NUCL320 Exam 2 - Dislocations
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(2/3)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What type of deformation does dislocation motion produce?
plastic deformation
True or false, dislocation depends on incrementally breaking bonds?
true
With respect to dislocation, what is the only way in which plastic deformation can occur?
plastic deformation can only occur if dislocations move
How is dislocating in metals?
dislocation motion is easier due to nondirectional bonding and the existence of close-packed directions for slip
How is dislocating in covalent ceramics?
dislocation motion is very hard due to the directional bonding of its atoms
How is dislocation in ionic ceramics?
dislocation is hard due to the necessity to avoid + and - neighbors
What is the definition of deformation by slip for single crystal and polycrystalline materials?
single crystal - slip occurs on distinct slip planes
polycrystalline - slip planes and directions are different within the different grain boundaries, the boundaries stop dislocations and yielding for each grain is different
What is the definition of dislocation motion?
The process of a dislocation incrementally moving through a plane
What is the definition of a dislocation?
the boundary between a slipped and an unslipped area on a slip plane within a crystal
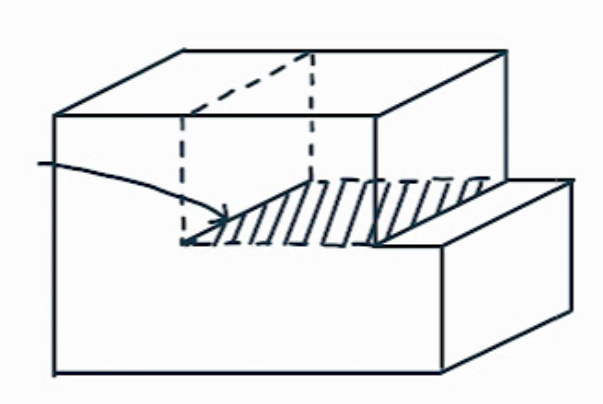
What is this dislocation feature?
the dislocation line
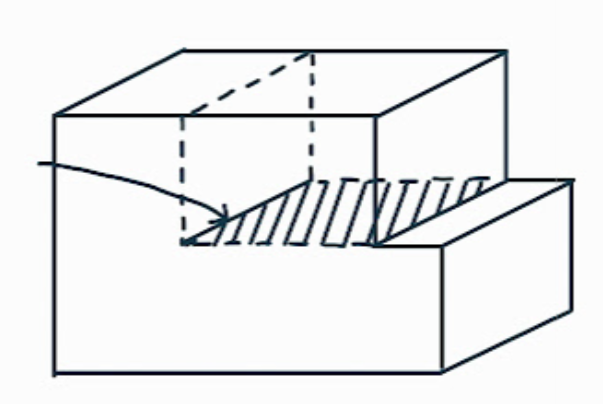
What is this dislocation feature?
the sheared area of a slip plane
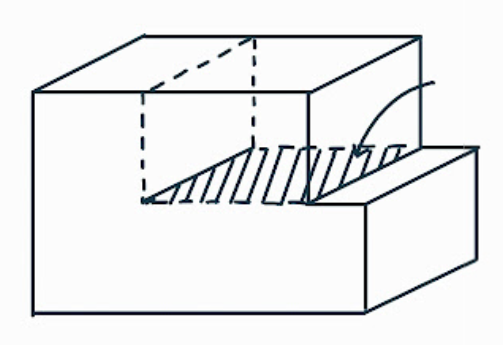
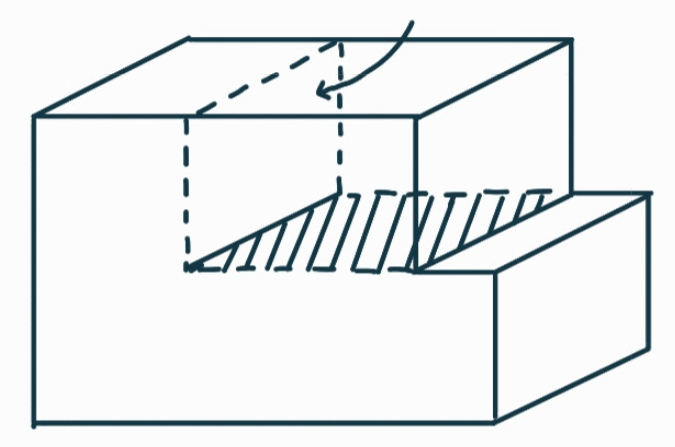
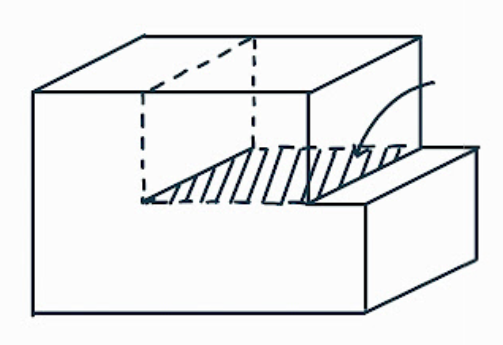
What is this dislocation feature?
the extra plane
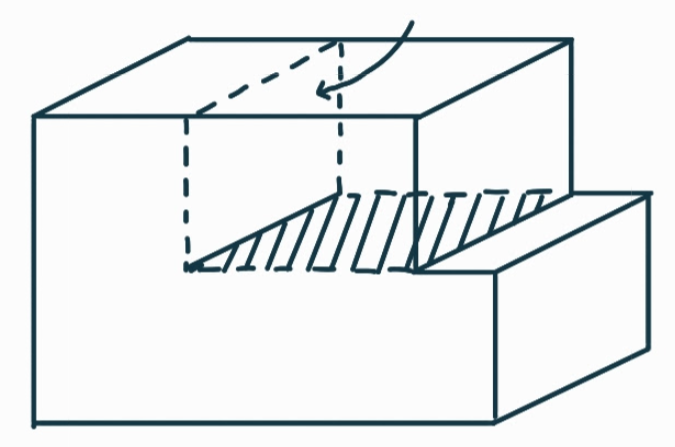
What is the definition of a loop dislocation?
when the defect line forms a closed loop, enclosing a whole region with a defect within a lattice
What is the definition of a local burgers vector?
starts by enclosing a region on a theoretical perfect lattice, compares to the real lattice, the burgers vector, b, completes the circuit on the real lattice
What is the definition of a true burgers vector?
starts by enclosing a region on a real lattice, compares to a perfect version of the same lattice, the burgers vector, b, extends past the end of the completed circuit on the perfect lattice
How do burgers vectors behave for edge dislocations?
the burgers vector is perpendicular to the dislocation line, the dislocation moves in the direction of the burgers vector, and the slip movement of the material is parallel to the burgers vector
How do burgers vectors behave for screw dislocations?
the burgers vector is parallel to the dislocation line, the dislocation moves perpendicular to the direction of the burgers vector, and the slip movement of the material is parallel to the burgers vector
True or false, a single dislocation has a unique burgers vector?
True
Can a dislocation end in a perfect crystal?
No, within a perfect crystal the dislocation would continue infinitely
How do dislocations come to an end?
by forming a closed loop
by reaching a surface
by reaching a grain boundary
by reaching a junction with other dislocations
What is the Frank Rule?
when three or more dislocations meet at a junction (a node) the burgers vector will be conserved
b1=b2+b3
if all burgers vectors point away from or towards a node
b1+b2+b3=0
Geometrically, what will the reactions be like for a perfect dislocation and perfect node formation?
they will be coplanar
Split of Dislocations
What is the definition of a perfect dislocation?
a perfect dislocation leaves a perfect crystal structure, the burgers vector corresponds to a complete lattice translation v
What is the definition of a partial dislocation?
a partial dislocation leaves an imperfect crystal structure (and therefore a stacking fault), the burgers vector is shorter than a full lattice translation
What is the definition of an extended (dissociated) dislocation?
a dislocation that has split into 2+ partial dislocations, separated by a stacking fault (this effectively spreads the dislocation over a larger region to reduce energy)
What is the stacking sequence of an FCC structure before and after planar defects?
ABC ABC ABC → ABC ABA CAB
What is the stacking sequence of an HCP structure before and after planar defects?
AB AB AB AB AB → AB AC AB AB AB
What is the stacking sequence of an BCC structure before and after planar defects?
there is no close packed plane, so no stacking sequence no faults
How do stacking faults effect energy?
the atoms within stacking faults are displaced from their regular positions, which leads to excess energy
What is the definition of stacking fault energy (SFE)?
the energy per unit area of a fault
What is the definition of a stacking fault?
a planar defect where the normal stacking sequence of atomic planes is disrupted, resulting in a misalignment of layers (most common in FCC and HCP crystal structures)
What controls the separation between partial dislocations? How?
stacking fault energy, as with low SFE → dissociation is unfavorable → small or no stacking fault → glide or cross-slip is possible, and with high SFE → dissociation is favorable → wider stacking fault → cross-slip is difficult
What is the definition of conservative motion?
dislocation glide where atoms move along the slip plane and no atoms move out of the slip plane
What is the definition of non-conservative motion?
dislocation slide where there is climb, and atoms move out of the slip plane
What is the definition of climb?
the movement of an edge dislocation perpendicular to its slip plane, due to the addition or removal of atoms via diffusion which causes the dislocation to shift vertically rather than along the slip plane (this is more common at high temperatures)
What is the definition of cross-slip?
when a screw dislocation moves from one slip plane to one that intersects it (allowing it to continue when something blocks its path, eg a grain boundary)
Is climb or slip influenced more by temperature?
climb is enhanced by temperature, slip much less so