Oral Radiography Exam 1 (Units 1 - 4)
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
What color XCP is used for bitewings?
Red

What are the reasons for taking radiographs?
To detect disease, monitor growth and development, guide treatment, document condition of teeth and bone, and provide legal records.
What are the duties/responsibilities of a dental radiographer?
Protect the patient from unnecessary radiation
Protect themselves and others from radiation exposure
Educate patients about radiographs
Maintain equipment
Follow legal and ethical guidelines
What is correct horizontal angulation for exposures?
The central ray is directed through the contact areas of the teeth, perpendicular to the receptor, preventing overlapped contacts.
What is correct vertical angulation for exposures?
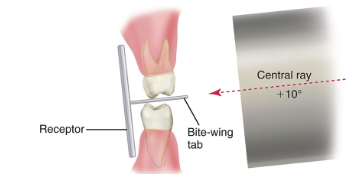
Bitewings: +10° (or +20° with PSP plate)
Periapicals: Angle depends on tooth/receptor position, but central ray must be perpendicular to the receptor and tooth.
What are the principles of the bitewing technique?
Receptor placed parallel to crowns of upper and lower teeth
Stabilized when patient bites on tab or XCP bite block
Central ray directed through contacts at +10° vertical angulation
Who was William Coolidge and what was his contribution?
Developed the first hot cathode X-ray tube (Coolidge tube), making X-rays safer and more stable.
Who was Frank Van Woert and what was his contribution?
First to use film (instead of glass plates) in dental radiography.
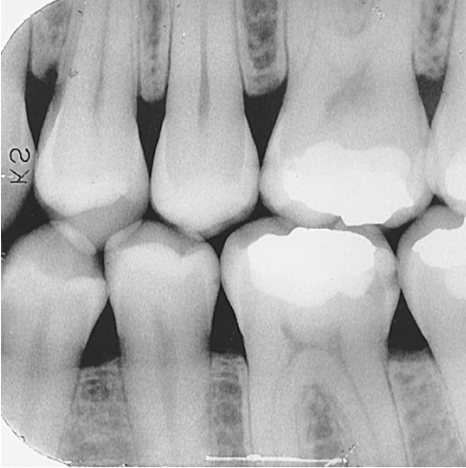
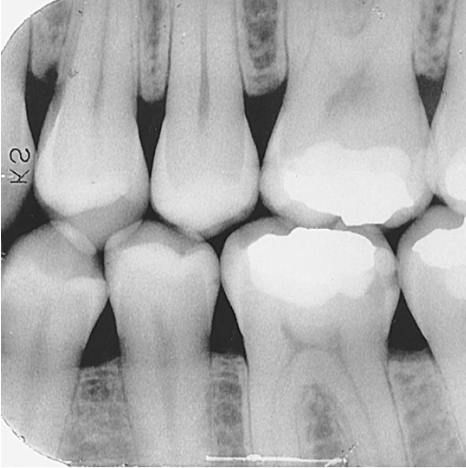
What does a bitewing image show?
The crowns of maxillary and mandibular teeth, the interproximal areas, and the crestal bone — all on the same image.
What does interproximal mean?
The area between two adjacent teeth.
What is the crestal bone?
The top edge of the alveolar bone between teeth.
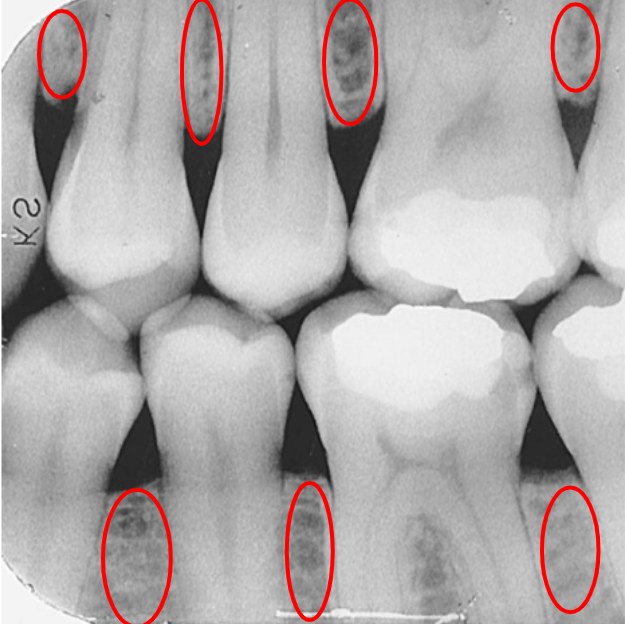
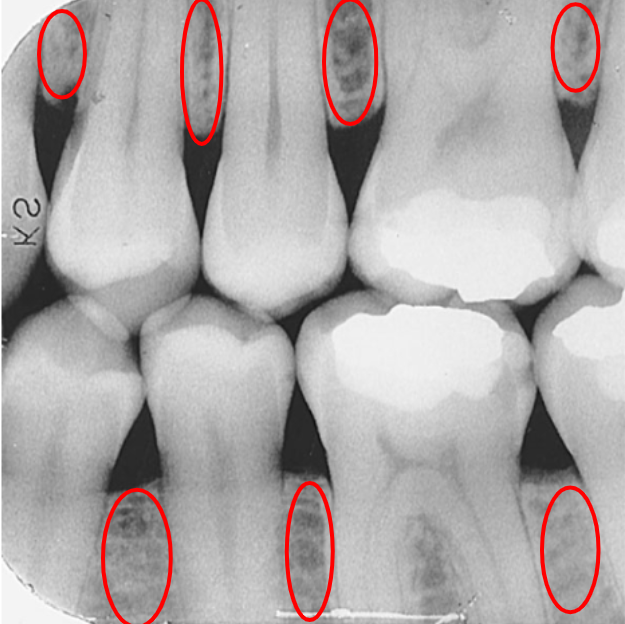
What is this?
Crestal bone
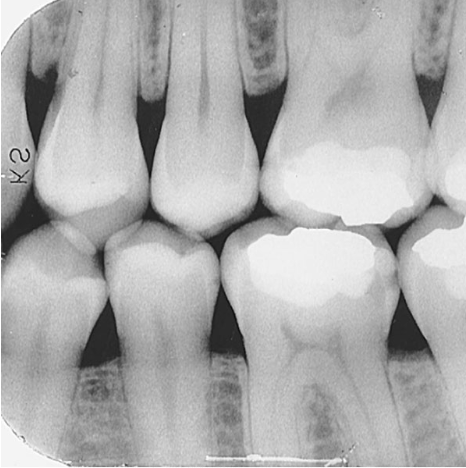
What is the primary use of a bitewing image?
Detecting interproximal caries (cavities).
What is a caries (carry)?
Tooth decay caused by bacteria.
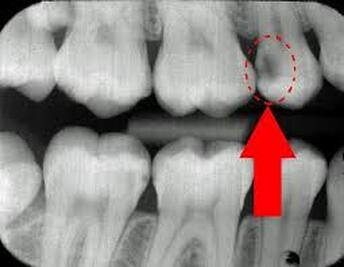
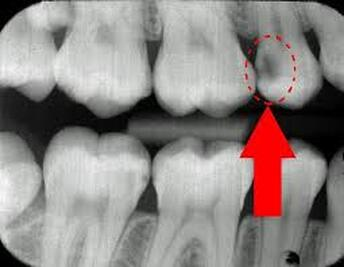
What is this?
A Carry
What is a lesion?
An area of tissue that is damaged, diseased, or abnormal.
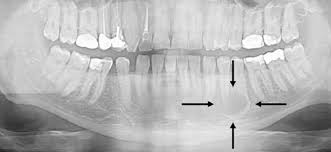
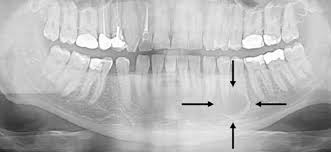
What is this?
A lesion
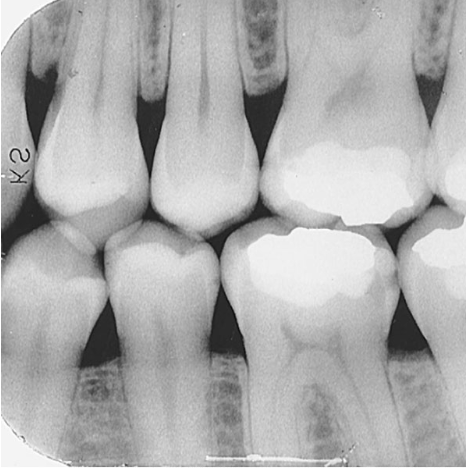
What are bitewing images used for?
Detecting interproximal caries
Monitoring caries progression
Examining crestal bone levels
Assessing restorations
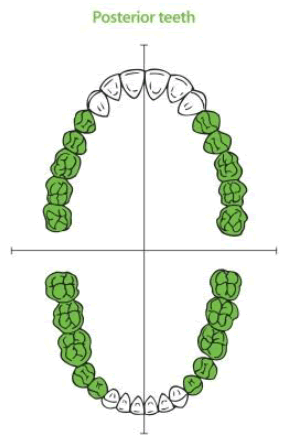
What part of the mouth are bitewings used in?
Posterior
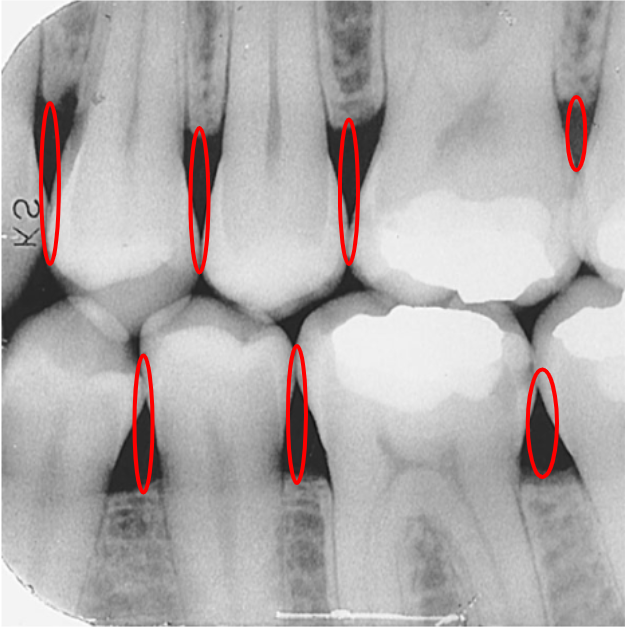
What is this?
Interproximal areas
What is an interproximal examination?
A single image that shows the crowns of both maxillary and mandibular teeth to examine the interproximal areas.
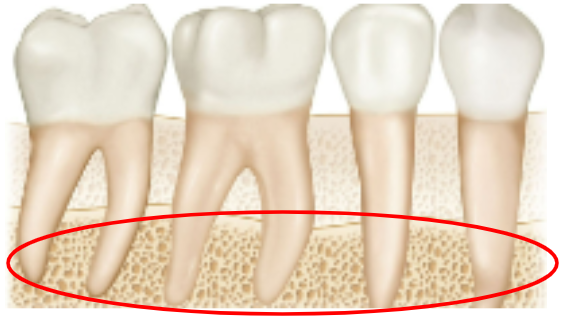
What is the alveolar bone?
The part of the jawbone that supports and surrounds the teeth.
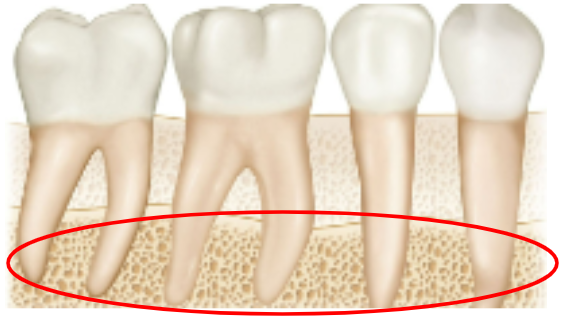
What is this?
Alveolar bone
What is a bitewing receptor?
The sensor or film used to capture bitewing images.


What is this?
Bitewing receptor
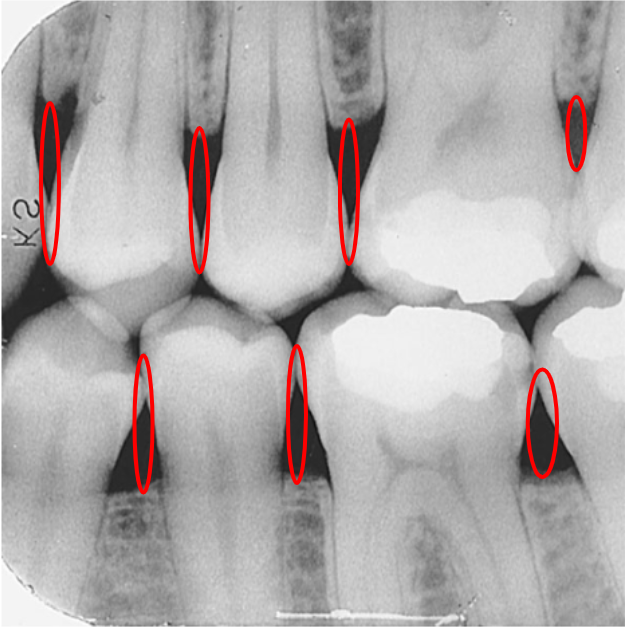
What are contact areas?
The places where adjacent teeth touch each other.
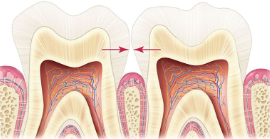
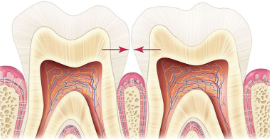
What is this?
Contact areas
What are open contacts?
Spaces where teeth do not touch, leaving a gap.
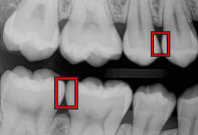
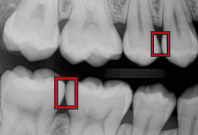
What is this?
Open Contact
What are overlapped contacts?
Areas on a radiograph where teeth appear to overlap due to improper horizontal angulation.
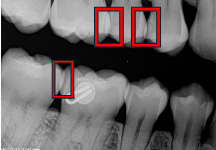
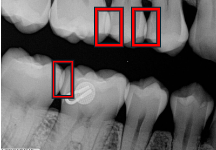
What is this?
Overlapped contact
What are the different types of bitewings?
Directional: Horizontal and Vertical Bite Wings
Structural: Molar Bite Wing and Premolar Bite Wing
What is a horizontal bitewing?
A bitewing image oriented horizontally, used mainly for detecting interproximal caries.
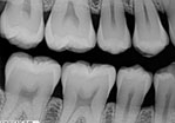
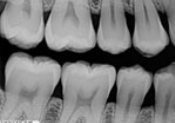
What is this?
Horizontal Bite Wing/Premolar Bite Wing
What is a vertical bitewing?
A bitewing image oriented vertically, used to examine alveolar bone levels (especially in periodontal patients).
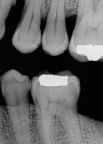
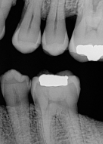
What is this?
Vertical Bite Wing
How many bitewing images are usually taken in a full series?
Four — two on the left side and two on the right side.
What does a premolar bitewing show?
The crowns of the maxillary and mandibular premolars, the distal half of the canine, and the mesial half of the 1st molar.
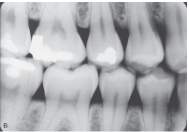
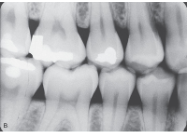
What is this?
Premolar bitewing
What does a molar bitewing show?
The crowns of the maxillary and mandibular molars (2nd & 3rd molars) and the distal half of the 1st molar.
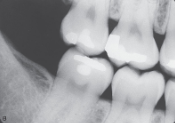
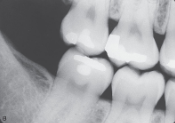
What is this?
Molar bite wing
When using a PSP plate for bitewings, what adjustment is recommended for the PID?
Increase vertical angulation by about +10° to correct for plate bending and keep contacts open.
What is a size 0 receptor used for?
For posterior teeth of children with primary dentitions.


What is this?
Size 0 receptor
What is a Size 2 receptor used for?
For posterior teeth of older children and adults; can be placed horizontally or vertically.
What is this?
Size 2 receptor
What is a Size 3 receptor used for?
Only for bitewings, but not recommended (too large).


What is this?
Size 3 Receptor
What is a bitewing tab?
A paper or plastic tab attached to the receptor that the patient bites on to hold it in place.


What is this?
A bitewing tab
What is angulation in dental radiography?
The alignment of the PID (tubehead) in relation to the receptor and the tooth.
What is horizontal angulation?
Positioning the PID side-to-side, directed through the contact areas.
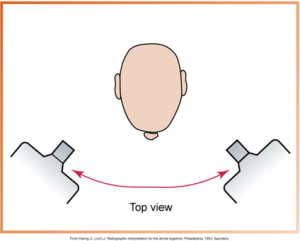
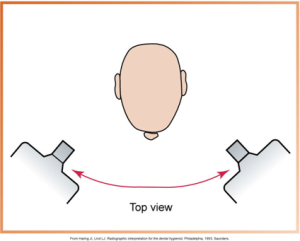
What is this?
Horizontal Angulation
What is vertical angulation?
Positioning the PID up-and-down, directing the beam above or below the occlusal plane.
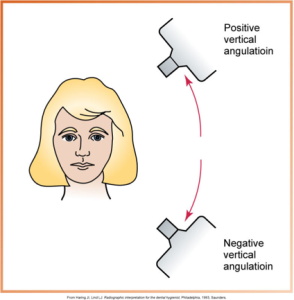
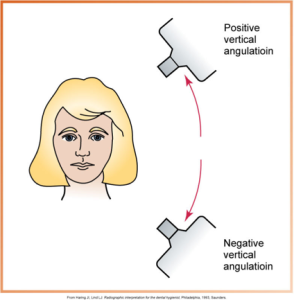
What is this?
Vertical Angulation
What does incorrect horizontal angulation cause?
Overlapped contacts.
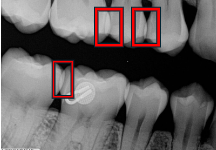
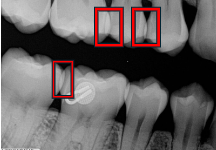
What causes overlapped contacts?
Incorrect horizontal angulation of the P Diddler 😧
What does incorrect vertical angulation cause?
Distortion (elongation or foreshortening).
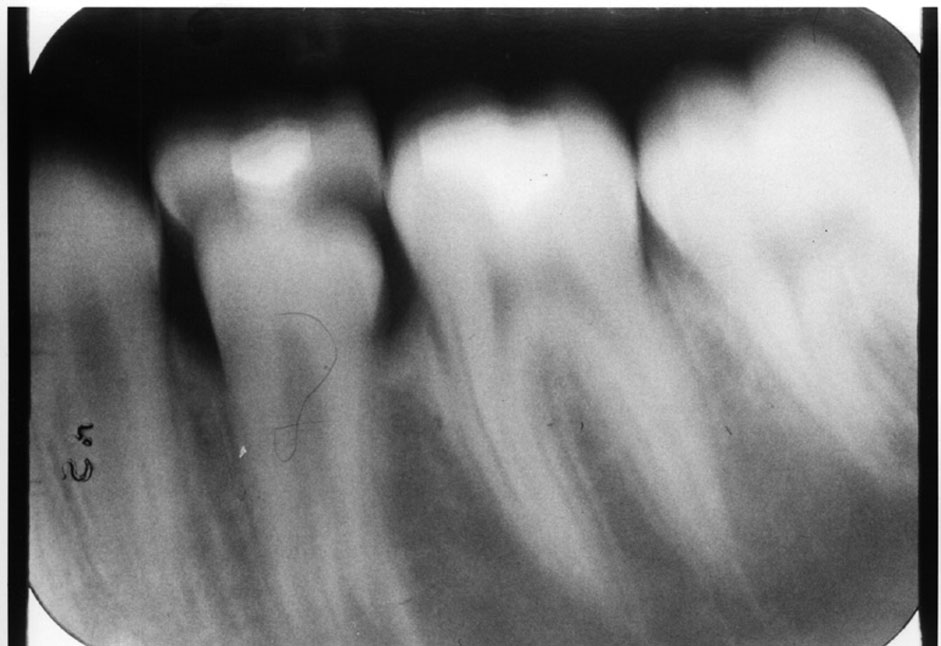
What causes distortion?
Incorrect vertical angulation of the PID
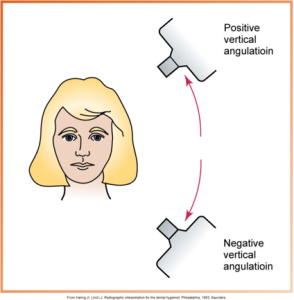
What is correct horizontal angulation?
The PID is positioned so the central beam is directed through the contact areas and hits the receptor perpendicularly. This prevents overlapped contacts.
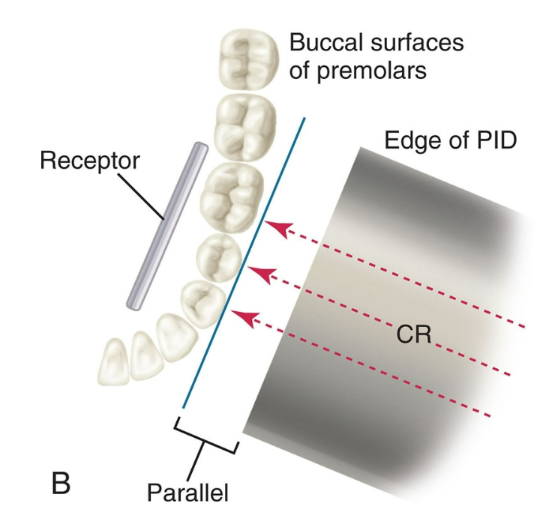
What is correct vertical angulation for bitewings?
The central beam is directed +10° above the occlusal plane, so the crowns and crestal bone are clearly seen without distortion.
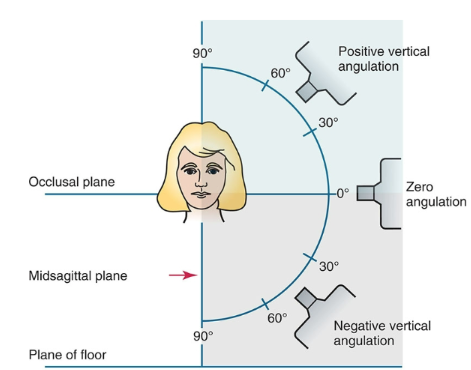
What vertical angulation is recommended for a PSP plate bitewing?
About +20° (extra 10° added to correct for plate bending).
What vertical angulation is recommended for a digital receptor bitewing?
About +10° (standard angulation).
What is the recommended exposure sequence for a full-mouth series?
Start with anterior periapicals, then posterior periapicals, then bitewings.
What is the exposure sequence if taking bitewings only?
Start with premolars, then molars.
What is receptor placement?
The specific area where the receptor is positioned before exposure, based on the teeth and surrounding structures.
What are the steps for receptor placement and exposure (IMPORTANT WILL BE ON EXAM)?
Position receptor → set vertical angulation → set horizontal angulation → expose.
How do you manage edentulous spaces during receptor placement?
Use a cotton roll to support the receptor.
How do you manage bony growths (tori) during receptor placement?
Position the receptor between the tori and the tongue.
What are the steps for exposing radiographs?
1. Patient preparation
2. Equipment preparation
3. Exposure sequence for receptor placements
4. Receptor placement
Premolar bitewings must show…
Distal of the canine
Molar bite wings must show…
Distal of 2nd premolar
What is Radiation?
Energy carried by waves or particles.
What is X-Radiation?
High-energy radiation capable of penetrating tissue to create an image.
What is an X-Ray?
The beam of X-radiation that passes through the body.
What is Radiology?
The study and use of X-rays to produce diagnostic images.
What is a Radiograph?
The actual image produced on film or a digital receptor by X-rays.
What is a Dental Radiographer?
A person (such as a dental assistant or hygienist) trained to expose and process dental radiographs.
What is an Image in dental radiology?
A picture or representation of a dental structure produced by X-rays.
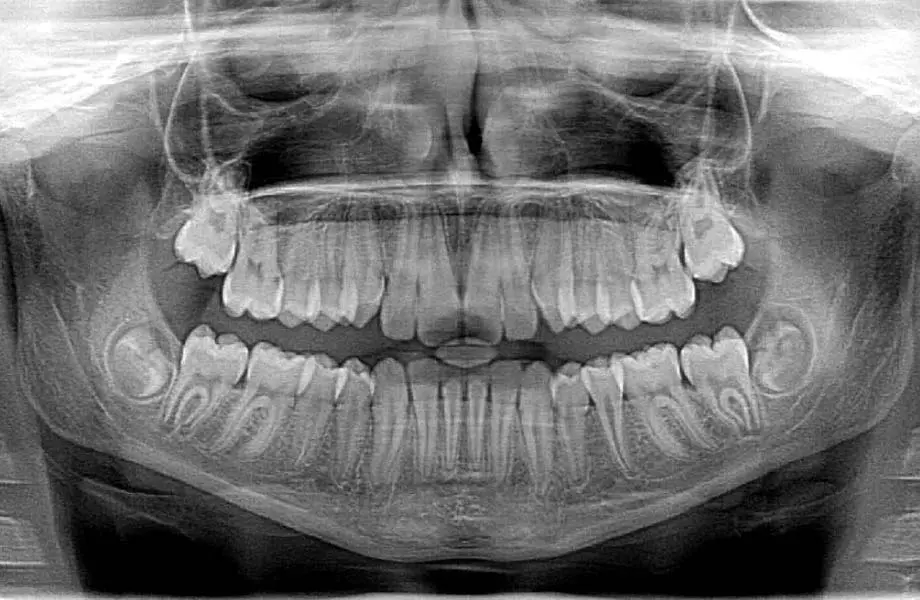
What is an Image Receptor?
The material/device that captures X-ray energy and forms an image (film, sensor, PSP plate).
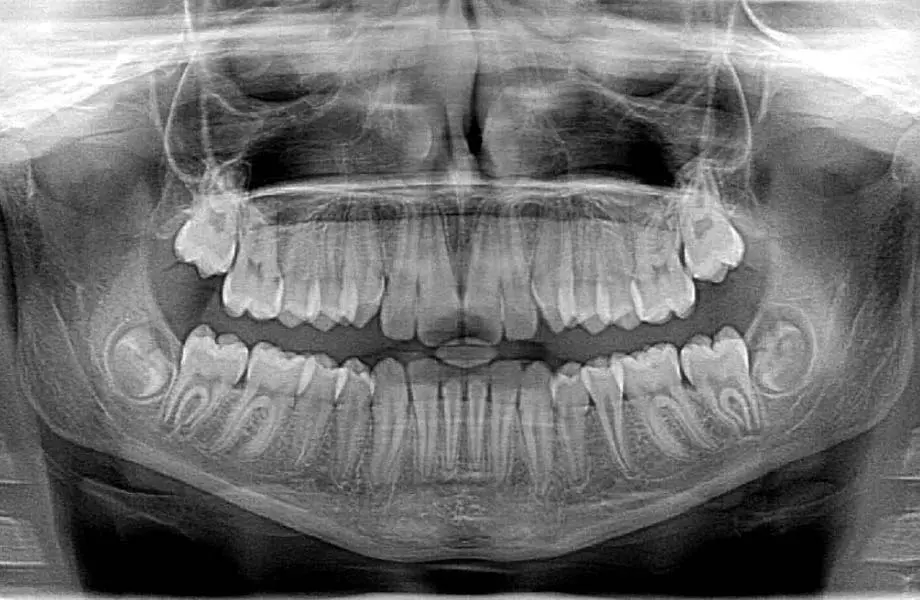
What is Dental Imaging?
The creation of digital, film, or scanned images of teeth and surrounding structures.
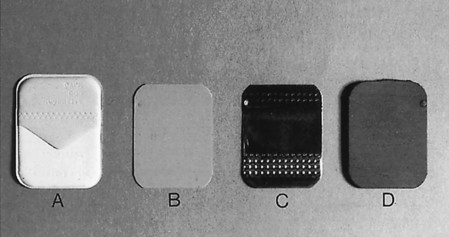
What are examples of Image Receptors?
Film, digital sensors, and PSP plates.
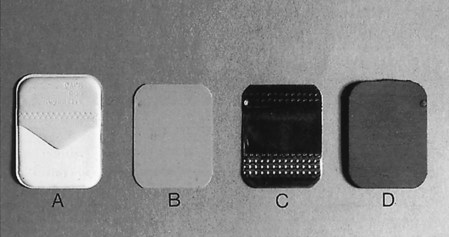
What is the Importance of Dental Images?
They help in diagnosing diseases, detecting conditions not visible clinically, guiding treatment, and monitoring changes.
Who was Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen?
The German physicist who discovered X-rays in 1895.
Who was Otto Walkoff?
Took the first dental radiograph of a living person (his own mouth).
Who was W.J. Morton?
Took the first dental radiograph in the U.S.
Who was C. Edmund Kells?
One of the first to use dental radiographs in practice; took the first radiograph on a living patient in the U.S.
Who was William H. Rollins?
Known as the “Father of Radiation Protection”; developed safety guidelines after experimenting with X-rays.
Who was Howard Riley Raper?
Wrote the first dental radiology textbook and introduced the bitewing technique.
What is the role of the federal government in dental radiography?
Regulates the manufacturing and safety of X-ray machines.
What is the role of the state government in dental radiography?
Oversees machine inspections, and issues licenses and certifications.
What is risk management?
Policies and procedures to reduce the chance of legal action.
What is informed consent?
When a patient is told about risks, benefits, and alternatives before treatment and agrees to proceed.
What is disclosure in dental radiology?
Informing the patient about exposure, risks, and the need for images.
What is liability in dental radiography?
Both the dentist and dental auxiliary can be held legally responsible for actions.
What is malpractice?
Professional misconduct or failure to provide standard care, leading to harm.
What is negligence?
Failure to provide reasonable care that a competent professional would give.
What is the standard of care?
The quality of care a reasonably skilled dental professional would provide in similar circumstances.
What is the statute of limitations?
The time period during which a patient can file a lawsuit.
Who owns the dental records?
The dentist, but patients have the right to reasonable access.