Unit 4 - Contractions: The Mechanics
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are Muscle contraction
he process of muscle fibers
shortening, allowing for
movement. It is crucial for
everything from voluntary
actions to organ function
What is a Sarcomere
A segment of fiber; one
contractile unit
What is Myosin
Thick filaments
What is Actin
Thin filaments
What physical thing does myosin have
a head(extension)
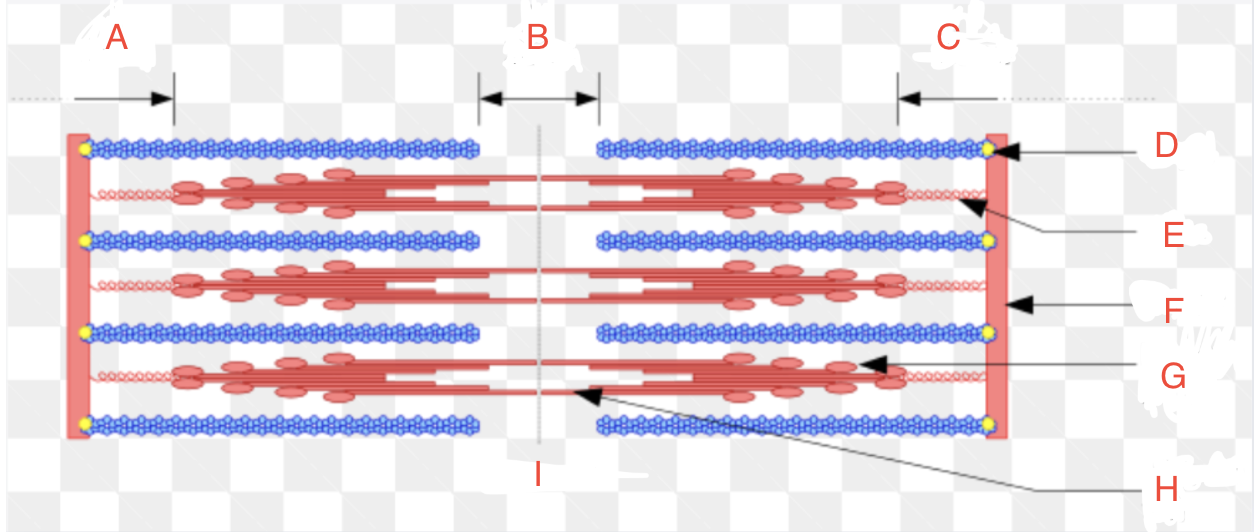
What is A
I Band left
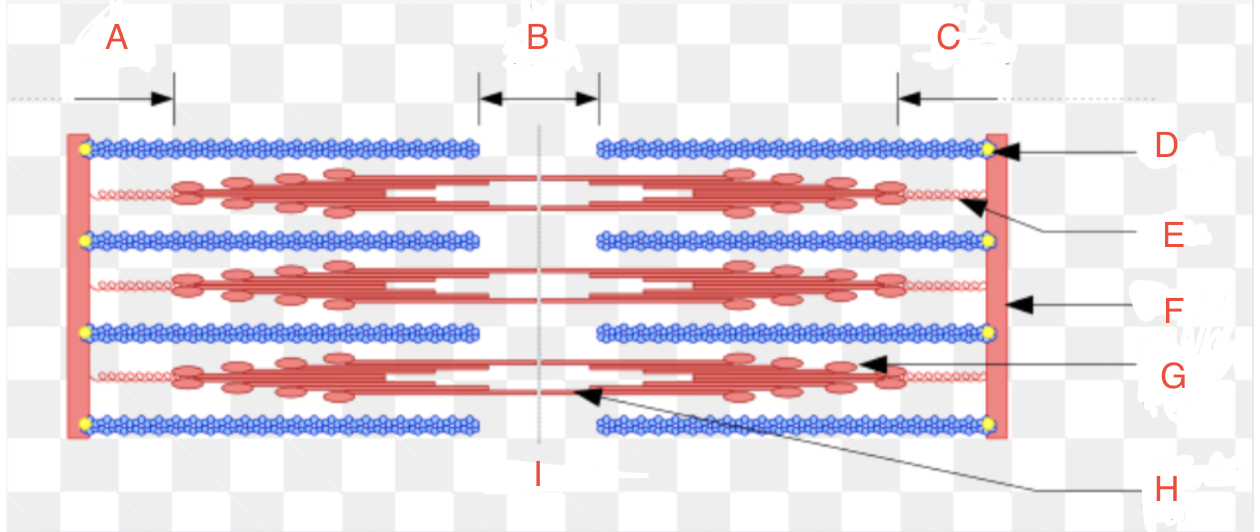
What is B
H zone
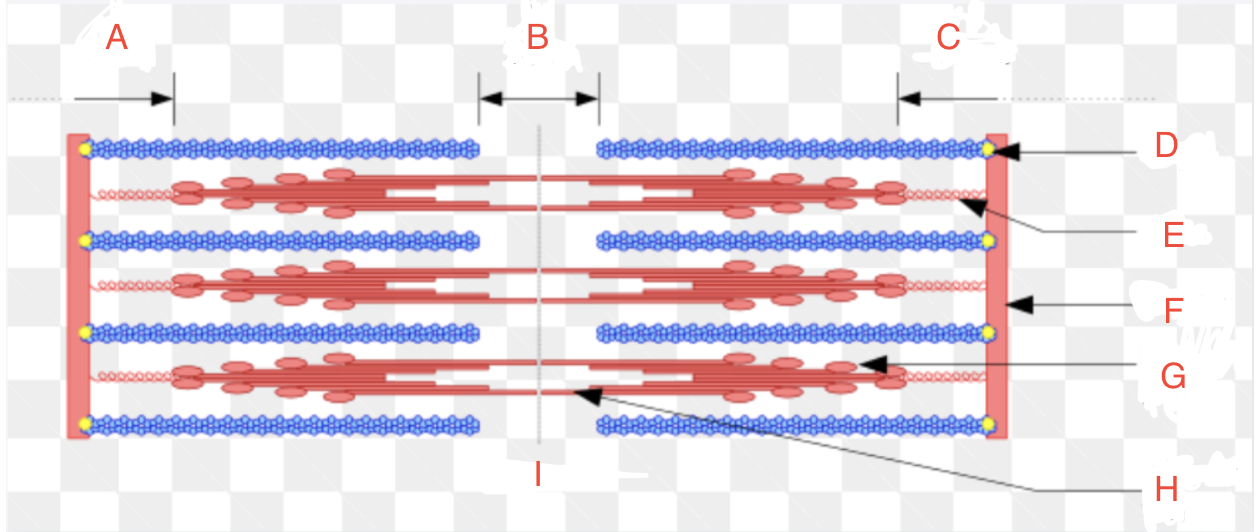
What is C
I band right
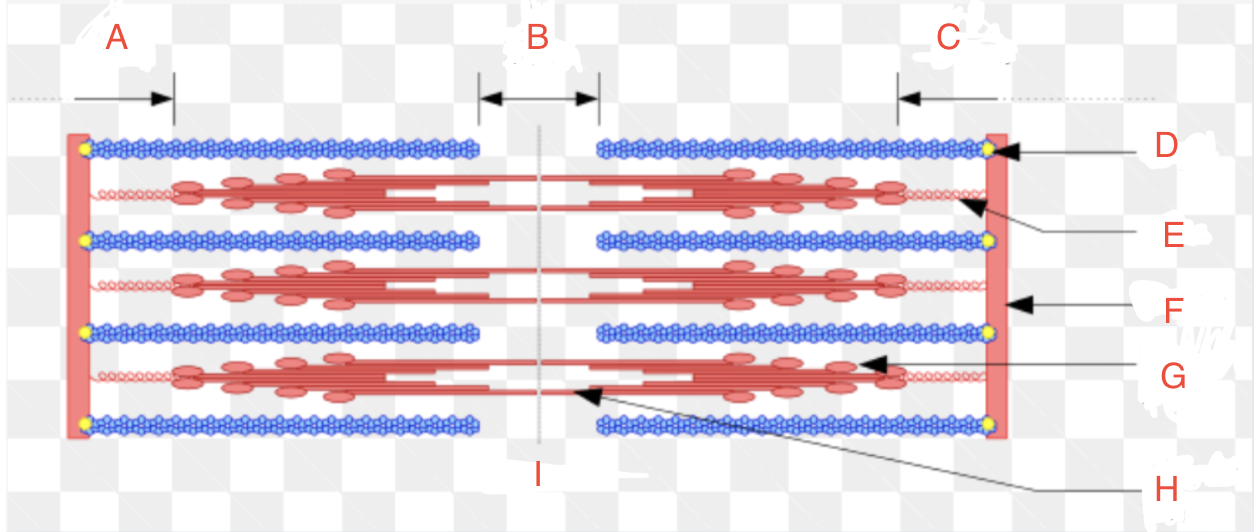
What is D
CapZ
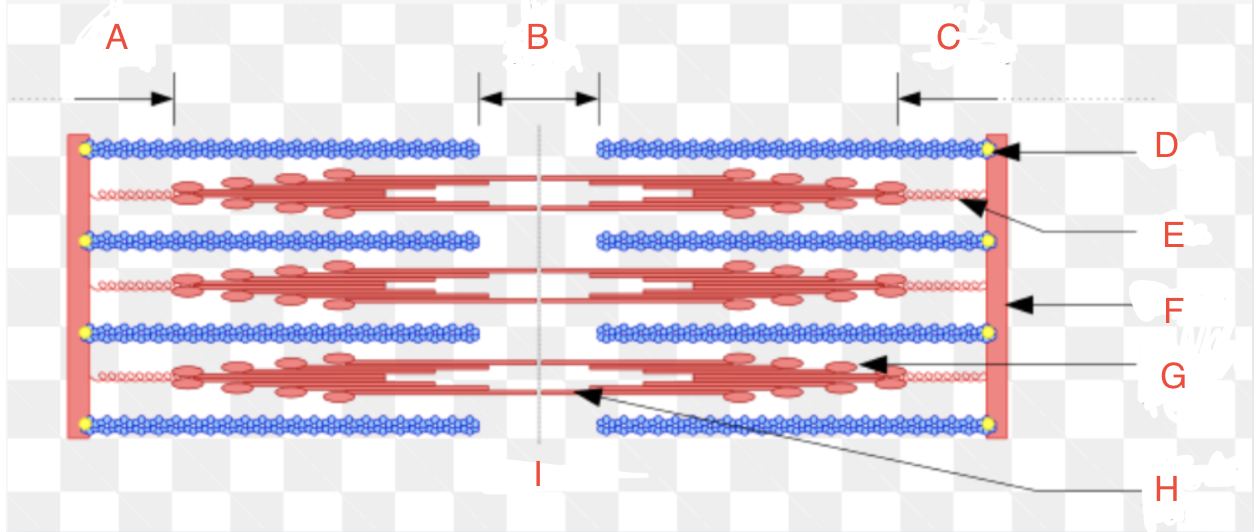
What is E
Titin
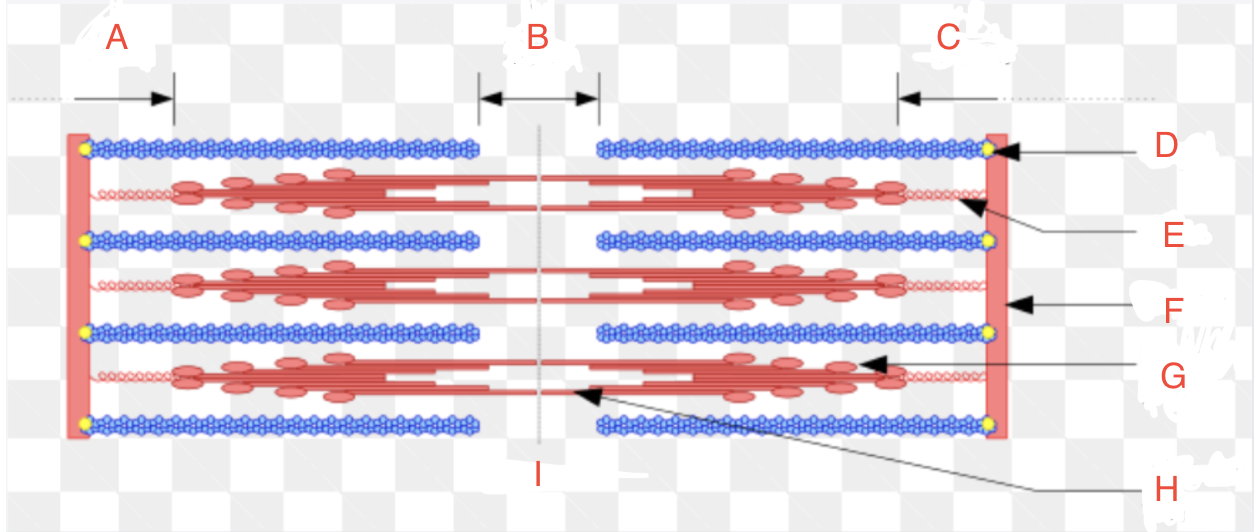
What is F
Z-disk
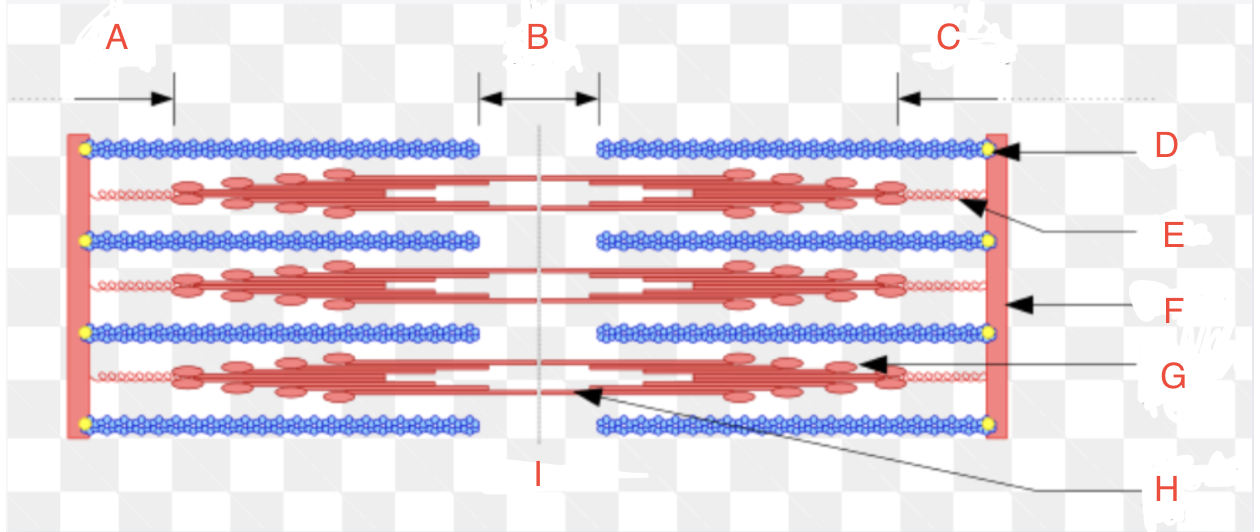
What is G
Myosin Head
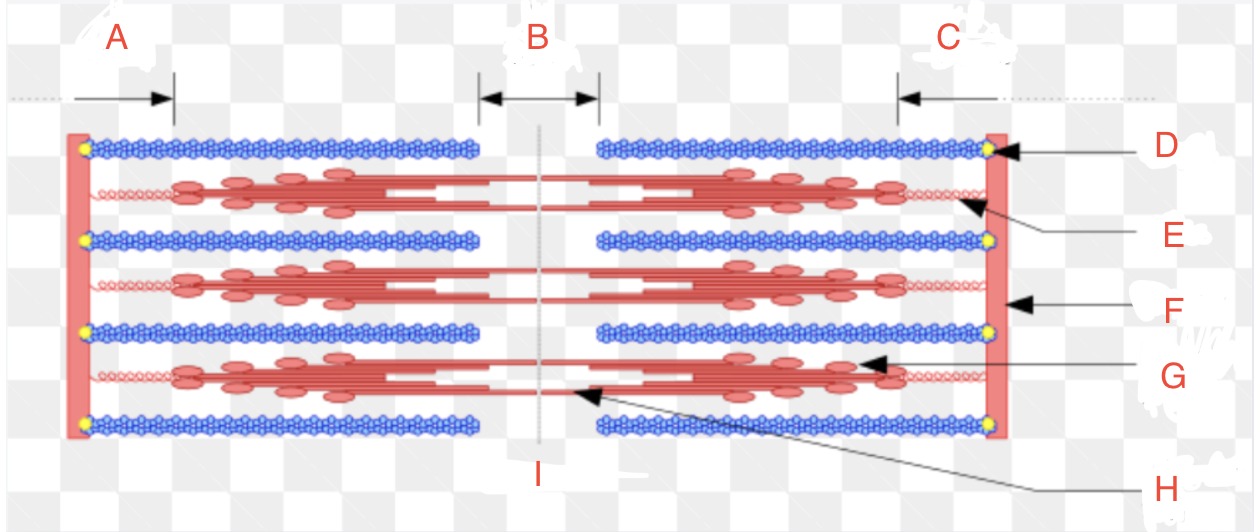
What if H
Myosin Tail
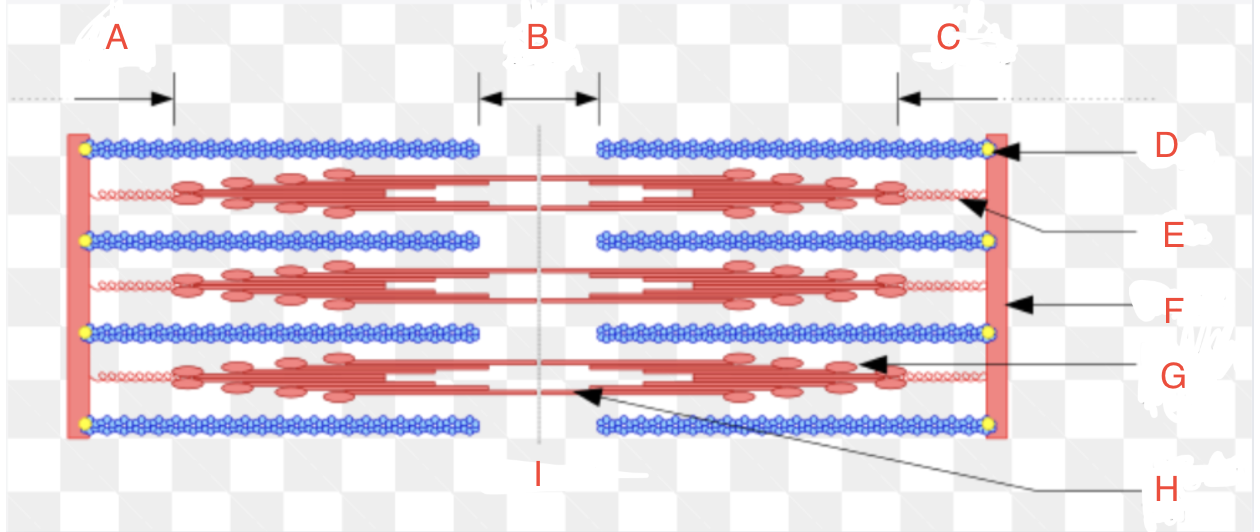
What is I
Relaxed
The myosin and actin overlap
false
What is the Z-disk
it marks the boundaries of each sarcomere
What is the I-band
the light region between the Z-discs and contains only actin filaments
What is the A-band
the dark region in the center of the sarcomere and contains both actin and myosin filaments.
Muscle contractions work by doing two things
contracting and relaxing
What kind of cells do muscles have
long, thin cells that are grouped into bundles
What happens when a muscle fiber gets a signal from its nerve
proteins and chemicals release energy to either
contract the muscle or relax it
When the muscle contracts what does it do to the bone
pulls the bones it's connected to
closer together which requires ATP
What is the first step of muscular contraction system
A nerve impulse travels down a motor neuron and reaches the neuromuscular junction
What is the second step of the muscular contraction system
The motor neuron releases the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) into the synaptic cleft.
What is the third step of the muscular contraction system
ACh binds to receptors on the sarcolemma. The binding of ACh causes depolarization of the sarcolemma, generating an electrical signal.
What is the fourth step of the muscular contraction system
The electrical signal triggers the release of calcium ions (CA+) from the sarcoplasmic
reticulum within the muscle cell. Ca+ bind to troponin, a protein on the actin filaments.
What is the fifth step of the muscular contraction system
The binding of Ca to troponin causes a shift in tropomyosin, exposing the active binding sites on the actin filaments. Myosin heads attach to the exposed binding sites on actin, forming cross-bridges.
What is the sixth step of the muscular contraction system
ATP is required to provide the energy needed for the myosin heads to move and slide along the actin filaments. Process continues causing contraction (shortening) of muscle movement.
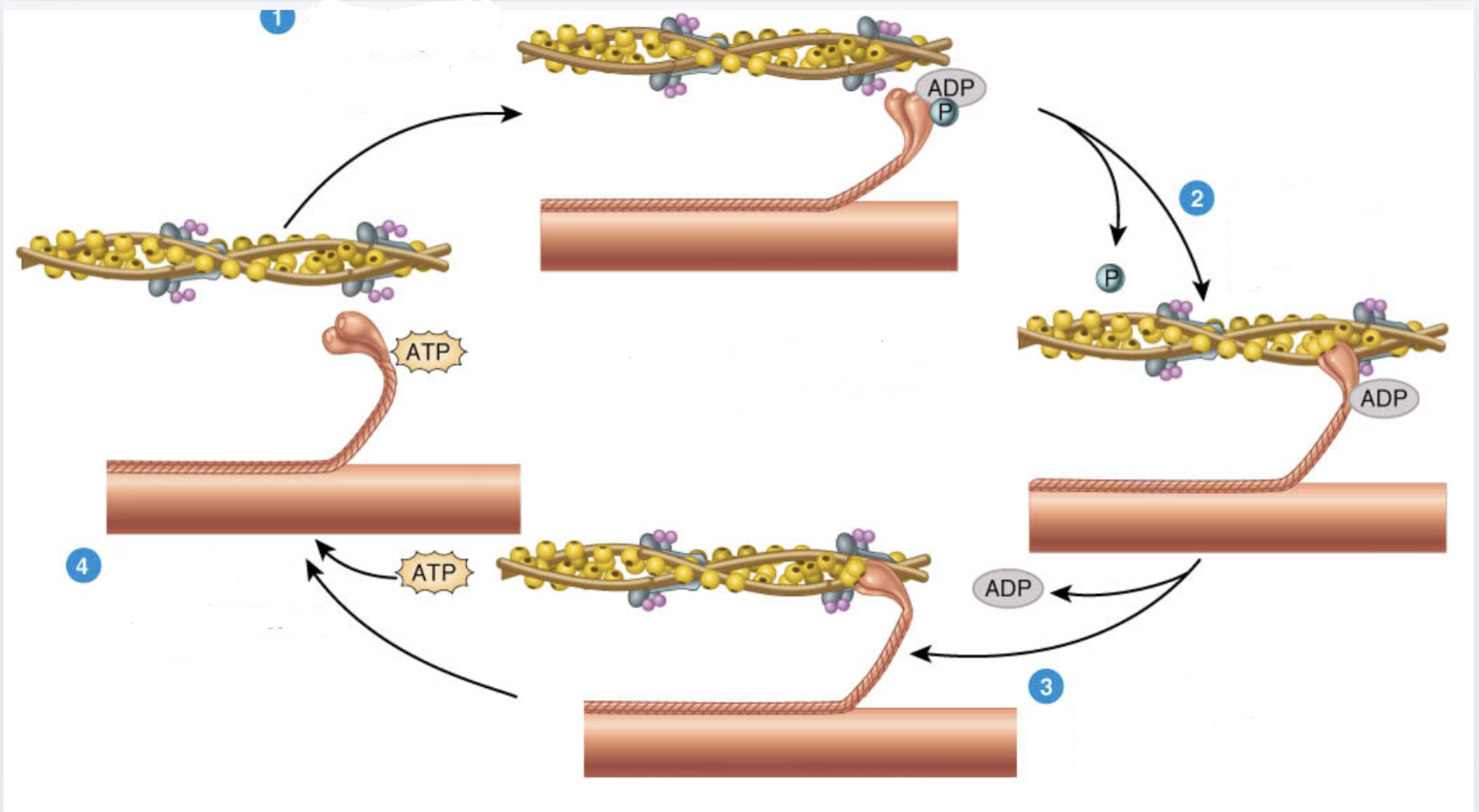
What is 1
Myosin heads split ATP and become reoriented and energized
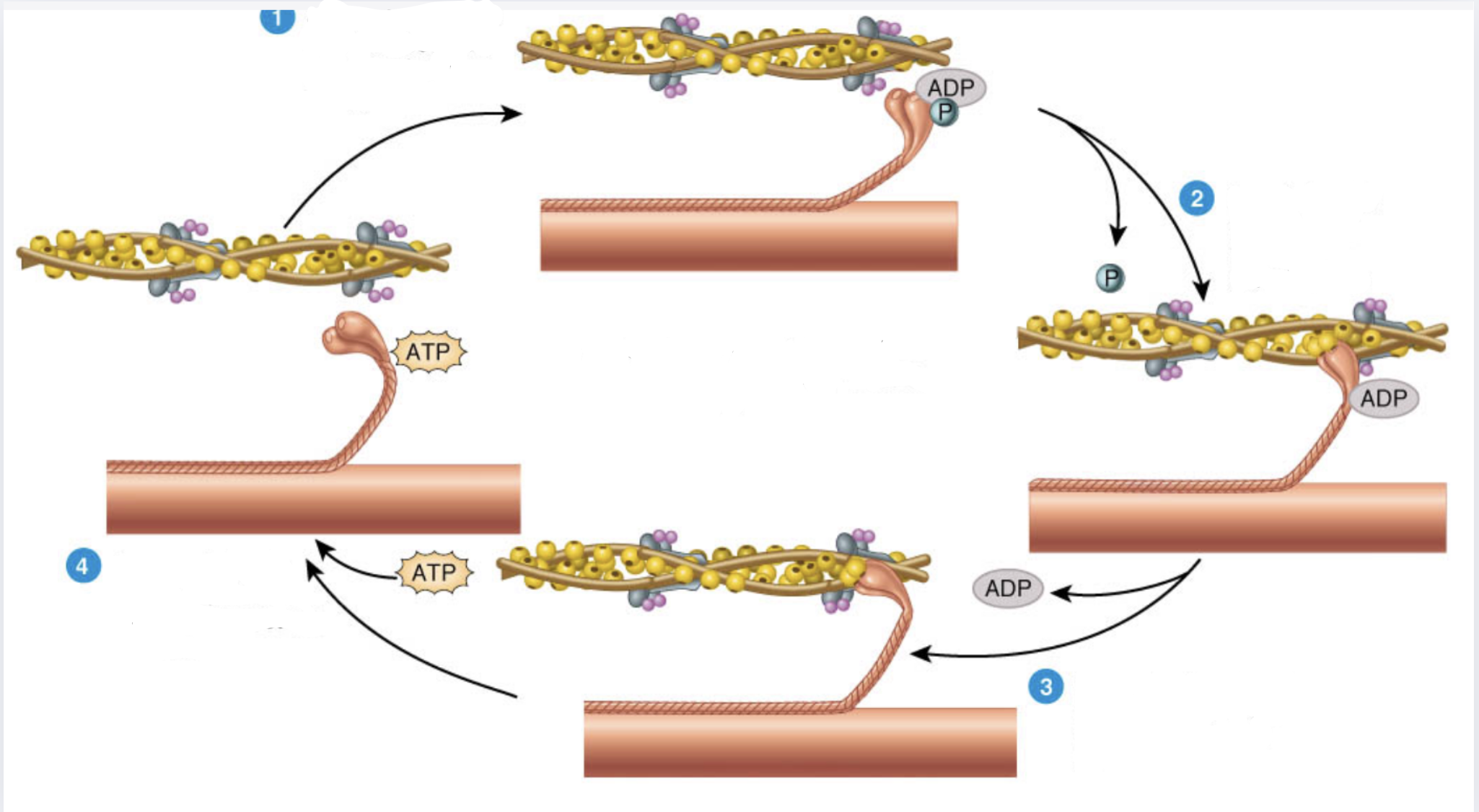
What is 2
Myosin heads bind to actin, forming crossbridges
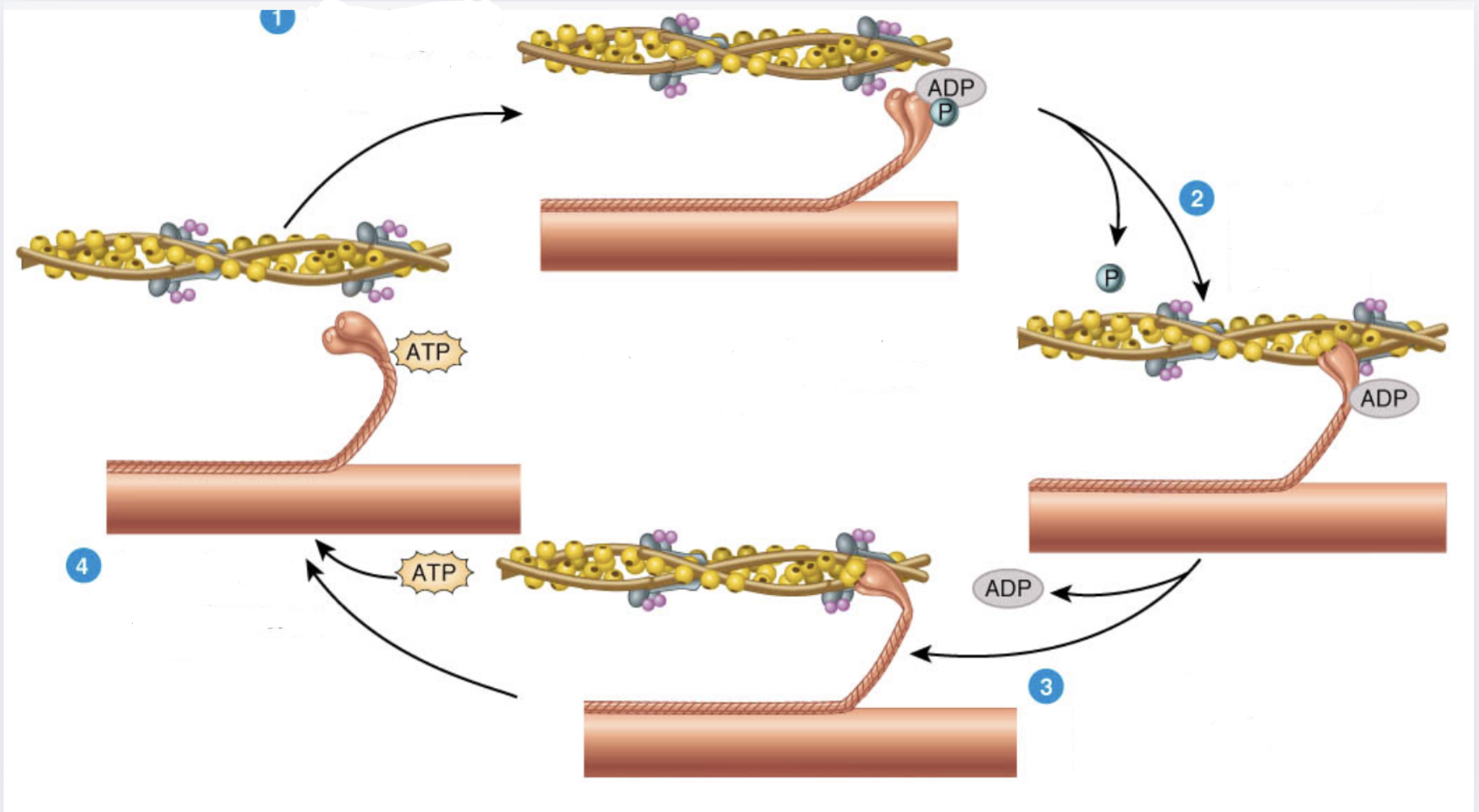
What is 3
Myosin heads rotate toward center of the sarcomere (power stroke)
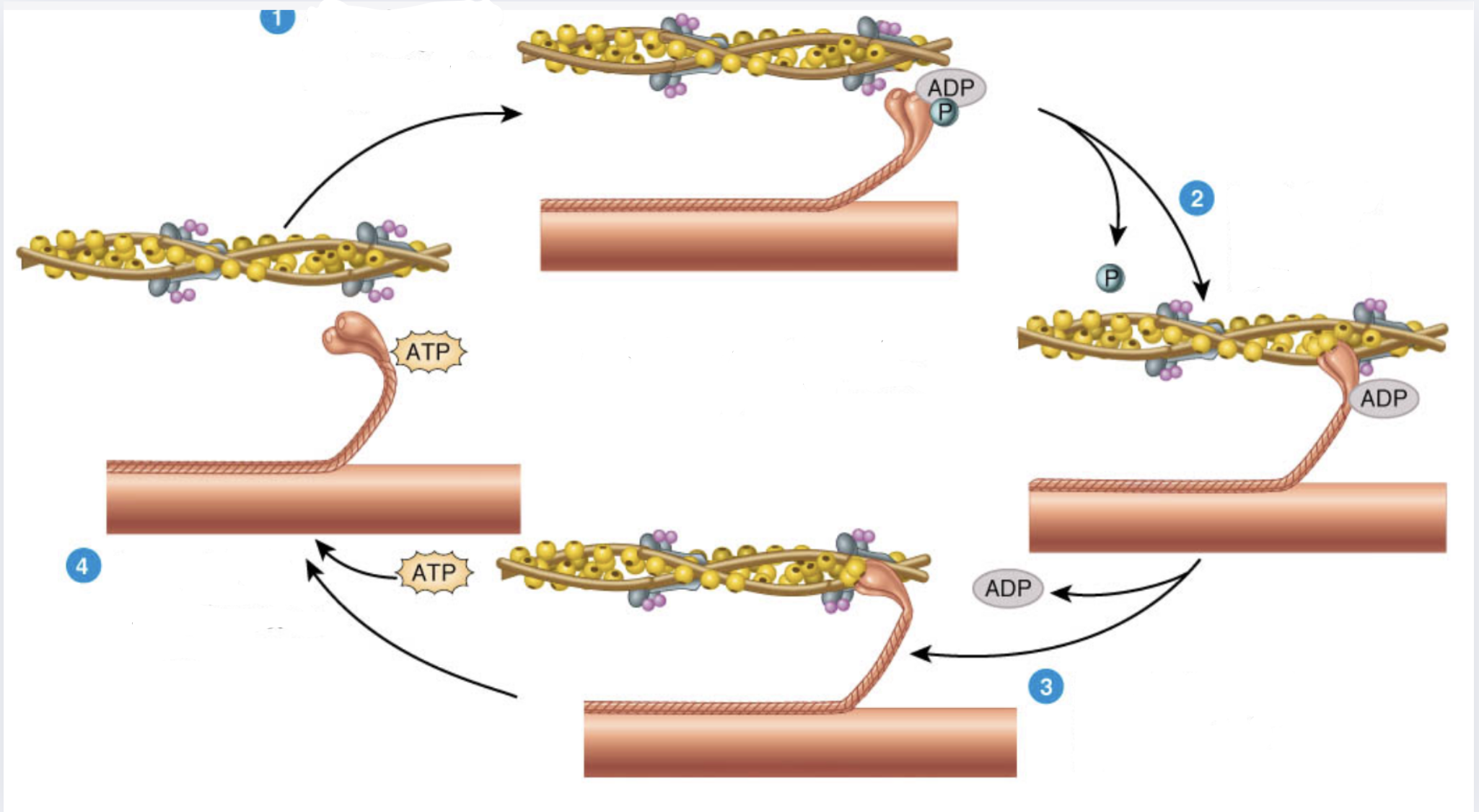
What is 4
As myosin heads bind ATP, the crossbridges detacl from actin
The contraction cycle only continues if what is available
ATP
The contraction cycle only continues if the level of what is high
Ca²+ in the sarcoplasm
What are the results of muscle contraction
shortened sarcomere and H-zone disapears