information
capital surveillance
private, informative, encourages competition, non-coercive
businesses track your digital history for advertisement/to sell a product or service
government surveillance
classified, non-transparent, monopolistic
unknown what the government is using the data for
What happens when the capital cooperates with the state?
cooperation discourages competition
result can be opaque monopoly capitalism
Ethnography
Describing of people through the study of their cultures.
Cultural Relativism
The principle of understanding other cultures without judgment; each culture is a unique entity with its own special genius, world view, and behavioural characteristics.
Universal Moral Values
Belief that some moral values are valid regardless of culture.
Participant Observation
Method where ethnographers live with the people they study.
Language Acquisition Device
Innate ability for humans to learn language, as proposed by Noam Chomsky.
can not grow up without learning language
language is an innate and universal ability
moral standards are innate and universal
we learn specific languages from others in our society
but all humans learn a language
not instant, but by the age of 6
Deep Structure
The underlying syntax that generates different surface structures in language.
deep structure in languages are the same
verbs, nouns, noun phrases, etc
Moral Relativism
The belief that moral standards are not absolute and depend on culture.
Political Economy
The relationship between economic behavior and political structures affecting society.
Surface Structure
The actual form of sentences generated from deep structures in language.
Taboo
A prohibition or restriction against certain practices or discussions in cultures.
discourse analysis
A research method used to analyze spoken or written communication, focusing on the context, structure, and meaning of language in social interactions.
study of text
syntax
The set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a language, including word order and sentence formation.
study of sentences
morphology
The study of the structure and formation of words in a language, including prefixes, suffixes, and root forms.
study of words
phonology
the study of the sound system of a language, including the organization and patterns of sounds.
study of sound units
phonetics
the study of the physical properties of sounds in human speech, including their articulation and auditory perception.
study of sounds
Surface Structure
generated by the deep structure
the actual sentence itself
Universal Moral Values
there exists moral values that exist regardless of culture
opposite of moral relativism
not the opposite of cultural relatvisim
Cultural Relativism
cannot judge other cultures based on their practices
allows for moral universals and particulars
Moral Relativism
cannot judge cultures at all
moral values are dependent on cultural context.
Other
a person or group defined as being excluded of another group; non dominating
Colonial definition of anthropology
“science of the colonial Other”
What was colonial anthropology?
a Western science; the field consisted of White people studying conquered peoples
What were the Other to the West?
“primitives”, “natives,” “without history”, “without writing”
What is “folklore”?
the exclusion of the study of Western civilization in anthropology
What was the Orient?
“non-primitive” people → who had writing systems
China, Persia, India, Islam, South Asia & South East Asia
metropolitan
centred in the colonizing countries
What are the Four Fields of Anthropology?
physical/evolutionary anthropology
archaeology
cultural
linguistic
physical anthropology
study of characteristics and physical appearance
archaeology
study of material culture
cultural anthropology
study of customs, ideas, social organization
linguistic anthropology
study of spoken languages
ideology & representation
the makings of meaning
culture & language
political economy
interrelationships among people and groups
the “body politic” → the makings of society
What is culture?
What is learned from each other
What is language?
tool of social construction & social transmission
communication
identity formation
What is affect?
emotion; the conscious emotion that occurs in reaction to a thought or experience
sameness in identity formation
affect → community
differences in identity formation
affect → othering
What is an important law of language?
every language has nouns, verbs, and word order
languages have more in common than not
geographical proximity
nouns & verbs
word order & grammar
Culture & Language in Universals and Particulars
culture & language are human universals
specificity in culture & language are human particulars
define niches
specific languages and cultures developed to cope with specific environmental and social contexts
cultural variables
systematic way to study differences
naturalization
when people mistakenly come to think of what is socially constructed to be from nature
social location bias
the upbringing, background, culture, bias, aptitude, etc a person has
semiotics
language
signifying systems that study the signs and symbols in communication and their meanings.
the study of signs and symbols and their interpretations
define Social Construction
Social construction is the theory that concepts, practices, and realities are developed and maintained through social interactions and cultural practices, often seen as subject to varying interpretations; an “invention” society agrees upon collectively
works with material reality and transforms it into social reality
race
socially constructed
not real
imagined common descent
folk notion, not scientific
national; regional; linguistic
racialization
the process through which social categories, such as race, are constructed and assigned meanings based on perceived differences.
race: biology vs. social construction
different races have different genetic characteristics,
yet are still socially constructed race can correlate with colour and certain genetic traits
but not consistently enough to justify scientifically the notion of human races
One-Drop Rule
if you had any “Black blood” (African ancestors) you were considered Black
socially constructed and racialized as Black
encompassed other non-white groups
having any non-white blood made you not white
semiosis
the process of constructing meaning
signification (semiotics)
making sense of signs
3 nature of signs
signifier & signified
symbol, icon, index
denotation & connotation
parts of semiotics
language (linguistics)
semiotics proper (other signs)
A Classic (“Saussurean”) View of Semiosis
signifier + signified
material/immaterial
material: the object itself
together the signifier and the signified make
up the sign
sign ≠ the physical object
sign: ordinary language
the sign itself
signifier: technical language
yellow colours, silhouette of a car on slippery roads
signified: the message
slippery roads ahead
define sign
ordinary language; anything that communicates a meaning that is not the sign itself to the interpreter of the sign
signifier + signified = sign
define signifier
the part of a sign that represents the concept or meaning, often a word, image, or sound; technical language; the observable aspects of the sign itself
define signified
the message itself; what the sign represents or refers to
Charles Peirce’s Theory
symbol
icon
index
define symbol
arbitrary meanings attributed to a sign
define icon
quality/physical characteristics of a sign; shares some physical form with the referenced; motivated
define index
does not share any of their form with the reference; motivated
ethno-nationalism
the idea that one belongs to the people descended from the same ancestry
Relatedness
people who are “special” with whom we have a relationship with
descent
kinship
language groups
nationalism
marriage
corporate groups
acting as a group together in society
can be hierarchal
share residence, identity; unified
consanguineal
related by blood
affinal
related by marriage
avunculate
the most powerful male relative is the mother’s brother
popular in Wendat and Haudenosaunee culture
Hawaiian Kinship System
no distinction between biological and non-biological relatives
Sudanese Kinship System
different naming systems between the mother and father’s side
Eskimo Kinship System
nuclear family
Trobriand Islands Society Kinship System
avuncular system, biological father → an affectionate playmate
commensality
everyone eats together
Germanic languages
German
Swedish
English
Slavic languages
Russian
Polish
Bulgarian
Romance languages
Latin
Italian
French
Romanian
True or False: Language is a political social construct
True!
neoliberalism
free markets, less government control
precariousness
a state of having uncertain job security and income stability; the onus is put on employees to prove their usefulness
globalization
the process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or operate on an international scale, increasing interconnectedness across countries.
South to North (Capital)
investments: North to South
profits: South to North
few or no restrictions to the flow
South to North (Migration)
Global South wages are lower; people want to migrate but are heavily restricted; people can move freely, labour cannot → lots of production is outsourced elsewhere
How is globalization functioning now?
rivalry of alternative economies implies globalization is over → not true
neoliberalism continues but within the state
globalization → limited interference by national governments
post-globalization (today) → reinforce borders & liberalism in one’s own country