Important Information from Unit 1 and 2 of VCE biology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
The cell theory
All organisms are composed of one or more cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and organisation in organisms, and all cells come from pre-existing cells.
Prokaryotic cells
Large SA:V ratio (beneficial for diffusion), single cell (unicellular), no membrane bound organelles or defined nucleus, cell wall, and DNA is a single and circular chromosome. Some have flagella or pili for movement. Small 1-10um.
organelles - cytoplasm, ribosomes, plasma membrane, genetic material.
eg. Bacteria and archaea.
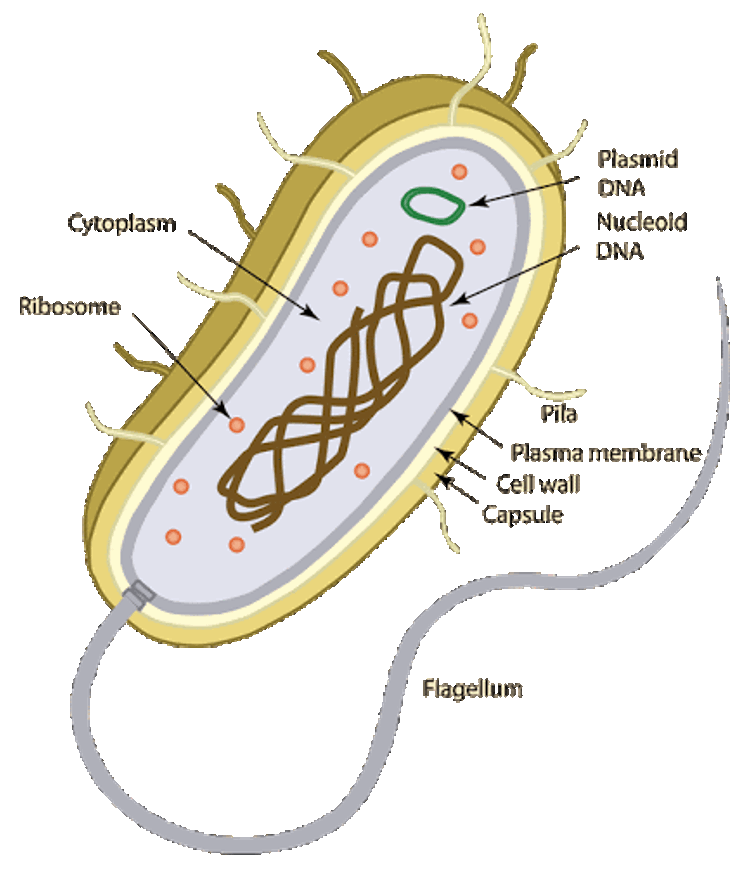
Prokaryotes - Archaea (the extremophiles)
Unicellular
Found in volcanic vents, the Dead Sea, alkaline soils, and ocean floor
Anaerobic (don’t tolerate oxygen well)
Prokaryotes - Bacteria
Unicellular
Most are aerobes, some can be anaerobic.
Eukaryotic cells
Membrane bound organelles that have specialised functions, membrane bound nucleus, and DNA is inside the nucleus.
Multicellular, ability to form organ systems. large 10-1000um.
True nucleus DNA with multiple chromosomes condensed with histones (proteins that DNA wrap around).
eg. plants, fungi, animals, protists.
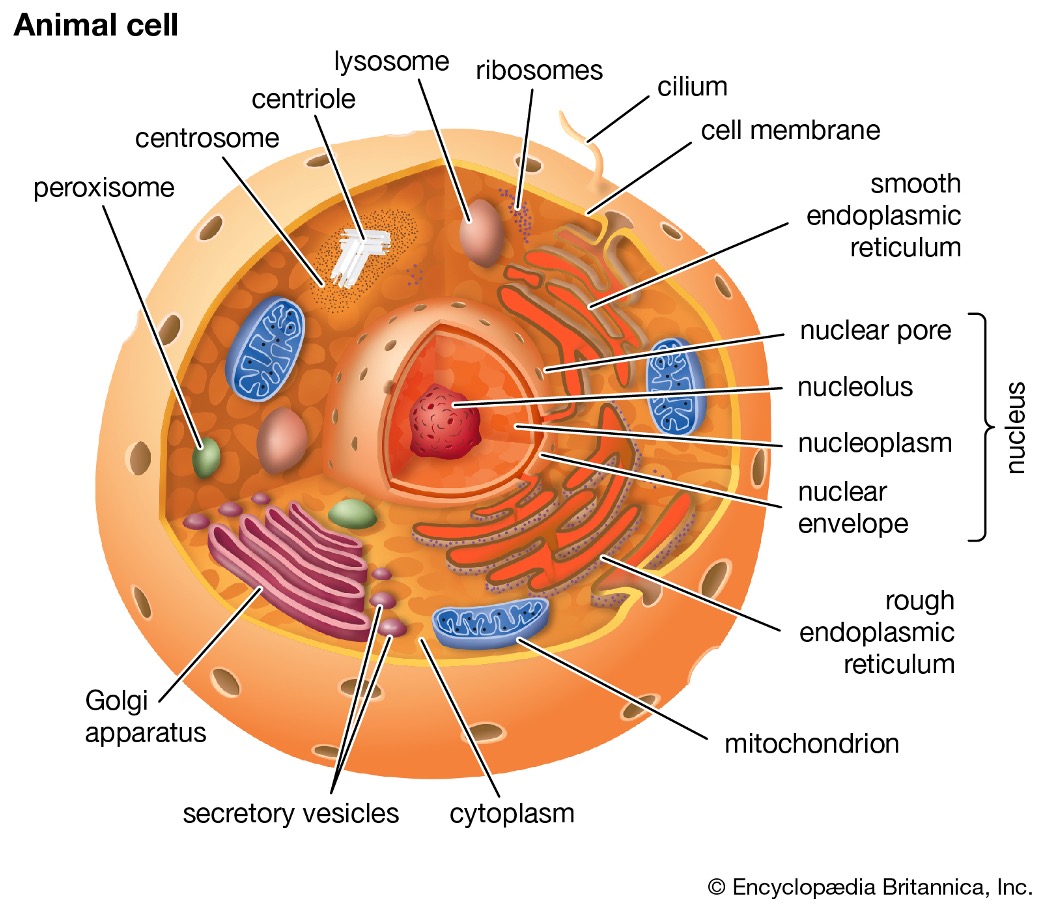
Eukaryotes - animal cell
Have 1 organelle that plant cells don’t, which is the centrioles.
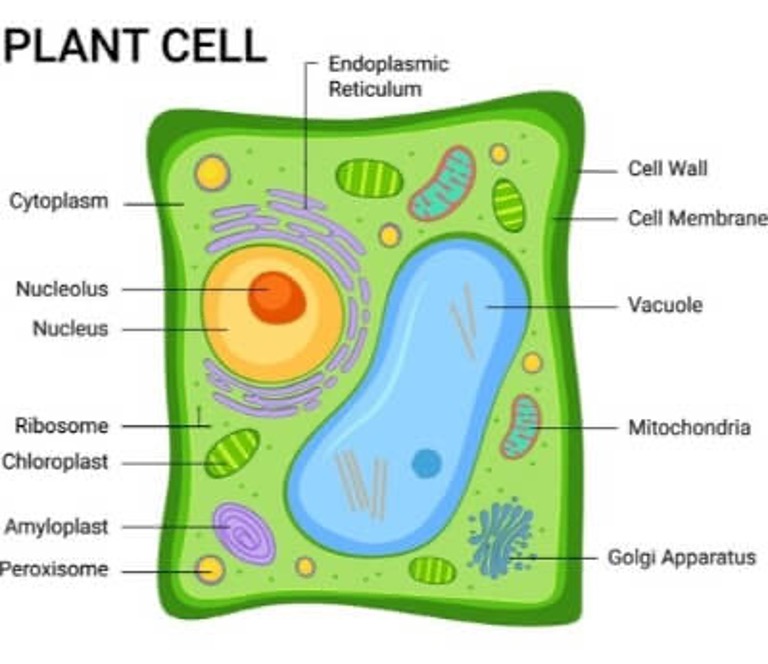
Eukaryotes - plant cell
have 3 organelles that animal cells don’t have, which are chloroplasts, permanent large vacuole, and cell wall.
Compartmentalisation
Eukaryotes have membrane bound compartments (called organelles) inside the cell which perform specialised functions.
Allows processes that require different environments to happen at the same time. Makes the cell less vulnerable to changes in the external environment.
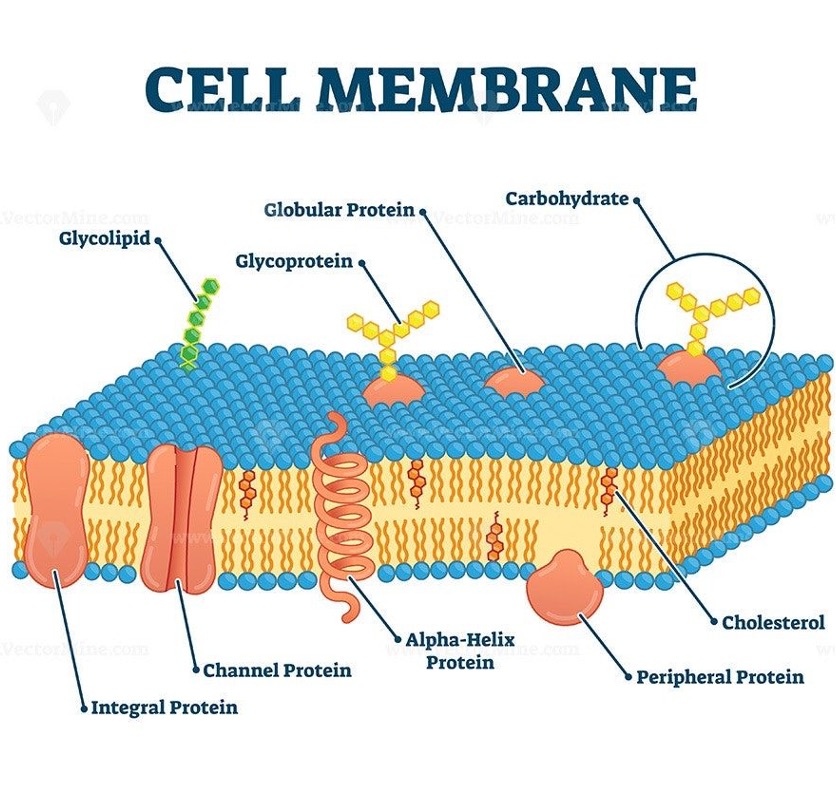
Plasma membrane (cell membrane)
Separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment.
found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
allows nutrients to enter the cell and waste the exit selectively.
has receptors that can communicate between other cells.
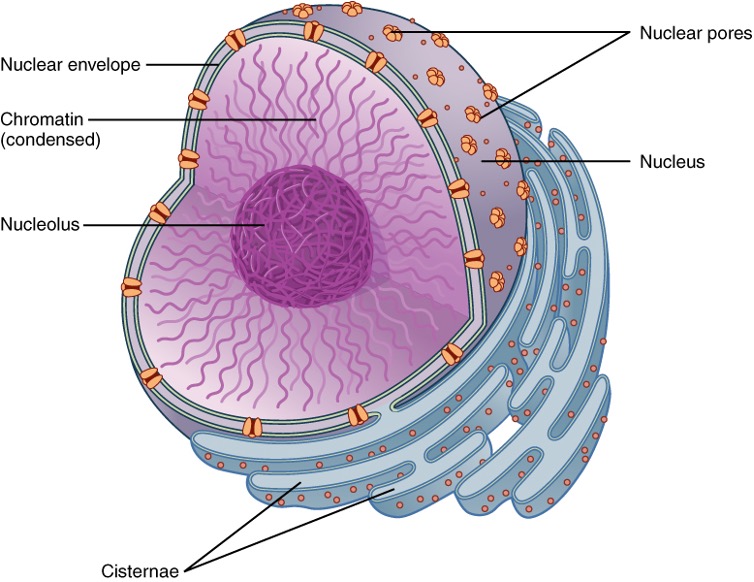
Nucleus
In eukaryotes, DNA and genetic information is contained in this.
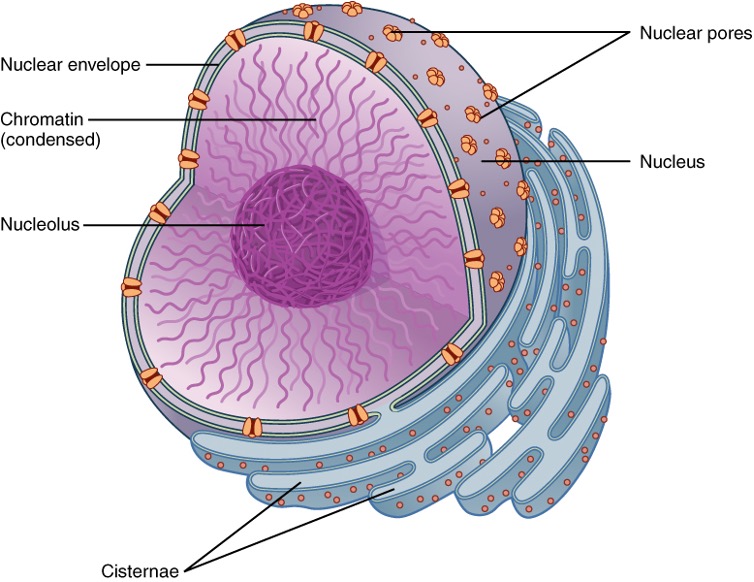
Nuclear envelope
Surrounds the nuclear membrane
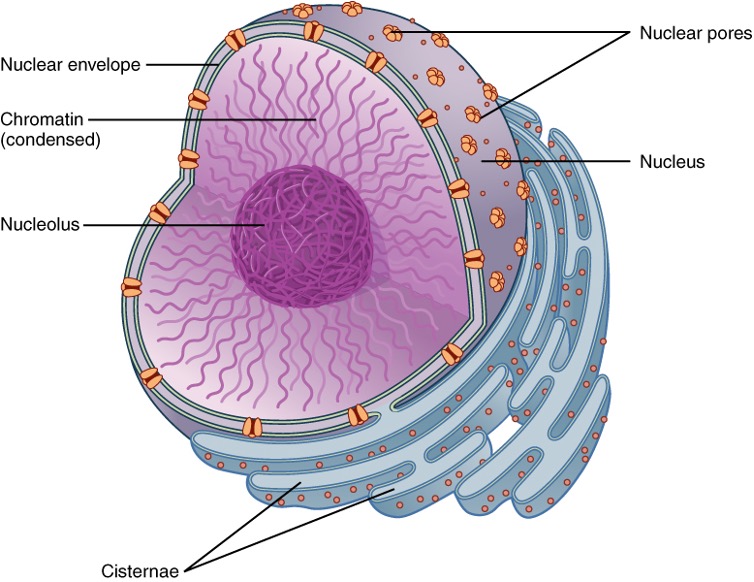
Nuclear pores
Allows nucleic acids in and out of the nucleus.
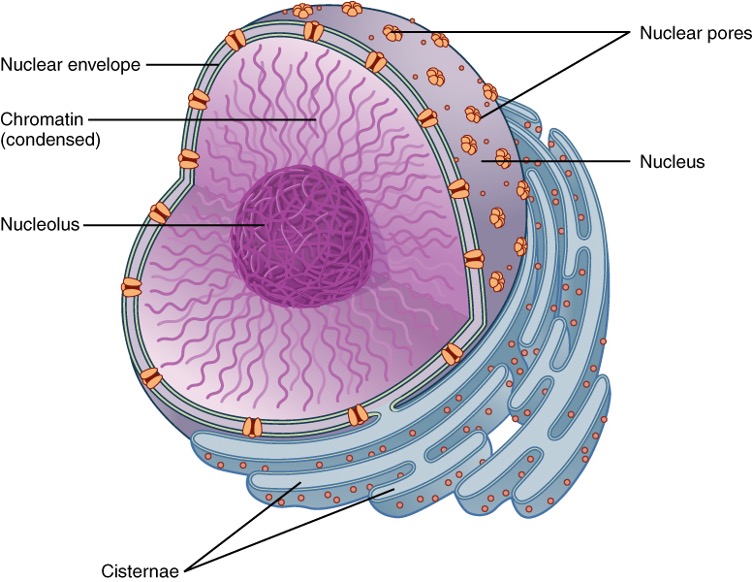
Nucleolus
Dense protein filled structure that creates ribosomal RNA and ribosomal subunits.
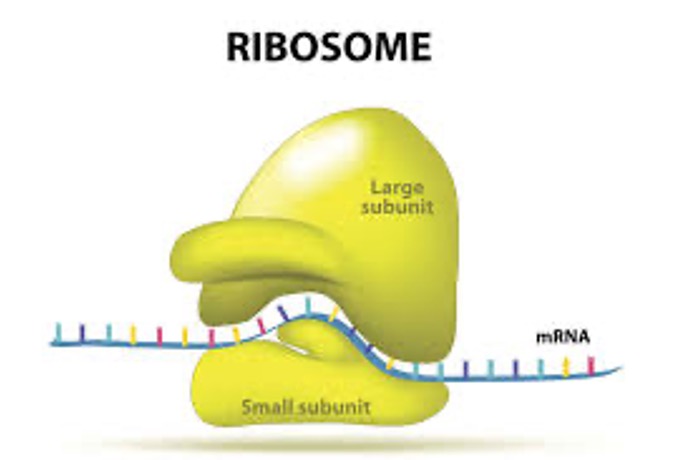
Ribosomes
The site of protein synthesis
One cell contains thousands of sub units (2 units joined together)
Found free in the cytoplasm or bound to rough endoplasmic reticulum
Found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Not membrane bound
Endoplasmic reticulum
Interconnecting system of thin membranes dividing the cytoplasm into compartments and channels - intercellular transporting system.
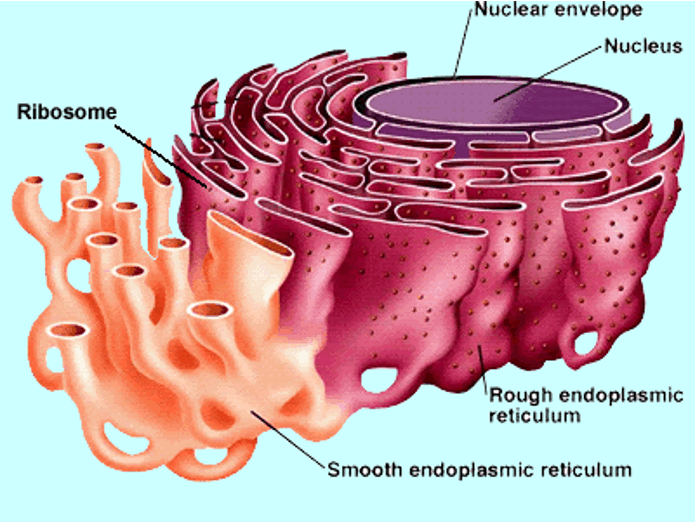
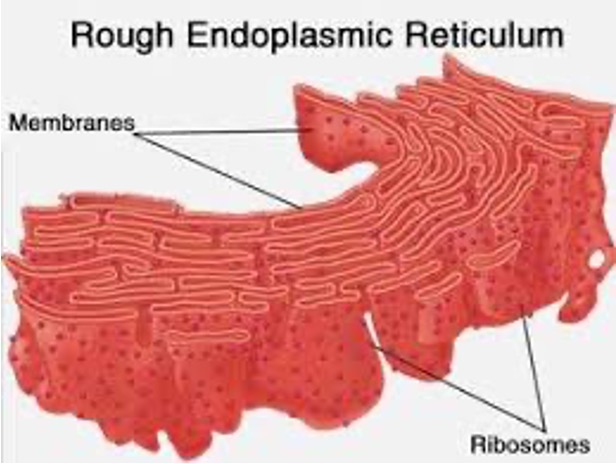
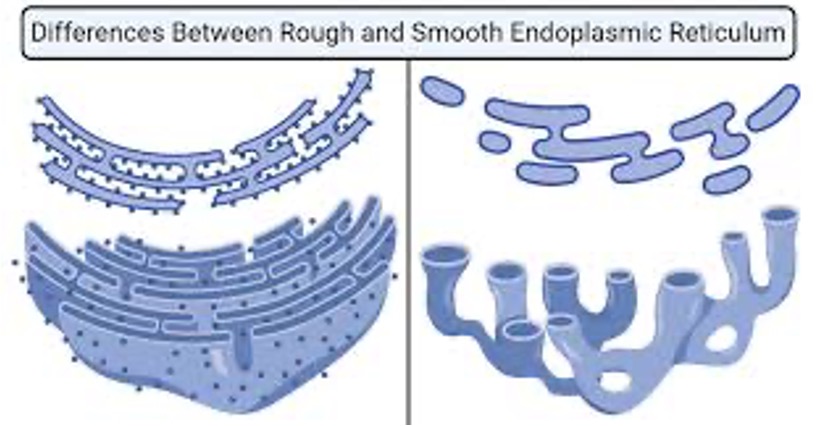
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Has ribosomes attached, which makes proteins
Once proteins are made, they pass through the ER containing enzymes
Enzymes add sugar molecules to the proteins
Move into Golgi apparatus to be exported from the cell.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Contains enzymes involved in the synthesis of molecules other than proteins (eg. phospholipids)
No ribosomes attached
Transport proteins, synthesis lipids and assist in producing the plasma membrane.
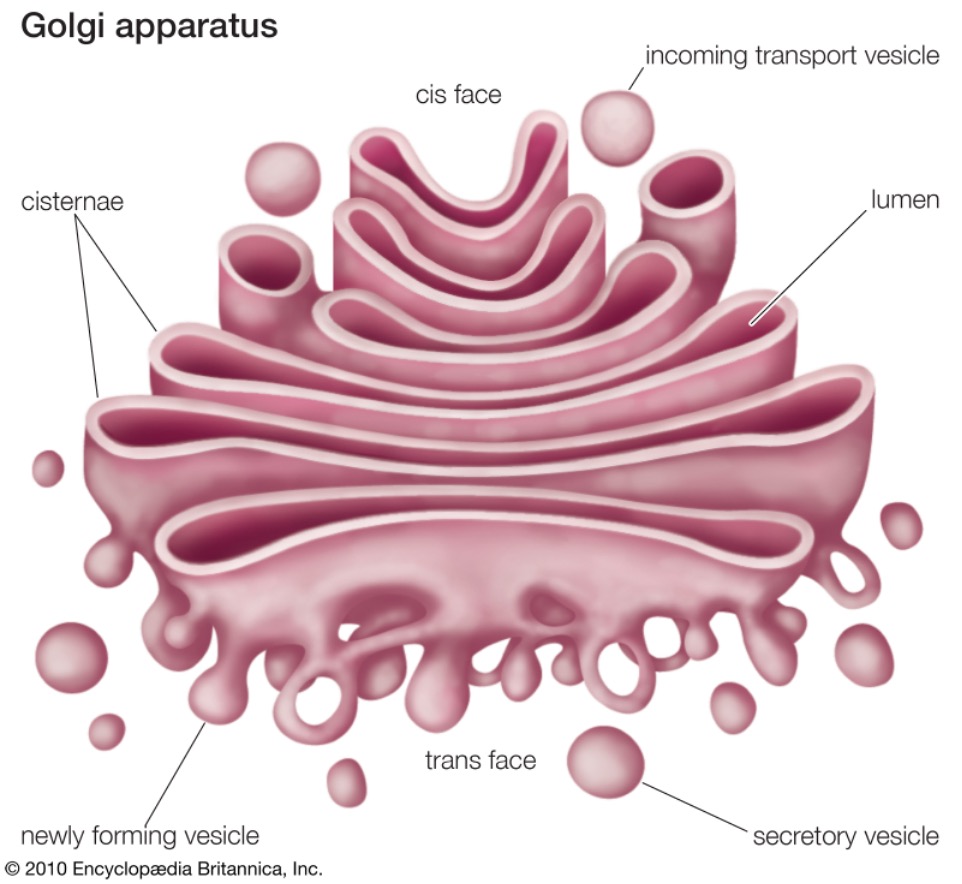
Golgi apparatus
Membrane bound
System of flattened membranes
Receive vesicles from the rough ER
Protein modification and final packaging of proteins before they are exported out of the cell (cell post office).
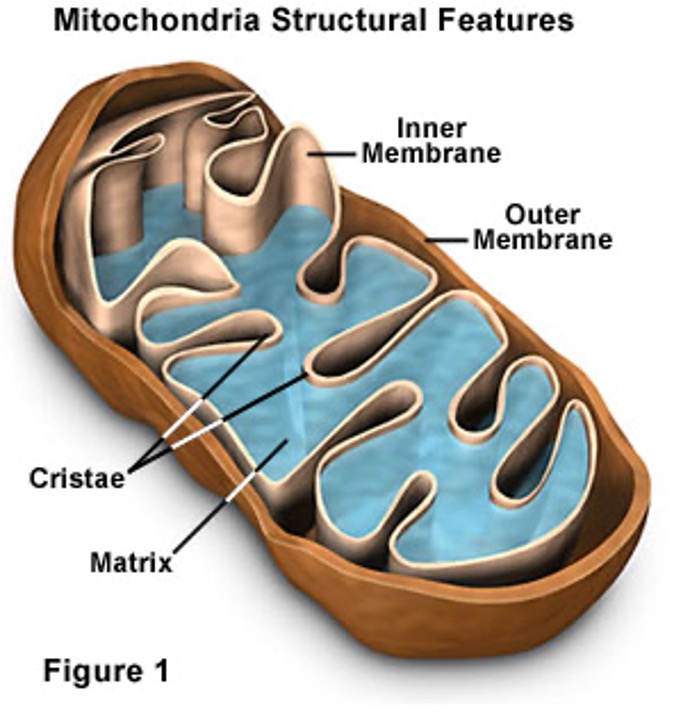
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration (energy producer - powerhouse of the cell)
Double membrane
Smooth outer membrane and highly folded inner membrane (creates a higher SA:V ratio)
Has its own circular DNA - passed down from the mother
Amount of this is relevant to the energy expenditure of the cell (eg. sperm cells have high numbers of this).
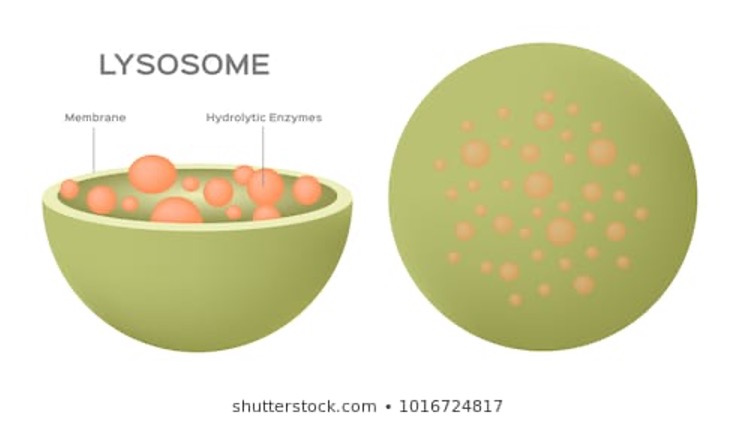
Lysosomes
The cell recycler
Membrane bound
Used in various cell processes such as the break down of unwanted matter
Contain digestive enzymes
Expels contents outside the cell (exocytosis)
Made by the Golgi apparatus
Only in animal cells.
Cytoplasm
Not organelles
All the content within the cell (organelles and cytosol)
Where chemical reactions are carried out
Cytosol
Not organelles
Fluid compartment of the cell that contains nutrients.
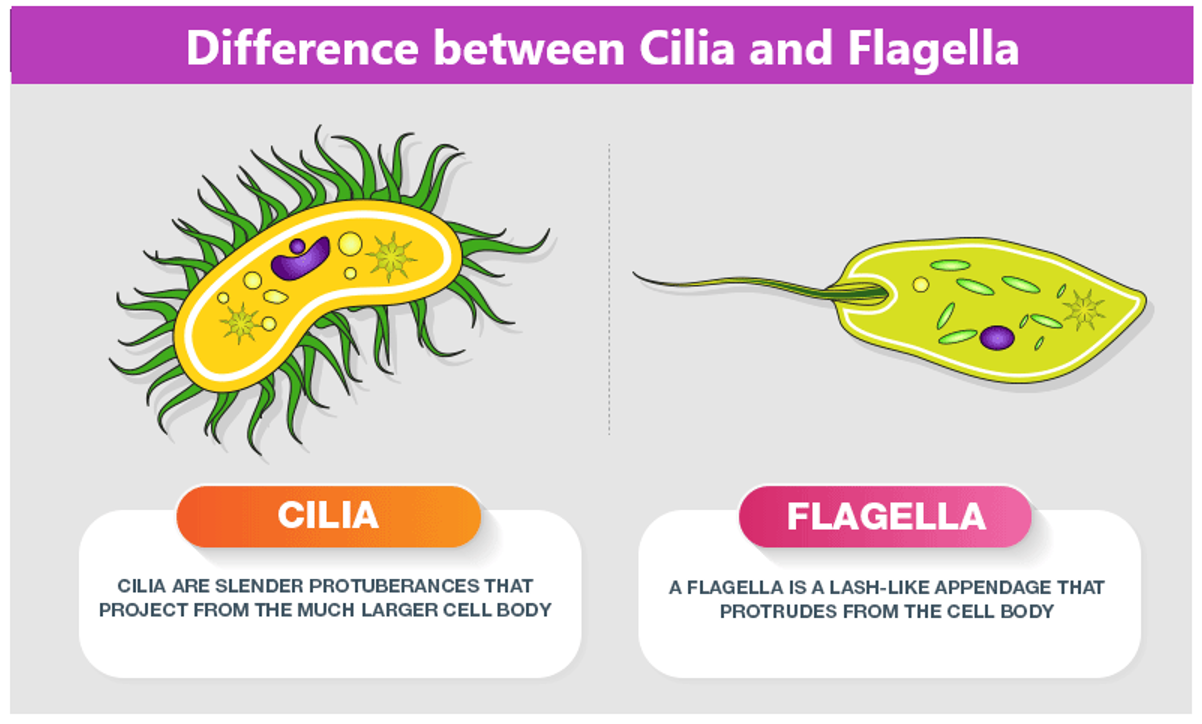
Cilia
Hair like structures on the surface of cells.
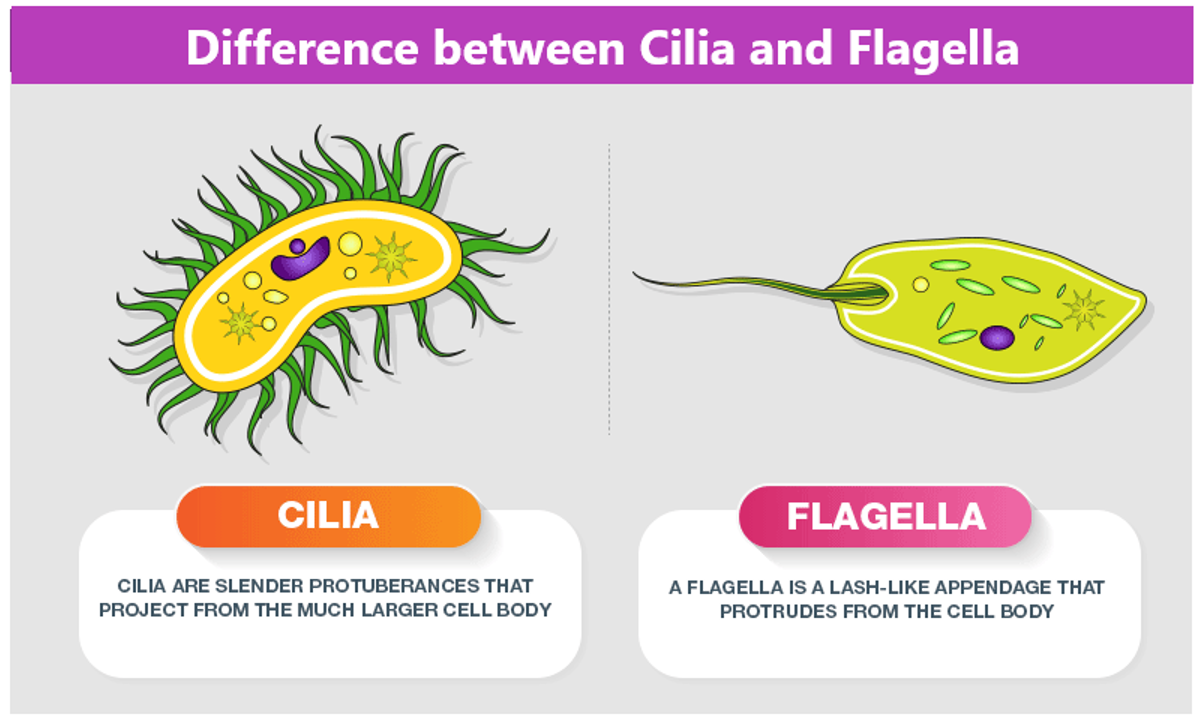
Flagella
Bacteria and sperm use this to swim/move.
Organelles
involved in specific functions, so their presence depends on the needs of the cell.
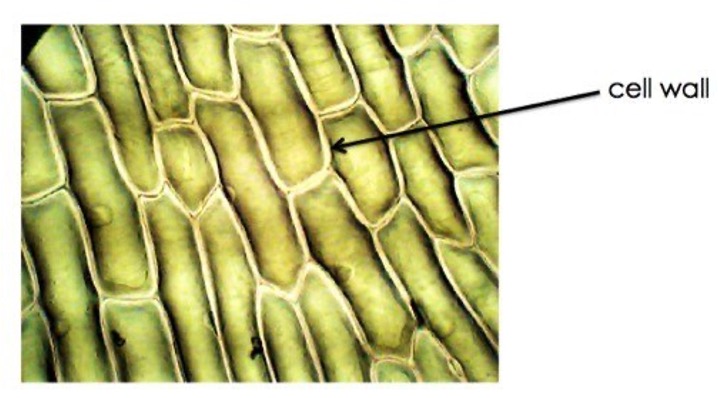
Cell wall
Provides structure and protection
In plants: cellulose (complex carbohydrate)
Plant, bacteria (peptidoglycan), fungi (chitin), and most algae have an additional one of this
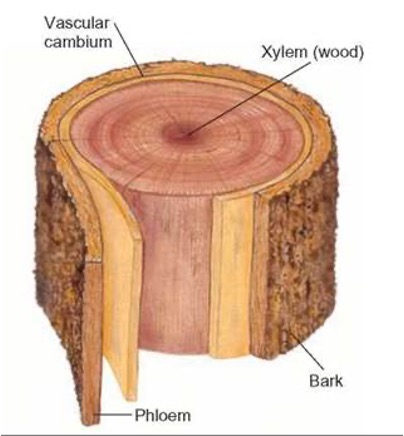
Xylem
As cells age they die and loose their contents and create tube like cells- carry water from the roots to the leaves.
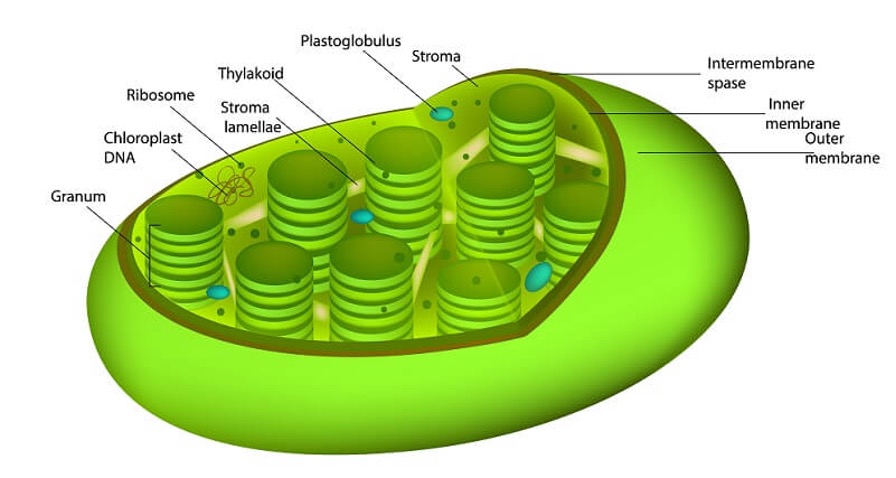
Chloroplast
Responsible for photosynthesis - converts light energy to chemical energy
Can move around the cell for optimal light absorption
Contains green pigment - chlorophyll
Thylakoid membranes are stacked many times to increase surface area.
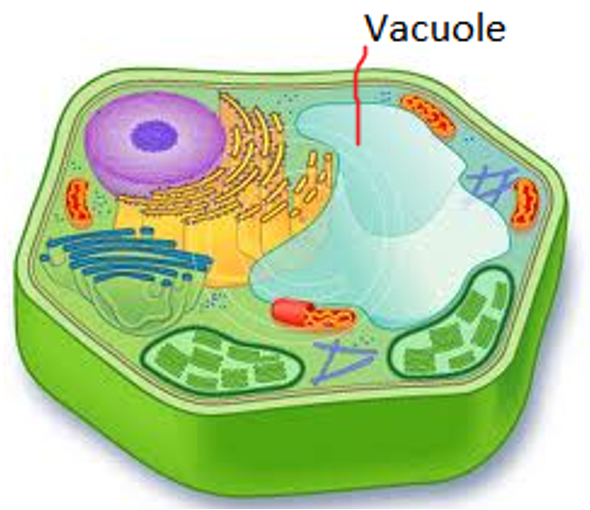
Vacuole
Takes up majority of the cytoplasm in mature plant cells
Filled with fluid which serves as storage for sugars, minerals, water and proteins.