EXSC187 | Growth, Motor Development & Aging | Module 1
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Only Module 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
accretion
increase in amount of cells
maturation
process of progressing to a mature state
hyperplasia
increase in the number of cells
development
refinement of behaviour
hypertrophy
increase in the size of cells
maturity
reaching a mature state
Proximodistal
Trunk grows first, then to the rest of the body
Cephalocaudal
Head grows first, then rest of body
zygote
the fertilized egg that develops into an embryo
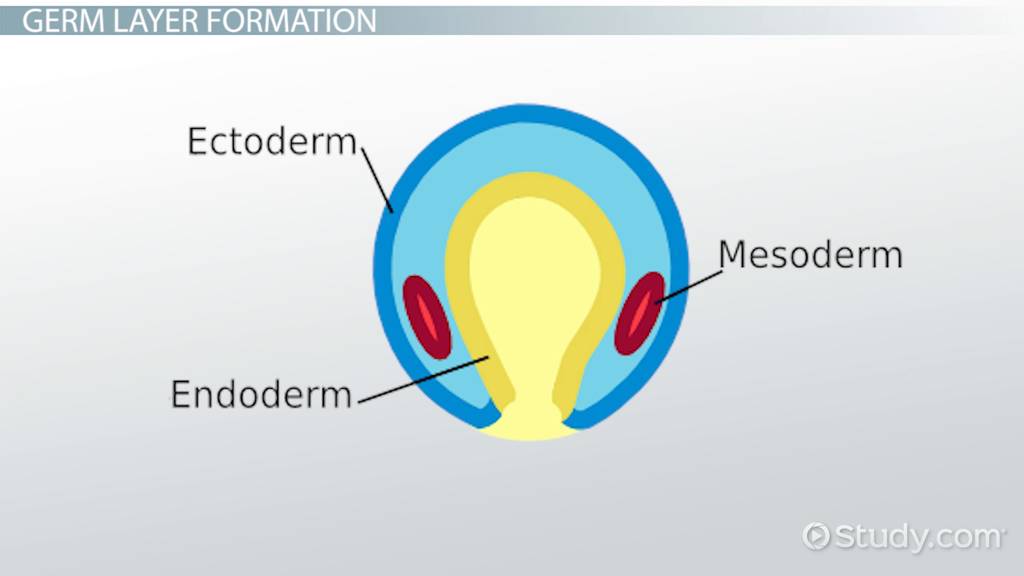
Endoderm Layer
Digestive systems
Liver
Pancreas
Lungs (Inner Layers)
Respiratory track lining
Mesoderm Layer
Circulatory Systems
Lungs (epithealial layer)
Skeletal Systems
Muscular Systems
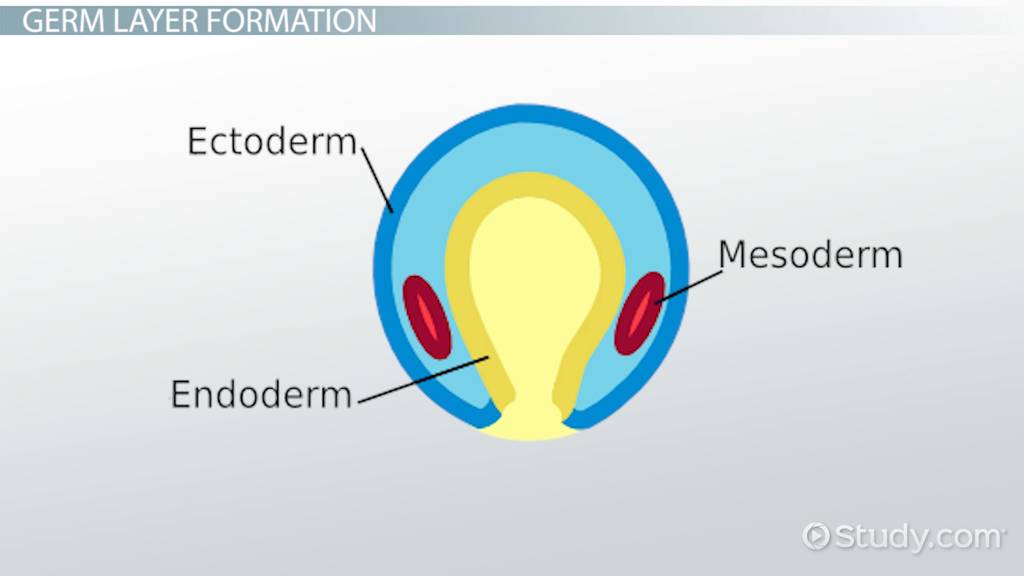
Ectoderm Layer
Hair
Nails
Skin
Nervous System
gonald
Refers to the primary reproductive organs, which are the testes in males and the ovaries in females
Pre-natal
1st 10 months
Infancy
Perinatal - around birth
neonatal - 1st month
Postnatal - 2-12 months
Neurulation
Neural plate becoming a neural tube
Notochord
Exists in neurulation, however later becomes the spinal chord
sex of the child determined
From the Y Chromosome, there is a sex-determining gene (SRY for short), which differentiates the gonads into testes
If at week 13, the SRY Gene is missing, the gonads become ovaries
Low birth weight
<1,500g
Teratogens
drug/chemical agent causes abnormal prenatal development upon exposure
Main teratogens
smoking
alcohol
enviroment (e.g. polluted air)
Medication
Sickness whilst carrying child
relaxin
hormone produced in the placenta
loosens up joints to prepare for childbirth
Gestational diabetes (GDM)
Condition that occurs when a pregnant woman's body doesn't produce enough insulin
Preeclampsia (PA)
Pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine
hypertension
Also known as high blood pressure
condition where the force of blood against your artery walls is consistently too high
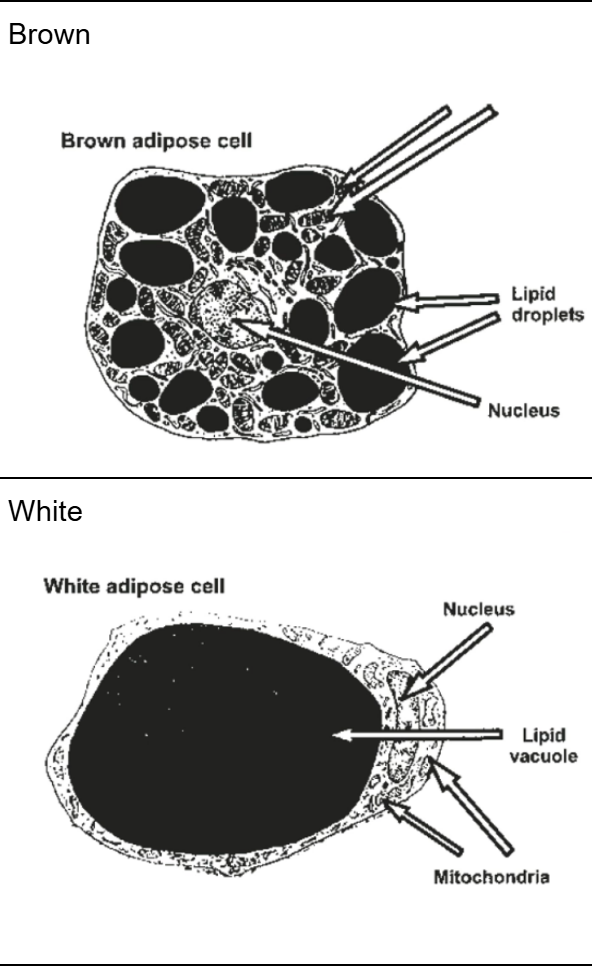
adipose tissue
white
brown