BSC1010 Final
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1) In what way do kinetochore microtubules facilitate the process of splitting the centromeres?
They create tension by pulling toward opposite poles.
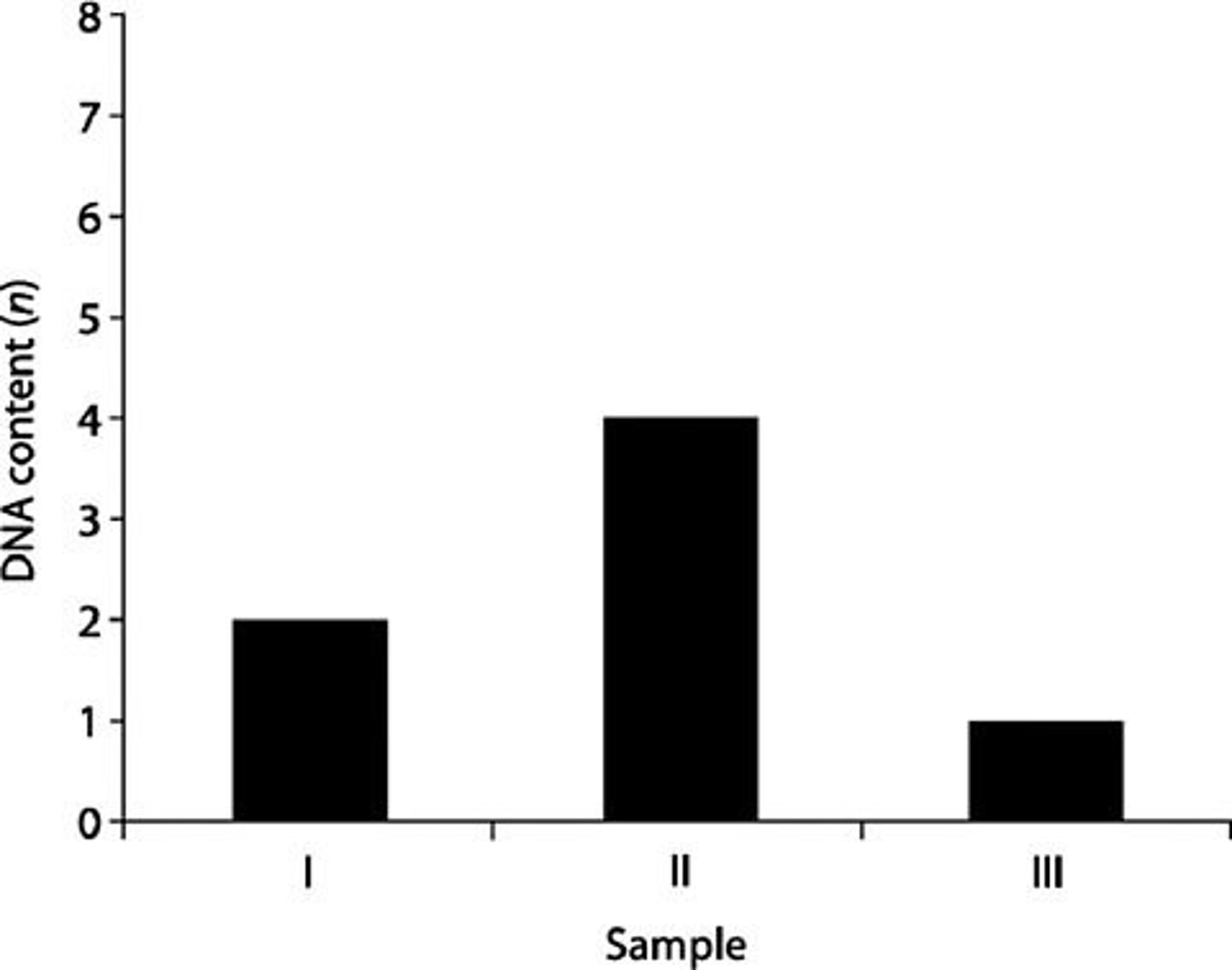
DNA was isolated from three different cell types of the same organism, the relative DNA content for each type was determined, and the results were
plotted on the graph shown in the figure below. Refer to the graph to answer the following questions.
2) Which sample of DNA might represent an animal cell in the G2 phase of
the cell cycle prior to meiosis?
II
Which of the following calculations require the use of the addition rule of probability?
Calculate the probability of a child having either sickle-cell anemia or cystic fibrosis if parents are each heterozygous for both.
According to the central dogma, what is the intermediate molecule involved in the flow of information in a cell that should go in the blank?
mRNA
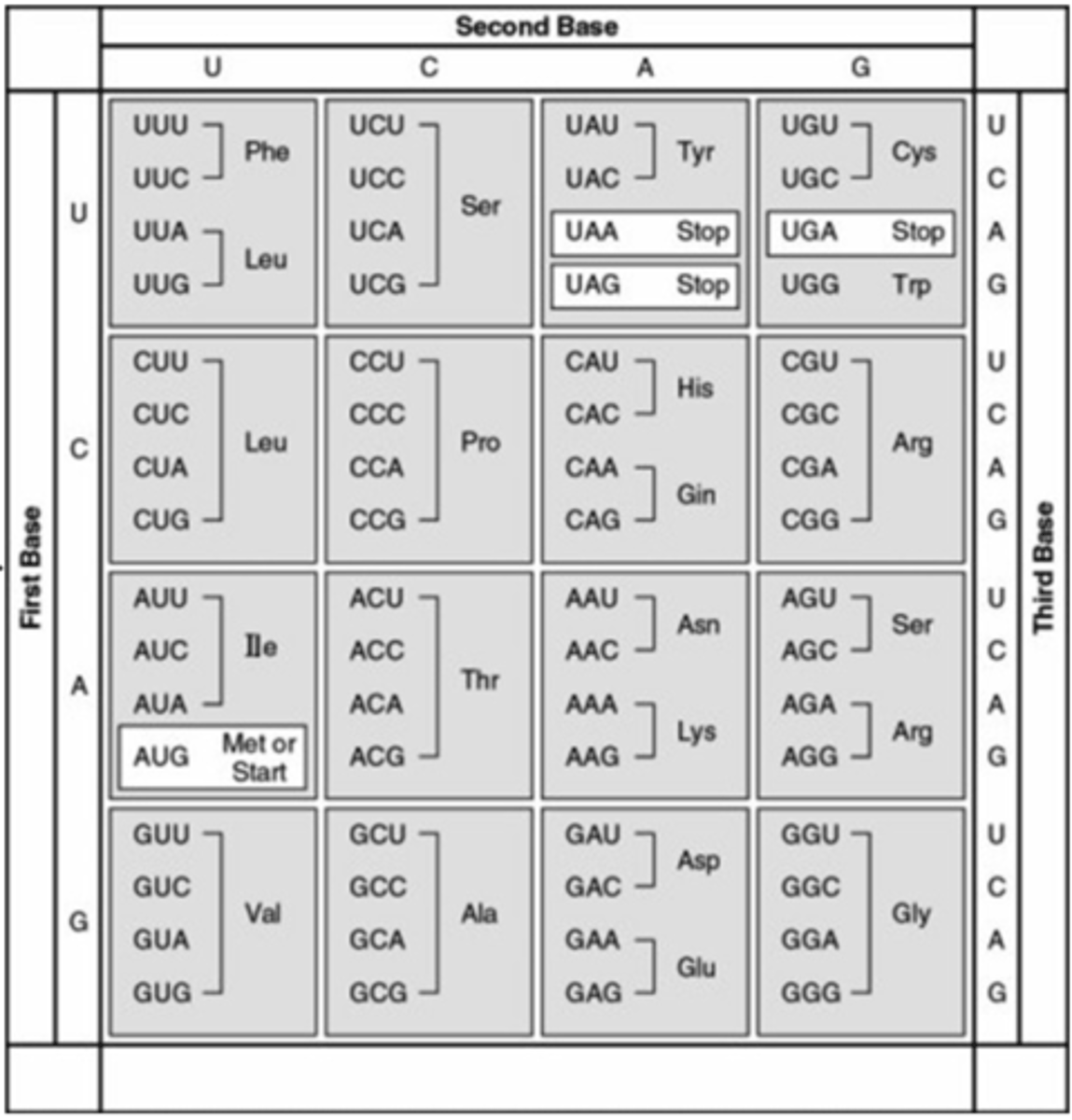
The following question refers to this table of codons.
Which of the following sequences of nucleotides are possible in the
template strand of DNA that would code for the polypeptide
sequence Phe-Leu-Ile-Val?
3′-AAA-GAA-TAA-CAA-5′
Which of the following processes occurs during transcription?
RNA is synthesized
Codons are three-base sequences in mRNA that specify the addition of a single amino acid to the growing protein chain during translation. How do eukaryotic codons and prokaryotic codons compare?
Codons are a nearly universal language among all organisms.
Red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans. Two people with normal color vision have a color-blind son. What are the genotypes of the parents?
XNXn and XNY
Gene S controls the sharpness of spines in a type of cactus. Cacti with the dominant allele, S, have sharp spines, whereas homozygous recessive
ss cacti have dull spines. At the same time, a second gene, N, determines whether or not cacti have spines. Homozygous recessive nn cacti have no
spines at all. The relationship between genes S and N is an example of which of the following inheritance patterns?
epistasis
In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous (CRCW) offspring of red (CRCR) and white (CWCW)
homozygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in the ratio of 1 red:2 roan:1 white?
roan × roan
Mendel's observation of the segregation of alleles in gamete formation has its basis in which of the following phases of cell division?
anaphase I of meiosis
Use the figure and the following description to answer the question.
In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D. Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves,
and plants with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A true-breeding, dark-leaved plant is
crossed with a light-leaved one, and the F1 offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted outcome of the F2 is
diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to
each box within the square.
Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to plants with a heterozygous genotype?
2 and 3

A whitefish gill cell contains 24 chromosomes. During prophase in mitosis, how many chromatids does it contain?
48
A black guinea pig crossed with a guinea pig with albinism produced 12 black offspring. When the albino was crossed with a second black
animal, six blacks and six albinos were obtained. What is the best explanation for this genetic situation?
Albinism is a recessive trait; black is a dominant trait.
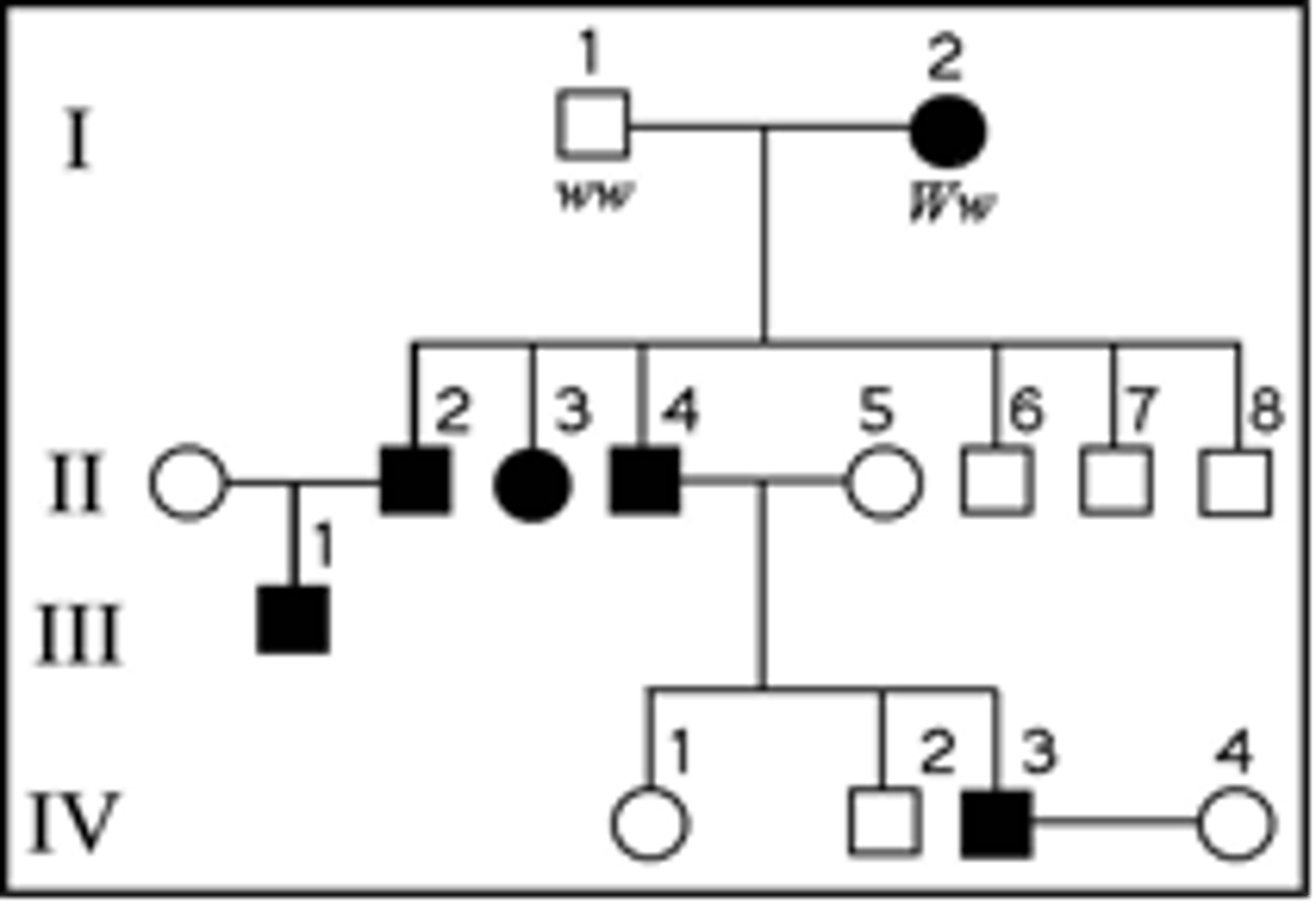
The following question refers to the pedigree chart in the figure for a family, some of
whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark
square or circle.
What is the likelihood that the offspring of IV-3 and IV-4 will have the trait?
50%
Hydrangea plants of the same genotype are planted in a large flower garden. Some of the plants produce blue flowers and others pink flowers.
This can be best explained by which of the following?
environmental factors such as soil pH affect the phenotype
What is the probability of producing the genotype AABBCC in a cross of individuals who both possess this genotype: AaBbCc?
1/64
Feather color in budgies is determined by two different genes: Y for pigment on the outside of the feather, and B for pigment on the inside of the
feather. YYBB, YyBB, or YYBb is green; yyBB or yyBb is blue; YYbb or Yybb is yellow; and yybb is white. A blue budgie is crossed with a white
budgie. Which of the following results in the offspring is most possible?
blue and white offspring
Feather color in budgies is determined by two different genes, Y for pigment on the outside of the feather, and B for pigment on the inside of the
feather. YYBB, YyBB, or YYBb is green; yyBB or yyBb is blue; YYbb or Yybb is yellow; and yybb is white. Two blue budgies were crossed. Over the
years, they produced 22 offspring, five of which were white. What are the most likely genotypes for the two blue budgies?
yyBb and yyBb
Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-purple offspring. The
flower color trait in radishes is an example of which of the following inheritance patterns?
incomplete dominance
Why did all of the F1 offspring of Mendel's classic pea cross always look like one of the two parental varieties?
One allele was dominant.
Which of the following statements correctly explains the fact that all seven of the pea plant traits studied by Mendel obeyed the principle of
independent assortment?
All of the genes controlling the traits behaved as if they were on different chromosomes.
Which of the following statements is correct in comparing sexual and asexual reproduction?
In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit half of their nuclear genes to each of their offspring.
Imagine that there are 25 different species of protists living in a tide pool. Some of these species reproduce both sexually and asexually, and
some of them can reproduce only asexually. The pool gradually becomes infested with disease-causing viruses and bacteria. Which species are
more likely to thrive in the changing environment?
The sexually reproducing species is likely to thrive.
During which of the following processes do sister chromatids separate from each other?
during both mitosis and meiosis II
Quaking aspen trees can send out underground stems for asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is not as common, but when it does
happen, the haploid gametes have 19 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are in the cells of the underground stems?
38
How do cells at the completion of meiosis compare with cells that are in prophase of meiosis I?
The cells have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA.
Which of the following characteristics do homologous chromosomes exhibit?
They carry information for the same traits.
Which of the following statements describes the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell after telophase of meiosis I?
The cells are haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids
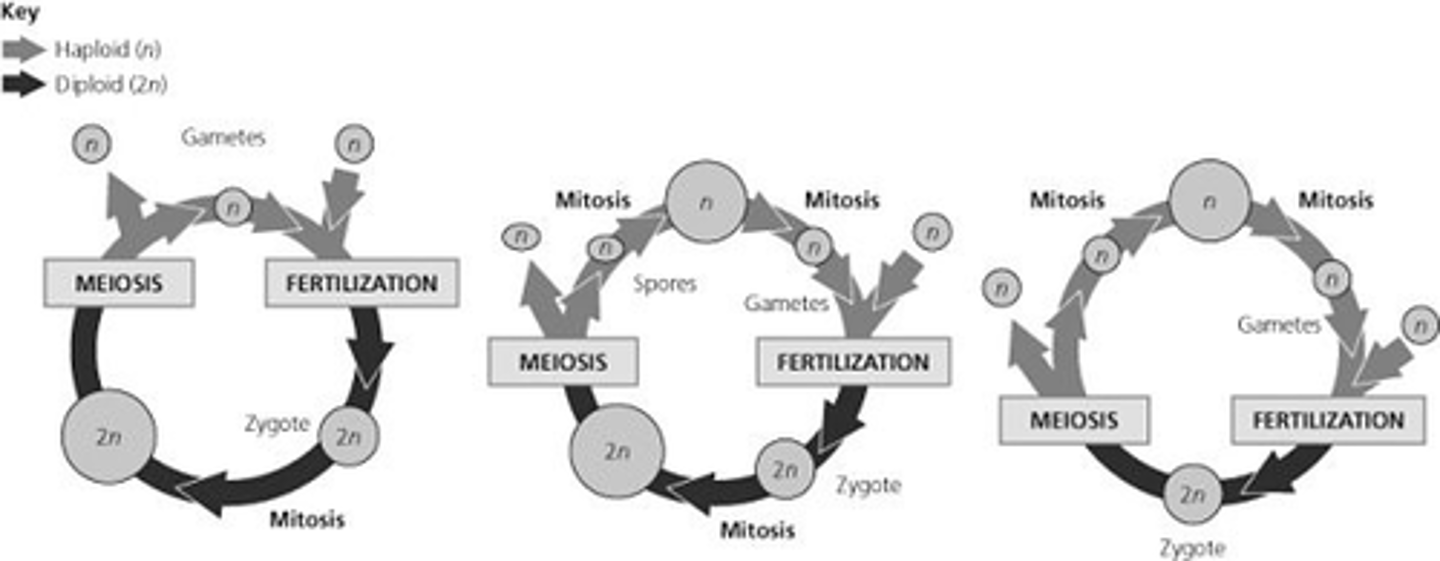
Refer to the life cycles illustrated in the figure below to answer the following questions.
30) Which of the life cycles is typical for most fungi and some protists?
II only
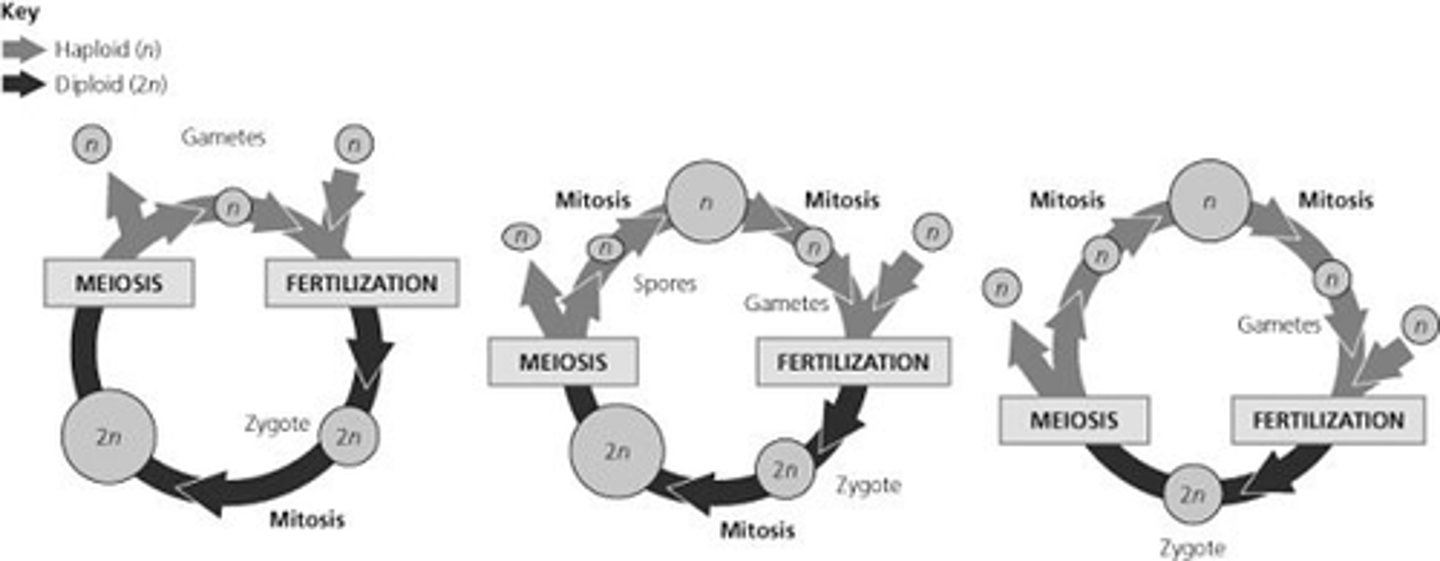
Which of the life cycles is typical for animals?
I only
The mitotic spindle plays a critical role in which of the following processes?
separation of sister chromatids
What would you expect to happen if MPF (maturation-promoting factor) is introduced into immature frog oocytes that are arrested in G2?
The cells would enter mitosis.
Besides the ability of some cancer cells to over proliferate, which of the following situations might logically result in a tumor?
lack of appropriate cell death
Certain unicellular eukaryotes, including diatoms and some yeasts, have mechanisms of nuclear division that may resemble intermediate steps
in the evolution of mitosis. Which of the following is a characteristic feature of nuclear division in these organisms?
Chromosomes are segregated by a mitotic spindle, but the nuclear envelope remains intact during division.
Exposure of zebrafish nuclei to cytosol isolated from eggs at metaphase of mitosis resulted in phosphorylation of NEP55 and L68 proteins by
cyclin-dependent kinase 2. NEP55 is a protein of the inner nuclear membrane, and L68 is a protein of the nuclear lamina. What is the most likely roleof phosphorylation of these proteins in the process of mitosis?
They are involved in the disassembly of the nuclear envelope.
The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the animal cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B?
cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis
G1 is associated with which of the following cellular events?
normal growth and cell function
Which of the following molecules is released by platelets in the vicinity of an injury?
PDGF
Metaphase is characterized by ________.
alignment of chromosomes on the equator of the cell