Ch 6 - Water Quality and Quantity
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Surface Water
Fresh water on Earth's land surface. Surface water is found in lakes, rivers, streams, and wetlands.

River System
A flowing network of rivers and streams draining a river basin
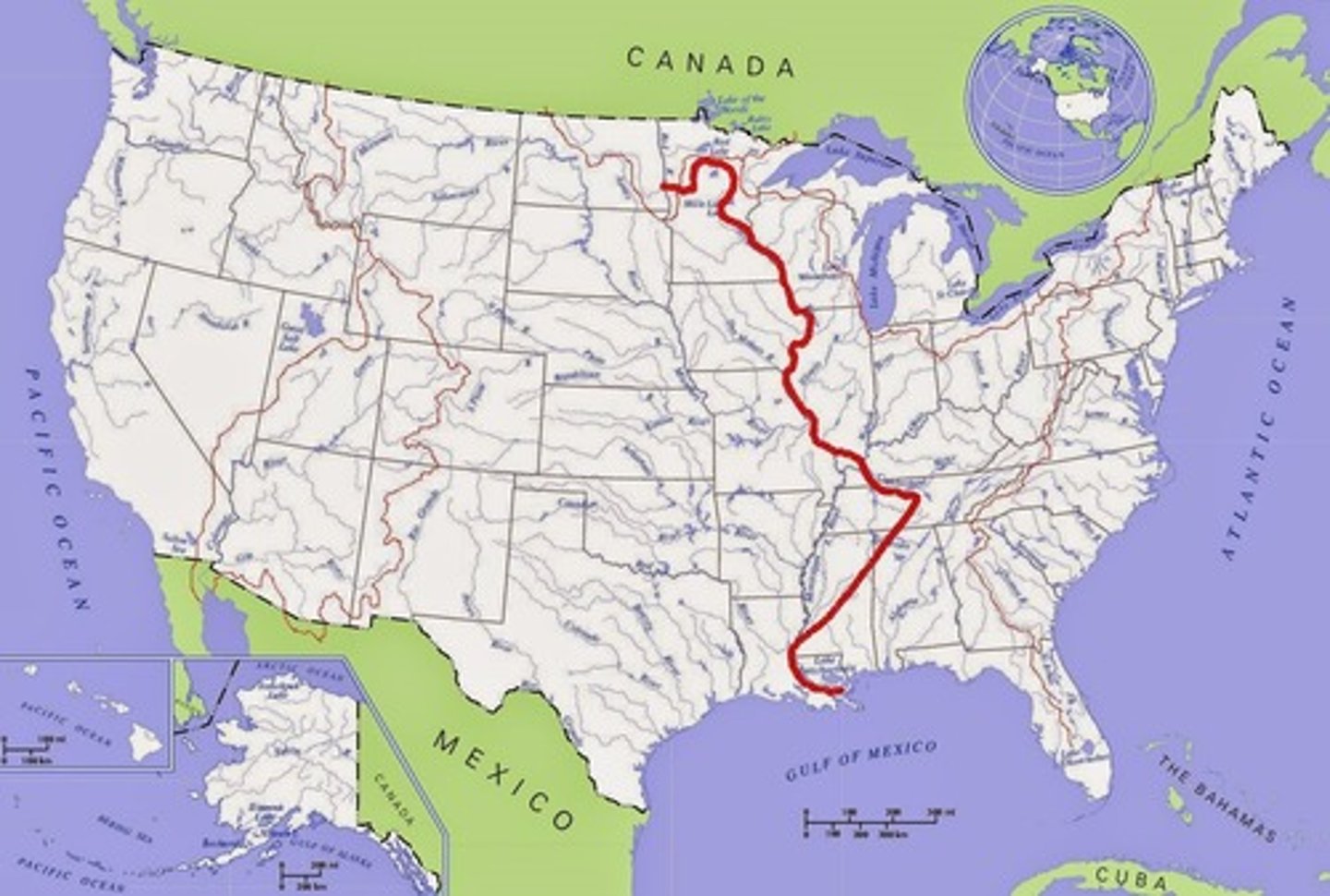
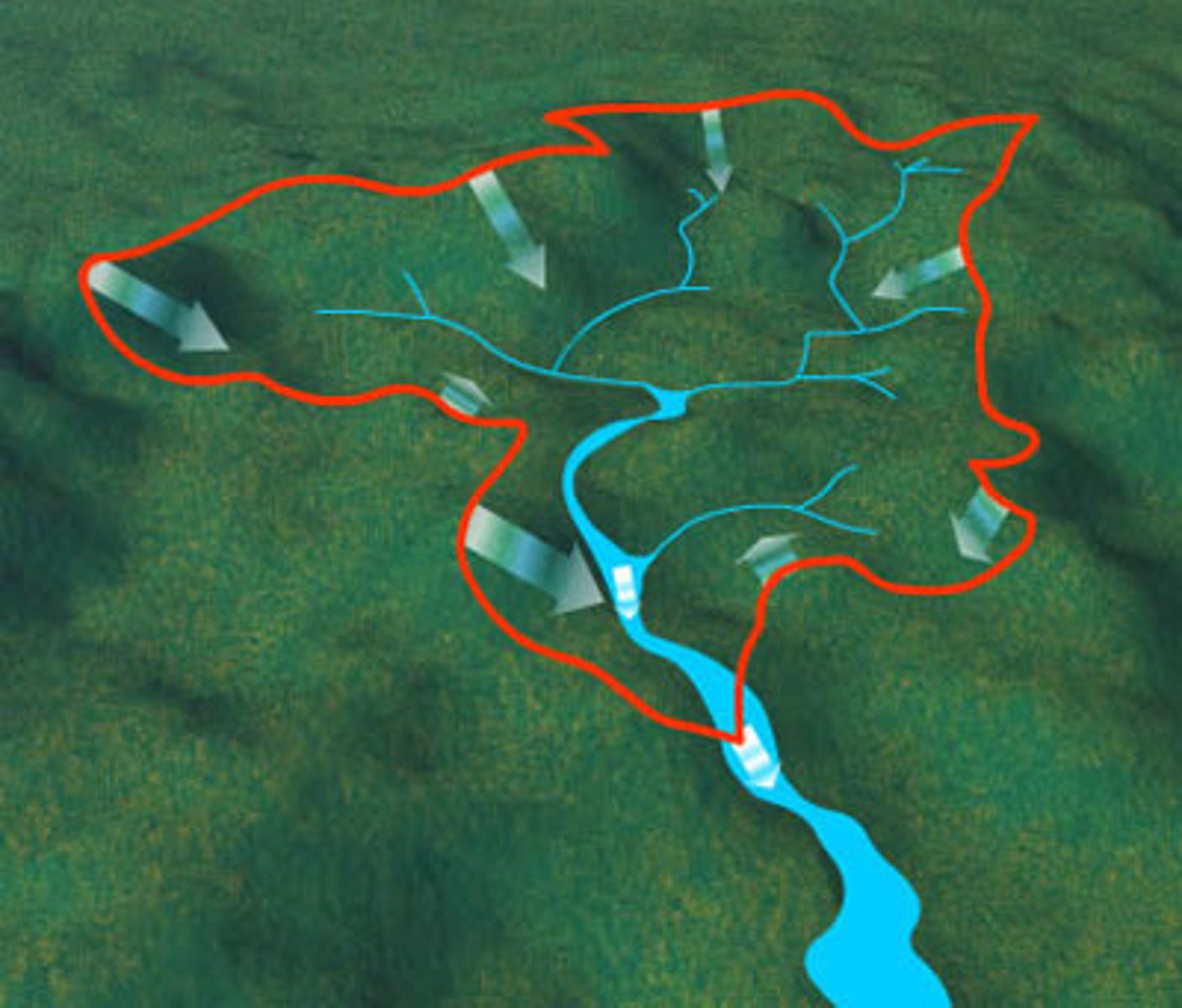
Watershed
The area of land that is drained by a water system
Ground Water
The water that is beneath the Earth's surface
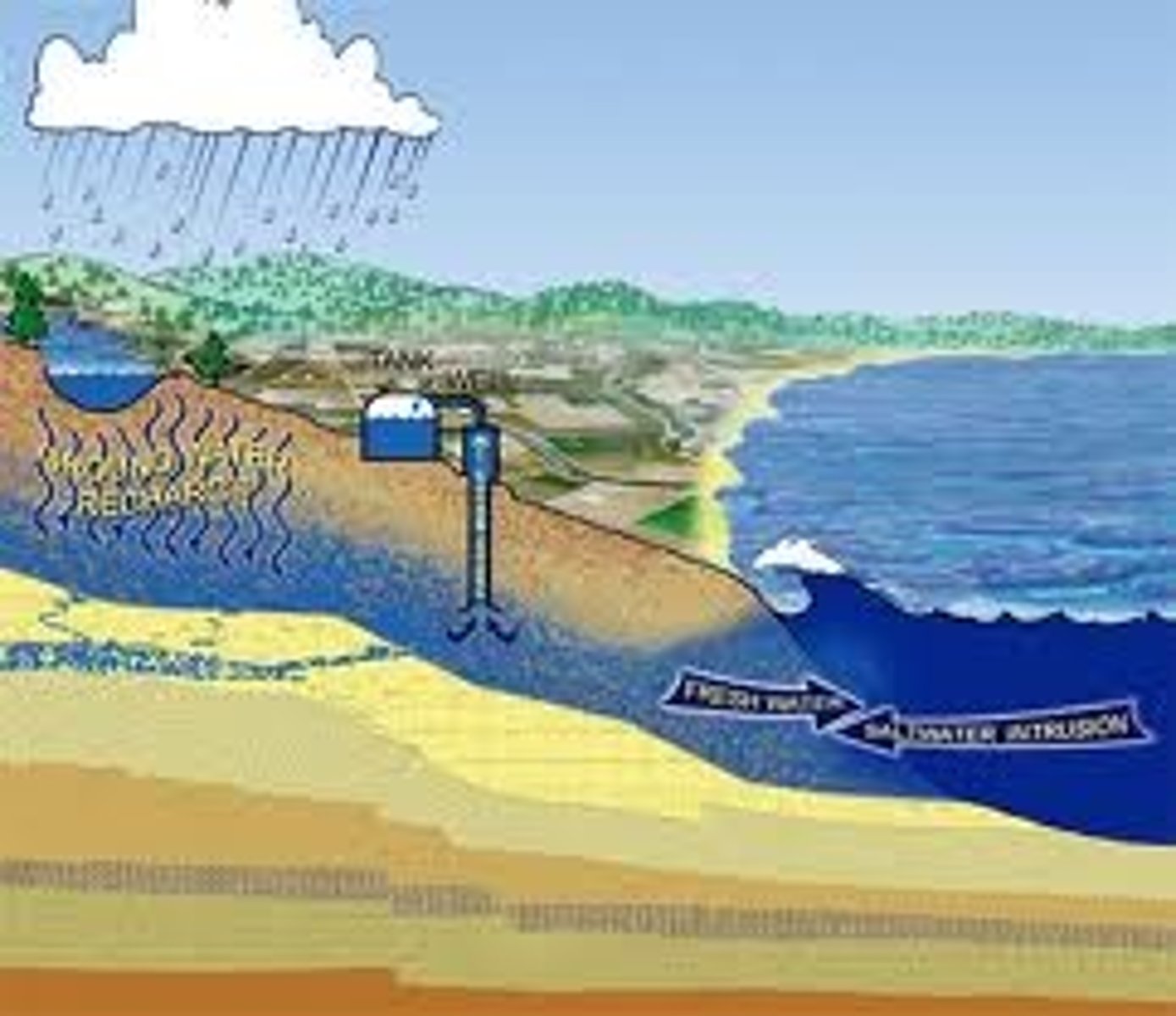
Aquifer
Porous rock that stores groundwater and allows the flow of groundwater
Potable
Suitable for drinking

Pathogen
A microorganism, another organism, a virus, or a protein that causes disease; an infectious agent
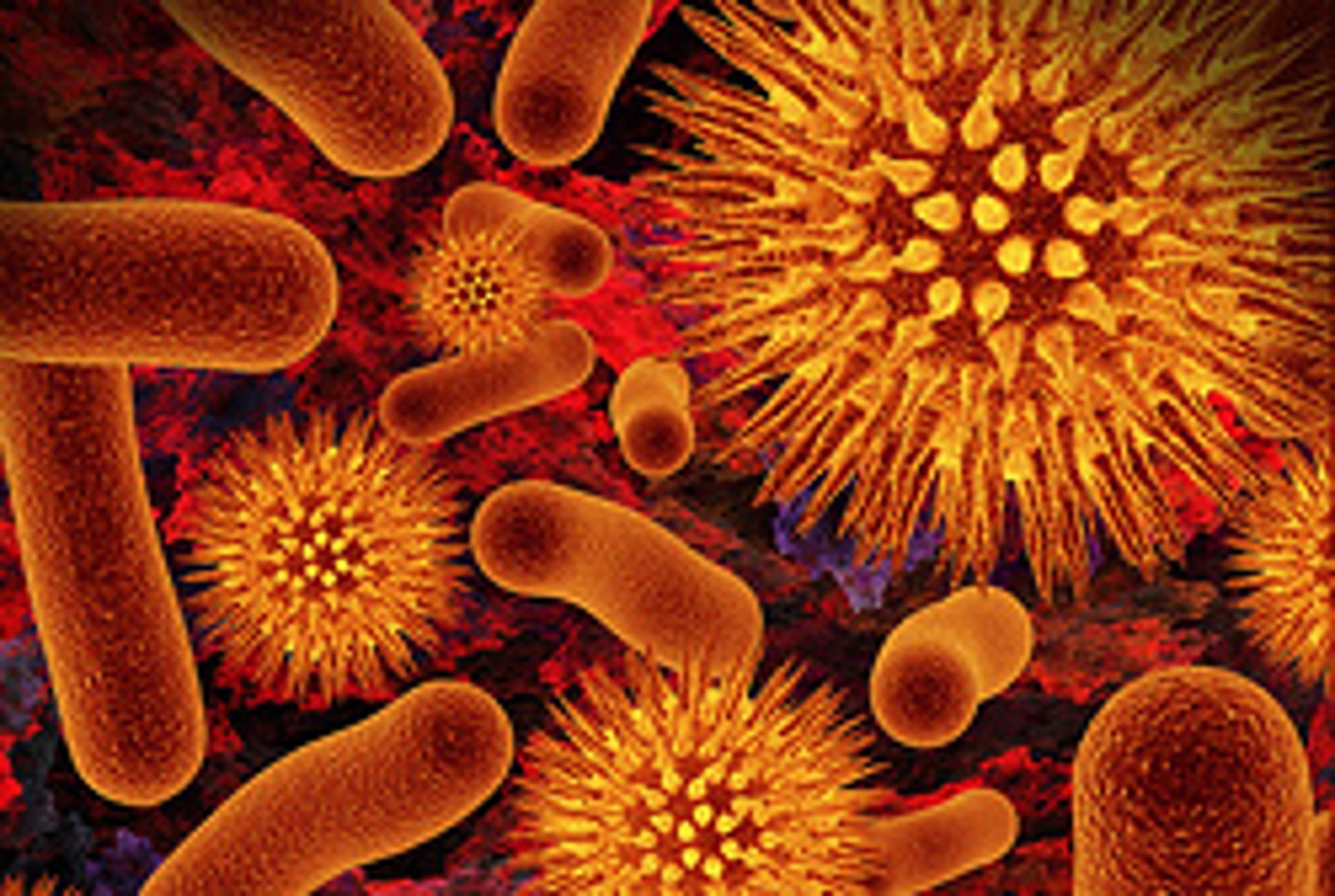
Water Pollution
Contamination of water by waste matter or other material that is harmful to organisms that are exposed to the water

Point- Source Pollution
Pollution that comes from a specific site; an example is pollution from factory water pipe into a stream.

Waste Water
Water that contains wastes from homes or industry
Artificial Eutrophication
A process that increases the amount of nutrients in a body of water through human activities, such as waste disposal and land drainage
non-point source pollution
undefined source of water contamination such as golf course, farm field, residential neighborhoods
evaporation
changing from liquid to gaseous state
condensation
changing from gaseous to liquid state
precipitation
any form of water (snow, sleet, hail) falling to earth
infiltration
water soaking into the ground
75%
% of water covering the planet
97%
% of water that is salt water
Primary Filtration
the first step in water treatment where large items are filtered out
Preliminary Treatment
the first step in sewage treatment where large sewage items are filtered out
Coagulation
alum takes toxins out of the water and creates flocs that sink
alum
white chalk material added to water for cleaning
floc
alum combined with water contaminants
Second Filtration
layers of rock and gravel filter any remaining impurities from drinking water
chlorination
chlorine is added to water to kill pathogens in water
aeration
water and air in close contact in order to remove dissolved gases (such as carbon dioxide) and oxidizes dissolved metals such as iron, hydrogen sulfide, and volatile organic chemicals (VOCs)
fluoridation
fluoride is added to prevent tooth decay
sludge
the solid portion of wastewater treatment
groundwater contamination
pollutants entering ground water by percolating down from the surface
1969
Year the Cuyahoga River caught on fire
Clean Water Act
1972, goal to make water clean for swimming and fishing by 1983, not achieved
Primary treatment
2nd stage of wastewater treatment where fine particles settle out to create sludge
secondary treatment
oxygen, chlorine, and maybe UV light is used to further treat waste water
tertiary treatment
wastewater is funneled through a gravel bed for final cleaning before it is released into a waterway
well
hold that is dug to obtain fresh ground water
hexavalent chromium
main contaminant in the class action lawsuit in Hinkley, CA (Erin Brockovich)
speed up
what will happen to the water cycle with global warming
Cake
the finished product of sludge that is used as a soil conditioner
charcoal
charred wood used for cleaning water (Brita water filter)
LifeStraw
created for developing countries to remove bacteria, viruses, and parasites from water to use for drinking
Organic Pollution
pollution that occurs when living things decompose
Biological Oxygen Demand
The amount of oxygen needed by microorganisms to decompose biological wastes into carbon dioxide, water, and minerals.
Cuyahoga River
River that in the 1960s carried so much flammable waste that it caught fire.
Huang Pu River
River that ended in Shanghai that had dead pigs in it. It significantly decreased BOD.
Gulf of Mexico Dead Zone
Area in the Gulf of Mexico that has low amounts of oxygen due to large amounts of nutrients. Contains large amounts of Phosphorus and Nitrogen in the water.
Organic Pollutants
pesticides, fertilizers, plastics, detergents, gasoline and oil, other petroleum based materials.
Inorganic Pollutants
acids, bases, salts, and industrial chemicals
sediment pollution
Excessive amounts of soil particles that enter the water as a result of erosion
alkalinity
measured to determine the buffering capacity of water
pH
goal of water is 7.0
dissolved oxygen
if this variable is high, the environment is healthy
ammonia
A small, very toxic molecule (NH3) produced by nitrogen fixation or as a metabolic waste product
chromium
Cr