Pre Colombian Societies
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Christopher Columbus
An Italian navigator who was funded by the Spanish Government to find a passage to the Far East. He is given credit for discovering the "New World," even though at his death he believed he had made it to India.

Bartholomeu Dias
Portuguese explorer who in 1488 was the first European to get round the Cape of Good Hope (thus establishing a sea route from the Atlantic to Asia) (1450-1500)

Magellan
Portuguese explorer who sailed around the Southern end of South America and eventually reached the Philippines, but was killed in a local war there

Prince Henry the Navigator
(1394-1460) Prince of Portugal who established an observatory and school of navigation at Sagres and directed voyages that spurred the growth of Portugal's colonial empire.

Incas
A Native American people who built a notable civilization in western South America in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. The center of their empire was in present-day Peru. Francisco Pizarro of Spain conquered the empire.
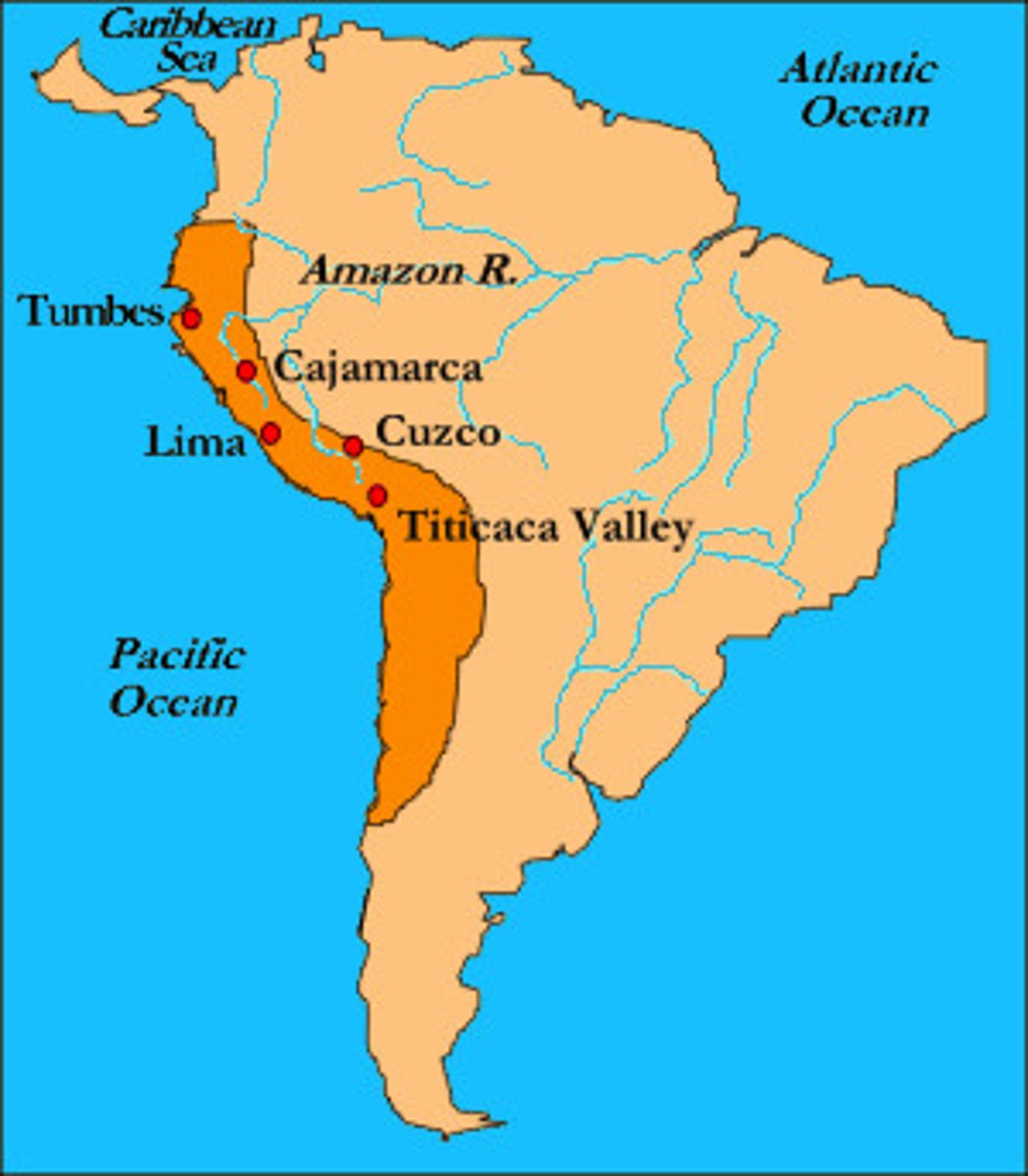
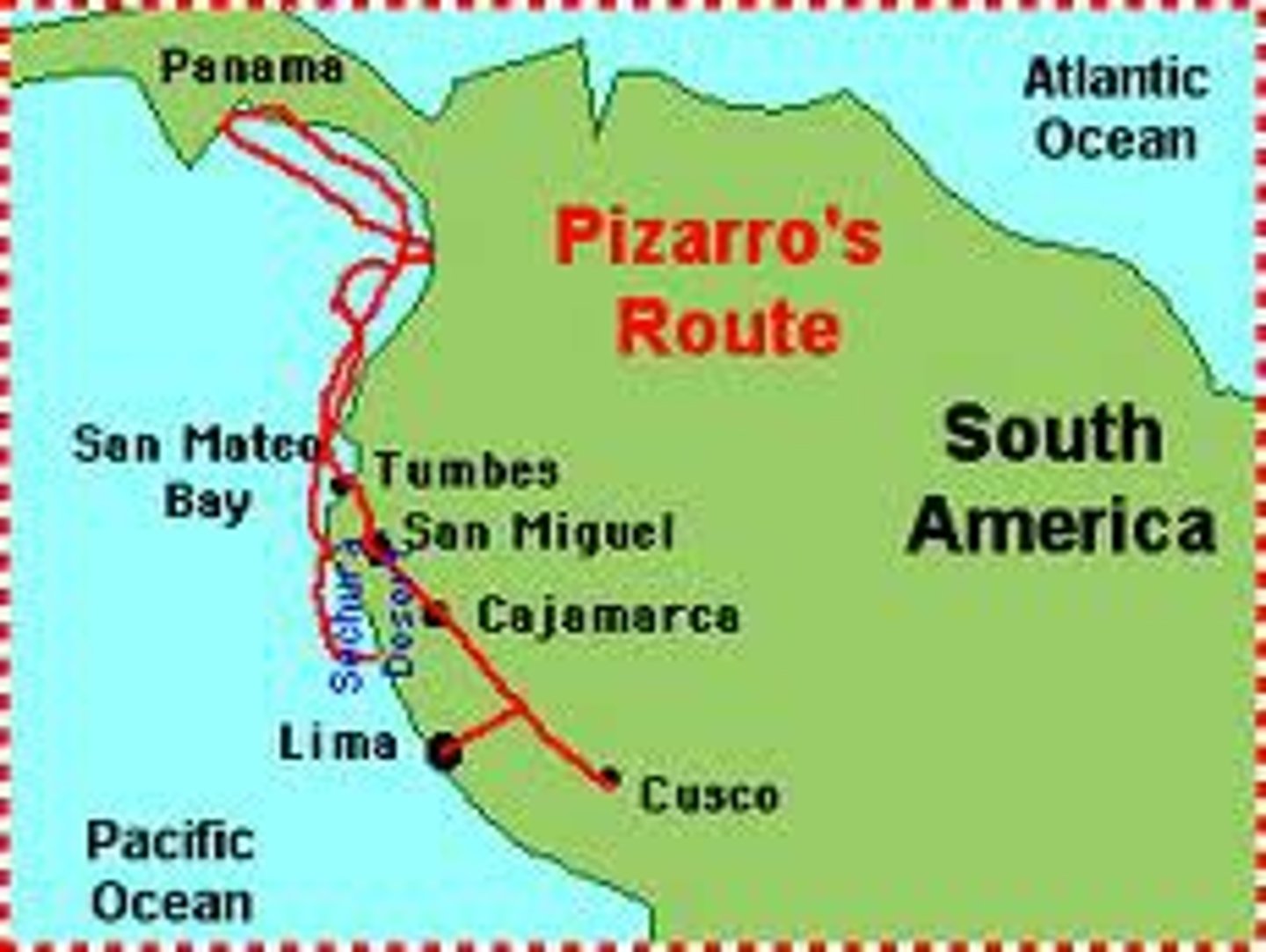
Pizzaro
For Spain. led a small army in an invasion of the Inca Empire. He conquered the Inca and gained huge amounts of gold and silver for himself and Spain.
Cortes
Spanish conquistador who defeated the Aztecs and conquered Mexico (1485-1547)

Mestizos
A person of mixed Native American and European ancestry
Spanish Armada
The great fleet sent from Spain against England by Philip II in 1588; defeated by the terrible winds and fire ships.

God, Glory, and Gold
The three motivations for Europeans to explore the new world

Marco Polo
Venetian merchant and traveler. His accounts of his travels to China offered Europeans a firsthand view of Asian lands and stimulated interest in Asian trade.
Pachacuti
Ruler of Inca society from 1438 to 1471; launched a series of military campaigns that gave Incas control of the region from Cuzco to the shores of Lake Titicaca

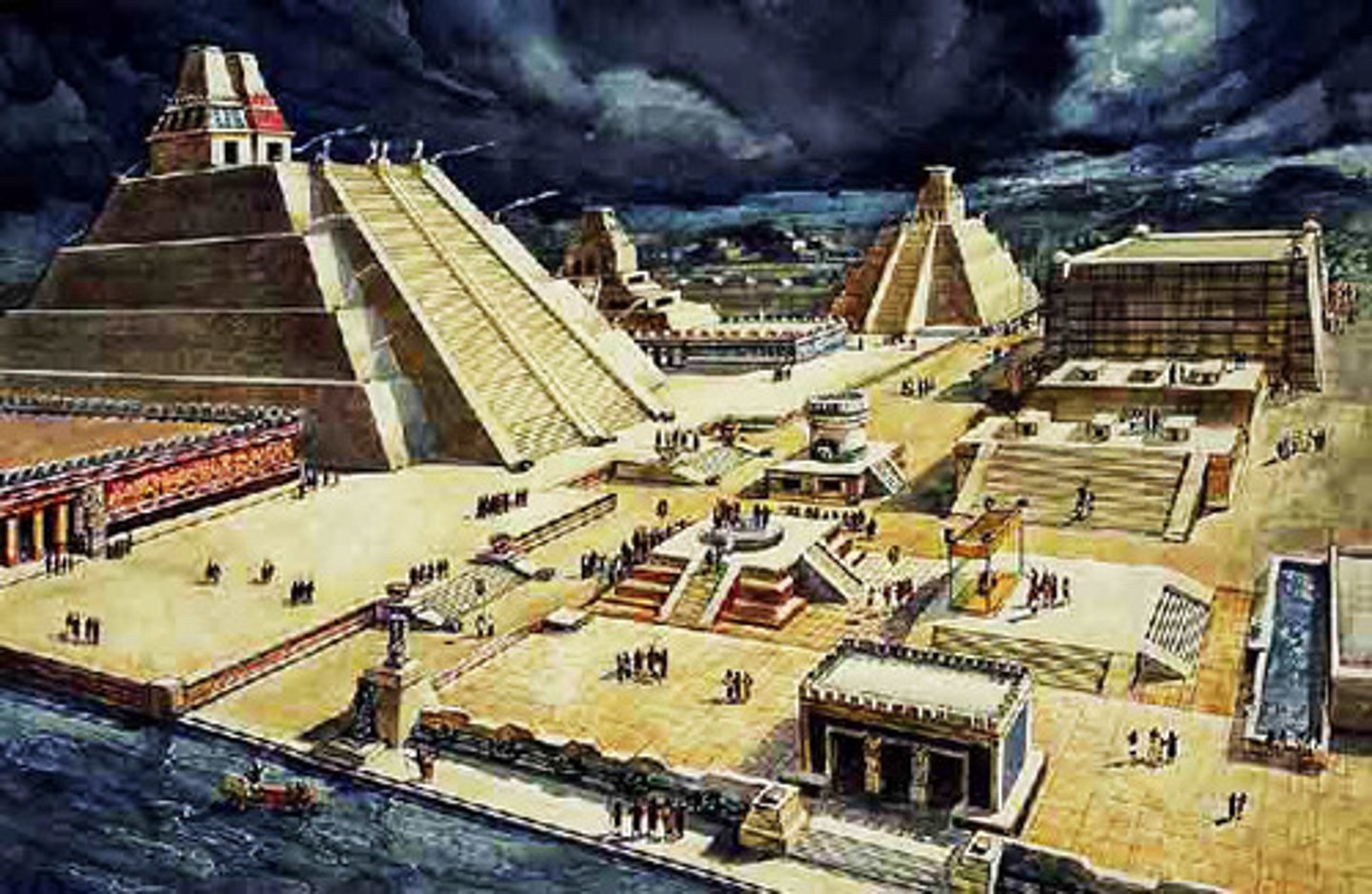
Tenochtitlan
Capital of the Aztec Empire, located on an island in Lake Texcoco. Its population was about 150,000 on the eve of Spanish conquest. Mexico City was constructed on its ruins.

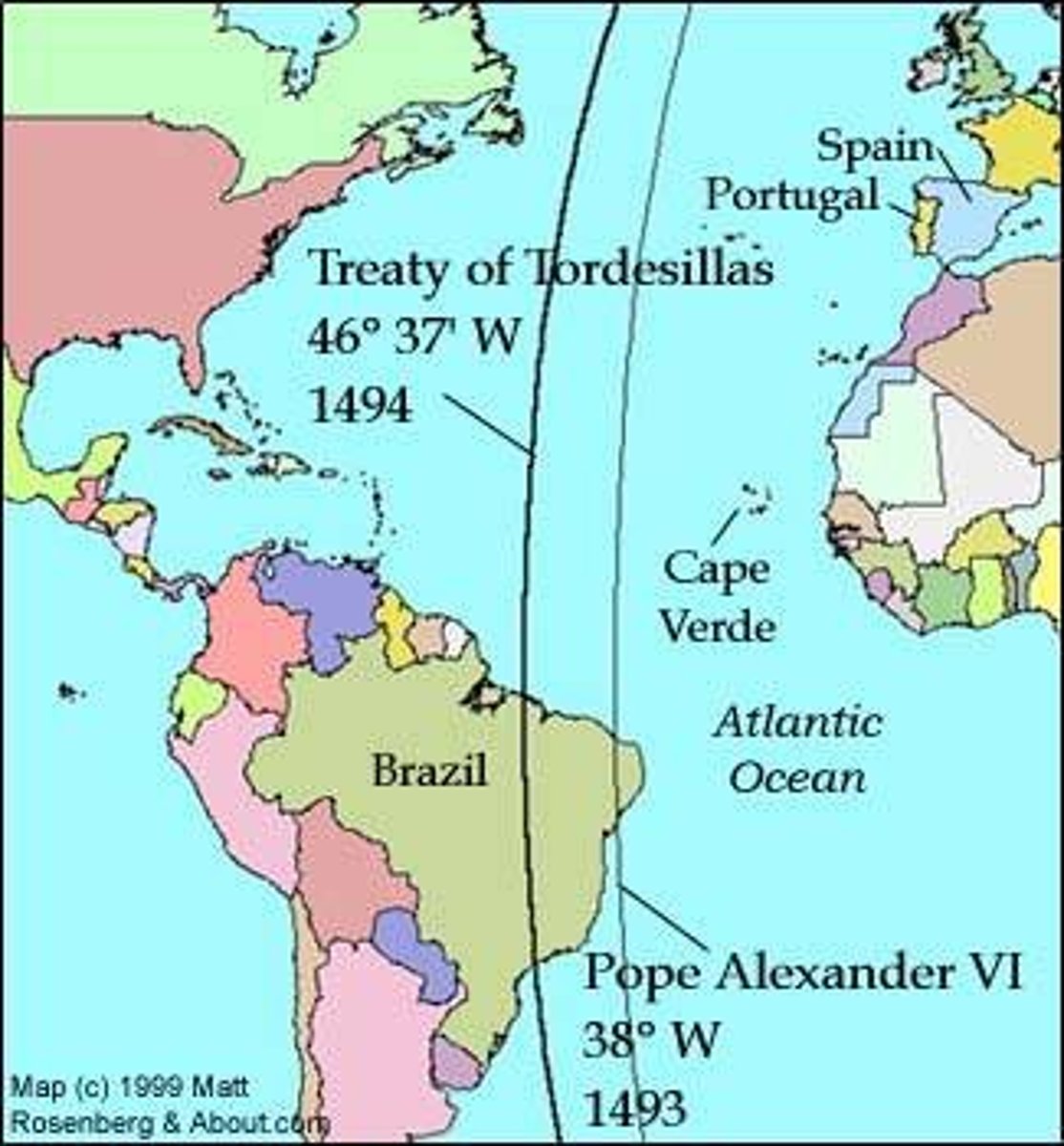
Treaty of Tordesillas
Treaty that split South America between Spain and Portugal, greatly benefited Spanish exploration.
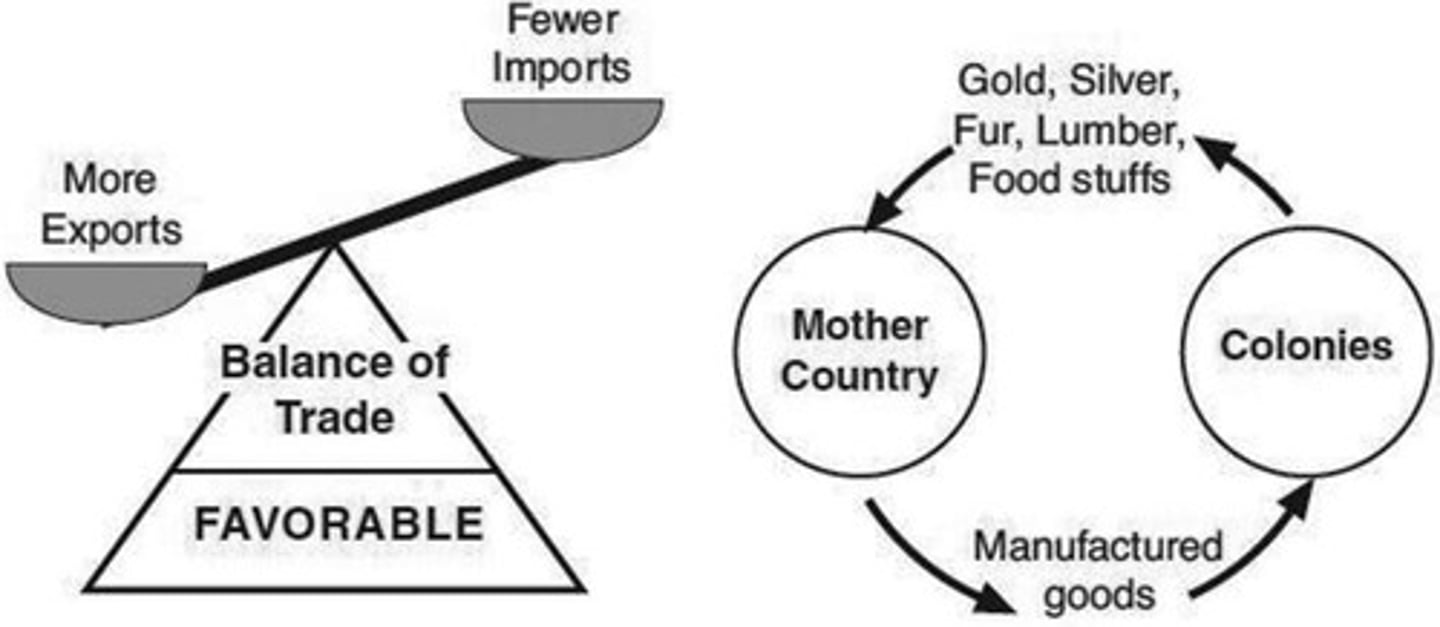
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
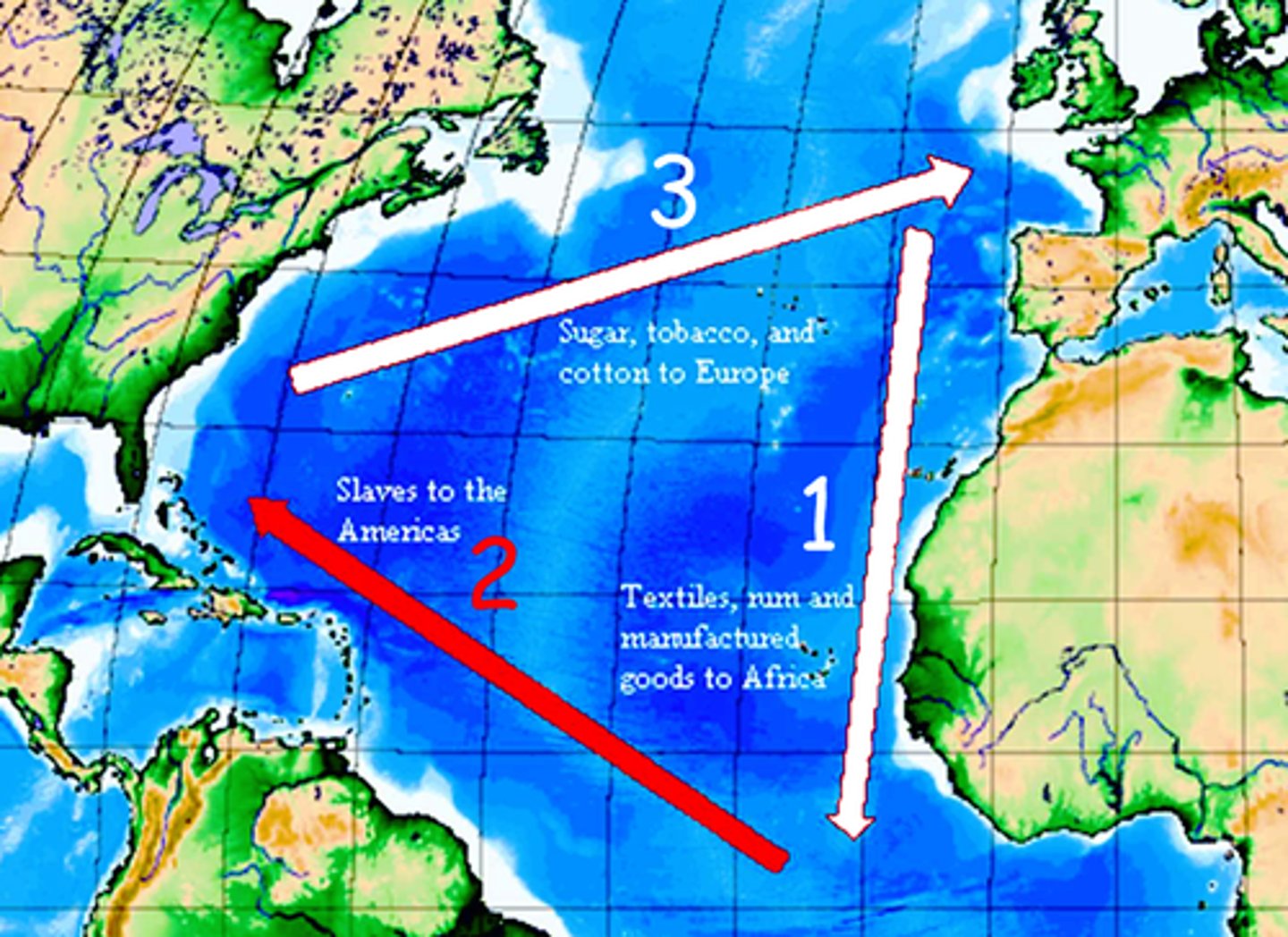
Atlantic Slave Trade
Lasted from 16th century until the 19th century. Trade of African peoples from Western Africa to the Americas. One part of a three-part economical system known as the Middle Passage of the Triangular Trade.
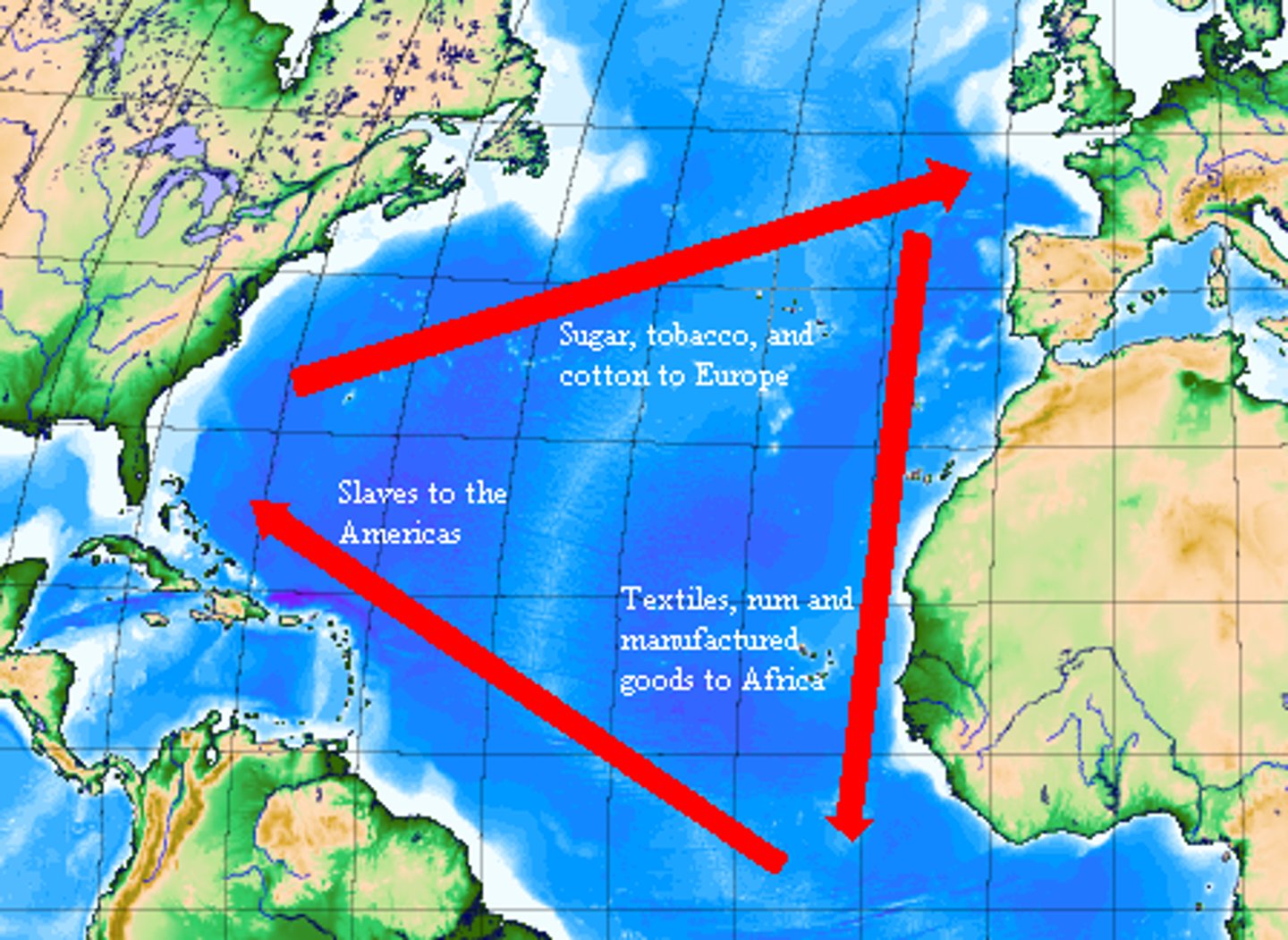
Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies
French Colonies
fur trading

English Colonies
In the East coast of the U.S. Jamestown, Virginia was the first settlement. Colonies were a safe haven for religious persecution.
Aztecs
(1200-1521) 1300, they settled in the valley of Mexico. Grew corn. Engaged in frequent warfare to conquer others of the region. Worshiped many gods (polytheistic). Believed the sun god needed human blood to continue his journeys across the sky. Practiced human sacrifices and those sacrificed were captured warriors from other tribes and those who volunteered for the honor.

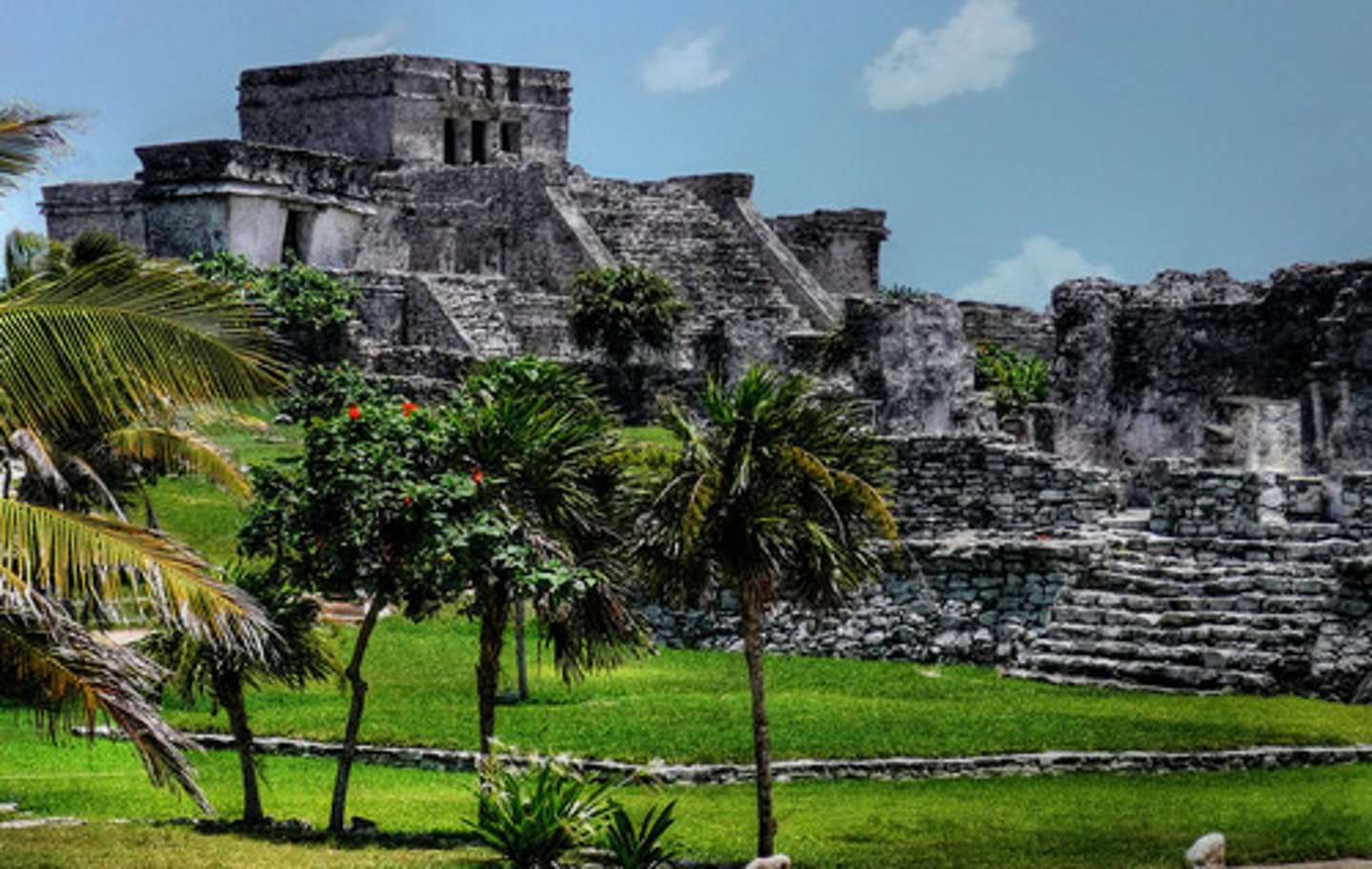
Mayans
1500 B.C. to 900 A.D. This is the most advanced civilization of the time in the Western Hempishere. Famous for its awe-inspiring temples, pyramids and cities. A complex social and political order.

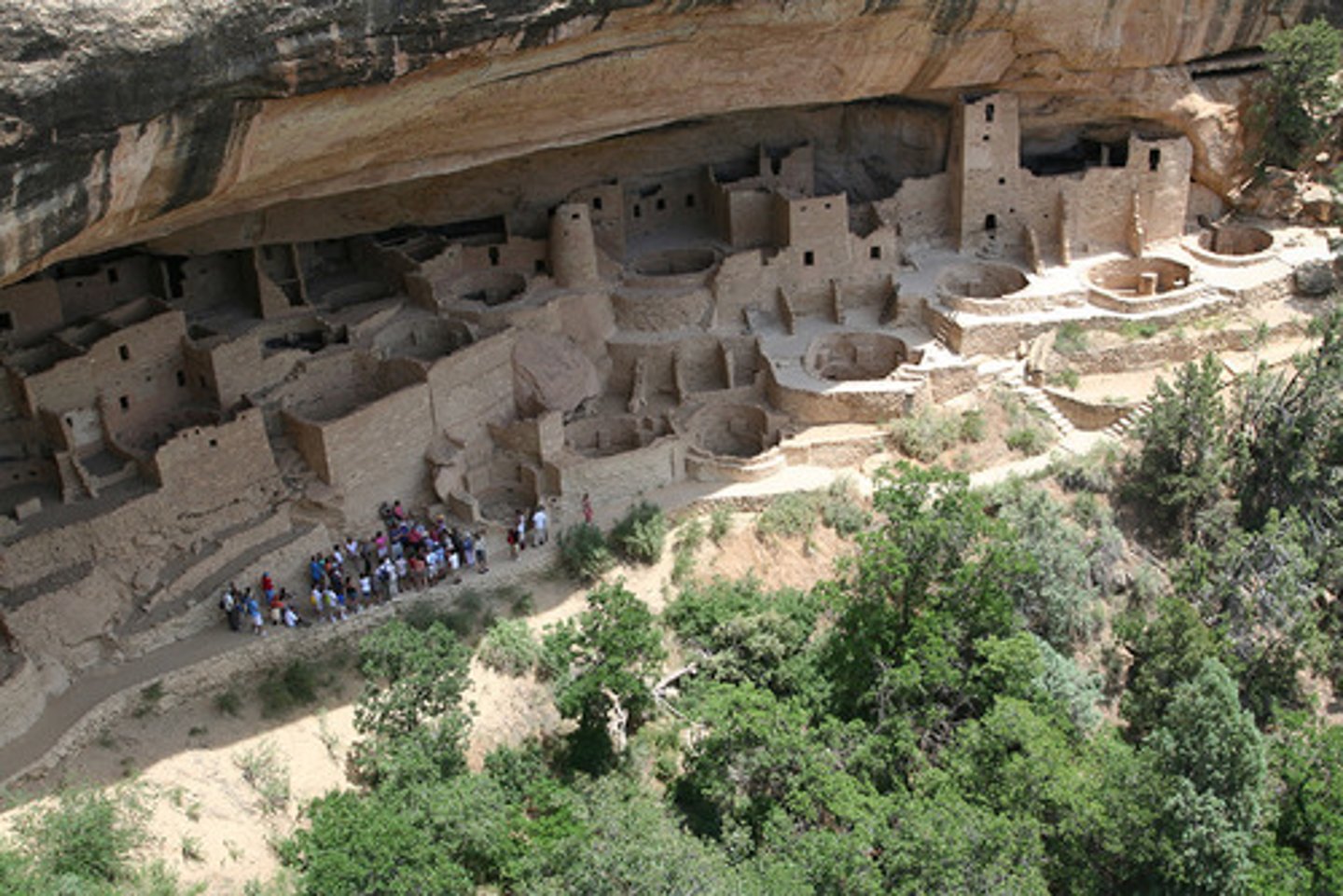
Anasazi
a member of an ancient American Indian people of the southwestern US, who flourished between c. 200 BC and AD 1500. The earliest phase of their culture, typified by pit dwellings, is known as the Basket Maker period; the present day Pueblo culture developed from a later stage.

Juan de Sepulveda
Spaniard who supported the Spanish Empire's right of conquest and colonization in the New World. He also argued in favor of the Christianize of Native Americans.

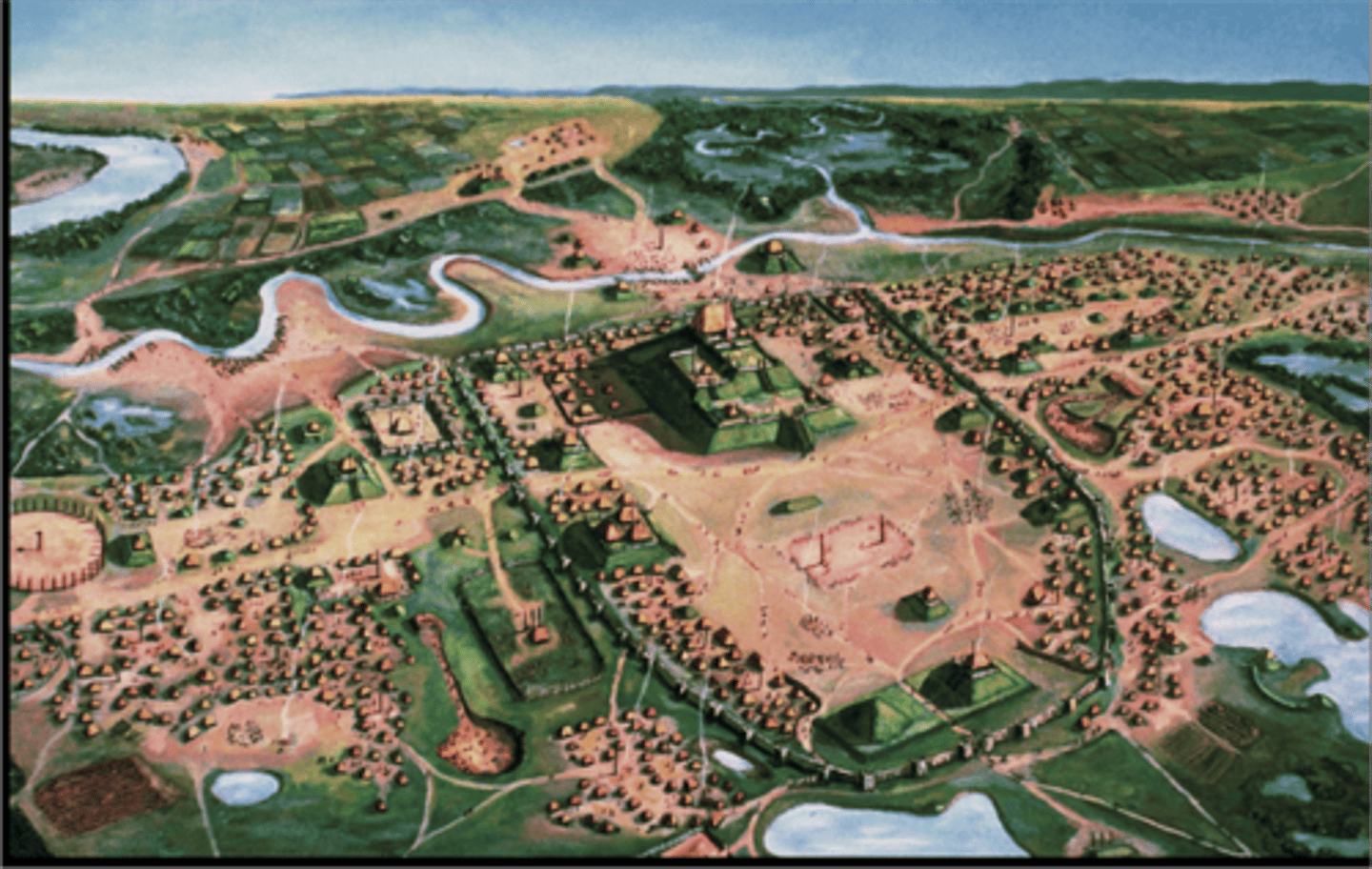
Cahokia
an ancient settlement of southern Indians, located near present day St. Louis, it served as a trading center for 40,000 at its peak in A.D. 1200.
Iroquois
A later native group to the eastern woodlands. They blended agriculture and hunting living in common villages constructed from the trees and bark of the forests
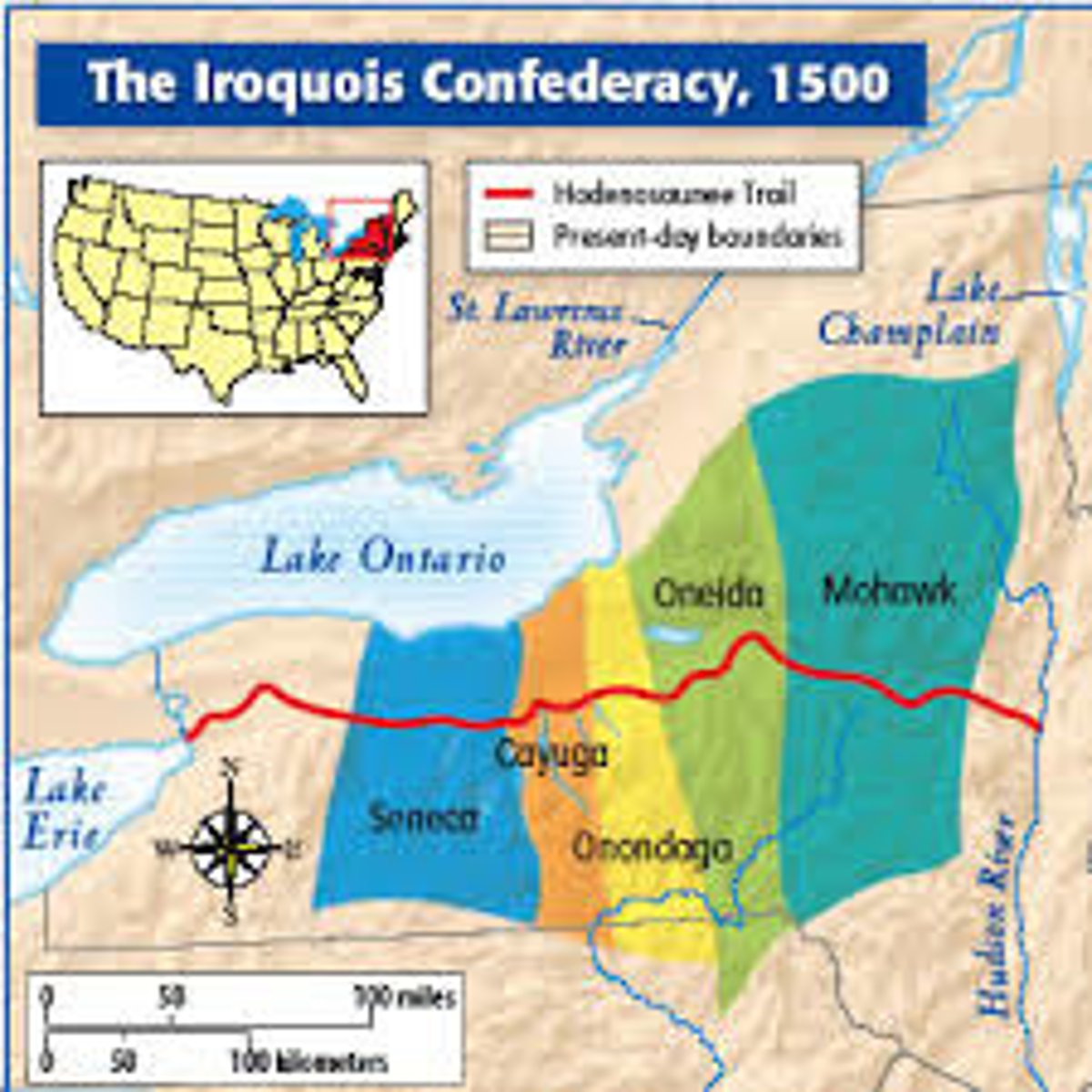
Iroquis Confederacy
the most powerful native group, made up of the five India nations; Mohawk, Seneca, Cayuga, Onondaga, and Oneida, that formed a defensive alliance in the 15th century, and gained a lot of power through trade with the English or French, controlling most of the Great Lakes region.

Encomienda System
system in Spanish America that gave settlers the right to tax local Indians or to demand their labor in exchange for protecting them and teaching them skills.

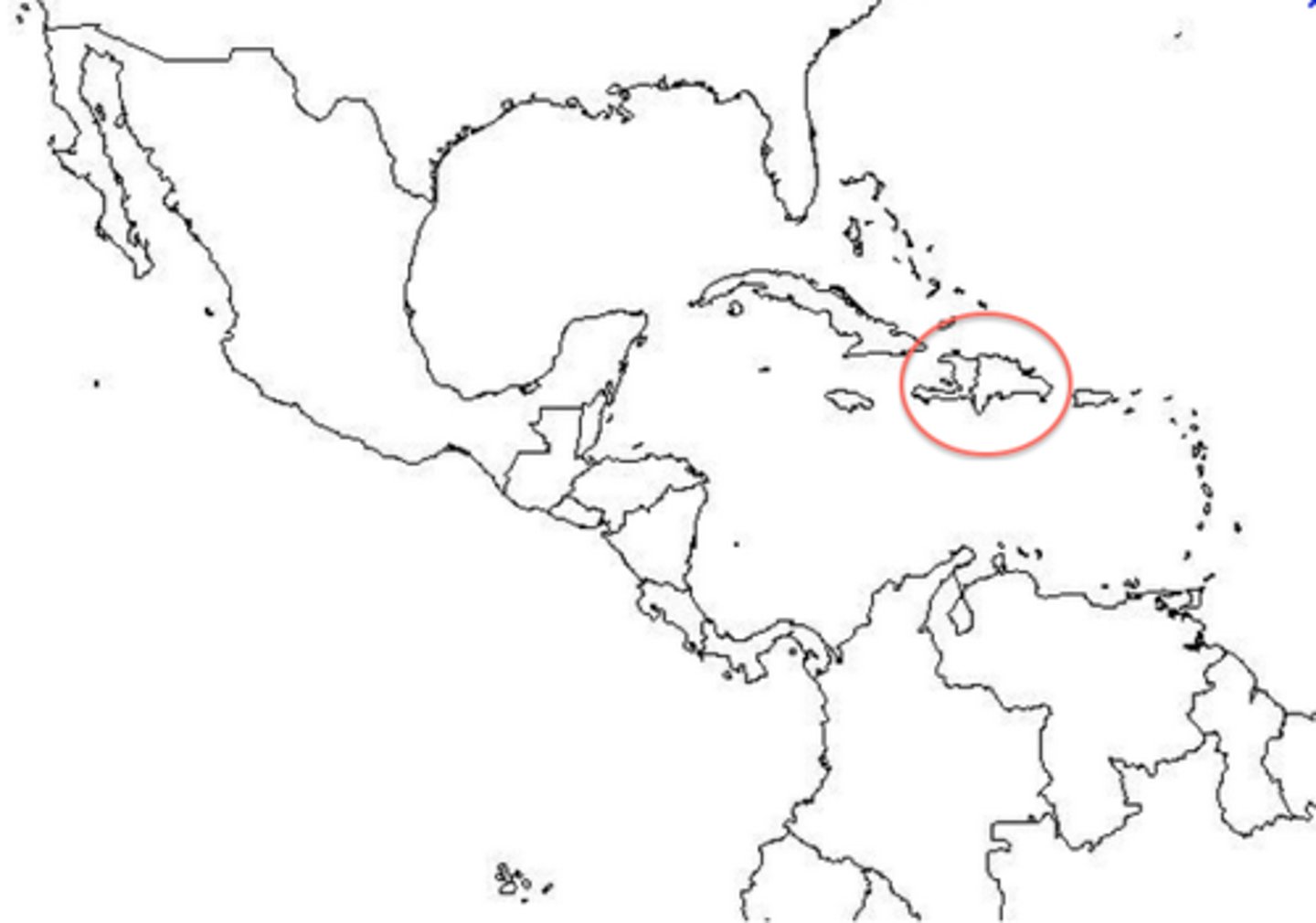
Hispaniola
First island in Caribbean settled by Spaniards; settlement founded by Columbus on second voyage to New World; Spanish base of operations for further discoveries in New World.
Protestant Reformation
A religious movement of the 16th century that began as an attempt to reform the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the creation of Protestant churches.

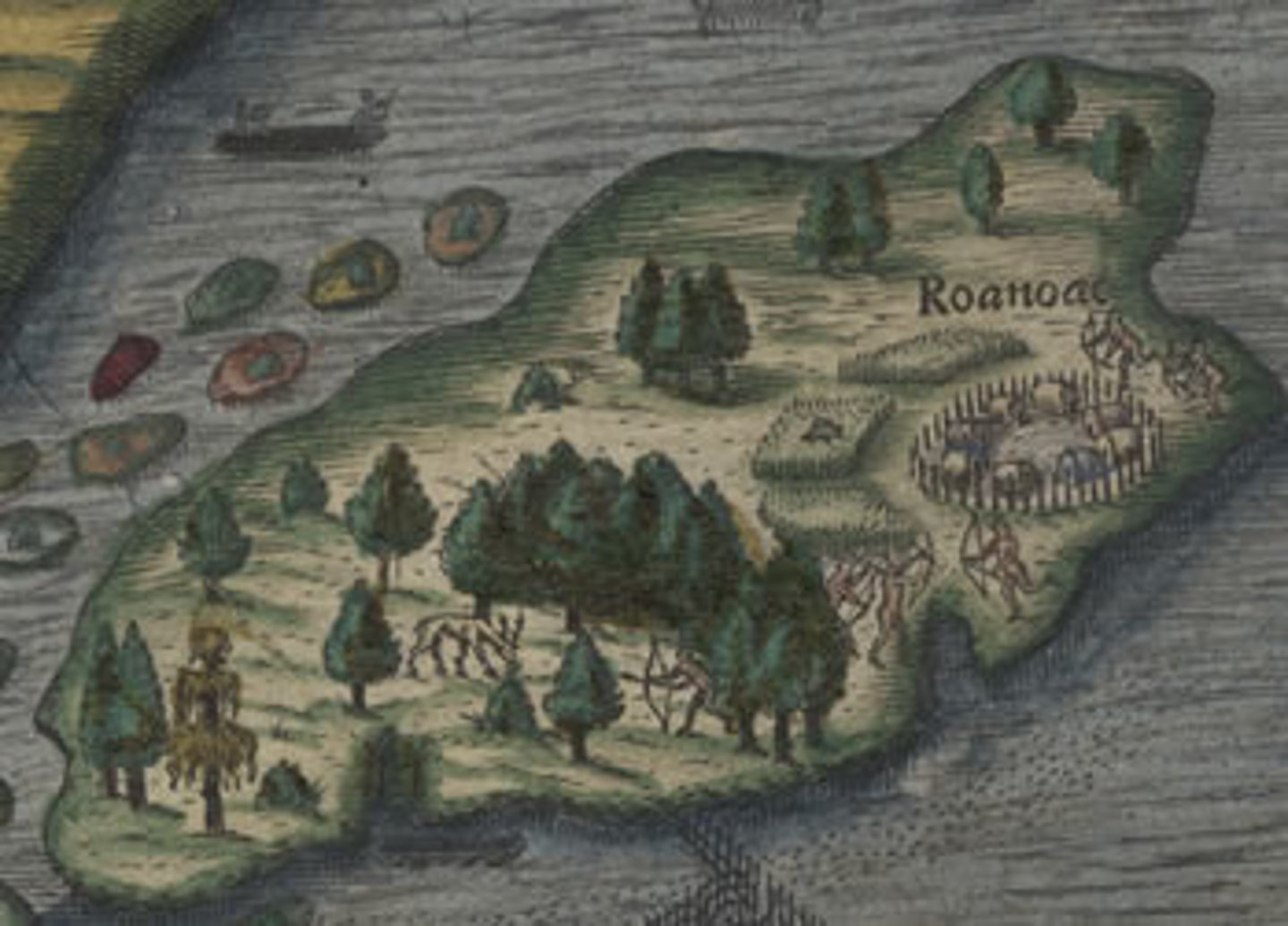
Lost Colony of Roanoke
English settlement in the Virginia Colony organized by Sir Walter Raleigh; abandoned the settlement or disappeared.
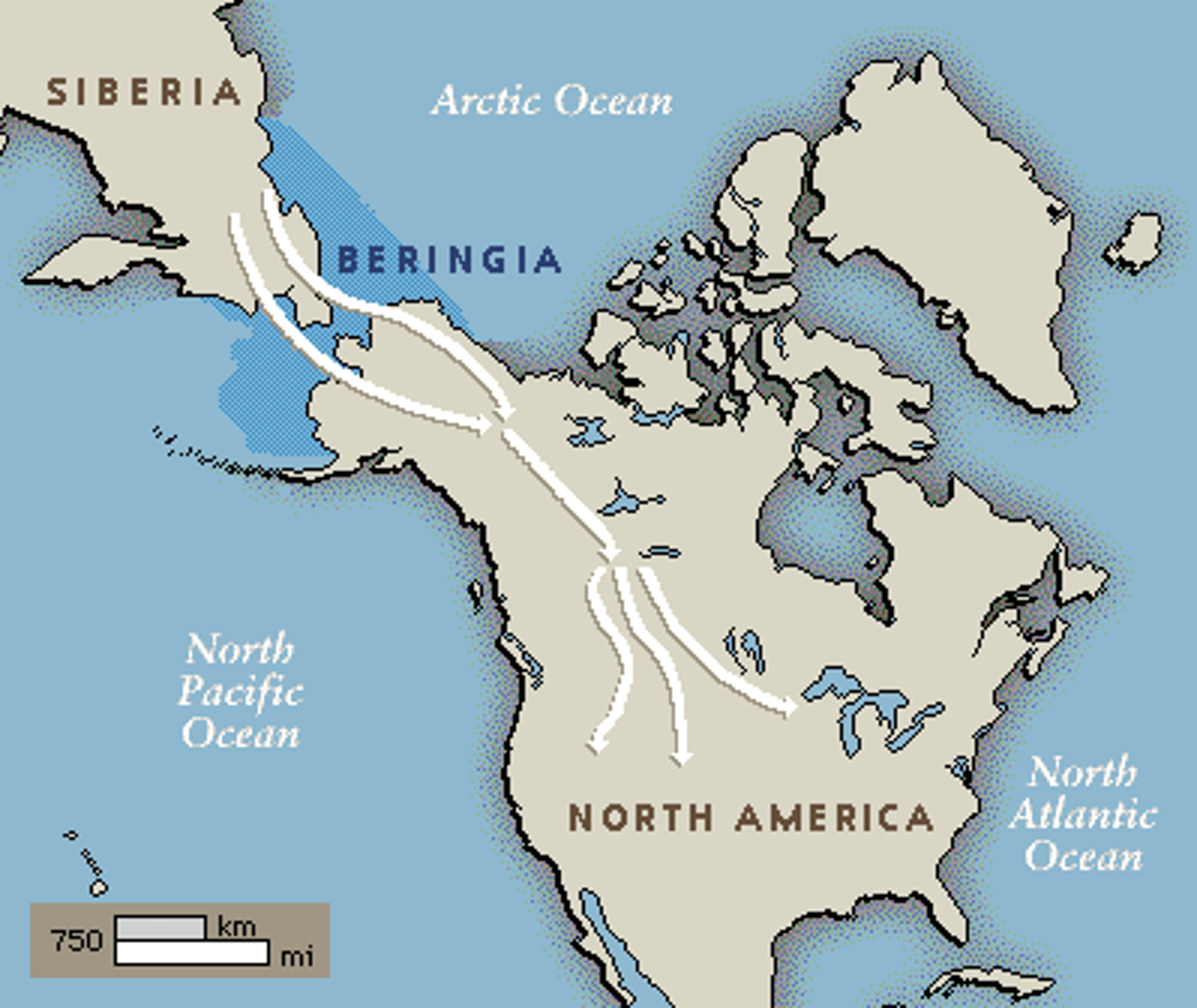
Bering Land Bridge
a strip of land connecting Alaska with Russia that emerged from underwater around 38,000 BC and allowed for Asian Hunters to migrate to North America.
Algonquin
northeastern Native American civilization in the Great Lakes region

Bartome de Las Casas
a 16th-century Spanish PRIEST who acted as a historian and social reformer. He was appointed as the first resident Bishop of Chiapas, and the first officially appointed "Protector of the Indians" as he was critical of Spanish Conquistadors.
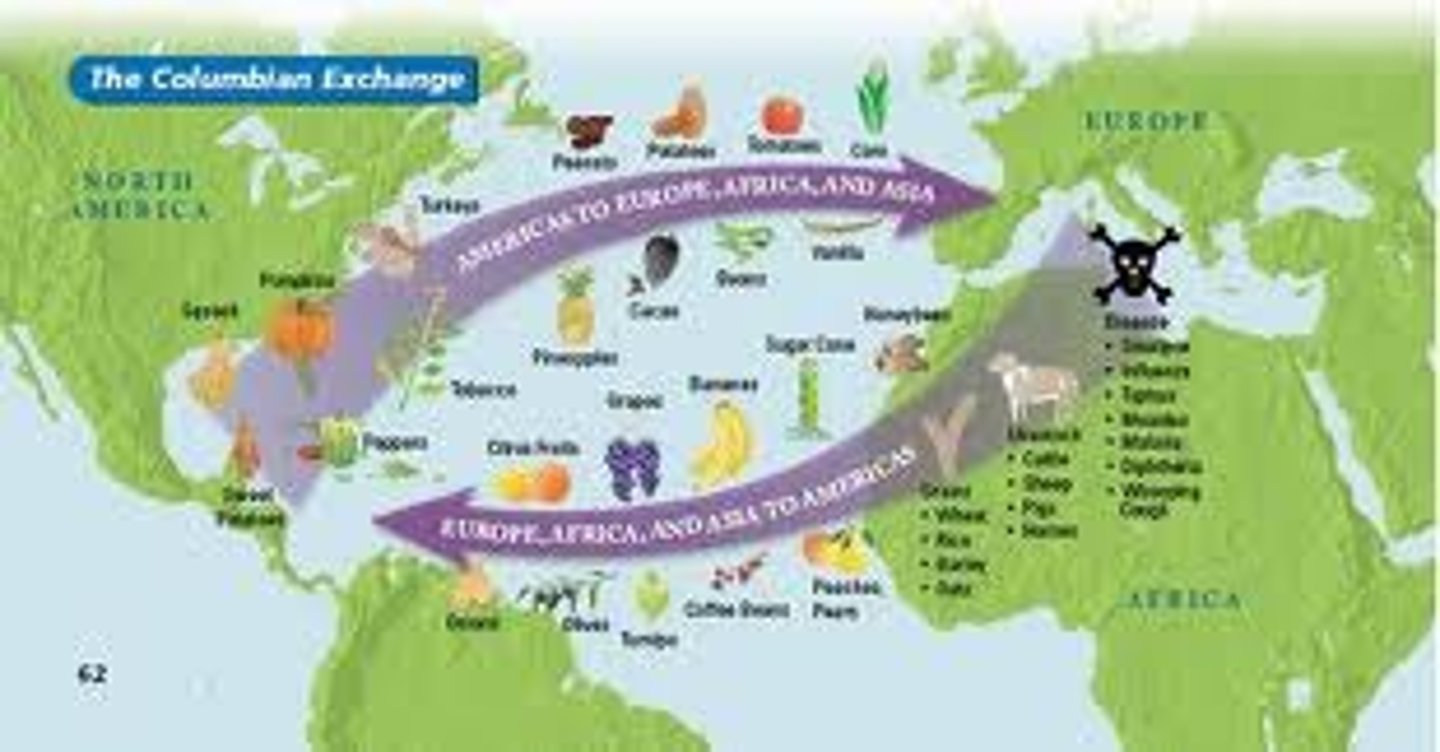
Colombian Exchange
the transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the Americas and Europe, Asia, and Africa
Amerigo Vespucci
A mapmaker and explorer who said that America was a new continent, so America was named after him.

Tiano people
The first group of "good noble" Native Americans tribe that was wiped out by Columbus and the Spaniards on the island of Hispanola.
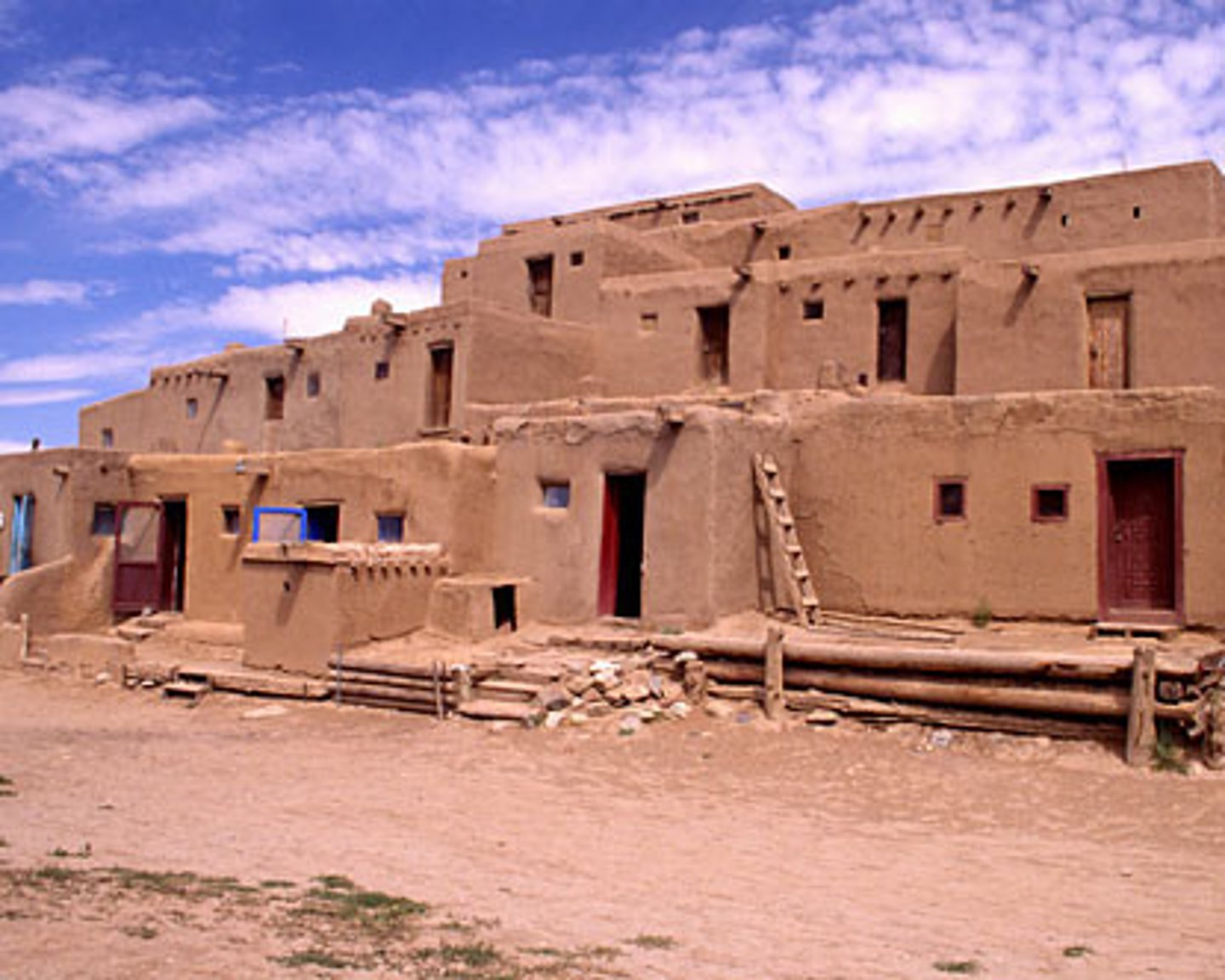
pueblo
a Native America communal village that thrived on the cultivation of Maize in the southwestern United States.

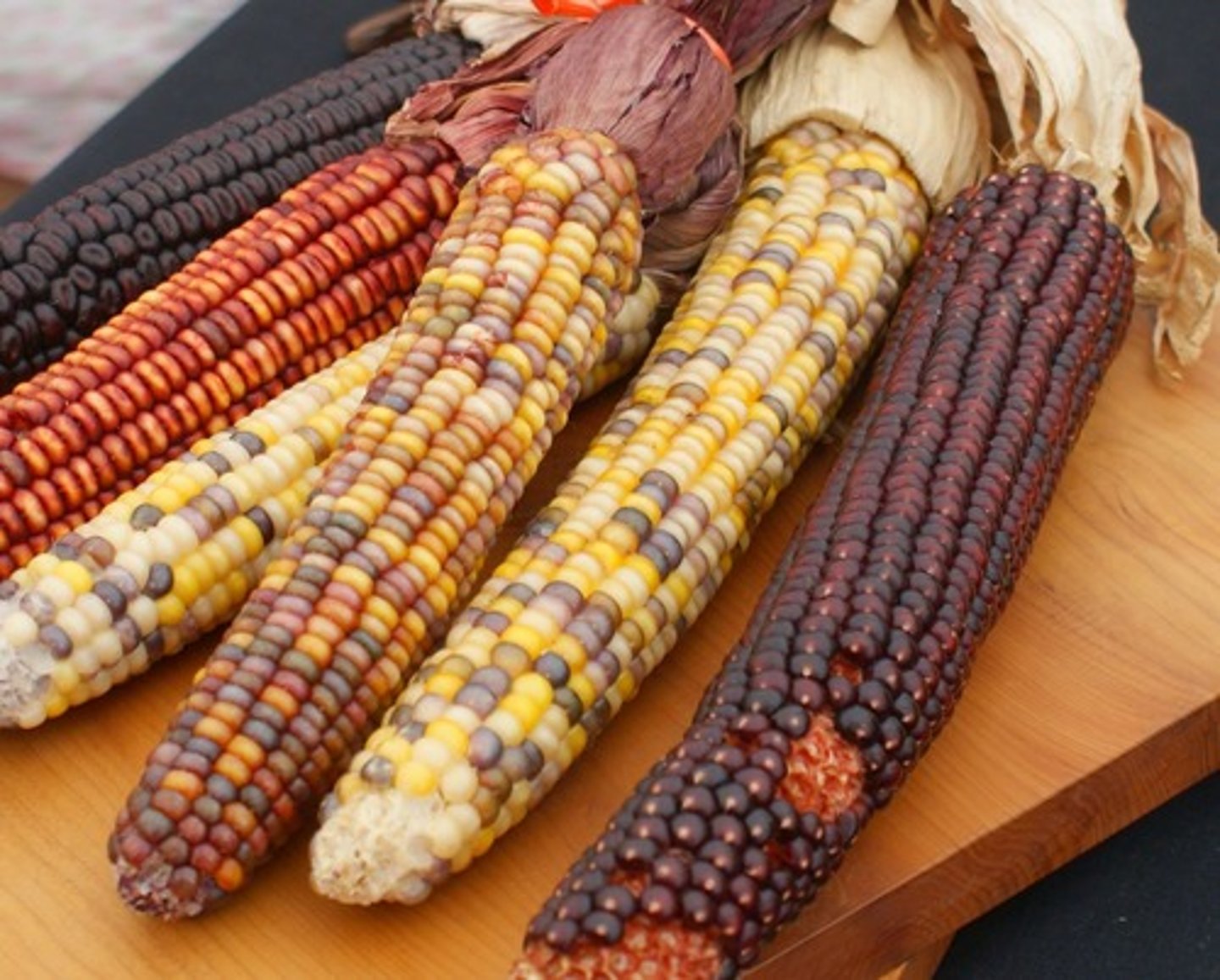
Maize
An early form of corn grown by Native Americans that sustained the first major settlements in North America.
