Cardiovascular Response to Exercise Training
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
VO2 max
maximal capacity of the body to transport and use oxygen
units = ml O2/kg x min
other terms: maximal oxygen consumption, maximal aerobic power, maximal aerobic capacity
METS
measure of intensity of physical activity
1 MET = intensity at rest = 3.5 ml O2/kg x min
Exercise Intensity

VO2 Max test
graded exercise test with open circuit spirometry directly measure VO2
requires laboratory equipment and other considerations (submaximal exercise protocol have been developed to estimate VO2)
Calculation of VO2 max
VO2 max: product of maximal CO and arteriovenous difference
VO2 max = HR max x SV max x (a-vO2) max
Differences in VO2 max in different populations (age, sex, training state, health conditions)
Factors affecting VO2 max
genetics accounts for 50% of VO2 max
training
age: with aging SA node activity decreases
body size: larger people may have a larger VO2max due to larger heart and lungs
sex: women have lower VO2max due to smaller heart and less hemoglobin
altitude: VO2max lower at high altitude due to less O2 available
Training Affects VO2max
VO2max = HR max x SVmax x (a-vO2) max
increases COmax due to increase in SVmax (HR max dependent on age)
increase a-vO2 diff (genetics role most apparent) and faster rise in oxygen uptake at onset of exercise with less disruption of homeostasis
volume of mitochondria, # capillaries, # enzymes involved in production of ATP via aerobic pathways
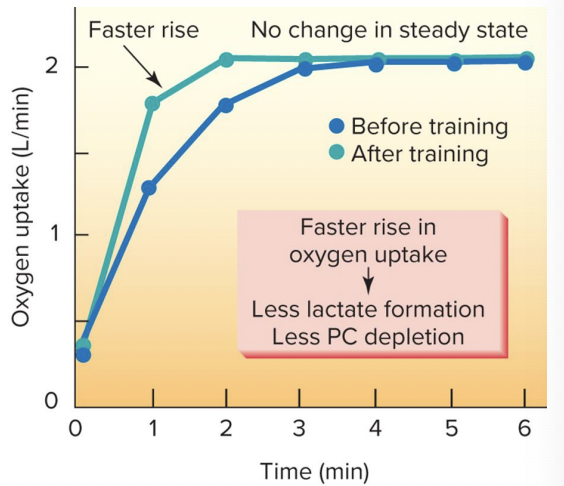
Endurance training-induced changes in VO2 max
improvements in VO2 max with training:
~50% increase SV and a-vO2
shorter duration training (4 months): increase SV > increase a-vO2
longer duration training (32 months): increase a-vO2 > increase SV
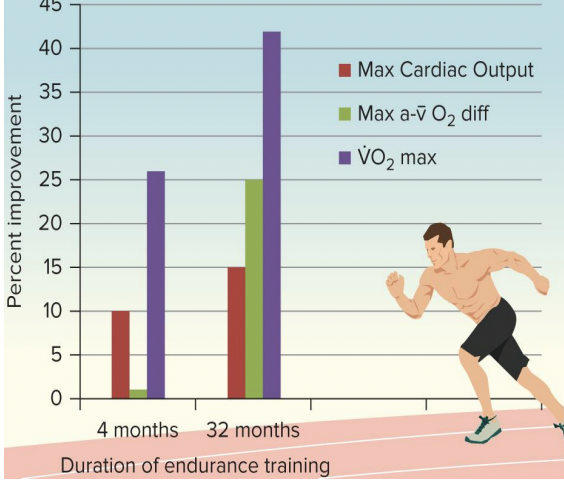
Endurance (Aerobic) training and VO2 Max
genetic predisposition: accounts for about 50% of VO2 max and prerequisite for very high VO2 max
training to increase VO2 max: dosage dependent
frequency > 3 times/week
intensity > 50% VO2 max
time: 20-60 minutes
Type: dynamic activity utilizing large muscle groups
expected increase in VO2 max: impacted by baseline when initiating training
average 15-20%
high initially VO2 max: 2-3% requires training intensity of >70% VO2 max
Low initial VO2 max: up to 50% training intensity of 40-50% VO2 max
Factors Increasing Stroke Volume
aerobic training effect:
increase rest, submaximal exercise, and maximal exercise
changes occur rapidly (6 days)
11% increase in plasma volume, 10% increase in SV and 7% increase in VO2max
Aerobic Training: blood composition
increase in:
plasma volume increase rapidly then levels off, # red blood cells after 4 weeks of training, total blood volume, high density lipoprotein (“good cholesterol”): may increase 2% after 6 months regular exercise
Decrease in hematocrit and decrease/maintained LDL (“bad cholesterol)
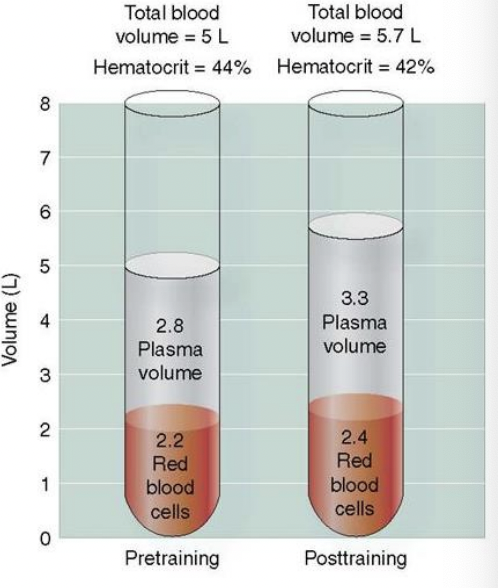
High Level endurance training impact on blood composition
sports anemia, sports-related hemolytic anemia, if CBC shows decrease hematocrit, decrease hemoglobin, and decrease ferritin may need treatment for iron deficient anemia
Sports Anemia
intensive endurance training can result in increase in plasma volume reflected in a decrease in hematocrit, hemoglobin, and red blood cell count in a blood sample
iron deficiency: alterations of transport of oxygen to tissues
associated with increased demands, dietary restrictions, decreased absorption and other factors
more common in athletes with heavy training loads
Sports-related hemolytic anemia
rupture and destruction of erythrocytes during physical exercise
occurs during impact forces of foot strike during running or power walking
other causes: repeated muscle contractile activity, vasoconstriction of internal organs, hyperthermia, dehydration, oxidative stress and other metabolic abnormalities
Aerobic training
increase ventricular volume and small increase in ventricular wall thickness
results in a volume overload
increase in ventricle volume is a normal physiologic adaptation to this volume overload
left side has greater changes than right
VO2max = (HRmax x SVmax) x a-vO2diff max
during acute aerobic ex cardiac contractile force increase (due to increase SNS activity)
Aerobic training:
decrease in afterload
vigorous aerobic training increase cardiac muscle strength
Skeletal muscle adaptation to endurance training
fast-to-slow shift in muscle fiber types
increase capillary and mitochondria density
increase FFA utilization and decrease blood glucose and muscle glycogen utilization
high intensity training; Increase LT
increase antioxidants
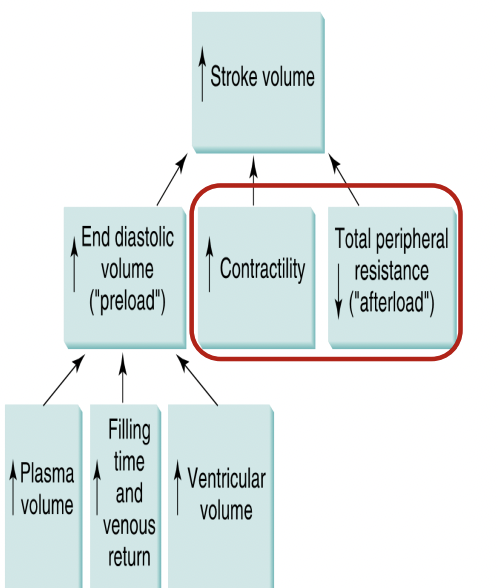
increase a-vO2 diffmax
increase in capillary perfusion (decrease in SNS vasoconstriction)
increase in capillary density in trained muscles
increase in mitochondria # in trained muscles
occurs rapidly, increase seen within 5 days of training
increase dependent upon intensity and duration of exercise; may be 50-100% increase within 6 weeks of training
increase in oxidative enzymes in trained muscles
Summary of Effects of Aerobic training
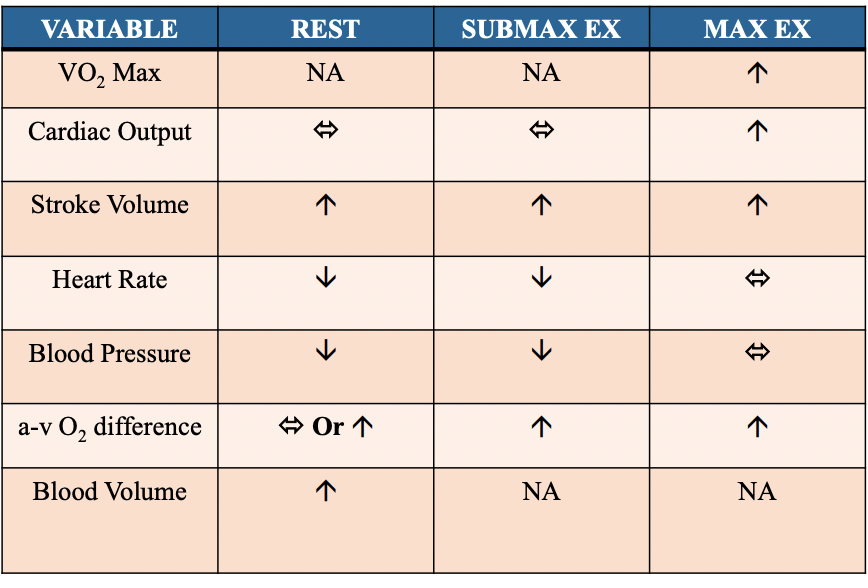
effects of training on recovery from exercise
more rapid reduction in HR, SV, CO, and SBP to baseline (trained individuals recover in a shorter time period)
heart rate recovery (HRR)
reflect balance in reactivation of PNS and withdrawal of SNS
utilized as a predictor for CAD, cardiovascular mortality, and other health outcomes
improved with aerobic exercise training
HRR
decrease in heart rate following cessation of exercise
effects of training on recovery from exercise
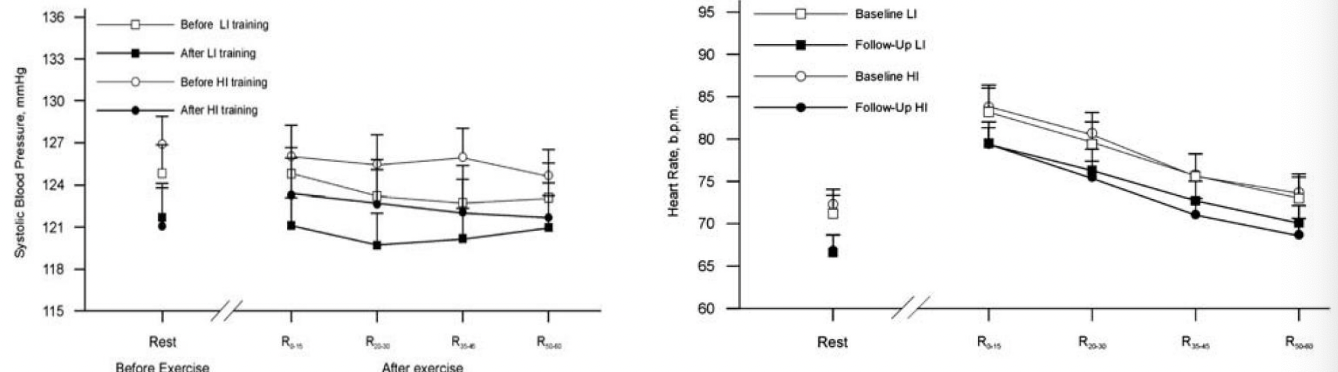
Aging aerobic training effecct
maximal HR decreases with aging
SV declines due to decrease in heart extensibility
VO2 max decreases 10% per decade after 25-35 years of age
adaptations can be realized at any age but extent of change may be limited by age
sex aerobic training effects
in general SV, CO are larger at sub-max and max work rates in men
arterial oxygen content less in women (less hemoglobin)
no gender differences in magnitude of CV adaptations to exercise between the sexes
Normal vital sign response to acute aerobic exercise
HR is expected to increase = bpm for every 1 MET increase in exercise intensity
SBP is expected to increase 8-12 mmHg for every 1 MET increase in exercise intensity
CV response to aerobic exercise training
decrease RHR 5-25 bpm
decreases SBP and DBP at rest; Dec’s SBP 10-15 mmHg
increases VO2max 15-20% in 12 weeks
improvement dependent upon fitness level. very deconditioned individuals may improve as much as 50%
Detraining and VO2 max
rapid decrease in VO2 max
decrease approximately 8% within 12 days; 20% decrease after 84 days
initial decrease in VO2 max due to decrease SV max with later decrease due to a-vO2 max
decrease SV max
decrease maximal a-vO2 difference (decrease mitochondria, oxidative capacity of muscle and type 2a fibers and increase type 2x fibers
dynamic resistance exercise with light to moderate loads
CO increase but not as much as aerobic exercise
mainly due to increase in HR; little change in SV
similar to aerobic exercise SBP, DBP remains relatively constant
Dynamic and isometric resistance exercise with very heavy loads
increase CO
increased HR
decreased SV due to: low preload and high afterload
Adaptations to resistance training
-resting HR
-reduction in BP in those with prehypertension, hypertension, and elevated cardiometabolic risk
-submaximal exercise
VO2 max
muscle oxidative properties and/or muscle capillarization
improvement in glycemic control
improvement in HDL
decrease in total cholesterol and triglycerides
inflamation
improvement in body composition
depression and anxiety decrease