CPI EXAM I REVIEW
1/295
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
296 Terms
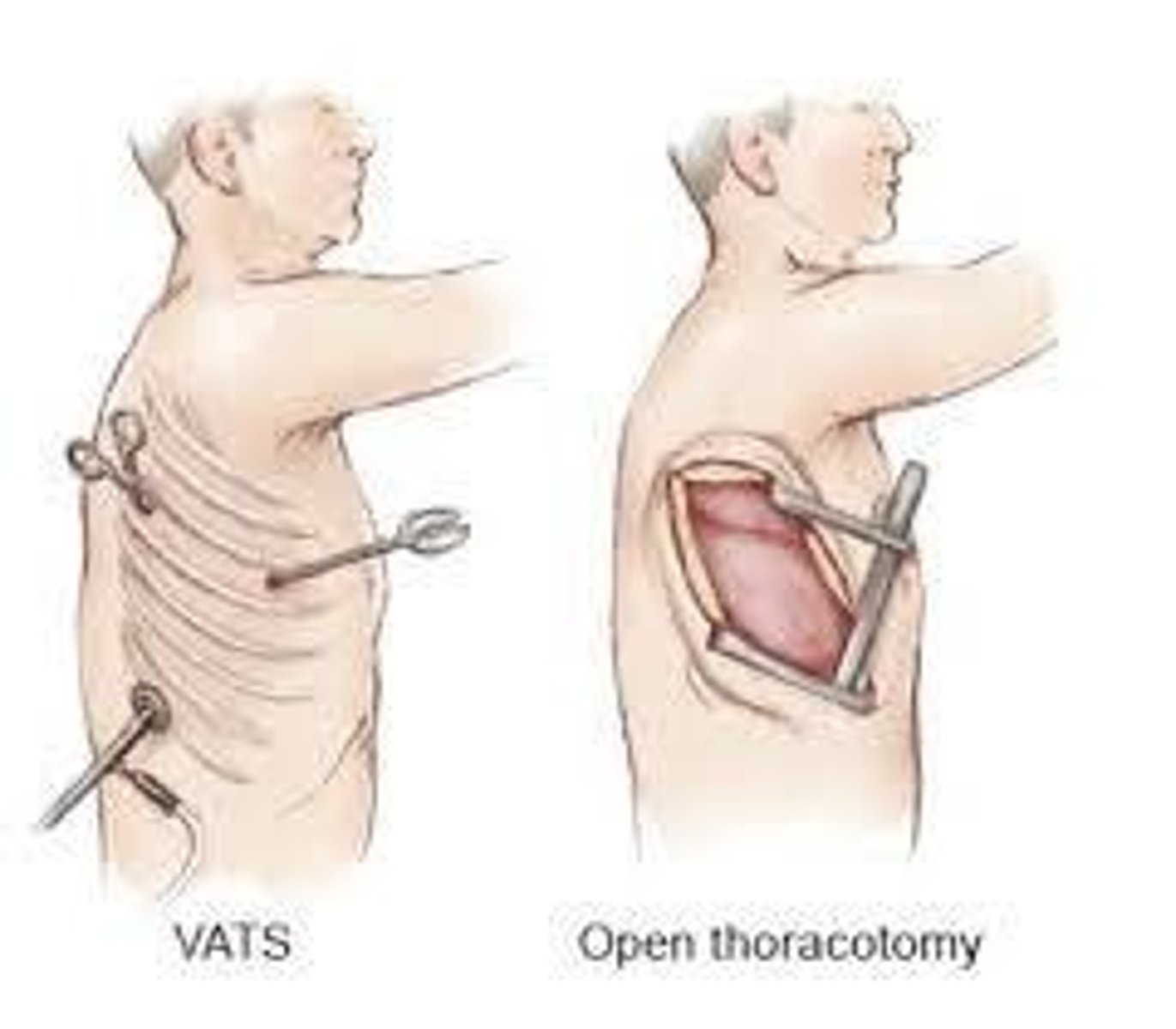
What are the common surgical approaches in pulmonary surgeries?
Thoracotomy (posterolateral, anterolateral, lateral, axillary), minimally invasive/video assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS), clamshell, and thoracoabdominal.
What is VATS and how does it differ from traditional thoracotomy?
VATS involves 1-3 ports and does not spread ribs, making it less invasive compared to traditional thoracotomy.
What are the common complications associated with thoracic surgery?
Respiratory complications (15-20%) including atelectasis, pneumonia, respiratory failure; cardiac complications (10-15%) such as arrhythmias and ischemia; and shoulder pain experienced by 80% of patients.
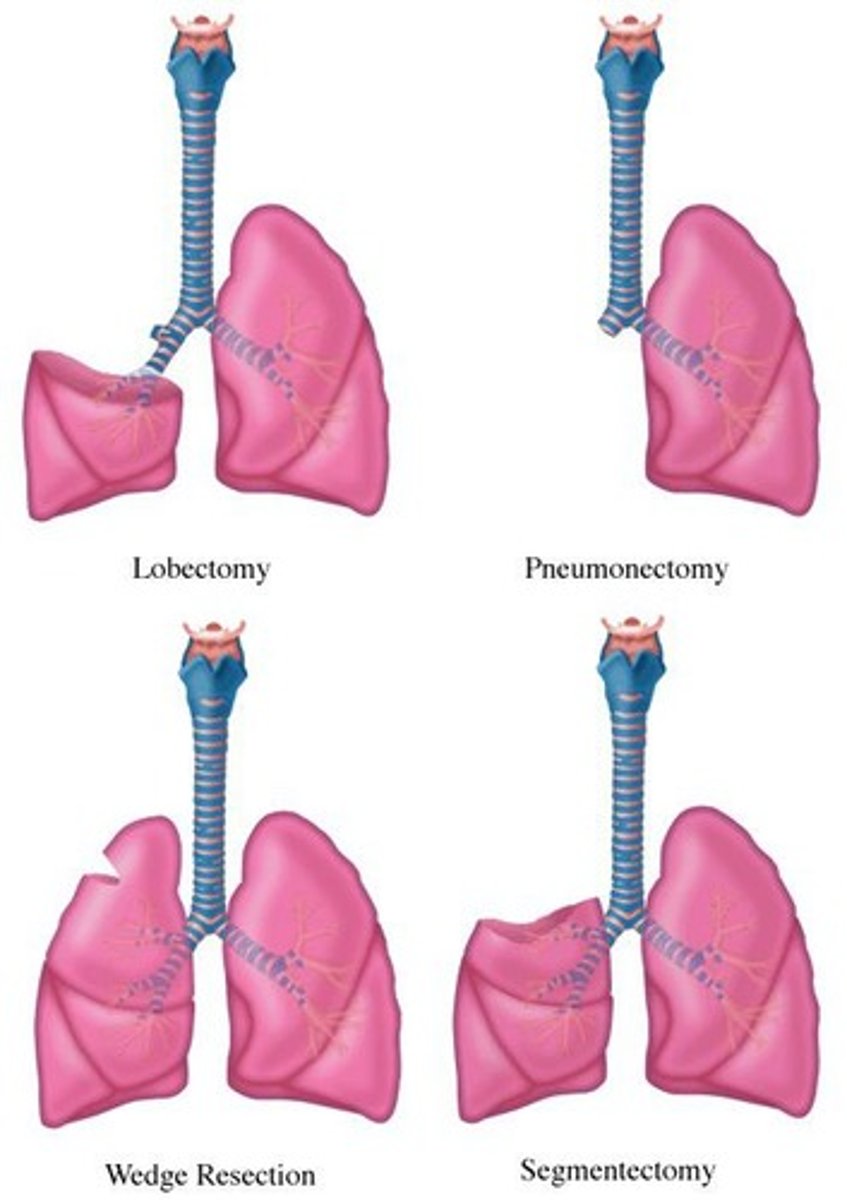
What is pulmonary resection and what are its indications?
Surgical resection of all or part of a lung, indicated for lung cancer, bronchiectasis, fungal infection, tuberculosis, and bullae excision.
What are the types of pulmonary resection?
Wedge resection, segmentectomy, lobectomy, bilobectomy, bronchoplastic/sleeve resection, and pneumonectomy.
What is a bullectomy and when is it performed?
A bullectomy is the excision of bullae (intrapulmonary air spaces larger than 1 cm) and is performed on patients with generalized emphysema or isolated lesions.
What are the post-resection considerations for patients?
Pain control, airway clearance, deep breathing/lateral costal breathing, and shoulder range of motion.
What is lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) and its outcomes?
LVRS involves removing 20-35% of lung tissue to improve thoracic distention, chest wall mechanics, work of breathing, FEV1, and exercise capacity.
What was the goal of the National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT)?
To compare survival rates and exercise capacity in patients undergoing lung volume reduction surgery and identify selection criteria.
What are the indications for lung transplant?
Common indications include COPD, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), cystic fibrosis (CF), and severe/progressive graft failure not responding to medical treatment.
What are the contraindications for lung transplant?
Active cancer, alcohol/drug abuse, HIV infections, limited ability to comply with medical regimen, and certain psychiatric conditions.
What is the Lung Allocation Score (LAS) and its purpose?
The LAS is a scoring system (0-100) used to prioritize lung transplant candidates based on urgency and likelihood of transplant success.
What are the early post-operative considerations for lung transplant patients?
Physical therapy begins on day of or post-op day 1, with restrictions on lifting, driving, and arm work for 6 weeks.
What are common post-operative complications of lung transplant?
Infections, ischemia-reperfusion injury, acute graft failure, and acute rejection.
What medications are typically prescribed after lung transplant?
Immunosuppressants, steroids, and prophylaxis for fungal, viral, and bacterial infections.
What are the signs of rejection after lung transplant?
Lower SpO2, increased shortness of breath (SOB), lower FEV1 and FEV1/FVC ratios, and possibly low-grade fever.
What is a pulmonary embolectomy?
A surgical procedure involving sternotomy with cardiopulmonary bypass to remove a clot in the pulmonary arteries.
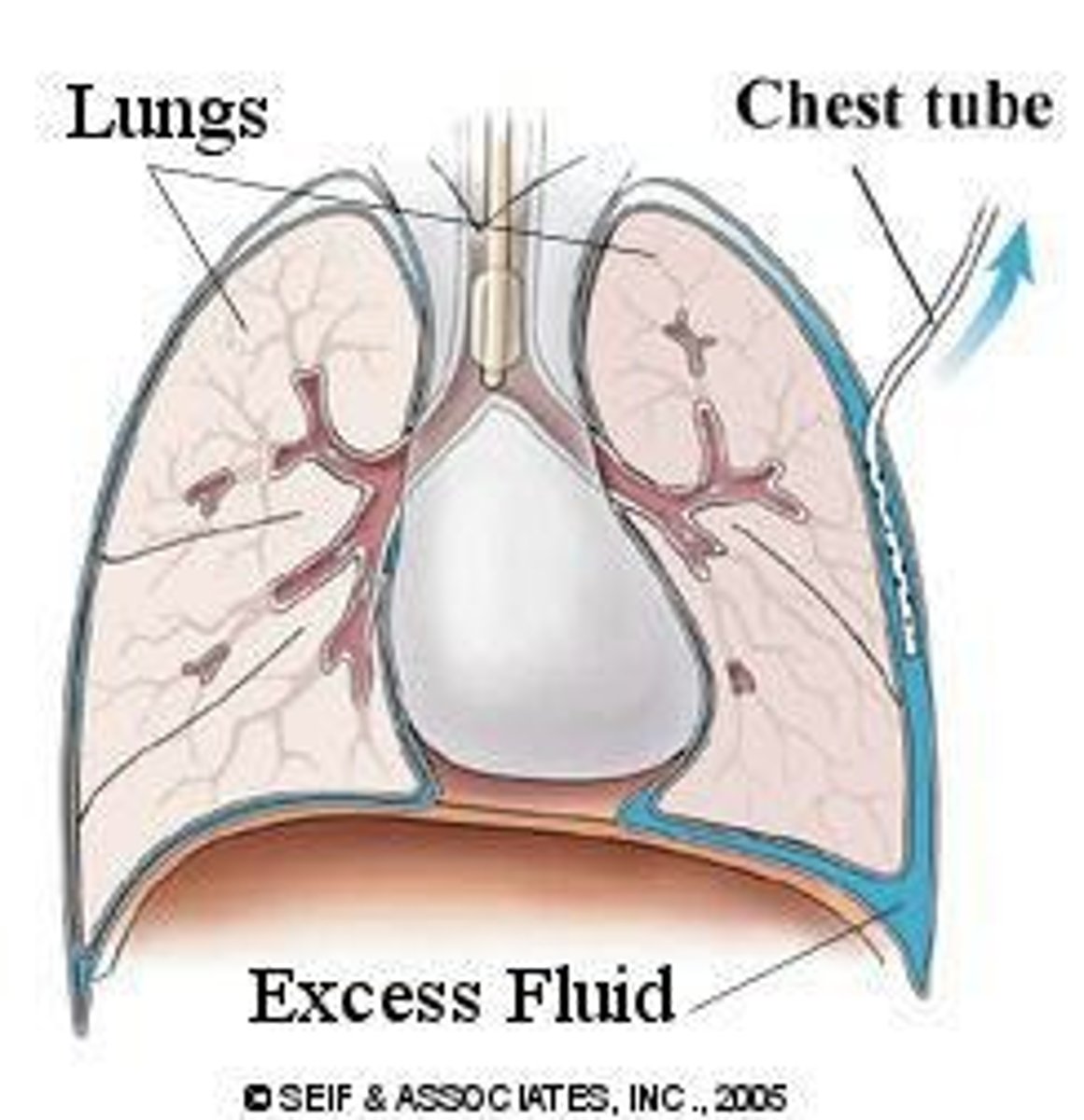
What is the purpose of chest tube placement?
To remove air, fluid, or blood to restore negative intrapleural pressure.
What is bronchial thermoplasty?
A procedure involving radiofrequency ablation of airway smooth muscle.
What is decortication in pulmonary surgery?
Excision of the parietal pleura and residual clot/scar tissue after hemothorax or empyema.
What is pleurodesis?
The obliteration of the pleural space using a sclerosing agent.
What is a pleurectomy?
Stripping and removing the parietal pleura to prevent reaccumulation of air or fluid.
What is a tracheal resection?
Excision of a portion of the trachea with end-to-end anastomosis via cervical incision.
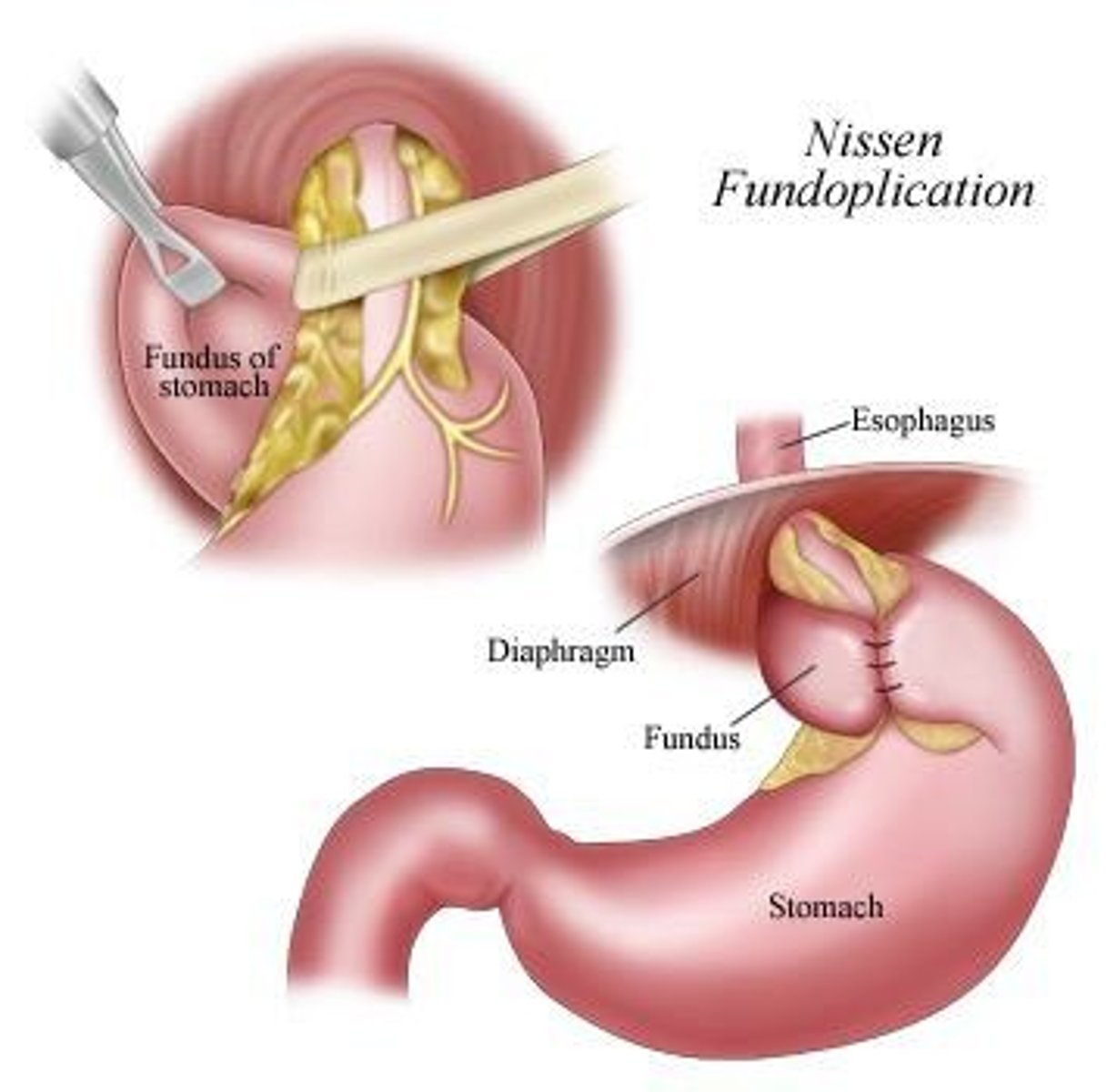
What is Nissen fundoplication?
A surgical procedure where the upper curve of the stomach is wrapped around the esophagus to create a new valve.
A pulmonary resection that removes a small, localized region of the lung is:
A wedge resection
The incision typically used for a lung transplant is:
clamshell
The diagnosis of a pulmonary embolism is most likely to be confirmed by:
A ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) Scan
A lung volume that is representative of the maximal amount of air that one can expire after a maximal inhalation is known as:
vital capacity (VC)
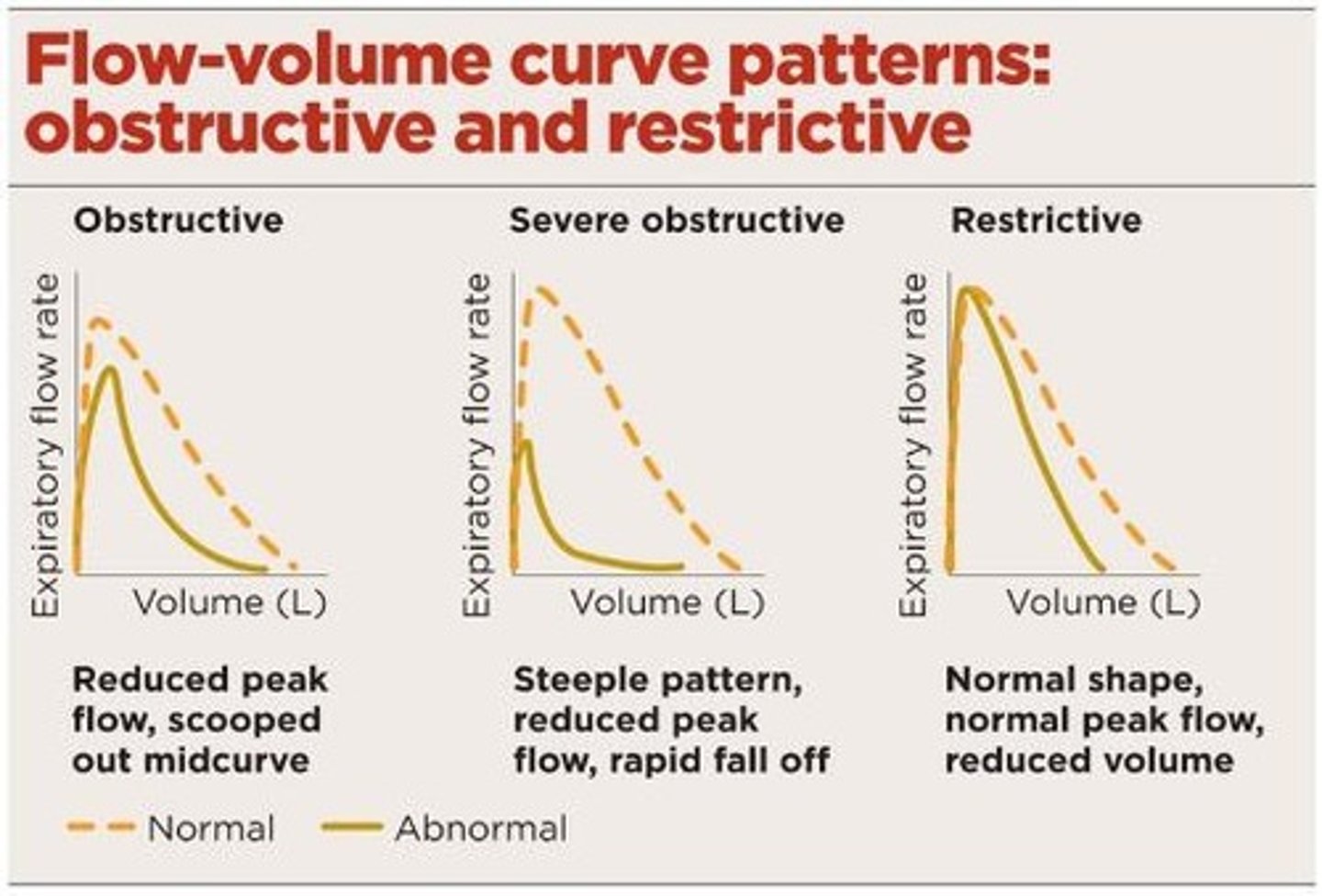
The shape of a normal flow loop/curve in spirometry is:
A sailboat sail peak
A patient with an FEV1/ FVC < 70% is indicative of:
Obstructive Lung Disease
Normal pH range
7.4
Normal PaO2 range
80-100 mmHg
Normal PaCO2 range
35-45 mmHg
Normal SaO2 range
95-100%
HCO3
22-26mmol/L
Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)
Data collected includes lung volumes and capacities, spirometry, maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV), and diffusing capacity (DLCO).
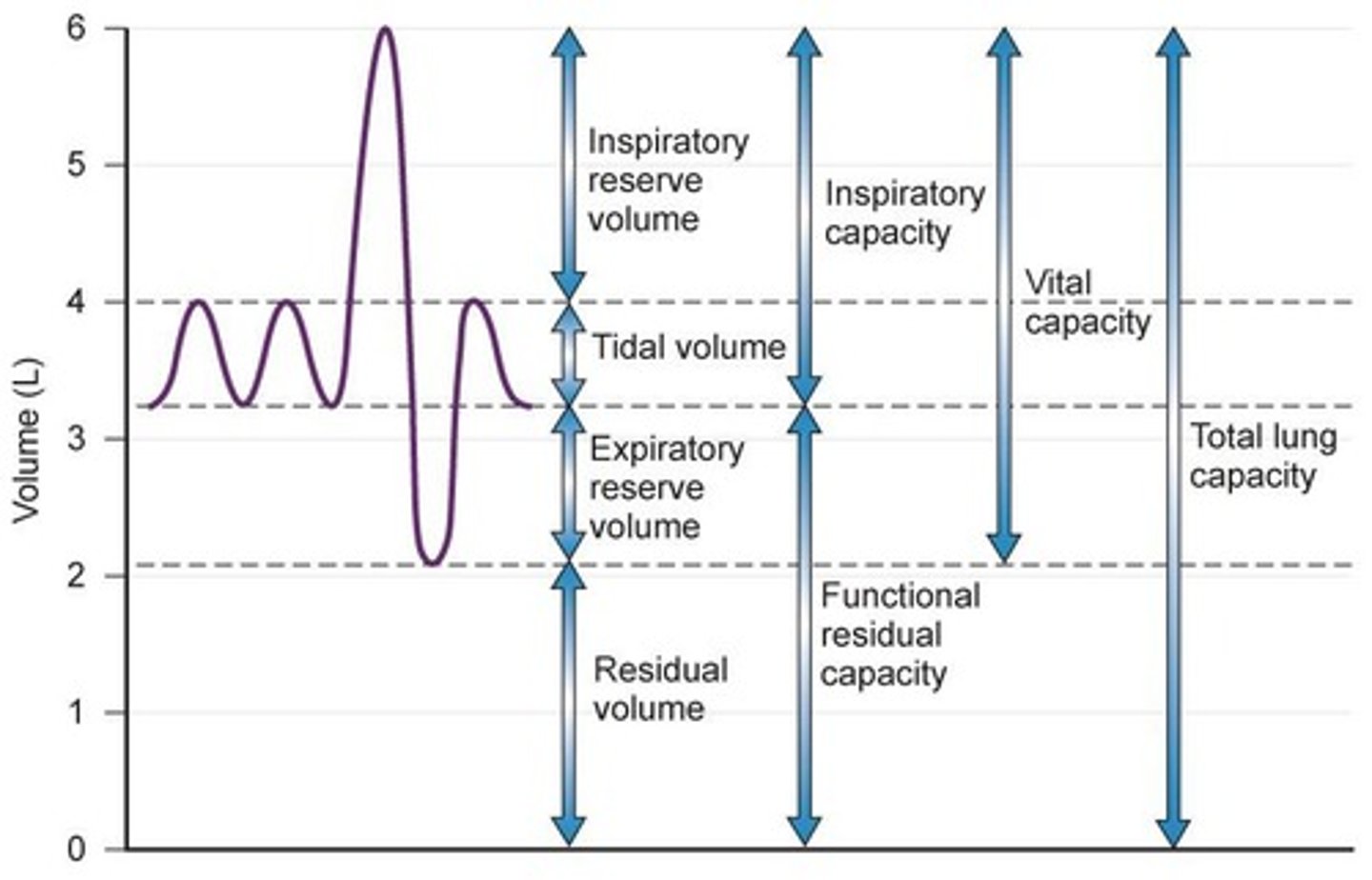
Tidal Volume (TV)
Normal breathing volume, typically between 350-500 mL.
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
Extra air inspired over tidal volume.
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
Extra air forcefully expired after the end of tidal volume.
Residual Volume (RV)
Air left in lungs after maximal expiration, also known as anatomic dead space.
Inspiratory Capacity (IC)
Maximum air inspired after normal tidal volume, calculated as TV + IRV.
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
Air in lungs after normal tidal expiration, calculated as RV + ERV.
Vital Capacity (VC)
Maximal air a person can expire after a maximal inspiration, calculated as IRV + TV + ERV.
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
Maximal volume lungs can contain after maximal inspiration, calculated as RV + ERV + TV + IRV.
Spirometry
Provides information about flow rates, compliance, and airway resistance.
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC)
Max volume that can be expired forcefully and rapidly after a maximal inspiration.
Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second (FEV1)
Volume of air expired in the first second of the forced vital capacity.
FEV1/FVC
Percentage of air expired in the first second of total FVC.
Forced Expiratory Flow from 25-75% (FEF25-75%)
Average flow in the middle of the FVC, reflecting tertiary airways.
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
Maximal flow rate obtained during forced vital capacity.
Maximal Voluntary Ventilation (MVV)
Largest volume that a patient can breathe per minute using forced rapid deep breaths, normal range is 80-180 L/min.
Respiratory Rate (RR)
Normal range is 12-20 breaths per minute.
Minute Ventilation (VE)
Calculated as VE = RR x TV, normal range is 5-10 L/min.
Diffusing Capacity (DLCO)
Normal in asthma and healthy lungs if greater than 60%; less than 60% predicted indicates desaturation with exertion.
PFT Patterns
Normal, obstructive (<80% predicted), and restrictive (<80% predicted) patterns based on FEV1 and FVC.
Bronchodilator Study
Perform a PFT, deliver a bronchodilator, then repeat PFT to evaluate possible improvement.
Methacholine Study
Perform PFT, deliver various levels of medicine to check for asthmatic response.
Normal FEV1/FVC
>= 70%
OLD diagnostic threshold
< 70% diagnostic of OLD
Normal FVC
>= 80%
RLD diagnostic threshold
< 80% diagnostic of RLD
Normal FEV1
>= 80%
Stage 1 (mild) FEV1
>= 80%
Stage 2 (moderate) FEV1
50 <= FEV1 < 80%
Stage 3 (severe) FEV1
30 <= FEV1 < 50%
Stage 4 (very severe) FEV1
< 30%
Normal TLC
80 - 120%
Normal RV
80 - 120%
Normal RV/TLC ratio
25 - 40%
Normal DLCO
25 - 30 mL/min/mm Hg or > 60
Pre- and post-bronchodilator tests
Were other tests performed?
FVC
Forced Vital Capacity, measured in liters (L), with normal values >= 80%.
FEV1
Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second, measured in liters (L), with normal values >= 80%.
FEF 25-75%
Forced Expiratory Flow at 25-75% of FVC, measured in liters per second (L/sec), with normal values around 3.70 to 4.38.
DLCO
Diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide, measured in mL/min/mmHg, with normal values between 25 to 30.
Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)
A test that measures the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, as well as pH.
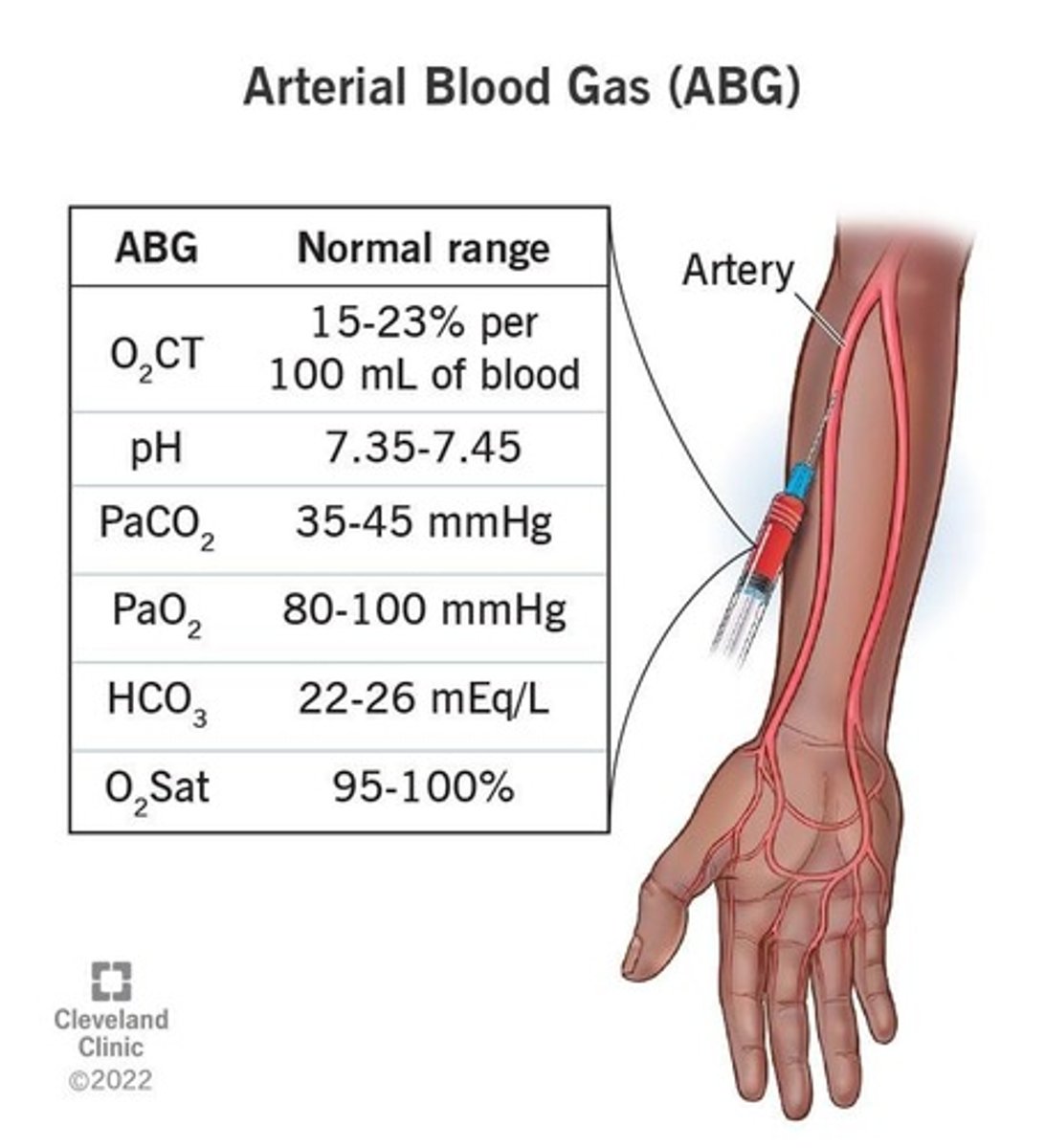
pH
A measurement of the H+ ion concentration in blood, with normal values between 7.35 and 7.45.
PaO2
Partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood, with normal values between 80 and 100 mmHg.
PaCO2
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood, with normal values between 35 and 45 mmHg.
SaO2
Arterial oxygen saturation, expressed as a percentage (%), with normal values between 95% and 100%.
HCO3-
Bicarbonate level in blood, measured in mmol/L, with normal values between 22 and 26.
Base excess/deficit (BE)
A measure of metabolic acid-base balance, with normal values between -2 to +2.
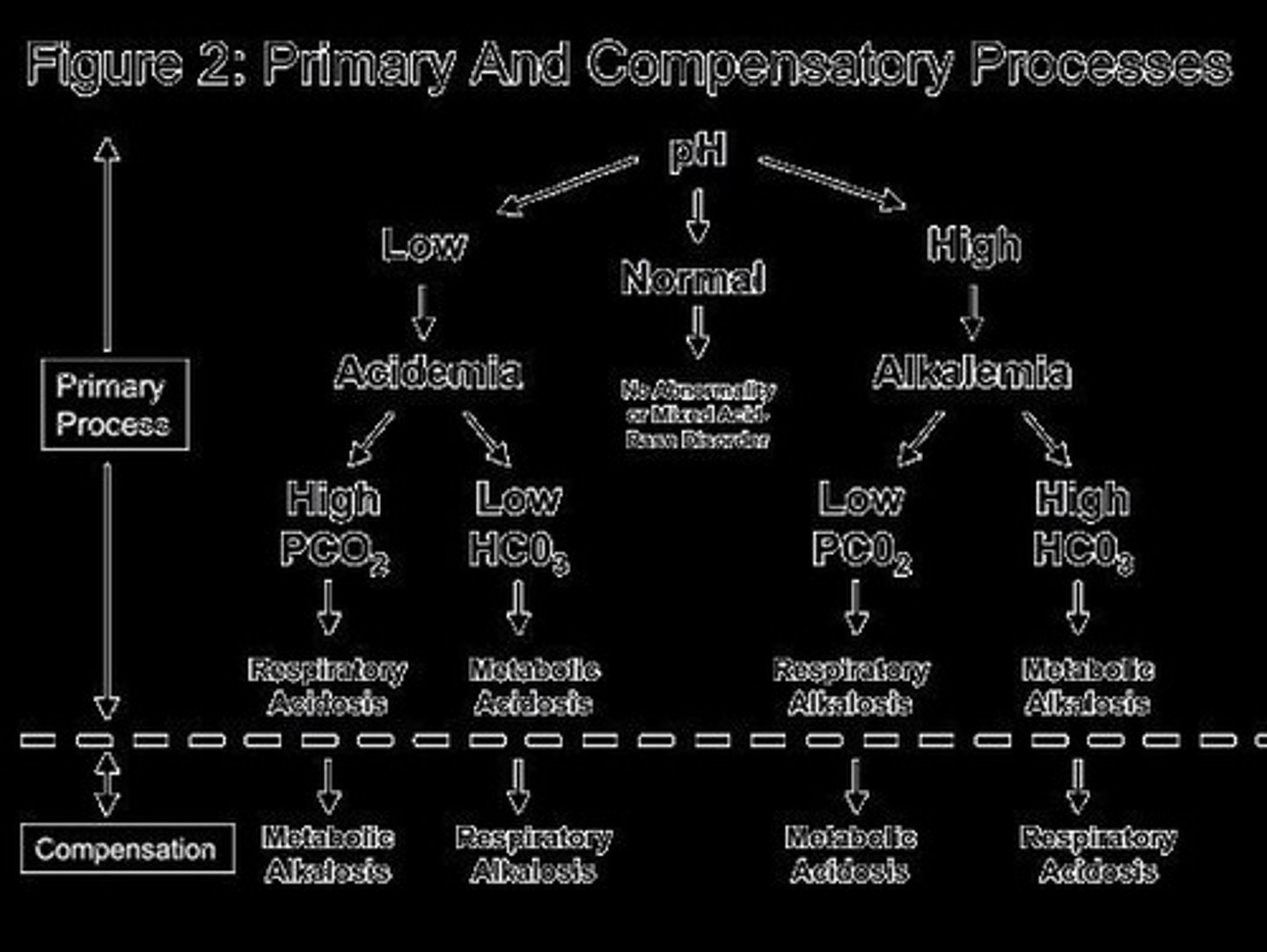
Respiratory Acidosis
A condition characterized by an increase in PaCO2, often due to hypoventilation.
Respiratory Alkalosis
A condition characterized by a decrease in PaCO2, often due to hyperventilation.
Metabolic Acidosis
A condition characterized by a decrease in HCO3-, often due to conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis.
Metabolic Alkalosis
A condition characterized by an increase in HCO3-, often due to vomiting or diuretic therapy.
OLD
Obstructive Lung Disease, assessed using FEV1 to grade severity.
RLD
Restrictive Lung Disease, diagnosed when FVC is < 80%.
Hypoxemia
A condition characterized by low levels of oxygen in the blood, often indicated by PaO2 < 55 mm Hg.
Oximetry
A non-invasive method to measure oxygen saturation in the blood.
CNS Depression
A condition that can lead to respiratory acidosis due to impaired respiratory drive.
Hyperventilation
A condition that can lead to respiratory alkalosis due to excessive breathing rate.
What types of diagnostic testing are used in pulmonology?
Exercise testing, cytology & hematology, pulmonary function testing, pulmonary imaging studies, arterial blood gases, and invasive diagnostics.
What is the purpose of the 6-minute walk test in pulmonary diagnostics?
To evaluate functional capacity and oxygen needs with exercise.
What does a complete pulmonary function test (PFT) measure?
It measures parameters such as arterial blood gases, EKG, blood pressure, and RPE, and can determine max VO2.
What is pulse oximetry?
A non-invasive test that evaluates oxygen saturation, but is not valid if the patient has elevated carbon monoxide levels.
What factors can affect the accuracy of pulse oximetry readings?
Nail polish, cold hands, decreased circulation, vibration, and movement.
What is the significance of green sputum in cytology?
It is 94% sensitive and 77% specific for a high bacterial load that benefits from antibiotics.
What imaging techniques are included in pulmonary imaging?
Chest X-ray, fluoroscopy, CT, MRI, and nuclear medicine.
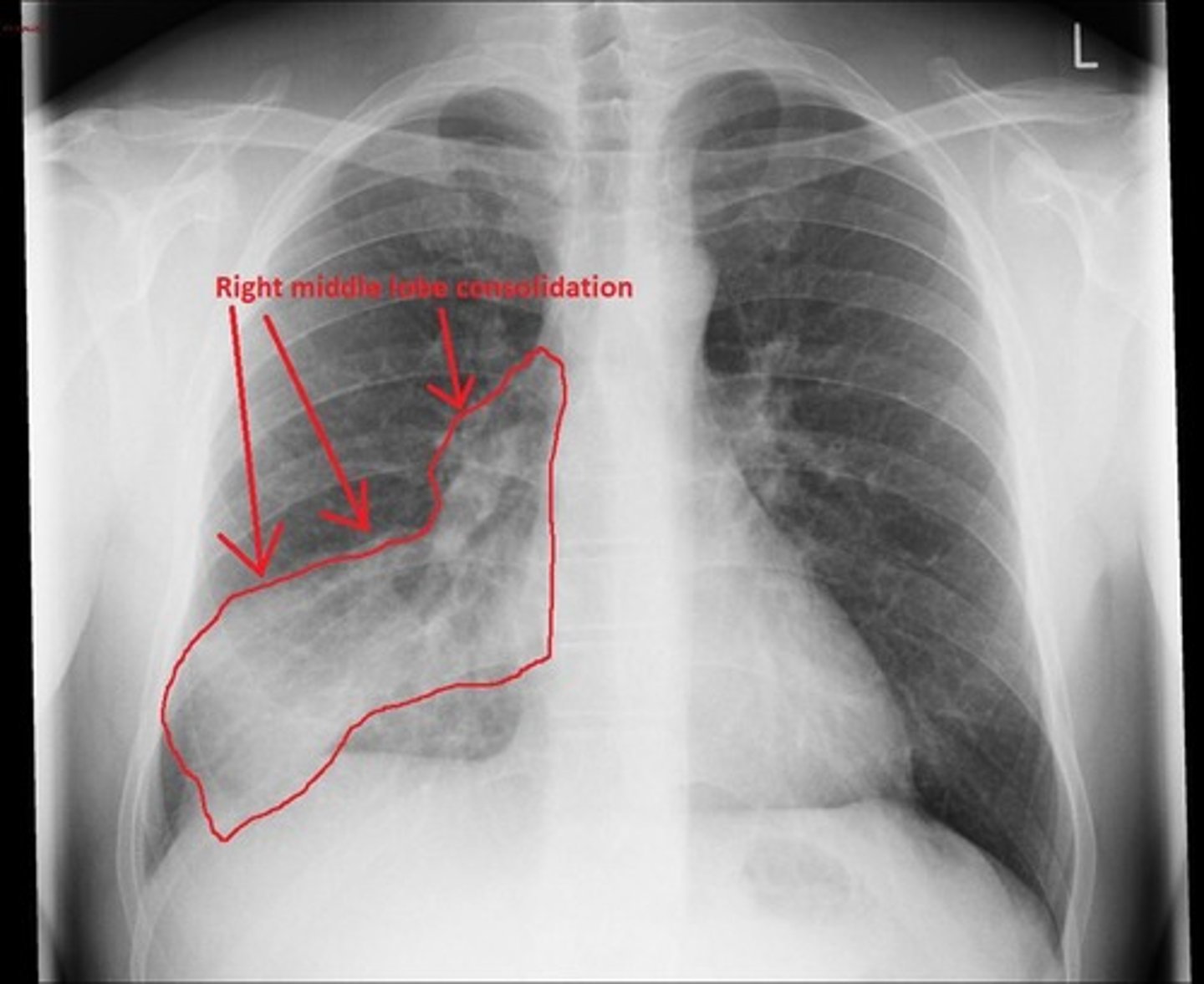
What can a chest X-ray detect?
Pleural effusion, pulmonary edema, consolidation, pneumothorax, and atelectasis.