maxillary lateral incisor
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
how many lateral incisors are there? which tooth is it from the midline?
two in the maxillary arch and two in the mandibular arch. it is the second tooth from the midline
what is the functions of the lateral incisor?
its functions in mastication are:
biting
cutting
incising
shearing
play an important role in
aesthetics
phonetics
what is the general form of the lateral incisor?
supplements the central incisor in function
resembles the central incisor in all aspects but on a smaller scale
the lateral incisor is smaller in all aspects but what? how else does it differ?
it is smaller in all measurements but root length, which is roughly the same
its relative crown dimensions, hence its shape, differ slightly from the central incisor. it is relatively longer inciso-cervically and narrower mesiodistally. it is also generally more of a round tooth than the central incisor
the upper lateral incisor displays what?
greater variation in form than any other permanent tooth, except for the third molars
when is the first appearance of the dental organ of upper lateral incisors?
5 m.i.u (months in utero)
when is the first evidence of calcification?
1 year
when is the enamel completed in upper lateral incisors?
4-5 years
when do upper permanent lateral incisors erupt?
8-9 years
when is the root completed?
11 years
how is the upper lateral incisor named in the different systems?
palmar system
2」∟2
universal system
#7, #10
FDI
12, 22
relation of lateral incisors
they make contact mesially with the distal surface of the maxillary permanent central incisors
they make contact distally temporarily with the mesial surface of the maxillary deciduous canine until it’s shedding at 12 years, then erupts the maxillary permanent canine
what are the surfaces and aspects of the lateral incisors? how many roots does it contain?
its surfaces are:
labial
lingual
mesial
distal
it contains one root
it has an incisal aspect
what is the geometrical outline of the crown at the labial aspect?
it is a trapezoid, long side is incisally and short side is cervically
the mesial outline at the labial aspect is what?
it is slightly convex at the crest of the junction of the incisal and middle thirds
which outline is more convex at the labial aspect? the incisal outline is more curved than what? the cervical line is convex in what direction?
the distal line is more convex
the incisal outline is more curved than the central incisor’s
the cervical line is convex root-wards
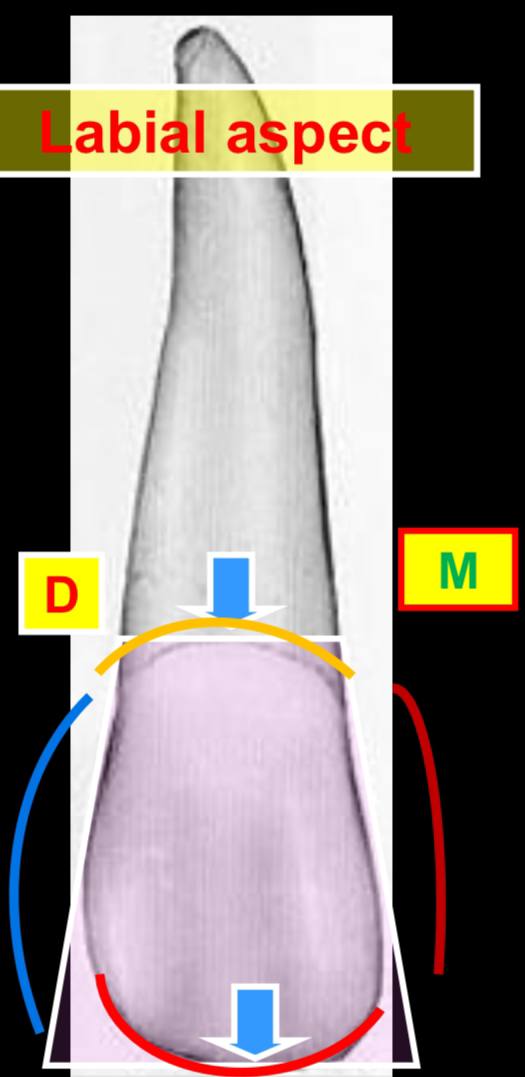

which incisal angle is more rounded?
mesio-incisal angle is rounded, but the disto-incisal angle is more rounded
is the surface of the lateral incisor more convex or concave than the central incisor?
it is more convex than the central incisor
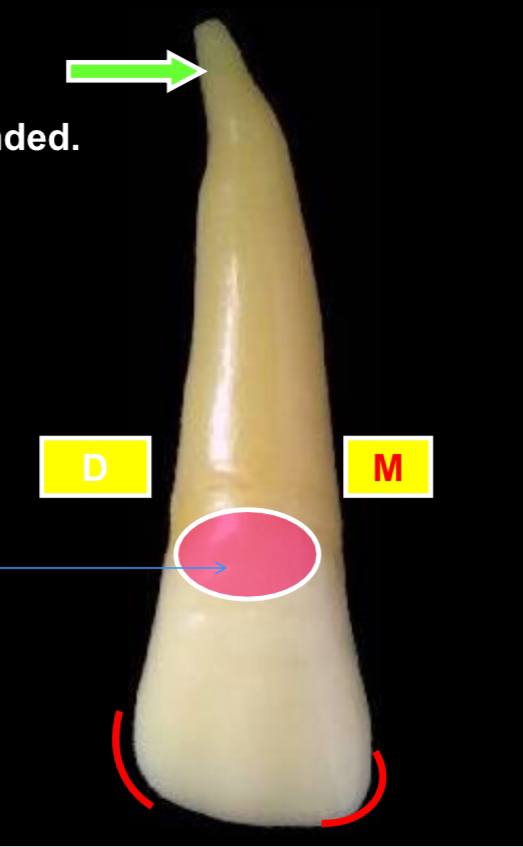
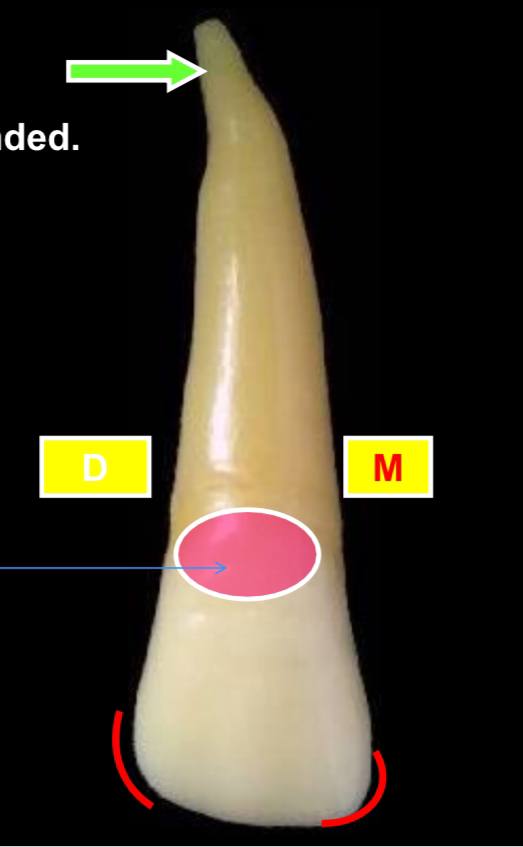
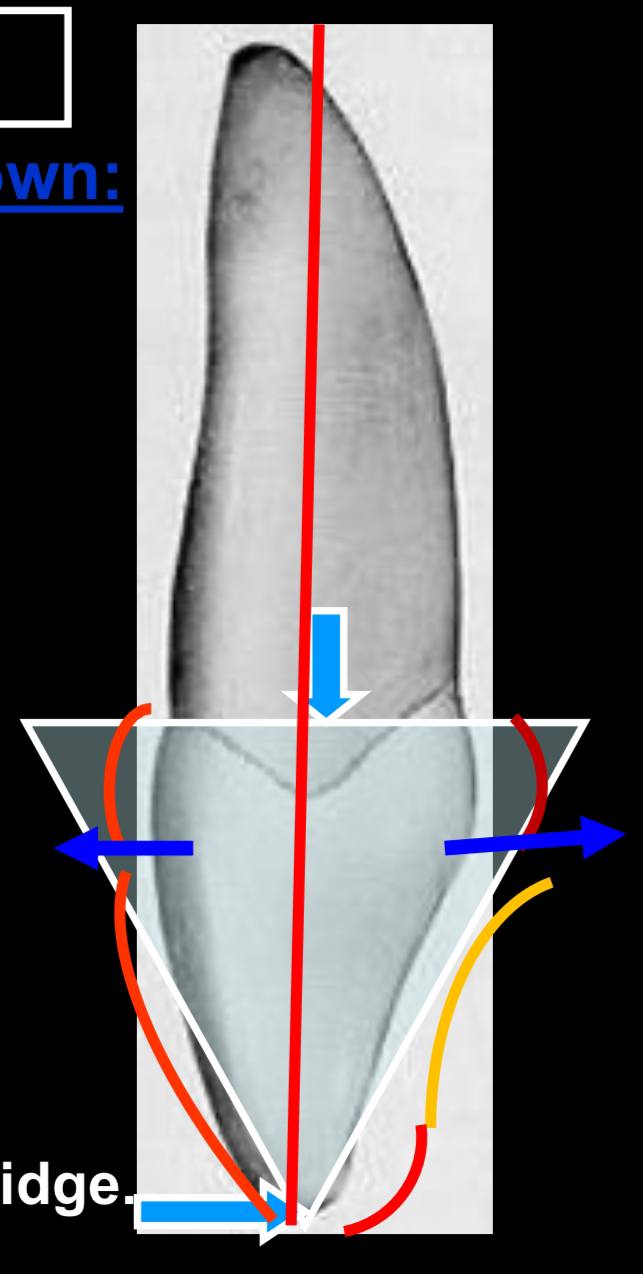
the red circle is what?
the cervical ridge, which is located the cervical 1/3
how many roots does the lateral incisor contain? what are its characteristics at the labial aspect?
one root, which tapers evenly to the apical 1/3. it then curves distally with a pointed apex
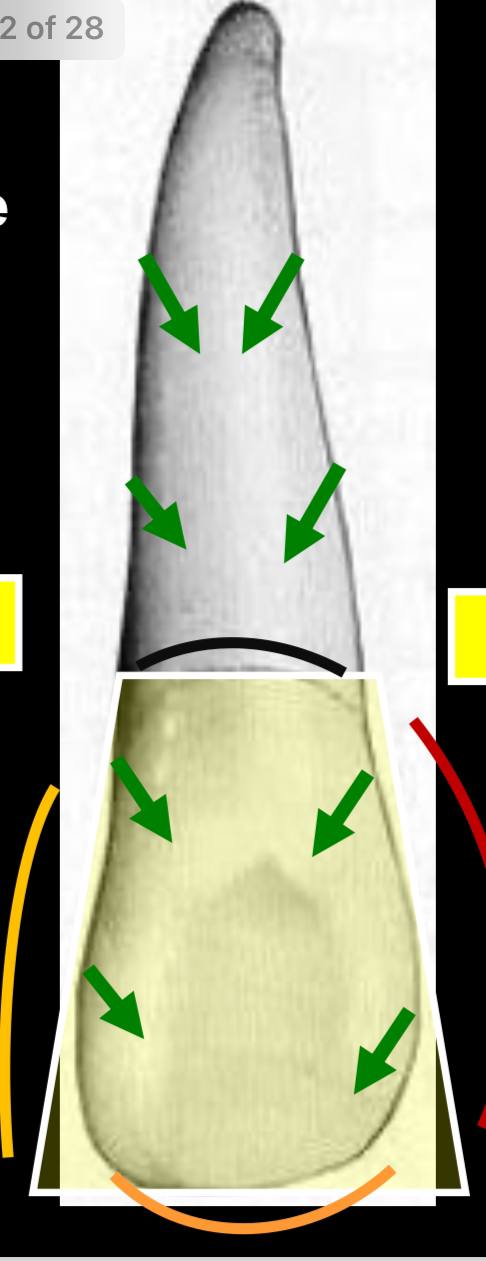
palatal / lingual aspect of maxillary upper lateral incisor
contains the same geometrical outline and outline as the labial surface
why do the mesial and distal sides of the crown and root converge lingually?
due to lingual convergence, which is to accommodate the horseshoe shaped alveolar process, making it narrower and smaller than the labial surface
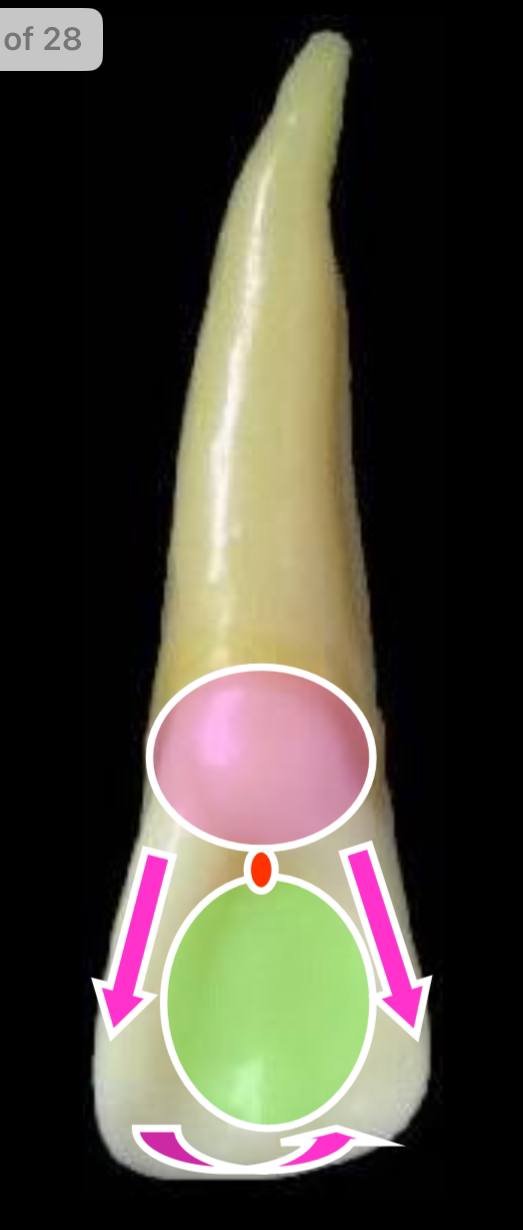

the pink circle is what elevation?
the cingulum (present at cervical 1/3)
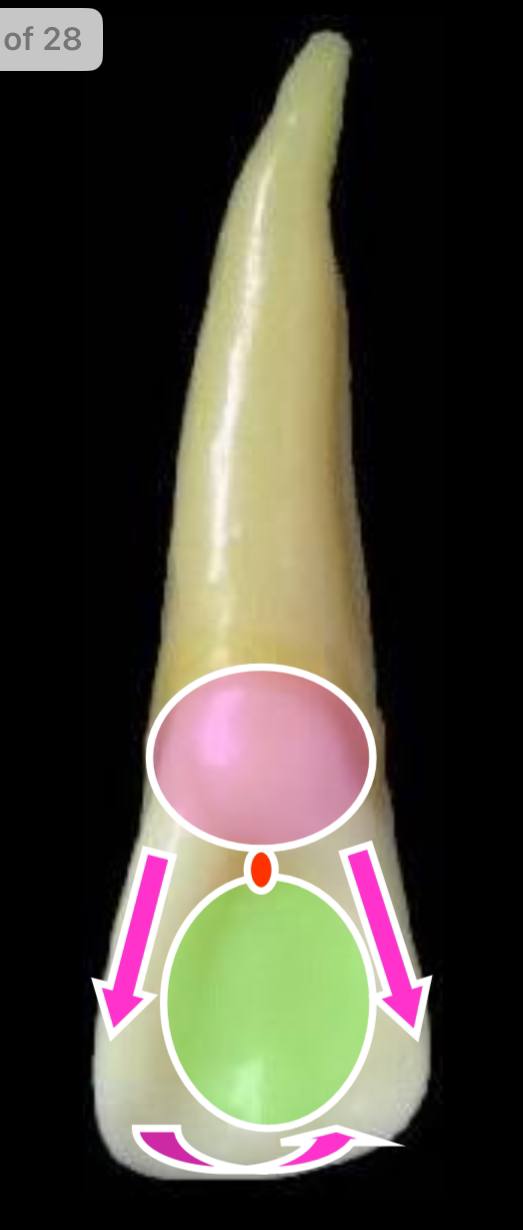

the pink arrows parallel to each other are what elevations?
the mesial and distal marginal ridges
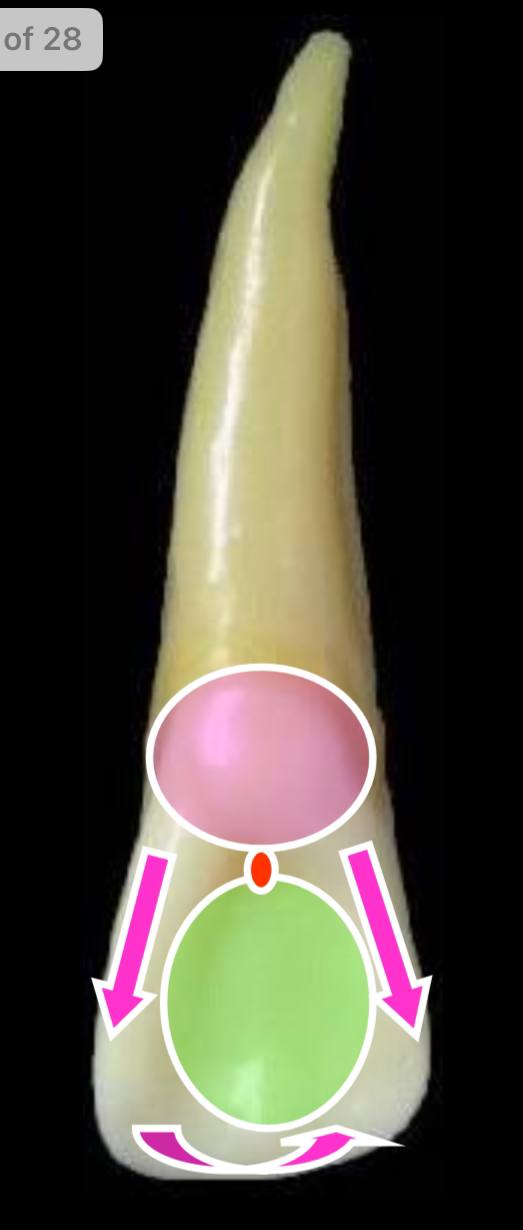

the rounded arrow is what elevation?
the incisal ridge
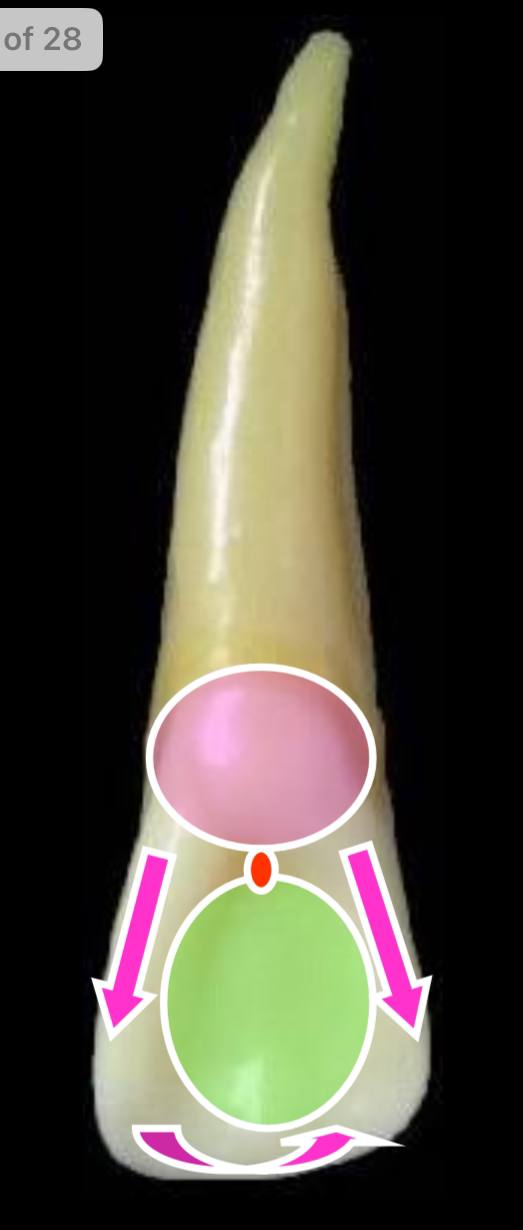

the green circle is what depression?
the lingual fossa, which lies between all the previous elevations. lingual pit is present between it and the cingulum
all elevations and depressions are more developed in what tooth?
it is more developed in the lateral incisor than the central incisor
geometrical outline of the crown at the mesial aspect
triangular in shape. base cervically and the apex incisally
incisal ridge is on the line that bisects the center of the root
labial outline of mesial aspect of lateral incisor
convex at cervical 1/3 (cervical ridge), which then becomes slightly convex to the incisal ridge
lingual outline of mesial aspect of lateral incisor
convex at cingulum (cervical 1/3), then it becomes concave at the lingual fossa, then slightly convex at the incisal ridge
the mesial cervicale line is convex where?
it is convex incisally
what is the labiolingual measurement of the lateral incisor?
about 6.0-6.5 mm, which is about 1mm less than the central incisor (6.5-7.0 mm)
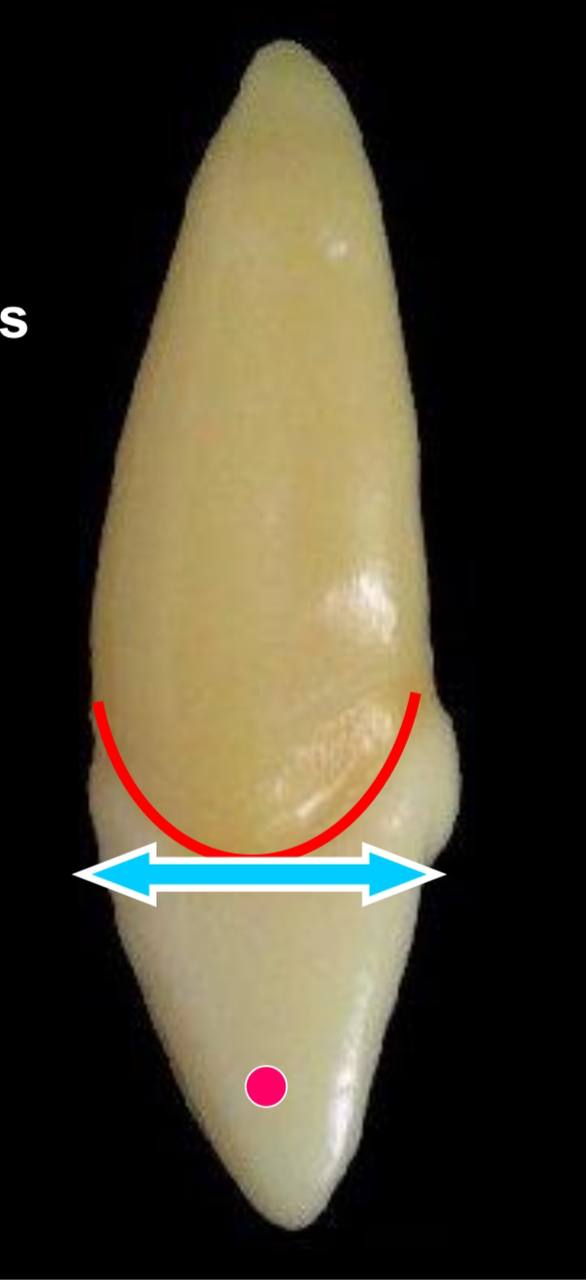
the red dot represents what?
the mesial surface is convex with the maximum convexity at the junction of the incisal and middle 1/3 (the contact area)
characteristics of root in mesial aspect
root appears longer than central incisor
it is cone shaped with blunt apex
distal aspect of lateral incisor
similar to the mesial aspect but differ in:
the cervical line curvature is less than the mesials by 1mm (mesial: 2.5 mm, distal: 1.5 mm)
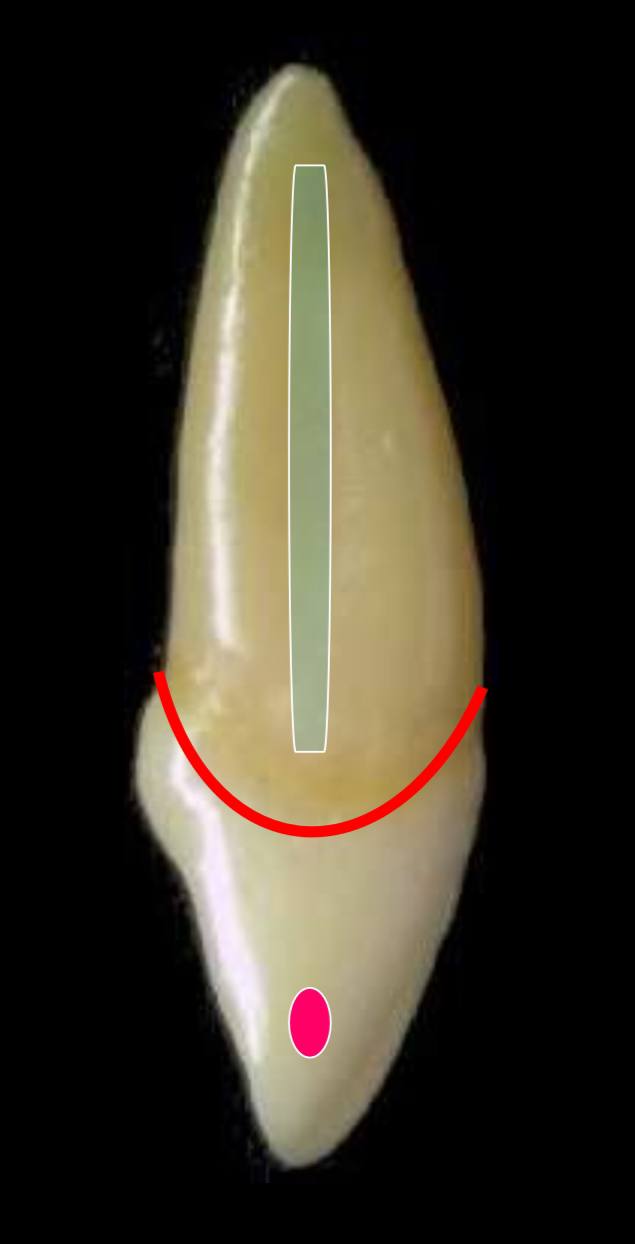
the red dot represents what? what is highlighted in blue?
contact area is the red dot, which is located at the middle 1/3 (more cervically)
highlight in blue is the distal developmental groove on the root
incisal aspect of lateral incisor
may resemble the central incisor or small canine
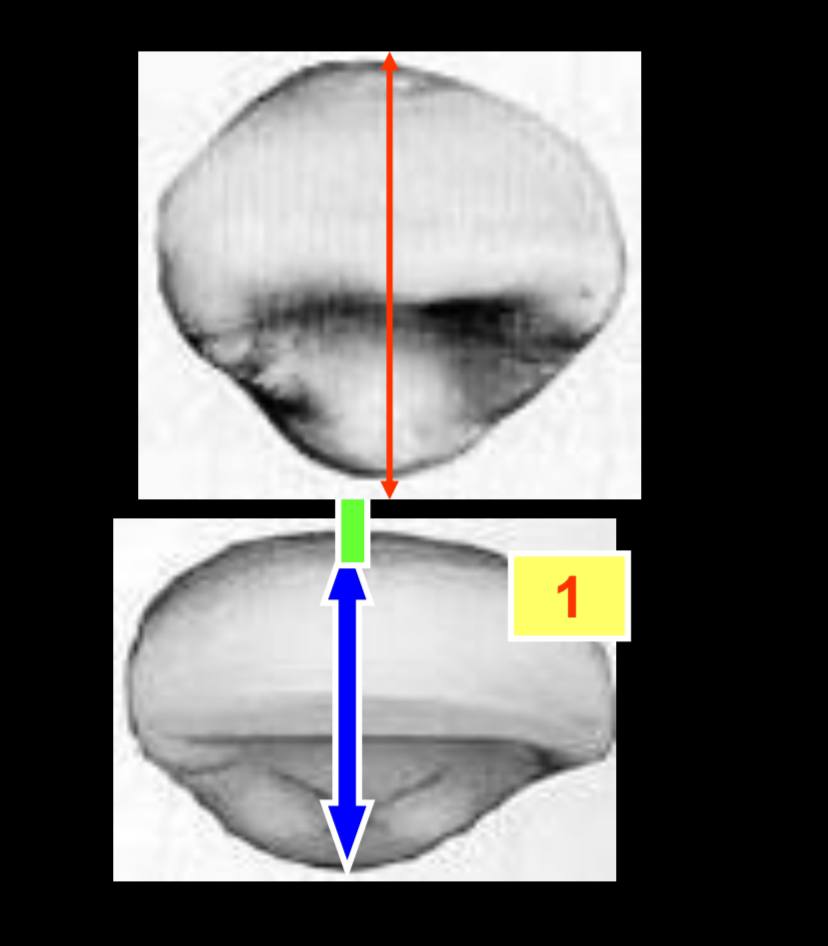
what dimension is greater?
labiolingual dimension is greater in comparison to the central incisor
cingulum is large and large incisal ridge is present
the incisal surface of the lateral incisor generally resembles the central incisor except for what? how else does it differ?
except for the cingulum, which is more prominent than the central incisor
it also exhibits more convexity labially and lingually than the central incisor and its outline may approach the rhomboidal appearance of the canine
what shape should the maxillary lateral incisor be for root canals?
a triangle, with base at incisal edge and the apex at cervical line
what is the average, minimum, maximum and range length of the tooth?
average: 32
maximum: 25.1
minimum: 20.5
range: 4.6
what is the percentage for one canal vs. two canals?
one canal: 93.4%
two canals 6.6%
meaning type 1 is most common
what is percentage for lateral canals?
10%
root curvature percentages?
straight: 30%
distal curved: 53%
mesial curved: 3%
labial curved: 4%
bayonet and gradual curve: 6%
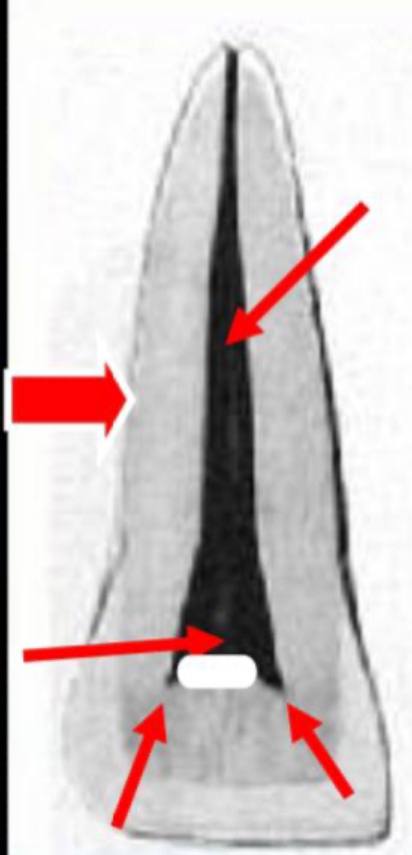
mesio-distal section of pulp cavity
pulp chamber is wide and conforms to the shape of the crown
it does not have 3 sharp pulp horns, it contains 2, which correspond to the developmental mammelons
the root canal tapers towards the apex
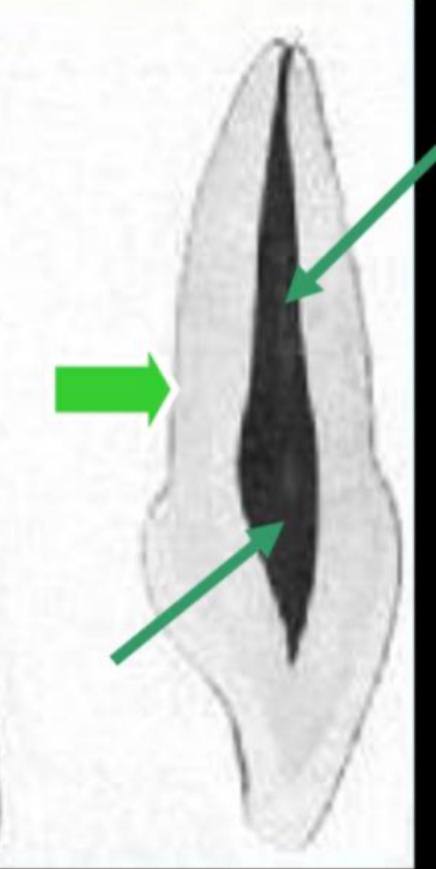
labiolingual section of pulp cavity
pulp chamber is pointed incisally, which then follows the increase in the crown dimension cervically
the root canal tapers gradually as it traverses the root ending in a constriction at the apex (apical foramen)
what is the shape of the tooth cross-sectioned?
cervical level: canal is ovoid labiopalatally
middle third level: canal is ovoid
apical third level: apical is generally round in shape
what are some malformations of the upper permanent lateral incisor?
peg-shaped lateral incisor
missing lateral incisor