Human geography alevels
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
How is TNCs a factor of globalisation
they appeal to local consumers through glocalisation - products especially designed for specific taste of consumers. Maharaja burgers in mcdonalds India. They take advantage of economic liberalisation by offshoring and outsourcing
What is globalisation?
The interdependence of countries through the flow of capital goods, trade and services as well as culture and ideas
How is transport and communication a factor of globalisation?
Fibre optic cables, internet and social media connect people around the world and spread global culture and ideas, especially from the west. Budget airlines create cheaper travel increasing tourism and creating time-space compression
How is technology a factor of globalisation?
Machinery have made the production of goods cheaper and efficient but has replaced human labour creating job losses.
What is economic globalisation?
The volume and spread of Trans National Corporations
How is international organisations a factor of globalisation?
Provide aid to foreign countries in need creating a global community. Though vested interests are involved.
How has markets a factor of globalisation
Globalisation have made people richer due to global markets and consumers. This has led to stock growth e.g. in london and shanghai
How has free tading blocs impacted globalisation
Countries remove trade barriers and tariffs to make trade cheaper and efficient. This creates strong political ties boosts economic growth, allowing TNCs to create a larger market. E.g EU and NAFTA
How has free market liberalisation helped
Improved economic wealth encourages business start ups
What is social globalisation?
International migration,improvements in global education and healthcare social interconnectivity via phone and emails

What is cultural globalisation?
Initially westernisation-American influence on other parts of the world. Now taking a multidirectional turn Bollywood over Hollywood.

What is political globalisation?
Institutions like UN, IMF and trading blocs like the EU. The EU reduces tariffs to promote free trade and has reduced other protectionist measures

How has globalisation advanced in the 19th century Britain?
Steam engines reduced travel times and allowed the transport of goods to move efficiently through Asia and Africa.
What has helped reduced lower costs of transports and why?
Containerisation- more goods could be loaded in a ship in a shorter amount of time
How has globalisation advance in the 21st century?
miles of fibre optic cables now connect continents allowing people to connect all over the world to communicate through the World Wide Web.
Tariff
A tax imposed on imported goods
Quota
A limit on the amount of goods that can be imported
Neo liberalisam
The political pholisophy of free trade, free markets, privatisation and increasing the role of businesses in society while decreasing the influence of government. Trade is easier and so more of it and poverty is reduced
Subsidy
Financial assistance given by the government to firms to increase competition or prevent collapse.
Free-market economy
A market economy dependent on supply and demand with little or no government
Free trade
A policy where the government doesn’t interfere with the imports or exports by applying tariffs, subsidies or quotas.
Protectionism
Policies that protect businesses, customers and workers by restricting trade with foreign nations
Privatisation
Transferring public ownership to private ownership for profit
Time space compression
As globalisation expands, time decreases as well as space because of faster transport and communication
Increased connectivity changes perception of distance, places feel closer than they did in the past
World Bank
Formed in 1944
HQ in Washington DC, USA
Gives advice, loans, grants to reduce poverty and increase economic development ,met and sustainable development
Main role - long term assistance instead of crisis support
IBRD now apart of organisation, tackling world poverty
WTO - free trade
Formed in 1995
HQ in Geneva Switzerland
Promote free trade on a global scale
Countries seek reduction of tariffs and trade barriers and the elimination of preference on a mutually advantageous basis
Evaluation of World Bank
Decision making powers lie heavily with most developed nations with most influence coming from USA.
Some World Bank funded projects caused significant environment impacts e.g. loss of carbon sinks through deforestation
Evaluation of WTO
Failed to stop the world’s richest countries such as USA and UK from subsidising own food producers. This protectionism is harmful to farmers in developing countries who want to trade on a level playing field
IMF - free trade
Found in 1944
HQ in Washington DC USA
Loans given by rich countries to countries that ply for help. In return they must run a free trade market economy so that TNCs can run there
Stabilise currency after WW2 by lending out loans to countries to prevent communism
Who are the Bretton woods institution
IMF! WORLD! WTO established after WW2 by leading and victories nations.
Set up a meeting of 43 countries in Bretton woods , New Hampshire , USA
FDI
A controlling ownership in a business enterprise in one country by a company or organisation based in another country
Offshoring - types of FDI
TNC build their own new production facilities in offshore low wage economies leg. Mexican plant for US guitars
Foreign mergers - type of FDI
Two firms in different countries join forces to create a single entity. Royal Dutch shell has HQ in UK and Netherlands
Foreign Acquisitions - type of FDI
TNC launches a takeover of a company in another country. Uk Cadbury was subjected to a hostile takeover by us food giant Kraft. Uk has few restriction on foreign takeovers. USA closely scrutinises inbound foreign takeovers
Transfer Pricing - type of FDI
TNCs channeling profits through a subsidiary company in a low tax country e,g Starbucks with Ireland
Trade blocs
Voluntary international organisation that exist for trading purpose, cringing greater economic strength and security to the nations that join
Comparative advantages in trade blocs
Countries specialise in a good or service so its of higher quality and production is more efficient
Countries don’t impose barriers to trading for these commodities which works well economically.
How can national governments affect globalisation through censorship policies
Restricts flow of information and knowledge through state controlled media outlets and internet restrictions.
Can be used to limit population knowledge of foreign culture and ideas like democracy which could undermine a dictatorship government.
How can national governments affect globalisation through limiting migration policies
Border control and migration monitoring
Rise of right wing, extremist views more countries have adopted strict migration controls.
How do national governments affect globalisation through trade protectionism policies
Trade protectionism involves subsidies , tariffs and quotas which help to a country to protect domestic industries e.g. cheap steel in china caused uk steel industries to close because Chinese government subsidies.
Advantages of trade blocs
Firms have larger potential market to sell to and so larger potential revenue to make.
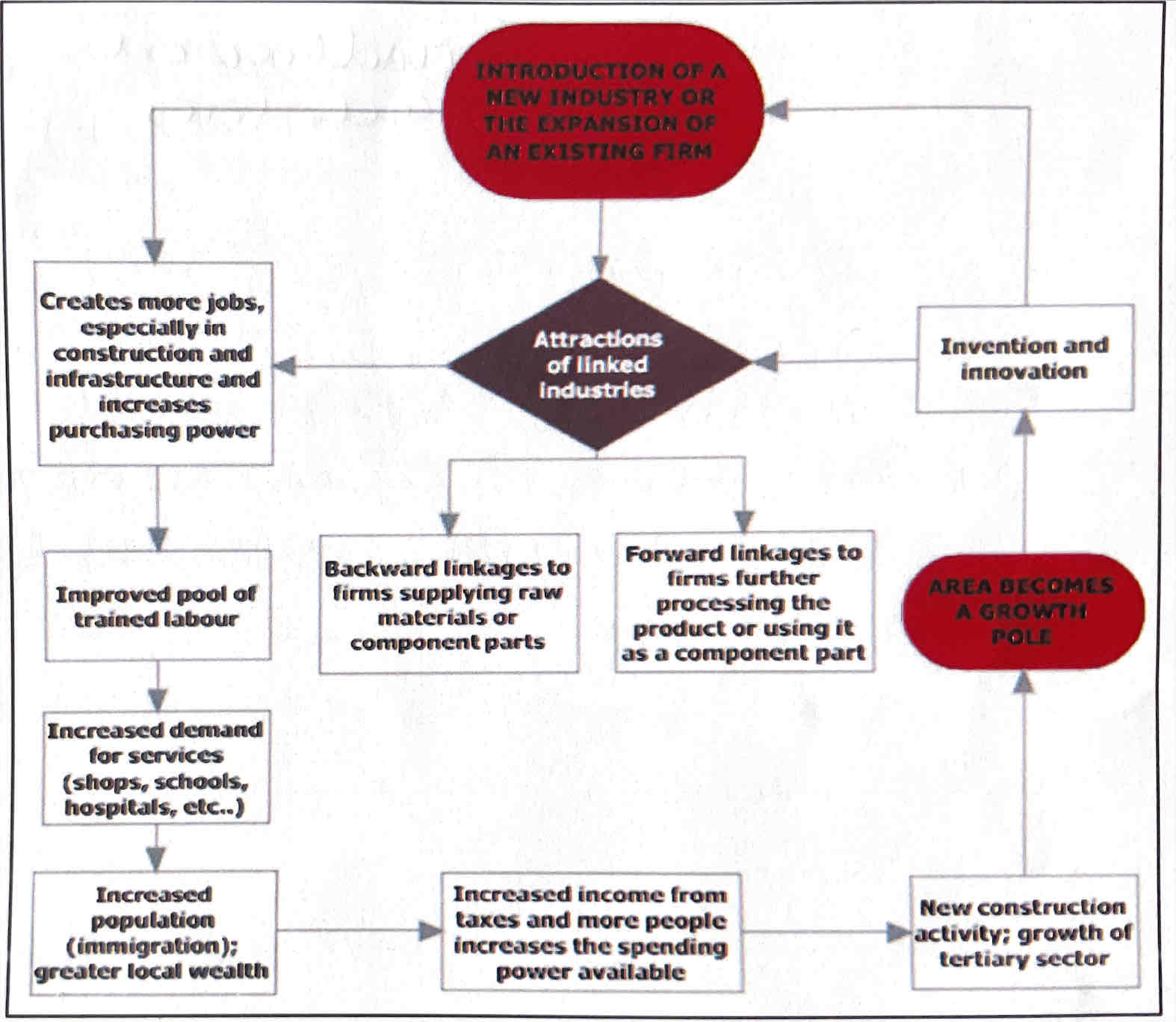
This increases demand so production must increase. Other business benefit by providing raw materials, workers or providing outsourcing opportunities e,g, positive feedback loop
Better pathways for essential goods and services and less economic risk
Disadvantages of trade blocs
Excluded countries find it difficult to trade
Foreign countries damaged due to competition or lack of opportunities due to trade blocs forming
Don’t guarantee fair treatment between countries.
What can countries do to trade other than joining trade blocs
Enter trade agreements, which lower costs of trade by lessening restrictions benefitting all countries.
Example - NAFTA, lowered and removed tariffs on imports and exports.
Special Economic Zones
Area where business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country to increase trade balance, employment, increased investment and production
Chinas open door policy
Mae Zedong governed a communist country so everyone benefits equally but improving industries weren’t successful.
Deng Xiaping in 1976 took power. He encouraged FDI, setting four SEZs, loosening governmental control over citizens personal lives.
Economic growth was rapid and overtook USA
How does China have a closed door approach to some global flows?
Social media TNCs such as Facebook and China have little to no access to the market in China.
34 foreign films screened in cinemas each year.
KOF Index
Measures globalisation of countries for political, economic and social indicators. Measured on a scale from 1 to 100
What is meant by the political, economic , social indicators in KOF index
Political - membership of international organisation and trade blocs
Number of foreign embassies located in the country.
Participation in international treaties
Economic - long distance flow of goods and services and capital
Flow of FDI
Social - international phone calls , tourist numbers
Information flow through number of internet users
Cultural proximity through things like the number of McDonald’s
AT Kearney Index
Measure of globalised cities, by a London business. Considers political, communication, technology, political factors
What is meant by political ,communication, technology and political factors in AT Kearney Index
Economic integration - immortal and exports, FDI
personal contact - telephone traffic, tourism and travel, remittances.
Technological activity. - internet users, internet hosts, secure servers
Political engagement- membership of international organisation
Signatories to international treaties, number of embassies
KOF index pros
allows comparison over time and between countries
Calculated for a number of countries and a number of variables
Readily available data
Employs a weighting system that reduces the affect that missing data would otherwise have on the total score for any given country.
KOF index cons
smaller countries overrepresented due to bias in how the final values are calculated e.g. distances between countries are smaller so easier for foreign travel
Low relevance of international mail and trade in books due to rise of emails and internet
Exclude informal economy but account for large proportion of actual trade
Illegal foreign immigrants aren’t included
Countries choose to be neutral and not participate in UN peacekeeping missions or international organisation. Doesn’t mean less globalised
AT KEARNEY index pros
allows for comparison between countries
It covers 96 percent of the worlds GDP
covers 84 percent of the worlds population
AT Kearney cons
Only 64 percent of the countries are included
Smaller countries dominate top 20 because they have higher FDI due to small domestic markets
High weighting of ICT connectivity gives USA a high score but low political engagement because they don’t have a lot of treaties signed
Can’t accurately measure cultural trend
What are 4 ways TNCS can grow
Mergers - 2 companies joining together to benefit both companies e.g Curry’s Pc world
Acquisition- one company owns another e.g. Kraft bought Cadbury
Joint ventures - 2 companies join and contribute different elements to a business
Franchising - individuals open up branches of a company under TNC. Individuals pay fee to parent company to set up firms
How can TNCs receive financial support from banks to help them grow
Investment from mainly HICs before
Recent trend of investment from developing countries - a reverse colonialism
How has improved transport and communication helped TNCs to grow
Faster and cheaper to make goods
Fibre optic cables- foreigners can buy online
Production meets demand at that moment e.g. fast food
Glocalisation
Adapting a global product/service to the specific recquirements of local practices and cultures expectation.
Outsourcing
Where business makes a contract with another firm to complete some of the work , rather than doing it within the company. This involves making the product or providing a service.
Switched on places
places where they are strongly connected to other places through the production and consumption of goods and services and other elements of globalisation known as core regions.
Switched off places
Places that are poorly connected and isolated from global networks. Known as peripheral regions.
What is a global hub
Switched in places that demonstrates a number of intense connection to the rest of the world. Places that other wish to connect to.
Example of switched on country
9million population. Banking centre of world and has the largest foreign exchange market in the world.
Heathrow the largest transport hub in world. Population speaks English so many foreign TNCs locate here.
How do physical resources help build switched on hubs
Physical resources - parts of the environment that are used to satisfy human needs and wants, non renewable or renewable. Countries invest in other countries that have valuable resources
OPEC oil states used petrodollars to make their cities(like Dubai) attractive to foreign investors and tourists ie global hubs
How does Human Resources help build switched on hubs
Human Resources - human labour , skills, language. Chongqing and Bangalore attract enormous amounts of FDI because of their Human Resources. Doesn’t guarantee that a place is connected and rich.
How does political factor hinder creation of switched on places
International trades don’t mean level playing fields for poor countries even with good physical resources.
Corrupt politics means wealth held by a few, not reinvested and given to poor people.
Cumulative causation - sustainably switched on
Initial injection of investment can lead to further investment and spending through a series of linked multiplier effects.
Negative effects of switched off places
Low literacy skills, infighting over resources, resources controlled by small elite or foreign TNCs due to old trade agreements.
Low prices for food exports, no real market potential - products unaffordable so little business
Weak flows of trade and investment
Switched off place example
North Korea - communist dictatorship run by one family who has total control over the population.
Since 1995 - policy of Junche ‘self sufficiency’ minimising trade with other countries.
Emigration and immigration prohibited.
No access to social media and internet because there’s a belief that all success are attributed to Kim Jong Un and the internet wouldn’t maintain this.
Radio and TV receivers are pre tuned to government station that pump out a steady stream of propaganda.
Trades with China and set Kaesong special Economic Zone employing 2000 people in SK.
What is the global shift
In the 70s and 80s the global shift began. It was the movement of manufacturing from Europe and the USA to Asia. Japan , Hong Kong, Sk became major players followed by China India
Why did the global shift happen
Individual Asian countries began to allow overseas companies to access their markets with new open door policy
TNCs began to seek new areas of manufacturing and outsourcing services.
FDI started to flow into emerging Asian countries
Physical reasons the global shift occurred in China
Close proximity to India and Japan
Secure energy e.g mix of coal and oil reserves
3 Gorges Dam providing HEP- Yangtze River
Large land mass- proletariat for growth and development
Large coastline.
Human Reasons why the global shift in manufacturing occurred in China
Low labour costs
Large population
Working long hours
Political reasons the global shift in manufacturing occurred in China
Chinas open door policy
joined the WTO
Social costs of outsourcing to China
Demand for urban housing increased so informal homes on edges of cities- crowding- increased. Farmland privately developed for houses without permission.
100 cities suffer from water shortages, 300 million don’t have access to safe drinking water
Environmental costs of outsourcing for China
Over 3 million hectares of arable land polluted with heavy metals. Fertilisers and pesticides pollute rivers
Coal Stations produce 70 percent of air pollution.
40 percent of land suffer from degradation
Social benefits of outsourcing to China for China
Reduction in poverty reduced by 680 million between 1981-2010.
95 percent literate. Education free and compulsory, skilled workforce
Economic benefits of outsourcing to China for China
Increase in urban incomes risen by 10 percent a year since 2005 due to relaxed one child policy
Investment in infrastructure- longest highway network 100,000 kn length of railway.
82 airports built since 2000 total is 250.
Detroit, USA a deindustrialised area case study- social problems
High unemployment due to global shifts- 8 percent unemployed.
Increased gun crimes
White flights- districts populated by African Americans, racial inequalities in housing systems
Depopulation as middle class Americans move out losing 1.1 million dollars
Economic problems in Detroit USA case study
Rise in informal economy - drug related crimes
Houses worth less than what they’re paid for.
Environmental problems in Detroit USA case study
Dereliction due to manufactures closing , disappearance of city’s automobile industries, vandalism and arson on factories.
Less model of migration
Migration is a complex decision influences by various factors such as barriers, push and pull factors.

Urbanisation and factors affected urbanisation
Urbanisation is a result of rural to urban migration and natural increase.
Factors: pull factors; better healthcare,education, access to clean water and more job opportunities
Push factors:lack of access to education and healthcare, clean water and poor wages.
Key facts of Karachi Pakistan case study
Most populated city in Pakistan - 24 million
2 largest seaports in Pakistan
Generates 25 percent of Pakistans GDP.
Social problems in Karachi case study
Unplanned settlements- 50 percent in Karachi live in slums or unplanned settlements e.g Orange Town largest slum in Asia and home to 2.4 million people.
Train systems overcrowding - 4500 passengers with a capacity of 1700.
Economic problems in Karachi caste study
75 percent living slums work in informal sectors so don’t pay taxes. The government doesn’t have the income to spend on improving education and healthcare which would improve the standards of living for people in the city.
Environmental problems in Karachi case study
Pakistan is the most water stressed country in the world according to World Bank due to lack of infrastructure to supply clean water.
WWF estimates the city loses 30 percent of its water through leaks in the system.
Mumbai social , economic and environmental problems mega city case study
Social- Dharavi largest slum in Mumbai. No access to basic services - water, sanitation, power and waste management
Economic -5000 people employed in recycling plastics , informal sector.
Environmental- plastic pollution Mumbai produces 8000 tonnes per day. Traffic congestion increases noise and air pollution. Mumbai is 4th most polluted mega city in the world
Elite migrants
Wealthy migrants welcomed to a country because of the investment and capital they bring.
Benefits of elite migrants
Boost host countries FDI e.g 82 percent of property deals in central London involve foreign buyers.
increases interdependence between regions. E.g Russian oligarchs to Londoners increased interdependence between uk and Russia as investment flows between the two countries.
Fills skills gap- skilled doctors move to work in the NHS
Low wage economic migration benefits for host country
Cheap labour to develop the infrastructure of the country e.g Indian migrants in UAE Gulf state make up 80 percent of construction workforce in Dubai.
Host country costs on low wage economic migration
Social tensions rise if people think migrants has led to lack of jobs and affordable housing.
Natural increase so local shortages of primary school.
Benefits of low wage economic migration on source countries
Benefits if remittances are sent home by migrants
Less public spending on housing and healtH
Children of migrants may return bringing in new skill
Creates interdependence between host and source countries
Costs of low wage economic migration to source country
Economic loss of a generation of Human Resources, schooled at government expense
Reduced economic growth as consumption falls
Higher dependency ratio as more elderly
Closure of universities due to lack of students
Closure of urban services and entertainment with a young adult market bringing decline and dereliction to urban environments.
What is culture
Culture is a set of values, traditions and beliefs that’s shared by a group of people.
Examples of cultural traits
All of theses traits are influenced my migration
Language- influenced by colonialism, school, internet,
Food-TNC(McDonald’s), social media, trading
Clothing- clothing media
Religion- religious refugees
Traditions
Cultural traits
Cultural can be broken down into individual parts such as tradition and language
Cultural imperialism
Practice of promoting the culture of one nation in another. The former is usually a larger, rich countries and the latter is small and affluent.
Unipolarity
Distribution of power in which one state exercises most of the cultural, economic and military influence.