3.1 Biodiversity & Evolution
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Biodiversity
the total diversity of living systems, composed of species, habitat, and genetic diversity
Species Diversity
the diversity of species in a given unit of area for a given period of time. 2 Variables: number of species (richness) and relative proportions (evenness)
Habitat Diversity
the range of different habitats in a given area
Genetic Diversity
the range of genetic material present in a population of a species
Genetic diversity is very important when considering…
the conservation status of a population, as the gene pool of a species indicates how resilient a species may be to change,since greater diversity of genes correlates with greater chance of adapting to change.
Resilience
the ability of a system to resist change and return to an equilibrium, despite inputs pushing it away from a stable state
High Biodiversity =
complex ecosystems with interconnected food webs, enhancing stability, as consumers can switch food sources
High Productivity =
diverse habitats, niches, species, and more complex systems and resilience
Genetic Diversity =
adaptability and stability in response to change
Complex Ecosystems =
negative feedback loops and steady equilibrium
Pioneer vs Climax Communities =
pioneer communities are less resilient, whereas climax communities are more complex and resilient
Communities in Harsh Environments =
simpler and less resilient due to environmental constraints
Human Impacts (Negative)
simplifies ecosystems by reducing productivity, biodiversity, and species interactions, making them less stable. Removing species shorten food chains, disturbs food webs, and lowers ecosystem resilience
Human Impacts (Positive)
Rewilding projects, protecting keystone species can increase resilience by enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem stability
Evolution
the cumulative change in heritable characteristics within a population or species over time.
Biodiversity
arises from random mutations in DNA, contributing to genetic diversity
Mutations
may have no effect, be harmful, or provide an advantage to the organism
Natural Selection
acts on theses variations, shaping biodiversity over time
Speciation
the formation of new species through evolution,
Adaptive Radiation
occurs when a single species evolves into multiple species, each adapted to different ecological niches, ex. Darwin’s Finches
Variation
individuals in a species differ due to genetic variation, which is heritable. Some individuals are better adapted to their environment than others
Overproduction
Species produce more offspring than needed to replace the parents, resulting in surplus population
Competition
limited resources create competition among individuals, fitter individuals with advantageous adaptations are more likely to survive and reproduce
Adaptation and Reproduction
Adaptations enhance survival are passed onto the next generation, over generations, advantageous traits become more common, increasing population fitness and diversity
Simpson’s reciprocal index
is used to provide a quantitative measure of species diversity, allowing different ecosystems to be compared and for change in a specific ecosystem over time to be monitored
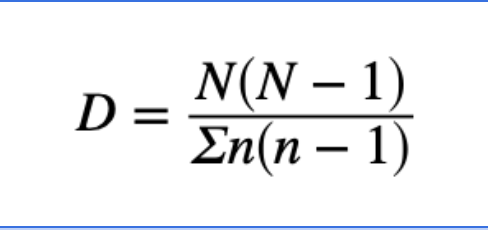
Numbers
D = diversity
N = total # of individuals in the population
n = the number of individuals in a single species
value of D will be higher where there is greater richness (number of species) and evenness (similar abundance), with 1 being the lowest possible value
Sampling Strategies
in a meadow, you can compare two areas for flowering plant diversity using random sampling
for insect diversity, you can use sweep nets and walk across whole area
for ground living insects you can use pitfall traps
in a woodland, you can count tree species diversity by counting trees
in a stream, you can look at macroinvertebrate diversity using the same method as in a meadow or kick sampling with small quadrants
in a lake, you can look at plankton diversity, at different depths or distances using specialist equipment
bird diversity can be measured using mist-netting, making bird sightings, or bird song recordings
small mammals can be sampled using small mammal traps
large mammals can be sampled through sightings