Unit 6 Urbanization
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Urbanization
the movement of people from rural areas to cities.
Urban Area
relating to a city and its surrounding suburbs.
City
relatively large, densely populated settlement with a large population.
Rural
area located outside of towns and cities, sparsely populated.
Site
the actual place where the settlement is located.
Situation
describes where the settlement is in relation to other settlements and features of the surrounding area.
Rural-to-Urban Migration
movement of people (typically farmers) from rural settlements to urban center in search of jobs.
Redevelopment
set of activities intended to revitalize an area that has fallen on hard times.
Megacities
cities with 10 million inhabitants or more; Cairo, Mumbai, Beijing, Dhaka, Osaka-Kobe-Kyoto.
Metacities
cities with 20 million inhabitants or more; Tokyo, Delhi, Shanghai, Sao Paulo, Mexico City.
Suburbanization
the process of population movement from within cities to the suburbs.
Urban Sprawl
the uncontrolled expansion of urban areas.
Edge Cities
a concentration of business, shopping and entertainment that developed in the suburbs, outside of a city's traditional downtown or central business district.
Exurb
a semi-rural district located beyond the suburbs that is often inhabited by 'well-to-do' families; Often found near farmland, beaches or mountains; More spread out and less walkable.
Boomburb
residential and economic area that is not the largest in their economic area, but has a large population (+100K), and tends to be spread along highways.
Decentralize
in an urban context, to move business operations from core city areas into outlying areas such as suburbs.
World City
a city that has influence, not only over their country, but across the globe; London, NY, Paris, Singapore, Tokyo, Hong Kong, Los Angeles, Sydney, etc.
Global Power City Index (GPCI)
evaluates cities according to their power to attract people, capital, and businesses from around the world.
Stock Exchanges
Financial markets where stocks are bought and sold.
Bond Markets
Markets where participants can issue new debt or buy and sell debt securities.
Foreign Currency Markets
Markets where currencies are traded.
World Health Organization (WHO)
An agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health, located in Geneva, Switzerland.
UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
A specialized agency of the United Nations aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, the sciences, and culture, located in Paris, France.
Urban System
A set of interdependent cities or urban places connected by networks.
Rank-Size Rule
The population of a settlement is inversely proportional to its rank in the urban hierarchy.
Primate City Rule
A city that is much larger (at least double the size) than any other city in the country, dominating the country's economic, political, and cultural life.
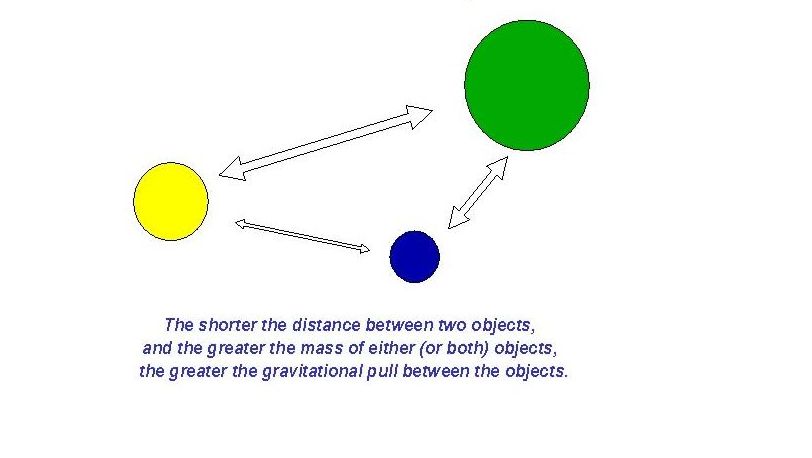
Gravity Model
A model that looks at distance and size of cities to study the interaction of towns and cities.
Central Place Theory
A theory developed by Walter Christaller that attempts to understand why cities are located where they are, based on threshold and range.
Threshold
The smallest number of consumers needed to make a business profitable.
Range
The maximum distance a consumer will travel for a good or service.
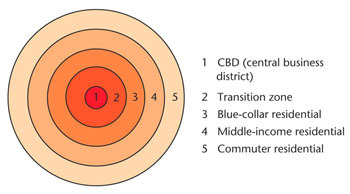
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
A model of a city's internal organization organized in five concentric rings that model the arrangement of different residential zones outward from a central business district.
Hoyt Sector Model
A model of a city's internal organization that focuses on transportation and communication as the drivers of the city's layout.

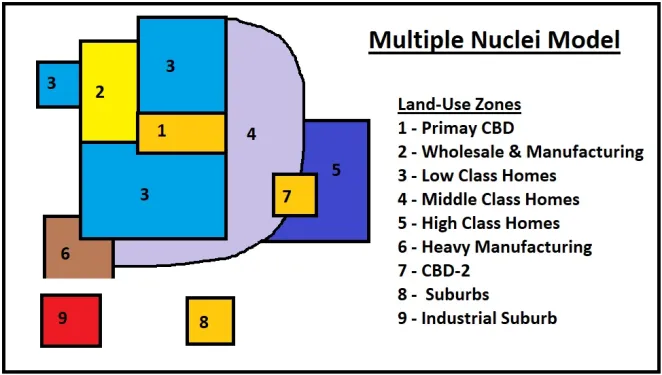
Harris and Ullman Multiple-Nuclei Model
A model that observes most large U.S. cities don't grow in rings or sectors but are formed by integration of multiple focal points, or nodes.
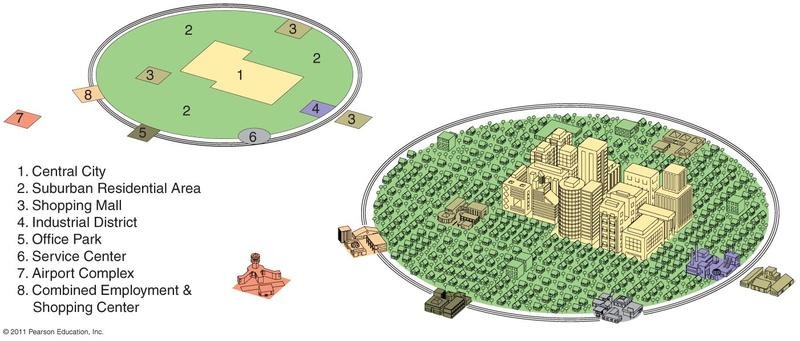
Galactic City Model
Describes a place where economic activity moves away from the central business district toward the urban fringe or suburbs.
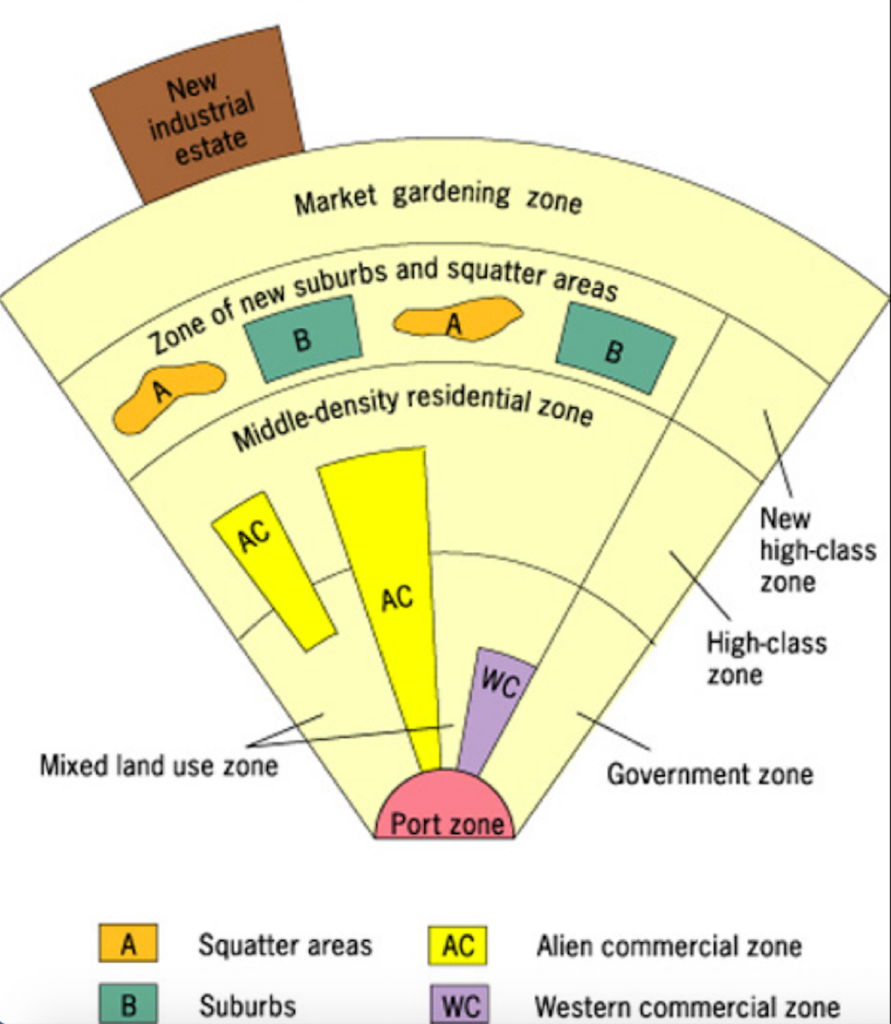
Latin American City Model
A model structure derived from Spanish urban planning laws that focused on a central plaza and included outer zones of squatter settlements.
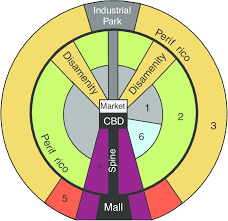
Southeast Asia Urban Model
A model that lacks a clearly defined central business district and only retains two constant zones: the port zone and the zone of intensive market gardening.
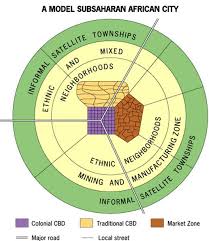
African City Model
Many African cities have three CBDs.
Core Countries
Countries with powerful economies that have the best infrastructure.
Peripheral Countries
Countries that don't have money to build high levels of infrastructure.
Semi-Peripheral Countries
Countries that have some economic development but still lack high levels of infrastructure.
Residential Land Use
Zoning can impact residential density by changing the type of allowed development.
Urban Sprawl
Urban areas expand in an unplanned and uncontrolled way, covering large expanses of land in housing, commercial development, and roads.
Greenbelts
A ring of parkland, agricultural land, or other types of open space maintained around an urban area to limit sprawl.
New Urbanism
Promotes designing growth to limit urban sprawl and preserve nature and usable farmland.
Walkability
Refers to how safe, convenient, and efficient it is to walk in an urban environment.
Redlining
When a lending institution refuses to offer loans based on a neighborhood's racial or ethnic makeup, deemed too risky.
Blockbusting
Promoted fear of minorities and the belief that houses in diverse neighborhoods were not as valuable, leading to white flight.
Environmental Injustice
Describes how communities of color and the poor are more likely to be exposed to environmental burdens such as air pollution or contaminated water.
Urban Renewal
A nationwide movement where cities were given massive federal grants to tear down and clear out crumbling neighborhoods and former industrial zones.
Gentrification
Process whereby the character of a poor urban area is changed by wealthier people moving in, improving housing, and attracting new businesses.
Suburban Sprawl
Building low-density residential housing on lands previously protected or used for farming, ignoring the environmental cost.
Economic Segregation
Occurs when individuals with lower incomes are forced to move farther from their workplaces, adding higher transportation costs to housing costs.
Urban Sustainability
Means addressing ecological challenges in innovative and lasting ways.