MOD 3 -Upper Extremity Fractures and Injuries
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for upper extremity fractures and injuries.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are the three main types of phalangeal fractures, and where do they occur?
Tuft (distal phalanx tip, comminuted), shaft (angulated/displaced due to ligament pull), and avulsion fractures (dorsal/volar, at ligament attachment sites).
What view is best for assessing phalangeal fractures and dislocations?
Lateral view.
What injury results from finger hyperextension?
Dorsal dislocation.
What is mallet (or baseball) finger and how does it occur?
A dorsal intra-articular avulsion fracture of the distal phalanx, caused by forcible flexion of an extended finger (e.g., ball hitting fingertip).
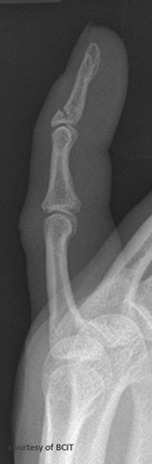
What is the treatment and possible complication of mallet finger?
Treated with a splint; complications include deformity and decreased range of motion.
What is a Boxer’s fracture and its common cause?
A fracture of the 5th (sometimes 4th) metacarpal neck, usually caused by punching a hard object with a closed fist.
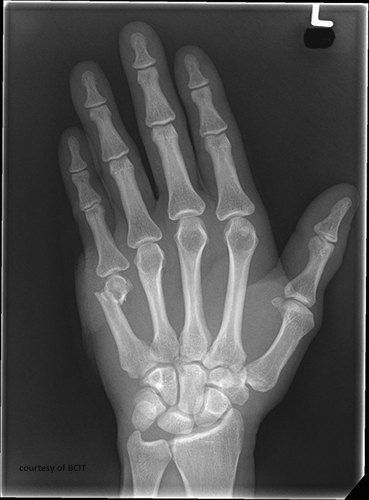
What is the treatment and main complication of Boxer's fracture?
Cast or K-wire fixation; complication includes rotational deformity of the finger.
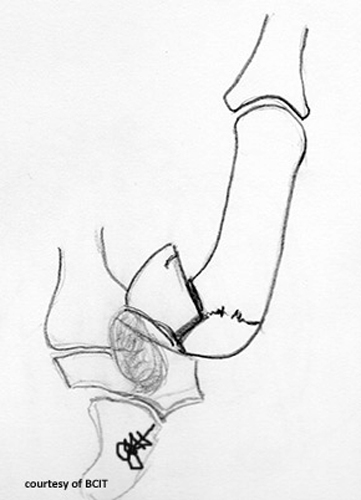
What is a Bennett’s fracture and how does it happen?
An oblique intra-articular fracture at the base of the 1st metacarpal with subluxation, caused by axial load, hyperabduction, or hyperextension of the thumb.
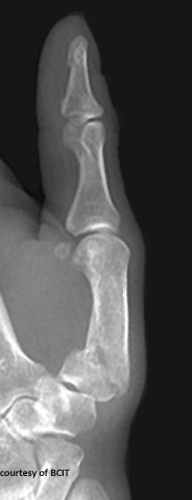
What is the treatment for Bennett's fracture and why is it significant?
Fixation with pins or K-wires; loss of thumb function (opposition/grip) is a serious concern.
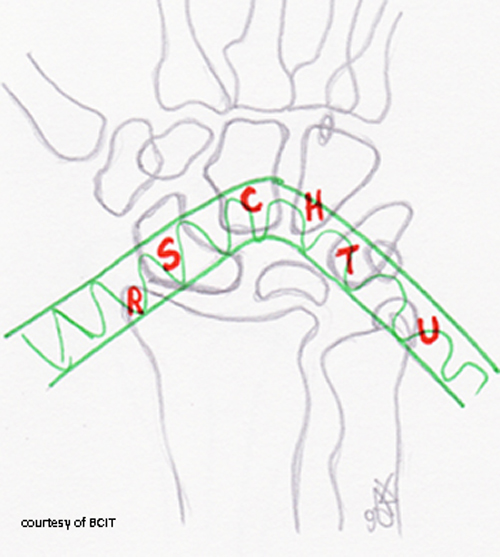
Where do most carpal bone fractures/dislocations occur?
In the vulnerable zone/arch of the wrist — ulnar side gets more severe injuries.
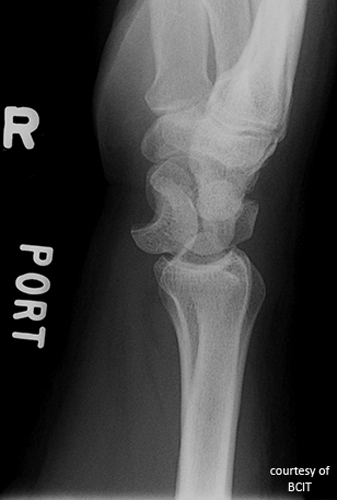
What does a 'spilled teacup' appearance indicate on lateral wrist imaging?
Lunate dislocation.

Why is wrist positioning critical in trauma imaging?
To prevent misinterpretation and to align radius, lunate, capitate, and 3rd metacarpal for accurate diagnosis.
What causes lunate dislocation and what are its features?
FOOSH injury; volar displacement, loss of articulation with capitate and radius.
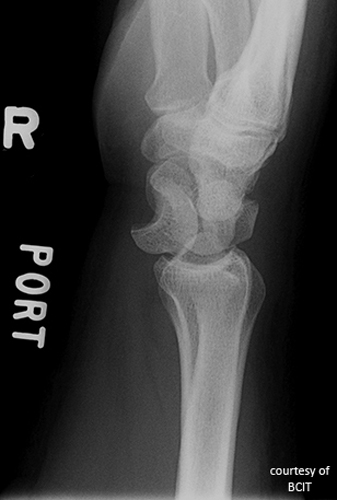
What is the treatment and complication of lunate dislocation?
Reduction, immobilization, often surgery; complications include arthritis and wrist instability.
How does a scaphoid fracture present and occur?
Tenderness in anatomical snuffbox; commonly caused by FOOSH.
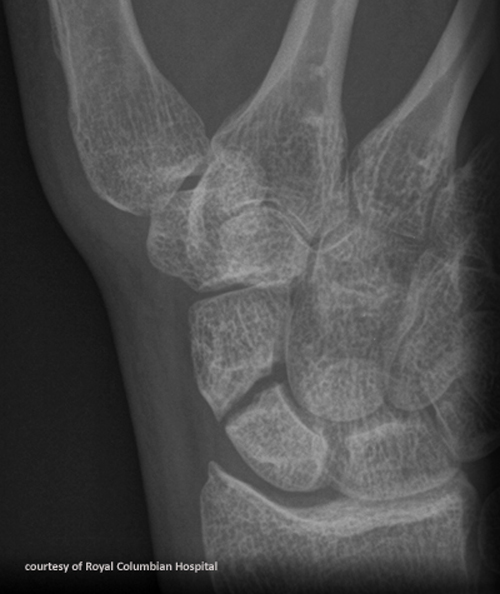
What is the main concern with scaphoid fractures?
Avascular necrosis due to poor blood supply.
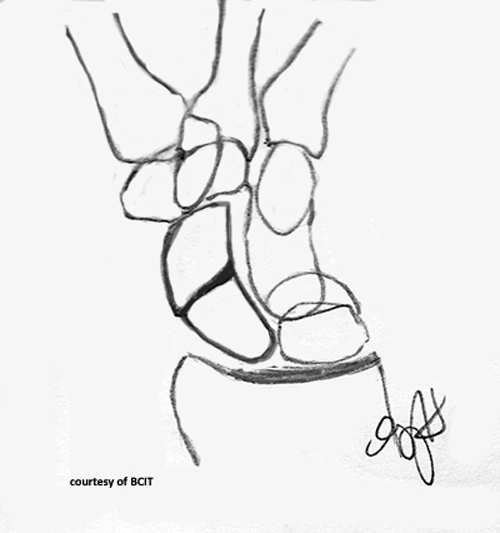
What is a Colles’ fracture and what causes it?
Distal radius fracture with dorsal displacement (“silver fork”), caused by FOOSH with wrist dorsiflexion.
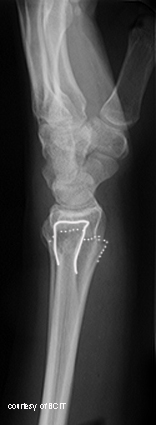
What is a Smith’s fracture?
Reverse Colles’ with palmar (anterior) displacement, caused by falling on a flexed wrist.
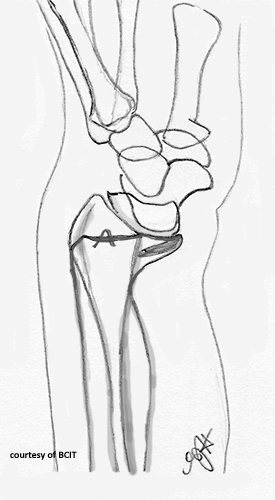
What are the treatments and complications for both Colles’ and Smith's fractures?
Reduction, immobilization, surgery if severe; complications include deformity, weak grip, and nerve issues.
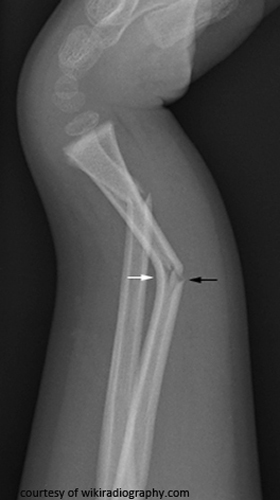
What is a Galeazzi fracture?
Fracture of the distal/mid-radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint.
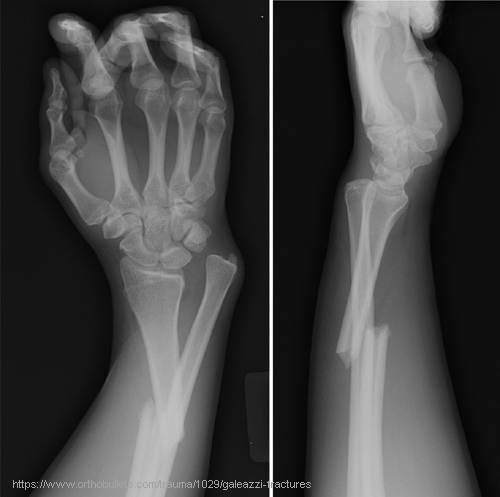
What is a Monteggia fracture?
Ulnar shaft fracture with anterior dislocation of the radial head.
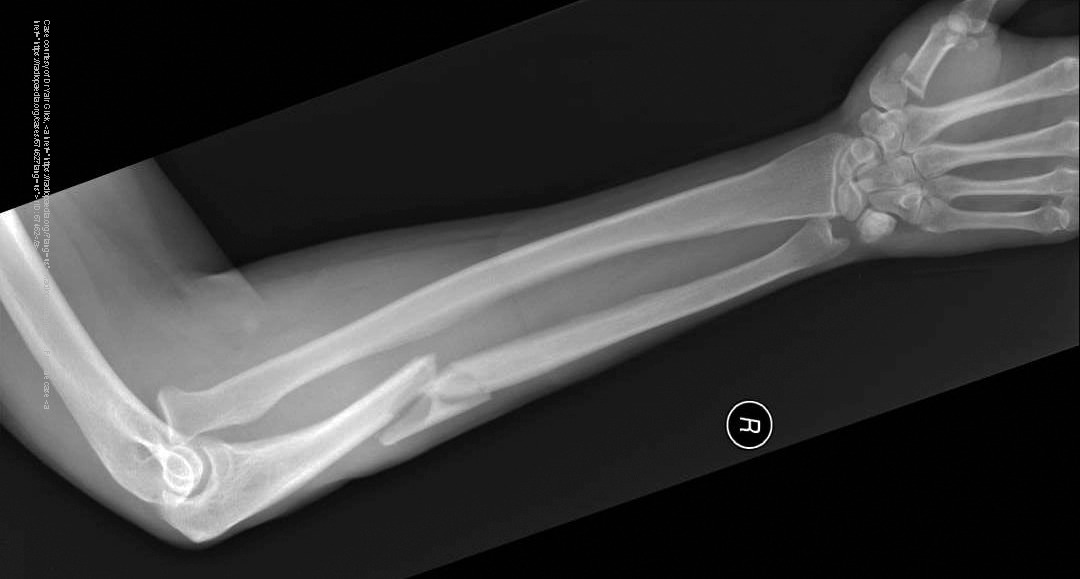
What causes Galeazzi and Monteggia fractures?
FOOSH with pronation; usually from blunt trauma or falls.
What injury is indicated by a visible fat pad (sail sign) on elbow X-ray?
Occult elbow joint fracture causing joint effusion.
What causes most posterior elbow dislocations, and what bone is often fractured?
FOOSH on an extended elbow; often involves coronoid process fracture.
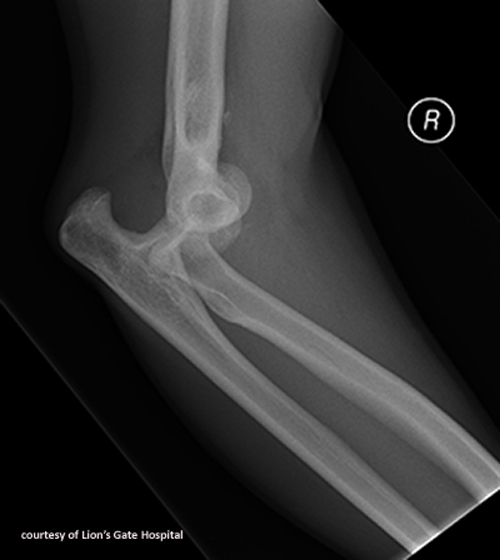
What is the most common elbow fracture in adults?
Radial head fracture.
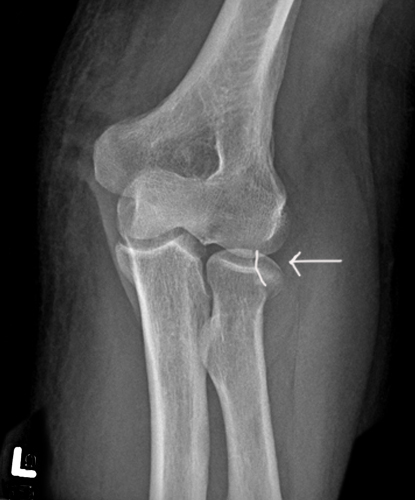
How are radial head fractures managed?
Splint/cast for simple fractures; surgery if severe. Early ROM exercises are critical.
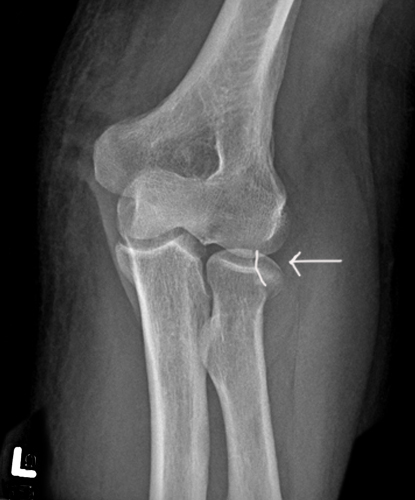
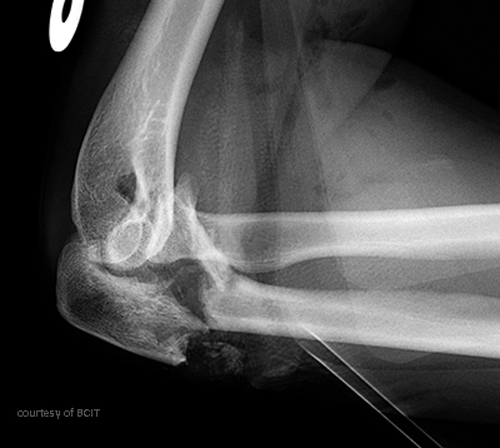
What causes olecranon fractures and what muscle is involved?
Fall on flexed elbow; triceps muscle pulls fragment proximally.
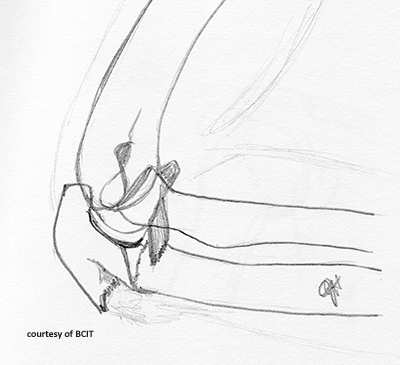
What are complications of olecranon fractures?
Loss of full extension, scar tissue, non-union.
What bones form the shoulder joint?
Clavicle, scapula, and humerus.
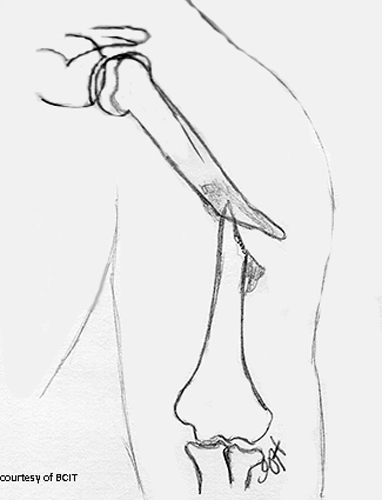
What nerve is at risk in humeral shaft fractures?
Radial nerve.
What type of forces cause different humeral fracture patterns?
Torsion = spiral, transverse = angled blow, high energy = comminuted.
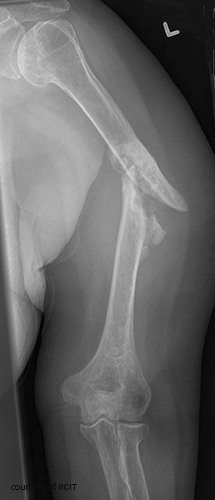
What condition increases the risk of proximal humerus fractures in the elderly?
Osteoporosis.
Which shoulder dislocation is more common and what causes it?
Anterior dislocation; caused by external rotation and abduction (e.g., fall or sports).
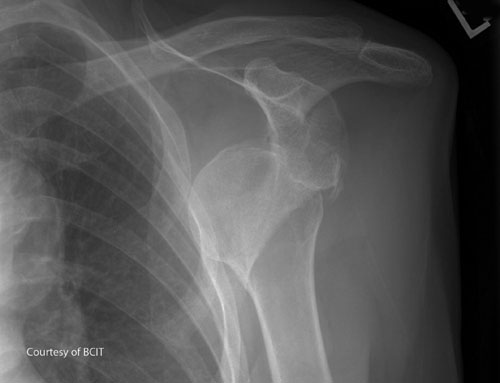
What is a Hill-Sachs lesion?
Compression fracture of the humeral head during anterior dislocation.
What causes posterior shoulder dislocations?
Seizures, electrocution, or axial load in internal rotation.
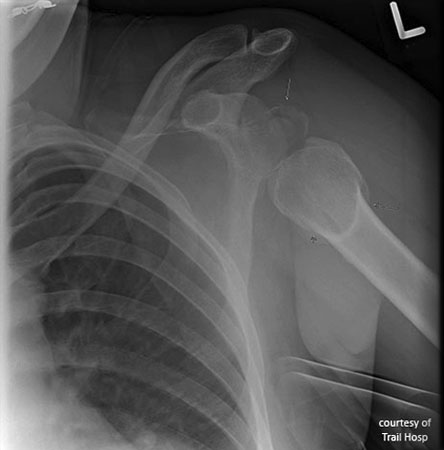
What are complications of shoulder dislocations?
Recurrent instability, Hill-Sachs lesions, arthritis.
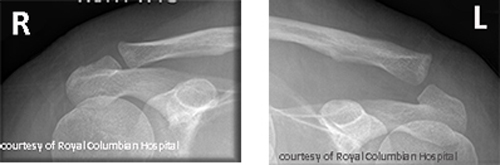
What are the types of AC joint injuries?
Sprain, subluxation (partial dislocation), and complete dislocation.
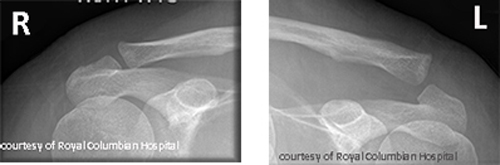
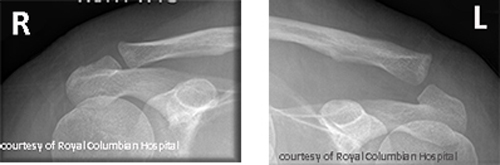
What causes AC joint injuries and how are they treated?
Fall on shoulder or sports impact; treated with sling or surgery if severe.
What are long-term complications of AC joint injuries?
Pain, arthritis, decreased ROM.
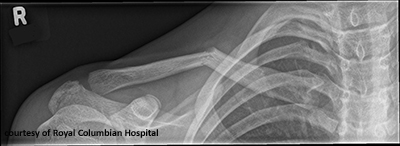
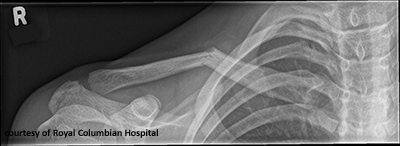
Where do clavicle fractures commonly occur and why?
Middle third, due to structural weakness and FOOSH mechanism.
What muscles affect displacement in clavicle fractures?
SCM pulls medial fragment up; arm weight pulls lateral fragment down.
What’s a common clavicle fracture in children?
Greenstick fracture.
What types of fractures are commonly caused by FOOSH?
Colles’, Smith’s, scaphoid, radial head, clavicle, and shoulder dislocations.
What is the main treatment goal for upper extremity fractures?
Restore function, maintain alignment, and minimize complications via reduction, immobilization, and physiotherapy.
What imaging views are essential for upper extremity trauma?
AP, lateral, and oblique to assess alignment and displacement.
What is a greenstick fracture and in whom is it most common?
A partial fracture where the bone bends and breaks on one side; common in children due to bone flexibility.
In what age group is epiphyseal separation of the proximal humerus most common?
Under 20 years old.
Why are epiphyseal injuries clinically significant?
They can affect future bone growth if not treated properly.
What serious complication can occur with Galeazzi or Monteggia fractures?
Compartment syndrome — increased pressure within a muscle compartment, potentially leading to tissue damage.
Why is the 'fat pad sign' important in elbow trauma?
It indicates joint effusion, often due to an occult intra-articular fracture even when the fracture line is not visible.
What is the normal range of the AC joint space?
Between 3 mm and 7 mm.
What radiographic sign is used to confirm proper carpal alignment?
The alignment of the third metacarpal, capitate, lunate, and radius on a lateral view (the “teacup” effect).
What force causes a spiral fracture of the humeral shaft?
Torsional force.
What type of force typically causes a transverse humeral fracture?
Direct blow to the angled shaft.
What are the key principles in treating upper extremity fractures?
Anatomical alignment, stabilization, early mobilization, and prevention of complications (e.g., nerve injury, nonunion).