Topic 7 - Organisms & Predation (BIOL 2300)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what does behavioral ecology increase our understanding of
how biotic factors influence distribution/abundance of organisms
to maximize fitness, organisms require
suitable environmental conditions (abiotic factors)
sufficient energy resources(abiotic and biotic factors) → acquire appropriate quantities of energy, acquire energy efficiently (gain>loss)
behavioral strategies have _______ under these selection pressures to maximize ______
evolved, fitness
predation
consumption of prey animals by a predator, where prey is alive when attacked
predator consumption rate depends on.. (3)
search efficiency for prey (search time, s)
time to pursue, subdue & ingest prey (handling time, h)
prey abundance per unit area (prey density) - all prey species
functional response
relationship between prey density and predator consumption rate
functional response - type 1
Linear
rarely observed
search time varies w/ prey density
handling time is constant but near zero
e.g. passive predators (spiders, filter feeders), herbivores - occurs if prey densities do not become high enough for satiation
as prey density increases, encounter rates increase, search time decreases. s > > h
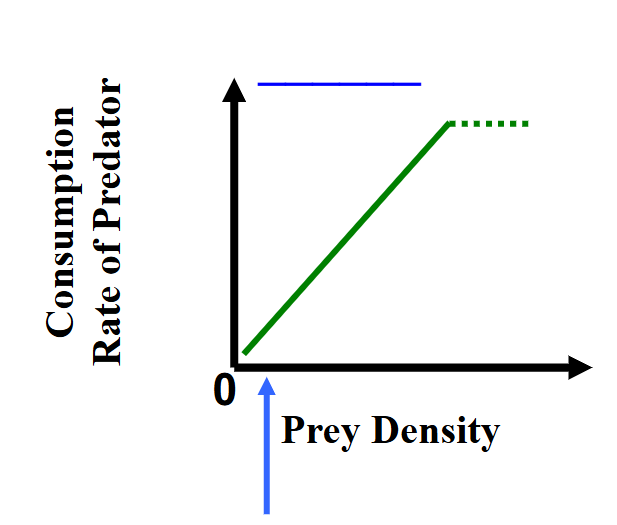
functional response - type 2
Linear
most common
search time varies with prey density
handling time is constant but above zero → consumption rate levels off at high prey densities (limited by handling time)
as prey density increases, encounter rates increase, search time decreases s > > h
where is starts to plato: as prey density increases, search time is zero but handling remains constant (above zero) h > > s
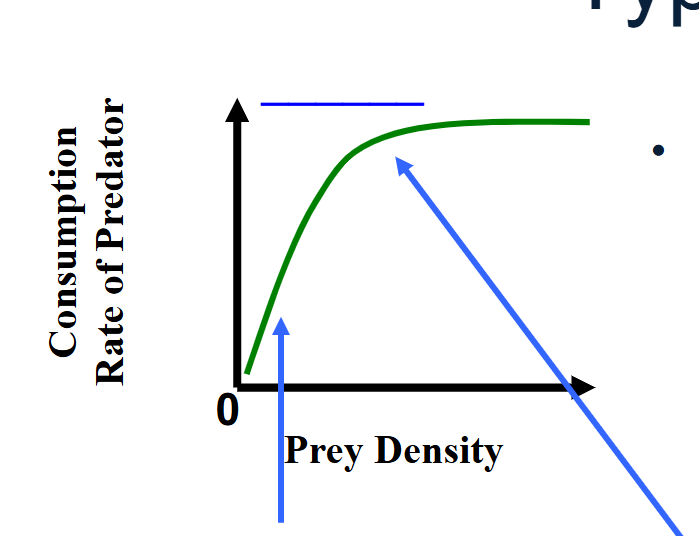
functional response - type 3
Exponential
rarely observed
search time and handling time vary w/prey density → consumption rate is lower at low prey densities
as prey density increase, h > s (same as type 2)
at low prey density, search time increases, and handling time = pursue, subdue & ingest prey
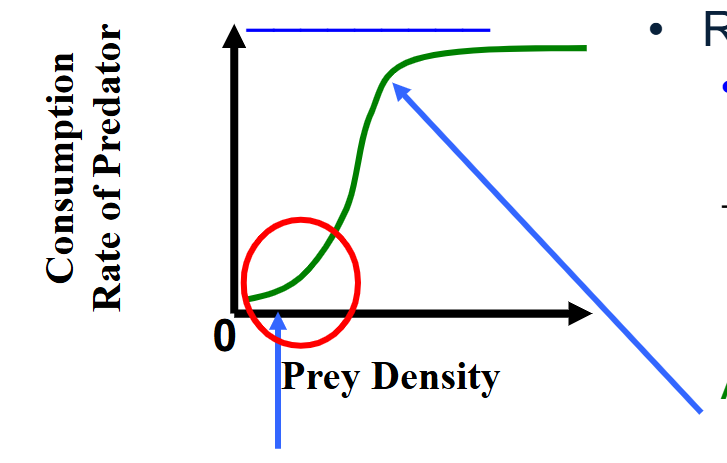
why is handling time lower at low prey densities then increase - type 3
search time: few prey encounters → have not learned high capture efficiency
refuge: high availability of cover for prey at low densities → low capture
compare and contrast 3 functional responses
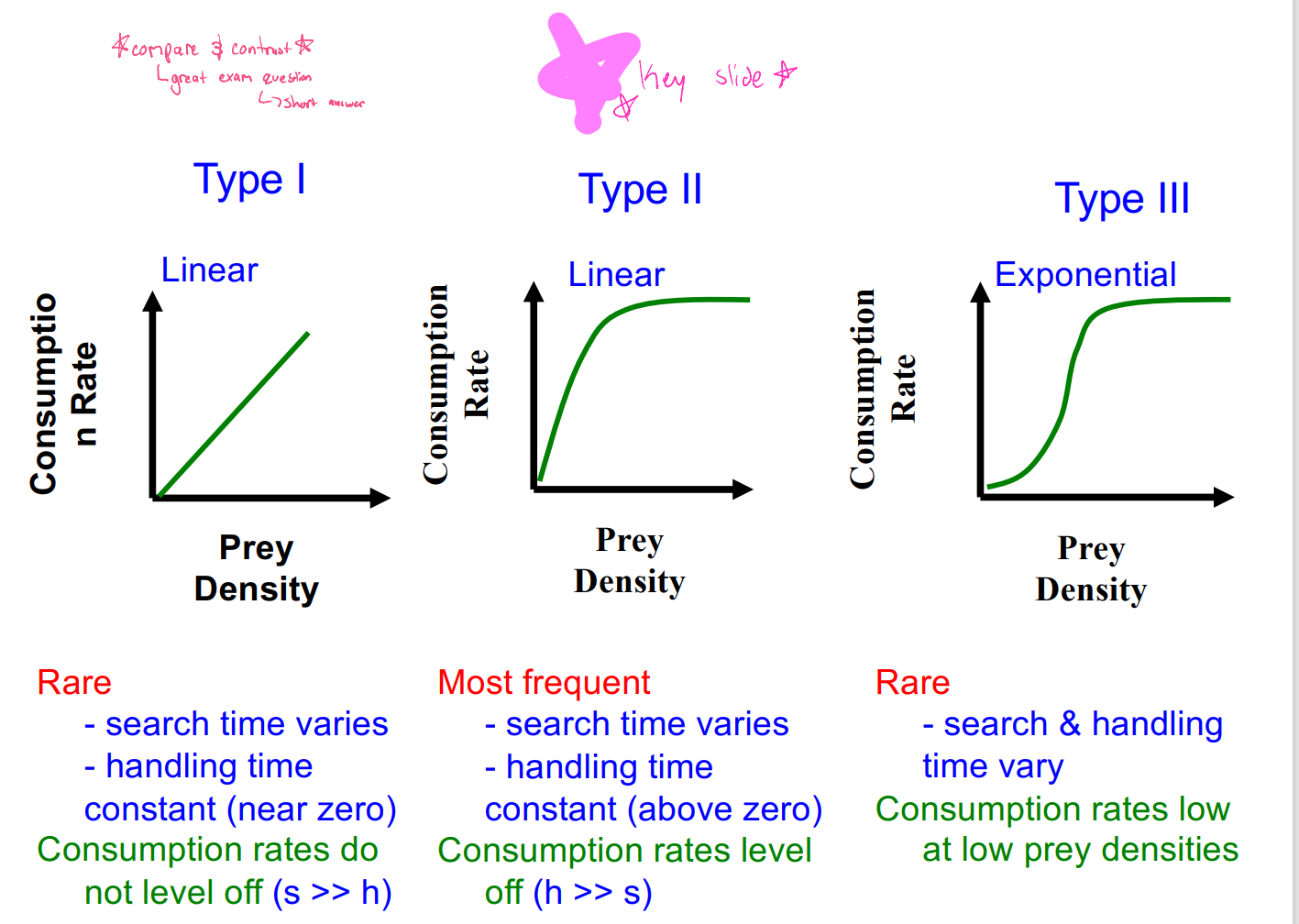
specialist
an individual takes one or few prey types
generalist
an individual takes many prey types
preference
proportion of a prey type in the diet is higher than its proportion in the envr. (“selectivity)
what doe preferences depend on
nutritional content of prey (e.g. vitamins, minerals)
energy**content of prey - more energy → more offspring → higher fitness
*preferences can be switched - switch may depend on the abundance of different prey types
foraging theory - goal
predict the optimal (or best) foraging strategy under certain conditions
based on math. models derived from economics
offers powerful way to understand foraging decisions of predators
foraging theory - assumptions
foraging behavior enhances fitness (i.e. foraging strategy is a behavioral trait favored by natural selection in the past)
animals maximize net energy gain (ensures high fitness) → predators must expend energy to forage: energy loss - searching & handling time, energy gain - consumption *efficiency depends on energy: energy gain - energy loss = net energy
diet model - specialists and generalists
if predator knows the energy content of each prey type:
specialists - consume more profitable prey, more energy searching
generalists - consume less profitable prey, less energy searching
*predators switch between these 2 strategies depending on conditions
diet model - predictions
if searching time > > handling time → generalists
if handling time > > searching time → specialists
*a predator should consume all prey types when overall prey abundance is low
what type of envr. should predators be generalists in
in a low productive envr
underlying diet model assumptions
predators know everything about their foraging envr.
predators perform complex mathematics to determine the profitabiliti’s of a variety of prey types