Unit 5: Chapter 13 - Patterns and Practices of Agricultural Production
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is agriculture now a contributor to, in addition to survival?
Agriculture is now a major contributor to state and global economies.
Agriculture has adapted to decades of changes and innovation, but what is an obstacle that still stands?
The main obstacle to an even distribution of resources is the differences in climate and soil fertility.
Where does most subsistence farming take place?
Most subsistence agriculture is practiced in rural Africa and parts of Asia and Latin America, where connections to global markets are limited and farmers have less access to credit and financial capital.
Many subsistence farmers live in poverty and do not have the economic resources to pay for labor or expensive machinery.
Where does commercial agriculture take place?
Most commercial agriculture takes place in core or semi-peripheral countries that have infrastructure in place to access and supply global markets.
With the use of modern farm equipment (tractors, pesticides, GPS, Drones), Commercial agriculture can be a lucrative but very expensive business.
Dual agriculture economy
two agricultural sectors in the same country or region that have different patterns of demand.
In this system you can have subsistence agriculture being practiced next to a commercial farm.
Common in Central and South America.
Agribusiness
the large-scale system that includes the production, processing, and distribution of agricultural products and equipment.
Agribusiness is predominantly in North America and Europe.
How much more food do farmers produce today?
Farmers today produce 262% more food with 2% fewer inputs than farmers in 1950.
Why do farmers produce more food?
Advances in technology, better fertilizers, more powerful pesticides and now the introduction of GMOs and Hybrid foods.
Hybrid foods
can be adapted to different growing seasons, grown in extreme climates, and more resistant to diseases.
Ex:
grains, fruits, and vegetables)
How can government policies greatly impact agricultural practices?
-Payments to farmers for growing certain crops or for not growing others.
-Governments also regulate imports and exports that can in turn increase or decrease farmer profits.
-Some governments offer price supports in the form of crop purchases at a guaranteed price quotas to control the supply of certain crops.
Family Farms
Family farms are the vast majority of farms worldwide.
84% of farms worldwide are less than 5 acres.
Family farms account for less of the world's total farmland. 12% of the total farmland is owned by family farms.
Farms in the United States
-the number of farms has decreased since the 1960s, holding steady in recent decades at just over 2 million.
-more than 90% of farms are classified as small; most of these are family-owned and operated.
Where is the vast majority of the share of farmland controlled by larger farms located?
The vast majority of the share of farmland controlled by larger farms is in the core countries like the US, Canada, Australia, and Western Europe.
Vertical Integration
occurs when a company controls more than one stage of the production process.
This is very difficult for small family farmers as it can be incredibly expensive.
Commodity chains
a complex network that connects places of production with distribution to consumers.
Commodity chains span regions and global locations. This is all possible due to globalization. Commodity chains are delicate and can be disrupted as we have seen since Covid.
Supply and Demand
When supply is high, prices go down.
Within agriculture, when there is high production success, prices can drop so low that production costs are higher than the value of the product.
This can be catastrophic for farmers who live off of what they grow and sell.
How has the U.S. government protected farmers?
the government provides low-cost loans, insurance, and subsides - direct payments for goods.
US farm subsidies currently amount to about $20 billion a year. Subsidies tend to benefit the highest-quality producers of commodities more than small farmers.
Tariffs
a tax or duty on a particular import or export.
Tariffs raise the price of imported goods, making them more expensive to purchase than goods made within the country and giving domestic producers an advantage.
What can tariffs also lead to?
Tariffs can also lead to trade wars, which can disrupt established commodity chains, lower the price of farm products, and cause farmers to lose business.
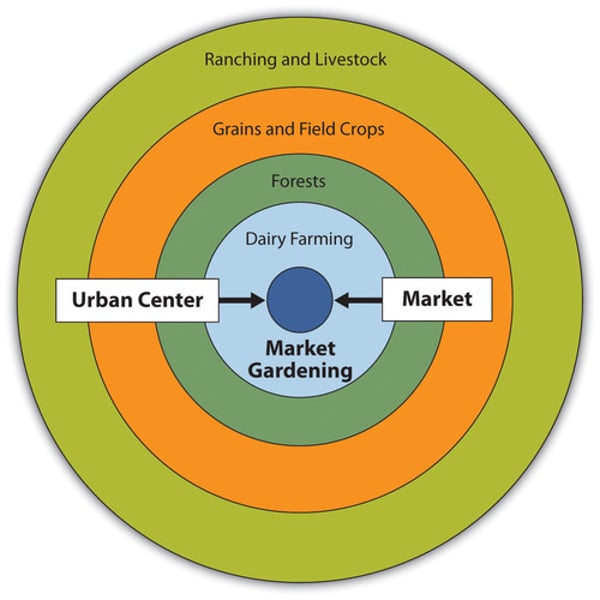
The Von Thunen model
focuses on the relationship between the cost of land and the cost of transporting goods
Your distance from the market determines what you will produce and how much of it you will produce.
Bid rent theory
More competition near the city center/market, therefore, higher rents.
The land near the city is more expensive, but transportation is cheaper, while the land far away is cheaper, but the transportation is more expensive.
What is the innermost ring of the Von Thunen model?
The innermost ring is the Market/Central Business District
The Market or Central Business District is where all products need to be delivered to. It is where all buying and selling occurs.
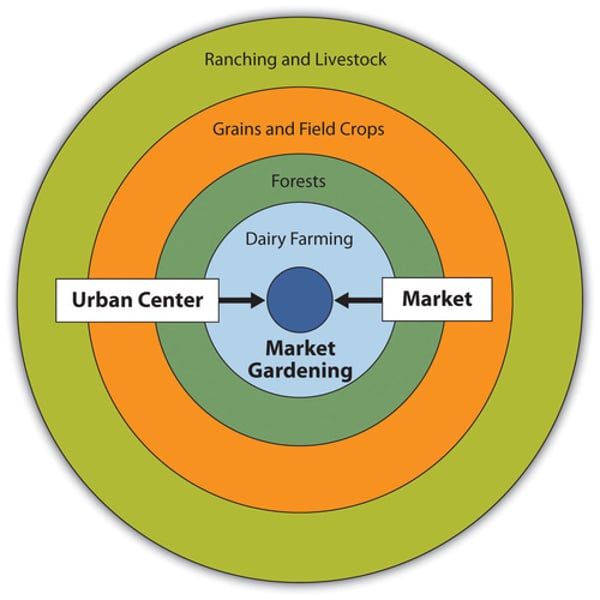
What is the second ring of the Von Thunen model?
The second ring is the Dairy farming and Market Gardening
Since vegetables, fruit, milk and other dairy products must get to market quickly, they would be produced close to the city.
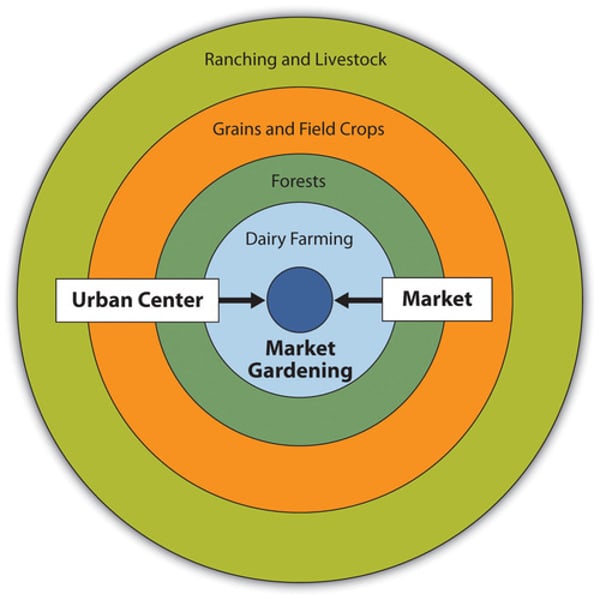
What is the third ring of the Von Thunen model?
The third ring is Forest
Forest resources (Timber and firewood) would be produced for fuel and building materials in the city.
Before industrialization (and coal power), wood (forest) was a very important fuel for heating and cooking. Wood is very heavy and difficult to transport so it is located as close to the city as possible.
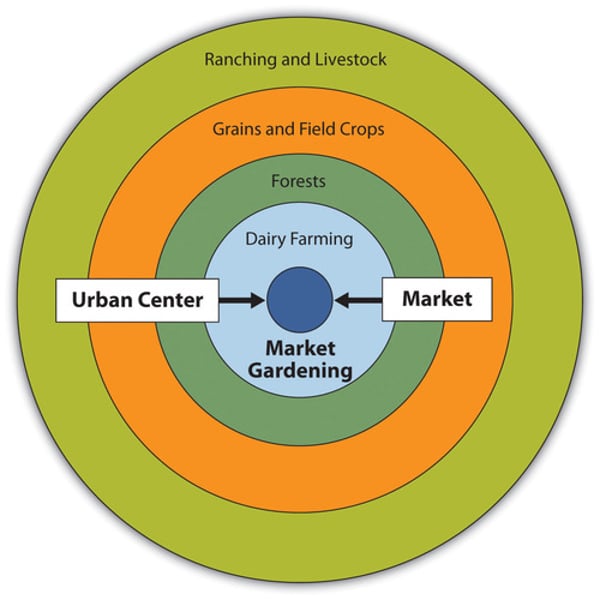
What is the fourth ring of the Von Thunen model?
The fourth ring is Grains and Cereal Crops
Grains and cereal crops last longer than dairy products and are much lighter than fuel, reducing transport costs, they can be located further from the city.
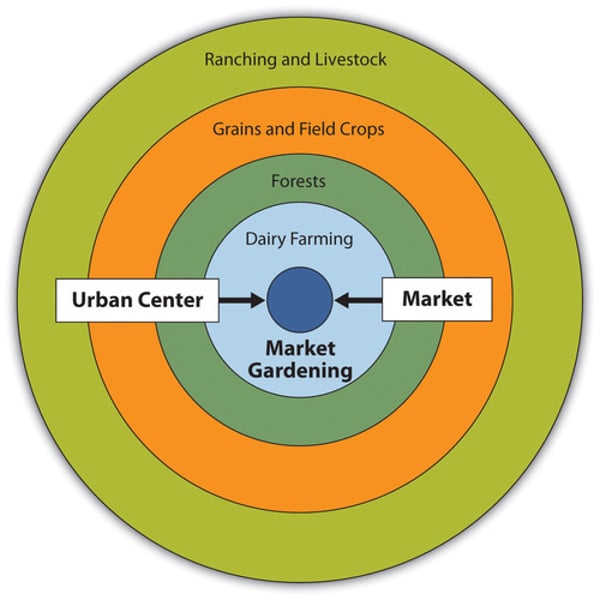
What is the fifth ring of the Von Thunen model?
The fifth ring is Ranching and Livestock
Animals can be raised far from the city because they are self-transporting. Animals can walk to the central city for sale or for butchering.
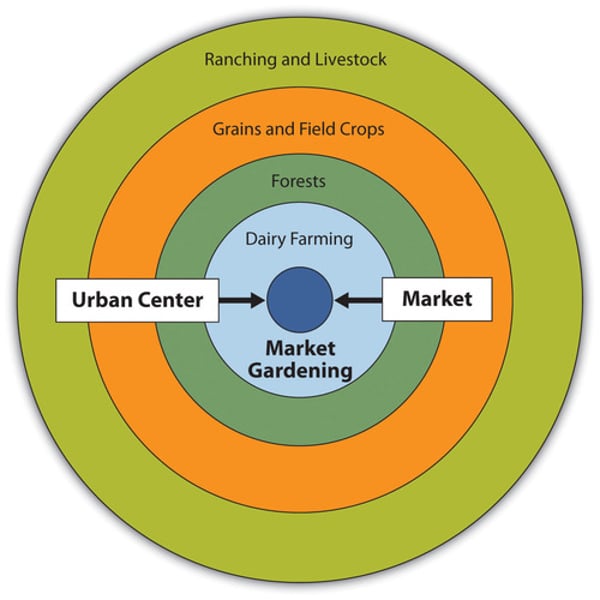
How has globalization affected agriculture?
Thanks to globalization, people can buy food from all around the world. Agriculture has become globally integrated and organized, connecting peripheral countries with core countries.
Global supply chains
the same as commodity chains but on a global scale.
Production will usually start in a peripheral country due to cheaper labor and then shipped to a core countries for processing and sale.
What are some global agricultural commodities?
wheat, corn, soybeans, cotton, coffee, tea, cacao, and vanilla.
Commodity dependency
a country dependent on a single cash crop for their exports.
Reliance on a single commodity is risky and unhealthy for a country's economy
Cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value (Money!)
What infrastructure is required to keep the global supply chain working?
-Communication systems
-Sewage, water, and electric systems
-Roads and transportation systems
Without the proper infrastructure, it is very difficult for a country to be a part of the global supply chain. This leaves a lot of periphery countries out of the system.
When do supply chains work best?
when trade partnerships are stable, reciprocal, and understood by all parties.
How do global supply chains trace their roots back to European colonial and imperial networks?
Some former colonies are still tied economically to their former colonizers.
Fair Trade
movement in a global campaign to fix unfair wage practices and protect the ability of farmers to earn a living.
Fair trade products are available everywhere but in limited quantities. Consumers may choose to buy fair trade products, which are priced higher, in order to support the movement's goals.
How have food preferences have altered patterns of production and consumption?
The increased interest in plant-based foods is creating new demand for the production of vegetable proteins.