ANAT1101 Module 3 Cells and Microbiome
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Cells
It is considered as the smallest living unit.
These are the building blocks of human.
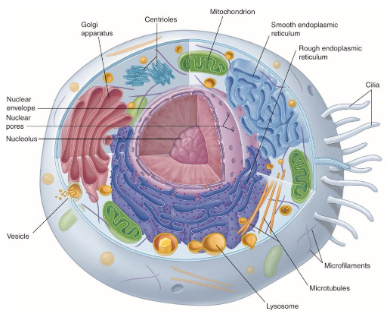
Basic Cell Structure
Plasma Membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
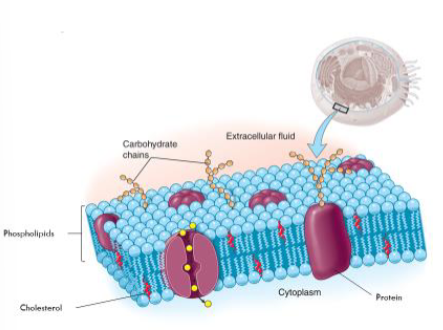
Plasma Membrane
It is the boundary (walls and doors) of the cell.
It regulates the passage of the substance.
It is composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, and protein.
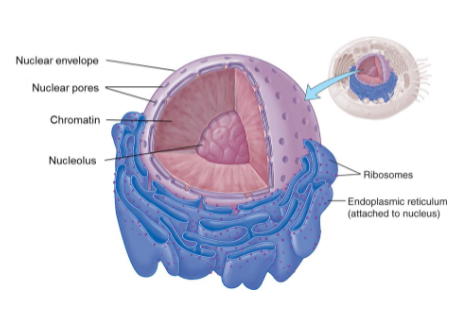
Nucleus
It is the boss.
It houses the instruction manual (DNA) for the cell.
It is surrounded by the nuclear envelope.
Mature RBCs do not contain a nucleus.
Cytoplasm
It fills space between plasma membrane and the nucleus.
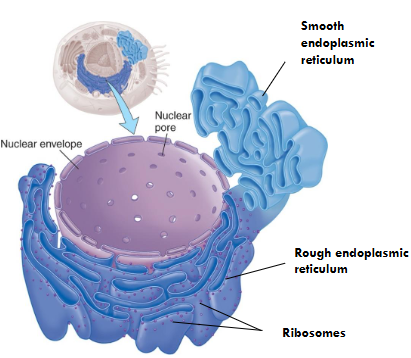
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
It is called the factory.
It synthesizes and moves proteins in channels.
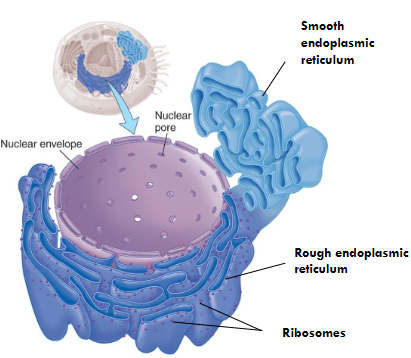
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
It has ribosomes attached that are used for making proteins.
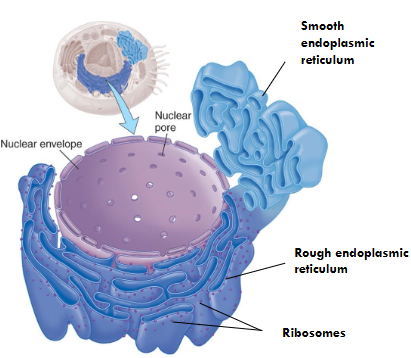
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
It makes some lipids and carbohydrates.
Golgi Apparatus
It is called the warehouse.
It receives proteins from the ER.
It modifies proteins and packages them in a vesicle that:
Fuses with the membrane and releases proteins.
Stored in the cell for later.
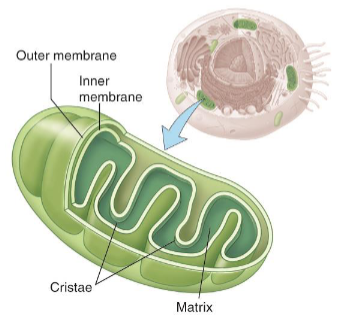
Mitochondria
It supplies energy.
It converts organic compounds into ATP.
Cells that do a lot of work contains lots of mitochondria.
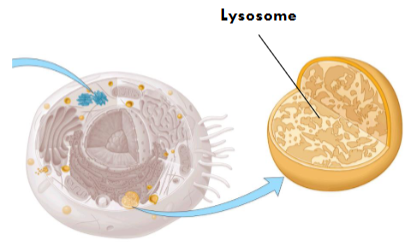
Lysosomes
It breakdown proteins that cell doesn’t use and recycles the amino acids.
It is used to destroy invaders like bacteria.
Cytoskeleton
It provides framework for the cell.
Determines cell shape.
Strengthens cell.
Allows cell to move.
Passive Transport
It requires no energy.
It includes diffusion, osmosis, filtration, and facilitated diffusion.
Active Transport
It requires energy.
It includes transport by pumps and vesicles.
Diffusion
It is the movement of solute from an area of high to low concentration.
It must be a gas or dissolved particle.
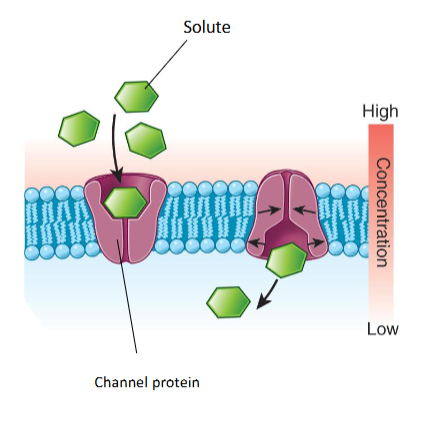
Facilitated Diffusion
The solute moves from an area of high to low concentration with the assistance of a protein.
Osmosis
It is the movement of solvent through a selectively permeable membrane.
Water goes in the direction where the solute concentration is higher.
Tonicity
It is the affect of osmosis on a cell when it’s in solution.
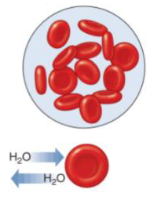
Isotonic
A solution with the same concentration of solutes as that inside the cell.
No net movement of fluid.
Hypertonic
A solution with a higher concentration of solutes as that inside the cell.
Fluid moves out of cell making it shrink.
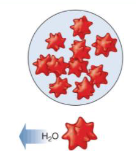
Hypotonic
A solution with a lower concentration of solutes as that inside the cell.
Fluid moves into the cell causing it to burst.
Filtration
It allows for the separation of a mixture through the movement of solvent and small solutes from an area of high pressure to low pressure.
Biome
A naturally occurring community of plants or animals occupying a particular habitat.
Microbiome
A collection of microorganisms residing within distinct communities on and in the human body.
No two individuals had the same microbiome.
It trains the immune system.
It includes:
Bacteria
Virus
Fungi
Archaea
Pathogens
These are harmful microorganisms.
Microbial Communities
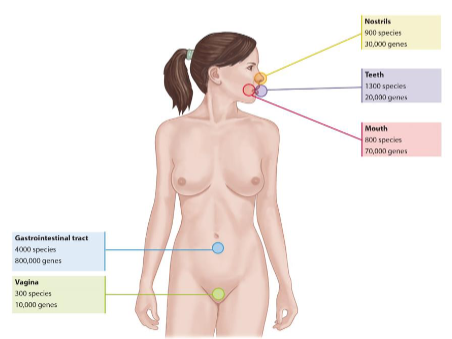
Gastrointestinal Tract
Mouth
Upper respiratory tract
Vagina
Microbiome Influences Health
Members of the microbiome release hormones and chemicals that influence organs far away.
Hormones secreted elsewhere influence members of the microbiome.
Importance of Microbiome
Digestion of food.
Absorption of nutrients.
Production of vitamins.
Energy production.
Ways to Acquire Microbiome
In utero
Vaginal birth
Breast milk
Other people
Environment
How Microbiome Changes
Birth - 2 years = microbiome is populated through birth canal, breastfeeding, environment.
Ages 2-5 = starts to resembles that of an adult.
Adulthood = little more stable; altered by food, environment, antibiotics, exercise, pre/pro-biotics.
Old age = decreased diversity.
Components of the Microbiome
Bacteria
Viruses
Fungi
Archaea
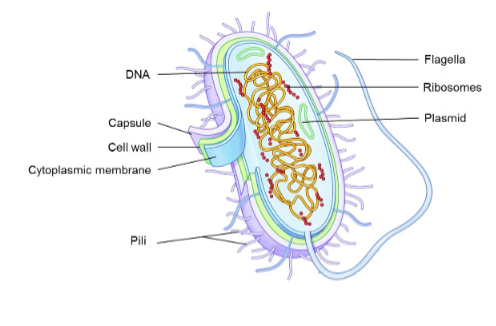
Bacteria
It makes up the majority of the microbiome.
These are living, single celled organisms.
It can be affected by antibiotics.
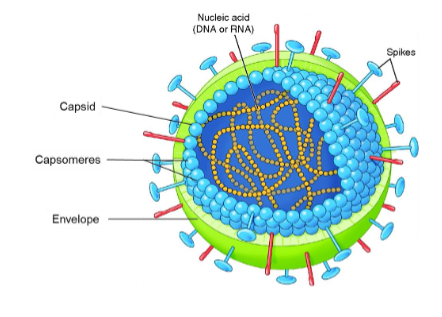
Viruses
It is not considered living cells.
Viruses inject their genetic material into host cells and use the host’s organelles to survive.
Antibiotics do not kill viruses.
Fungi
It includes molds and yeasts.
It can overgrow and cause illness when immune system is compromised.
Archaea
They are living single-celled organisms.