SA Fractures
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Direct fracture
-intramembranous ossification
-slower and takes months
Indirect fracture
-endochondral ossification
-takes weeks to months
Fracture gap strain =
Change in gap width / original gap width
What tissue strain can bone tolerate?
<2%
Increased rigidity
-reduces strain at fracture to promote direct healing
-NOT always an advantage cause can be slower healing and increases load on implants over time
Decreased rigidity
-stimulates indirect bone healing
-too much movement can impair healing and result in implant failure
What is important when you are taking rads?
1. Place object of known size as close to and at same height of targeted bone
2. Additional radiograph of opposite intact bone as a reference
Open fracture grading
1 = minimal soft tissue damage, "inside out"
2 = significant soft tissue damage penetration from outside
3 = severe soft tissue and vascular damage with bone loss and continued exposure
What if you can't tell if a fracture is open or not?
Look for air around the fracture on rads
Complete vs incomplete fracture
Complete = all the way through bone
Incomplete = not all the way through bone, also called greenstick/partial
Simple fracture configurations
-transverse
-oblique
-segmental
RECONSTRUCTABLE
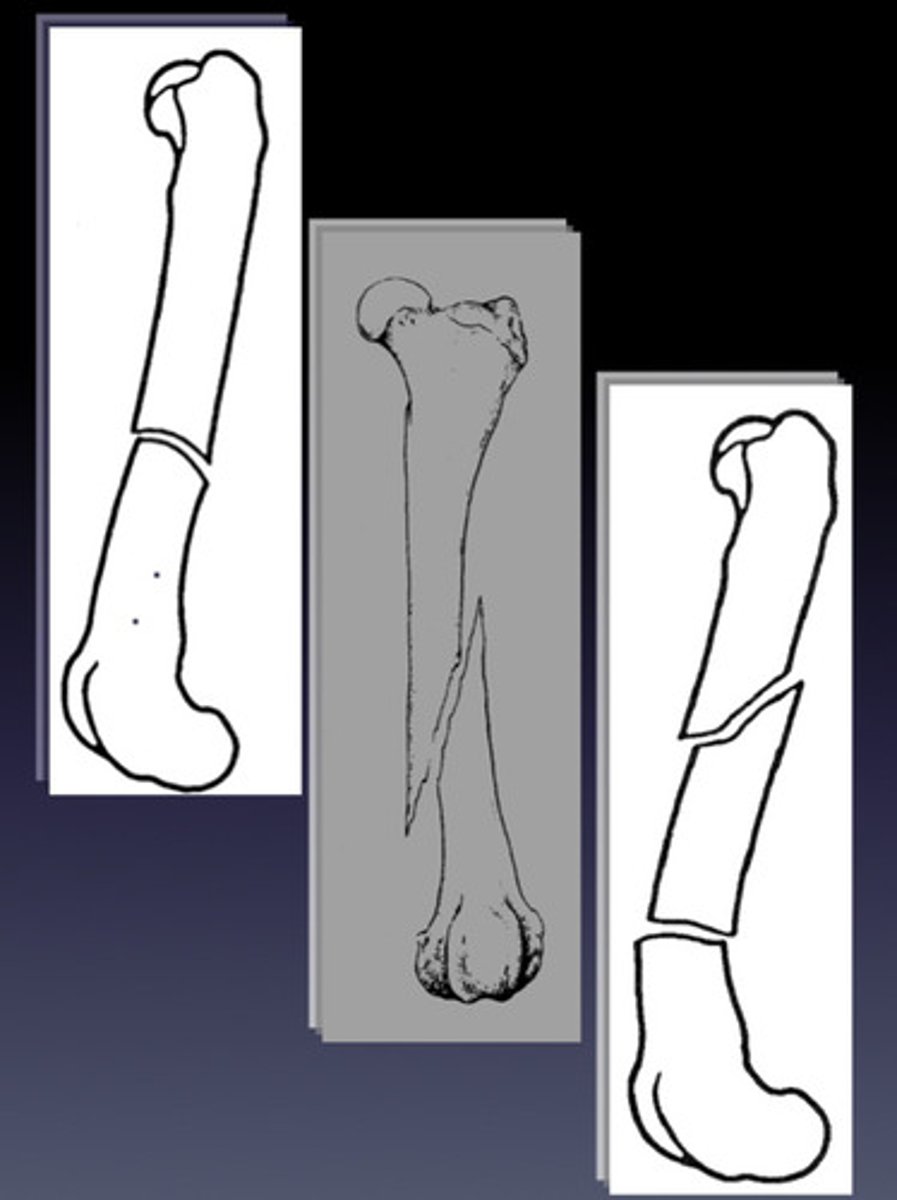
Comminuted fracture configurations
-multiple fracture lines!!
-majority are non-constructable and need biological bridging approach
-constructable forms are rare and need load-sharing approach
Fracture location
-which bone
-level (proximal, middle, distal)
-region (diaphysis/metaphysis, articular, physeal)
Fracture displacement
-Displacement of the DISTAL segment in relation to rest of body
-Can decide cranial/caudal with lateral view
-Can decide medial/lateral with AP view
Forces
1. Bending
2. Axial compression/shear
3. Torsion
4. Tension
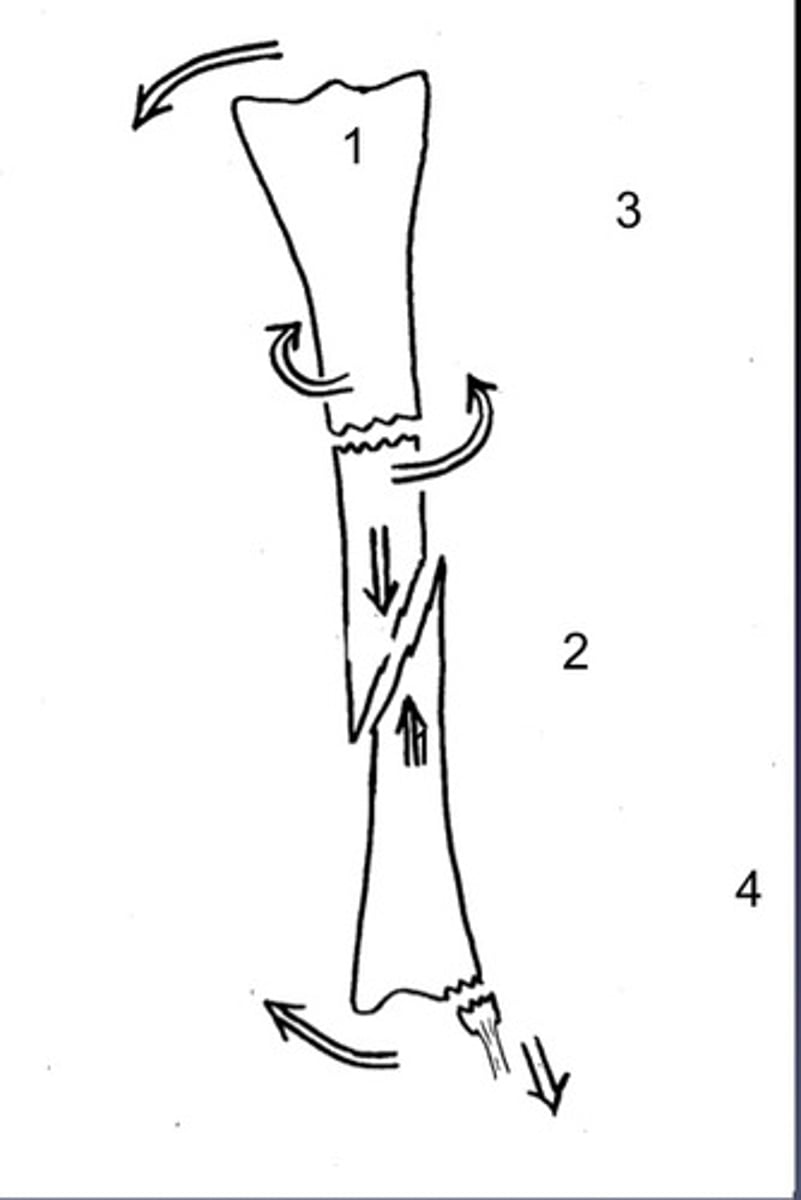
How to succinctly describe a fractured bone in under 10 phrases
1. Cause (traumatic or pathologic)
2. Soft tissue damaged (closed or open)
3. Fracture configuration (incomplete or complete, simple or comminuted, recon or non-recon)
4. Location (bone, level, region)
5. Forces
What does coaptation have good control over?
-Bending and rotation forces
-Useful on simple, transverse fractures
-Useful on fractures with internal support
What does coaptation not have good control over?
Axial compression forces (remember that dogs and cats are weight bearing!). Not suitable for unstable oblique or comminuted fractures.
What is important about joints when you are doing coaptation??
Must immobilize the joint above and below the fracture
What fracture reduction is required for coaptation?
>50% overlap of fractured ends on the worst two radiographic views
When should you use a cast instead of a splint?
Cast is good at resisting rotational forces
When should you use a splint instead of a cast?
-single vs multiple metacarpals and partial fractures
-step down from cast
-some soft tissue injuries
What are some morbidities of coaptation?
-no joint ROM
-muscle atrophy
-osteopenia
-pressure spores
-dermatitis
-maintenance and care
Why is ROM so important for joints?
o Articular cartilage gets nutrients from synovial fluid that comes from the ROM.
o Especially true for young dogs as they develop their articular cartilage
When should the digits NOT contact the ground from your bandage?
Injuries distal to carpus or tarsus = use casts and walking bars
What is important about coaptation in toy breeds?
AVOID in radius/ulna fractures because they have poor blood supply to these bones
What is ESF?
Pins that penetrate skin and bone cortices or pins that are locked to connecting bars via clamps
Advantages of ESF
• Affordable & reusable
• Closed or minimally invasive approach
• Improved access to wounds (open fractures)
• Can adjust stability for phase of healing
• Once fracture is healed, sedate and remove fixation
• Can combat all fracture forces!!
Disadvantages of ESF
• Pins can cause soft tissue irritation and are avenues for infection
• Not suitable for all bones or patients
• Eccentric position of connecting bar is weak
• Weekly post-op care is necessary
Indications for ESF
• Tibia-fibula & radius/ulna
• Open fractures
• Some mandibular fractures
• Most fracture configurations are suitable depending on location
• Exotics (birds)
• Angular limb deformity corrections & limb lengthening
ESF is NOT great for
• Articular fractures
• Pelvic fractures
• Upper limb
• Non-compliant owners
• Fractious patients
ESF components
• Fixation pins
• Connecting clamps
• Connecting bars
Types of frame configurations
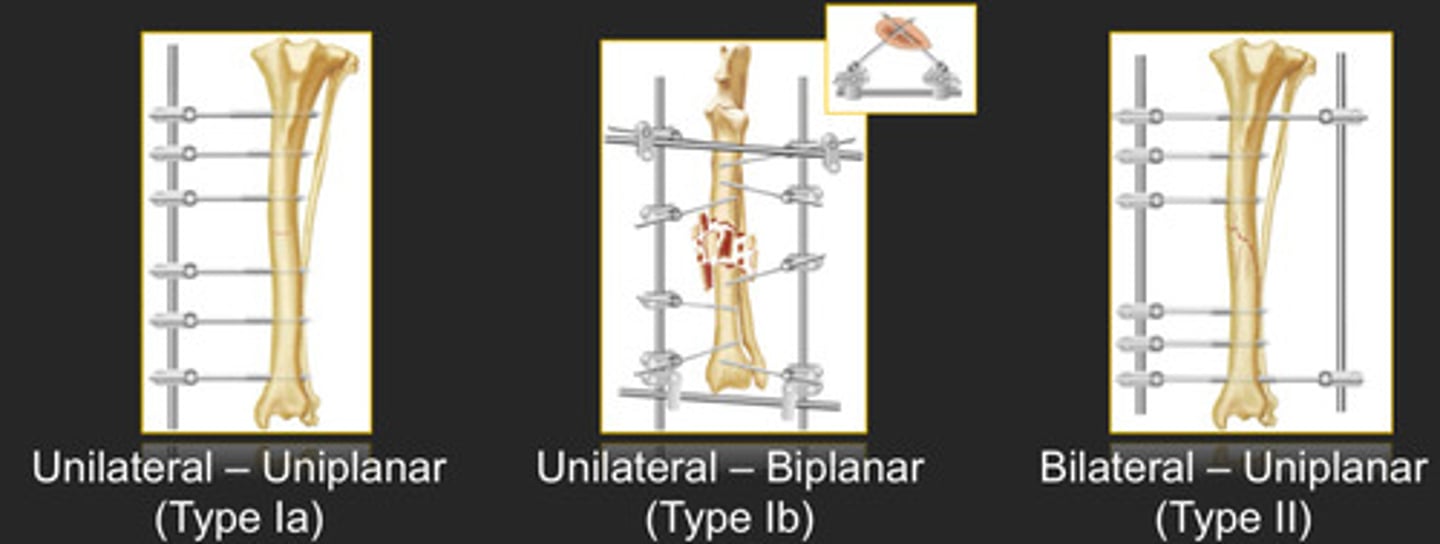
Level of strength from highest to lowest for frame configurations
Level of strength = type III > II > Ib > Ia >> Ia double-clamp
Advantages of IM pin/cerclage wire
Affordable and simple
Disadvantages of IM pin/cerclage wire
-limited fracture scenarios
-requires rapid healing
-provides limited stability
-prone to complications
What forces do IM pins do a good job of resisting? What forces do they do a bad job of resisting
Good = bending
Bad = compression/shear, rotation, tension
What can you add to IM pin to resist compression forces?
Add interlocking nail, ESF, bone place, cerclage wire
What does IM pin and wire combo induce?
Inter-fragmentary compression!
Can you use wire alone?
NO
Should the wire be tight or loose?
Tight because it won't impede blood supply that way
What fractures can you use IM pin plus wire on?
Long oblique, large oblique butterfly, long spiral
DO NOT USE ON COMMINUTION
What is different about an interlocking nail?
Helps to resist bending, rotation, and axial compression forces
IM pin and cerclage wire RULES
-perfect anatomic reconstruction
-properly spaced wires
-2 or more wires
-no loose wires
-do NOT entrap soft tissues
-IM pin 60-70% canal diameter
Advantages of plate/screw fixation
-can combat all fracture forces
-suitable for reconstruction and bridging
-early return to limb use
-low maintenance post op
Disadvantages of plate/screw fixation
-expensive
-extensive inventory
-technically challenging
Compression plating techniqure
-ideal load sharing
-reconstructable
-tightening of screw slides plate across bone and compresses fracture
Neutralization plating technique
-partial load sharing
-reconstructable
-plate holds everything in place
-axial load shared by implants and bony column
Bridge plating technique
-plate spans gap to prevent fracture collapse
-all weight bearing forces are transmitted through plate/screws
-can place pin to prevent bending forces and extend life of pin
Conventional bone plates
No rigid link between plate and screws = may loosen over time and backs out of bone. Squeezes bone to plate
Locking bone plates
-rigid link between locking screw and plate
-fixed screw angle
-bone plate is internal fixator
Lag screw
• Typically use for joint related fractures
• Drill near cortex the thread diameter and the far cortex the core diameter
Delayed union
Fracture that takes longer to heal than anticipated
Non-union
Fracture that failed to heal and will not heal without intervention
Age in MONTHS =
Time to clinical bone healing in WEEKS
Malunion
Fracture that healed in non-anatomic position
Varus
Inward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint, as in bowlegs
Valgus
Outward angulation of the distal segment of a bone or joint, as in knock-knees
Procurvatum
cranial bowing of a bone
Recurvatum
Caudal bowing of a bone
Pronation
Internal rotation
Supination
External rotation
Tolerations of malunion types
-re/pro-curvatum is well tolerated
-varus better than valgus
-torsional is the least tolerated
-shorter hind limb better than fore limb