hypothalamus and pituitary gland - lecture 14
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
hypothalamus
one of the most important parts of the brain, specifically important for concept of coordinating brain and body (psychological response to stimulus is in line with somatic response)
motivation
central brain circuitry
hormonal
pituitary/systemic
hypothalamus
positioned at base of brain towards the back, comprised of neurons that can project to other parts of the brain (prefrontal cortex), trafficked down axon
pituitary
extension of hypothalamus, bulblike structure, high risk for damage
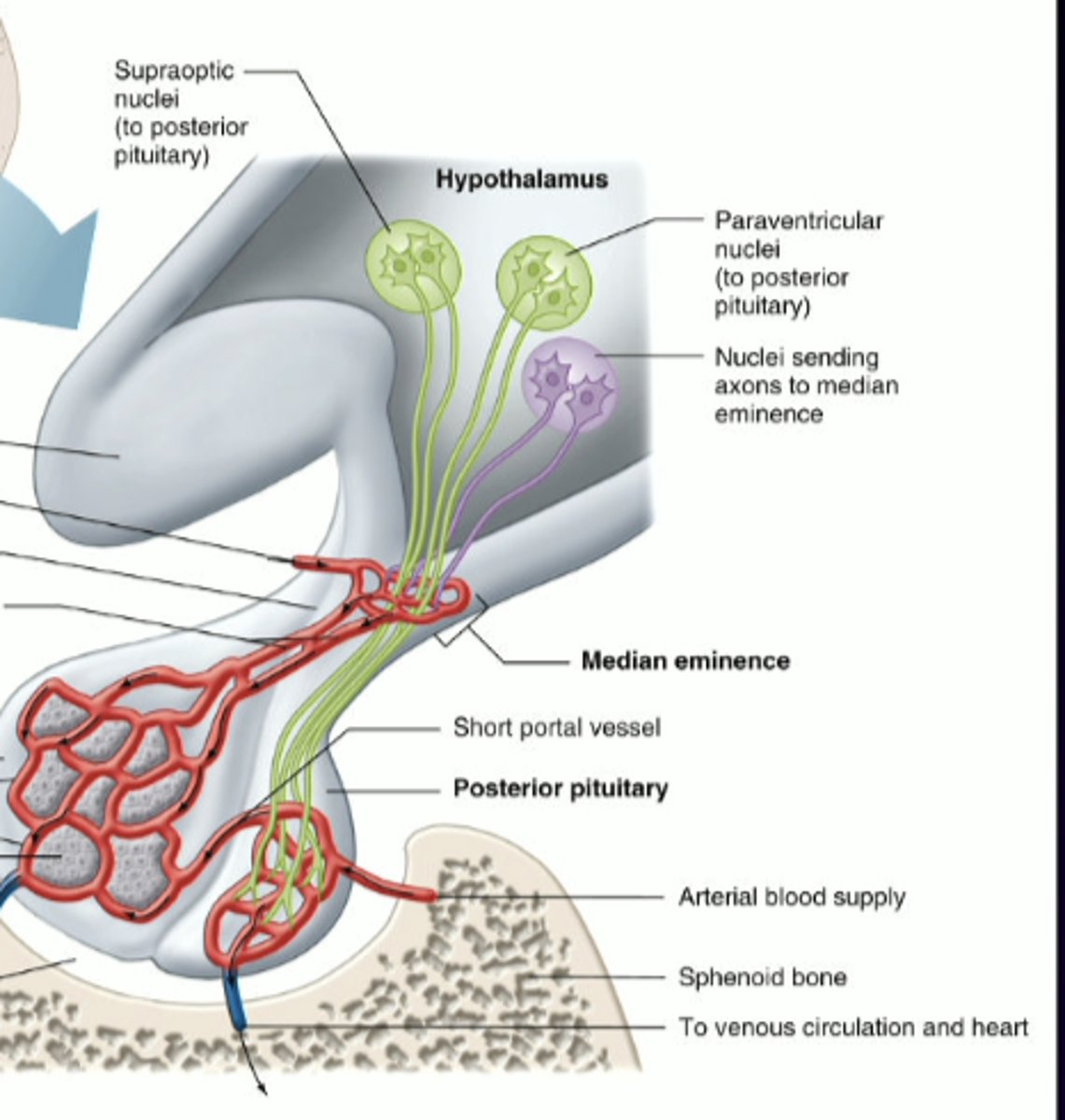
posterior pituitary
green neurons, very large and long, they originate in hypothalamus and follow these wiggly axons down to the back portion of pituitary
**make --> move --> release
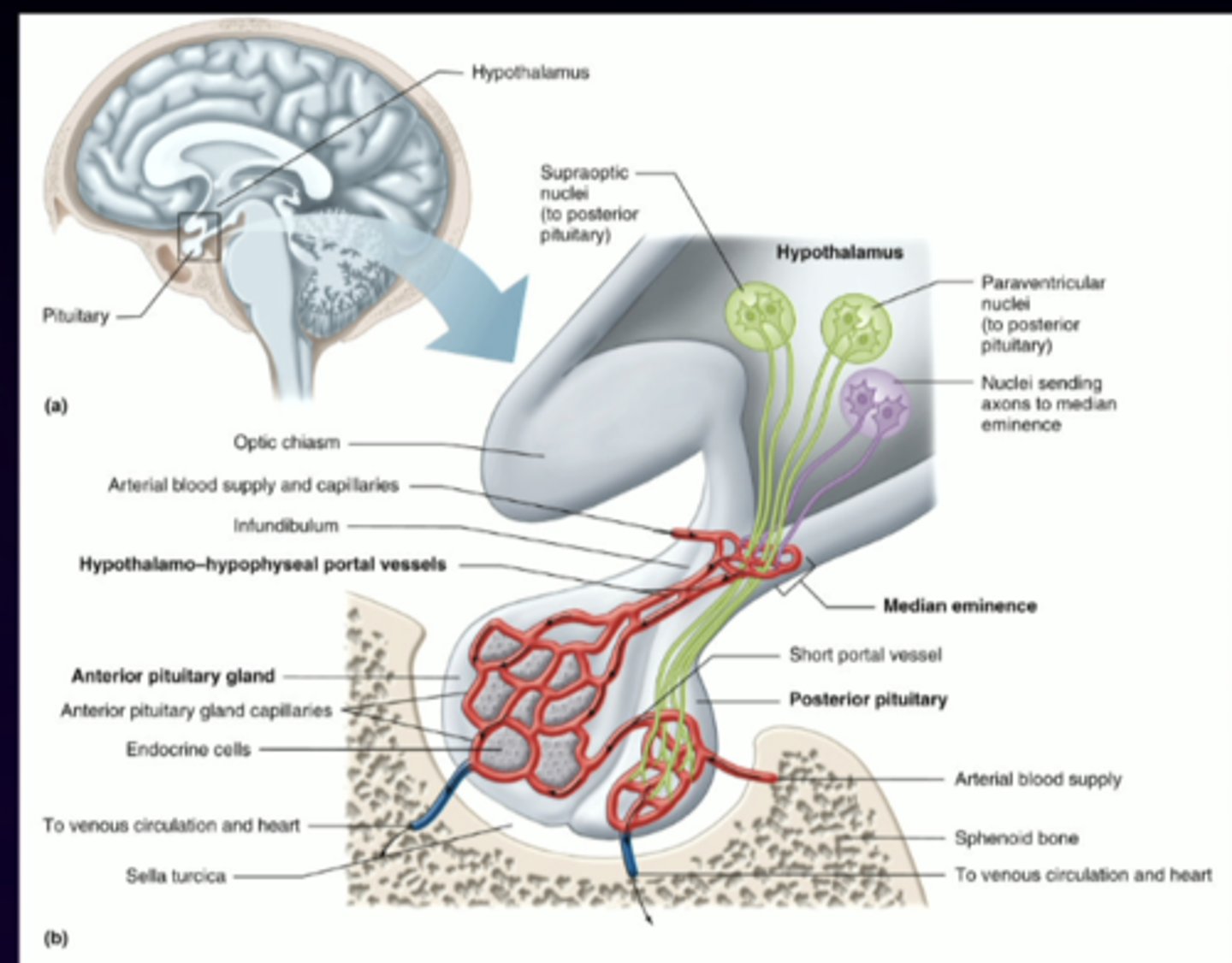
1. start at level of hypothalamus
2. one set of neurons that reach halfway down the stalk and release releasing hormone into median eminence (small capillary bed)
3. travels to anterior pituitary
4. stimulates true endocrine cell in anterior pituitary
5. stimulates again and releases "hormone 2" for the second chain of events
6. hormone 2 goes to the rest of the blood stream
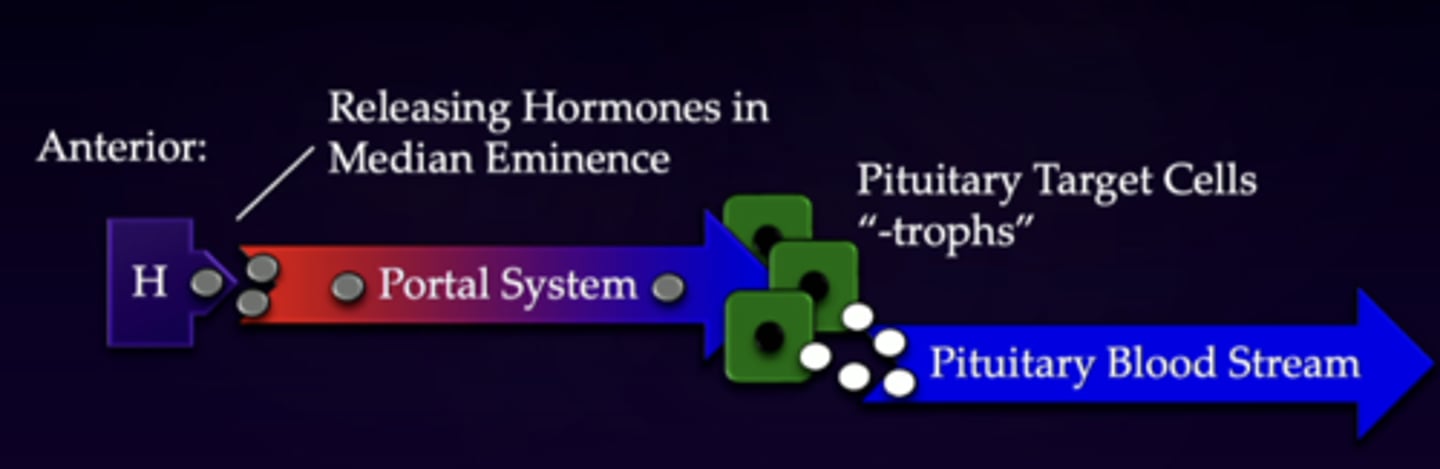
describe the anterior pituitary "2 chain event"
1. short, small neurons release hormone 1 into median eminence
2. traveling short distance to anterior pituitary
3. cells in anterior pituitary have characteristic terminology called -trophs (target cells from hormone 1)
4. those cells release another hormone for the second part of the chain
5. goes throughout the blood stream
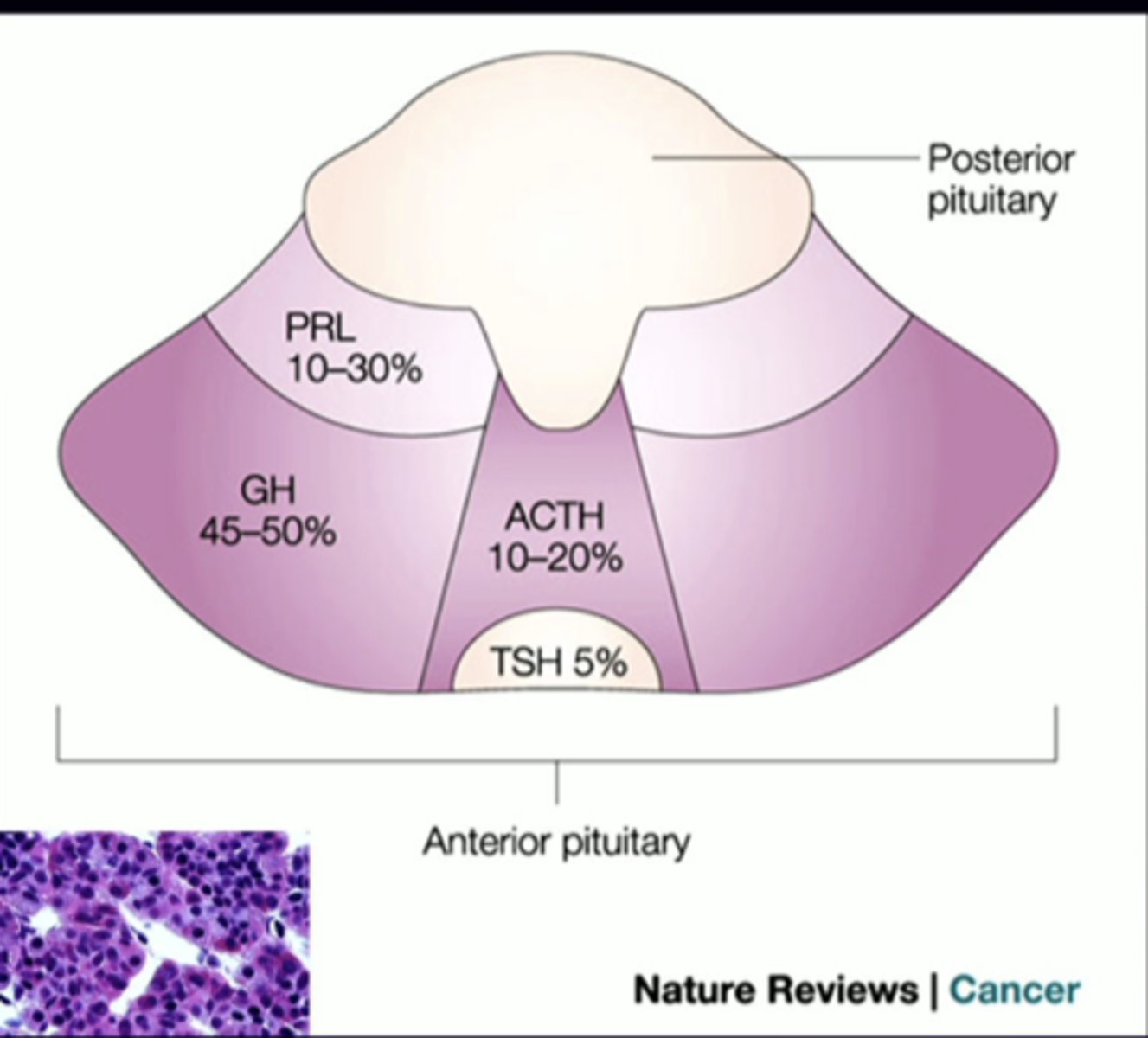
describe this imagine in relation to the anterior pituitary
PRL
anterior pituitary cell types (-trophs)
prolactin
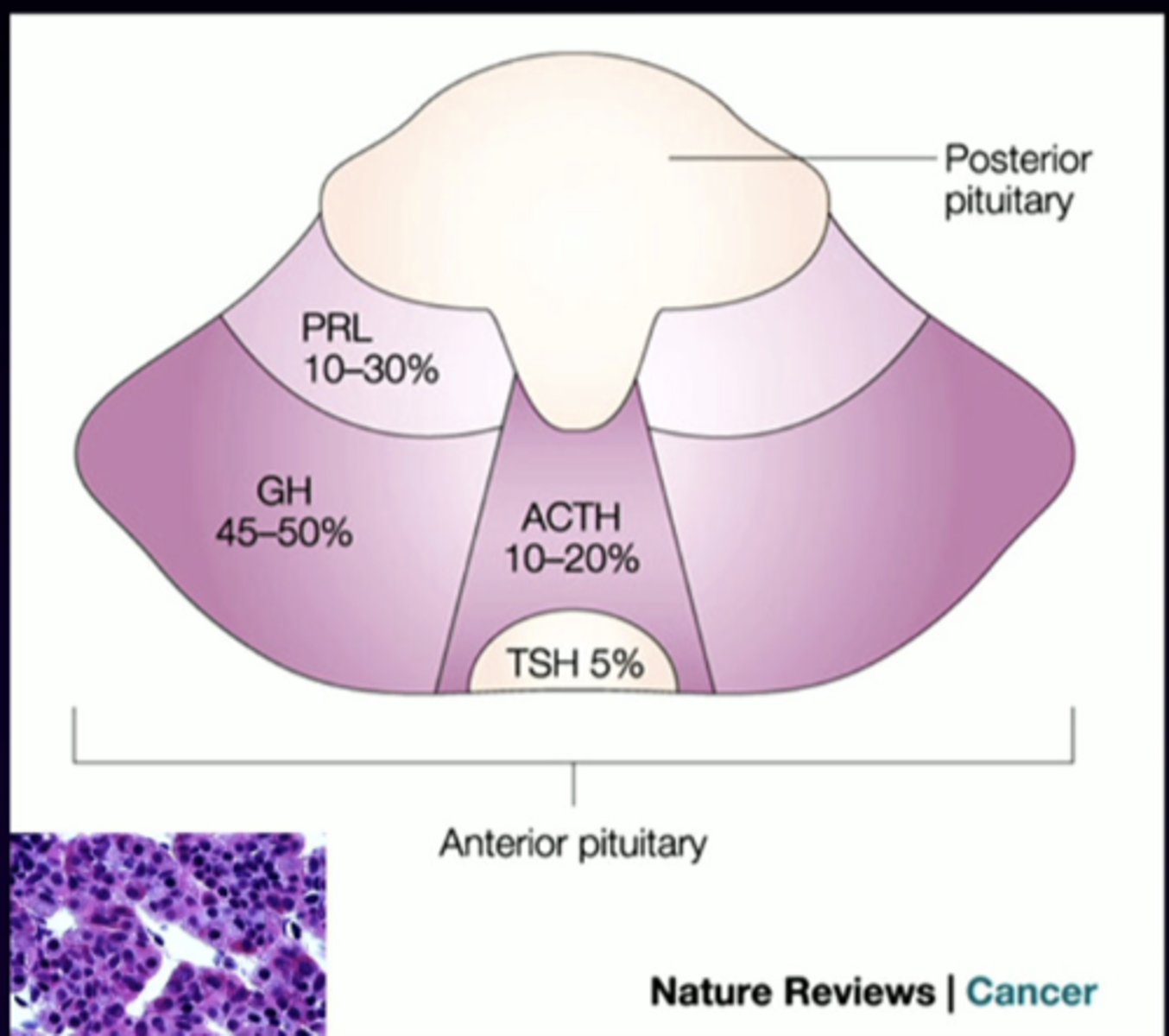
GH
anterior pituitary cell types (-trophs)
growth hormone
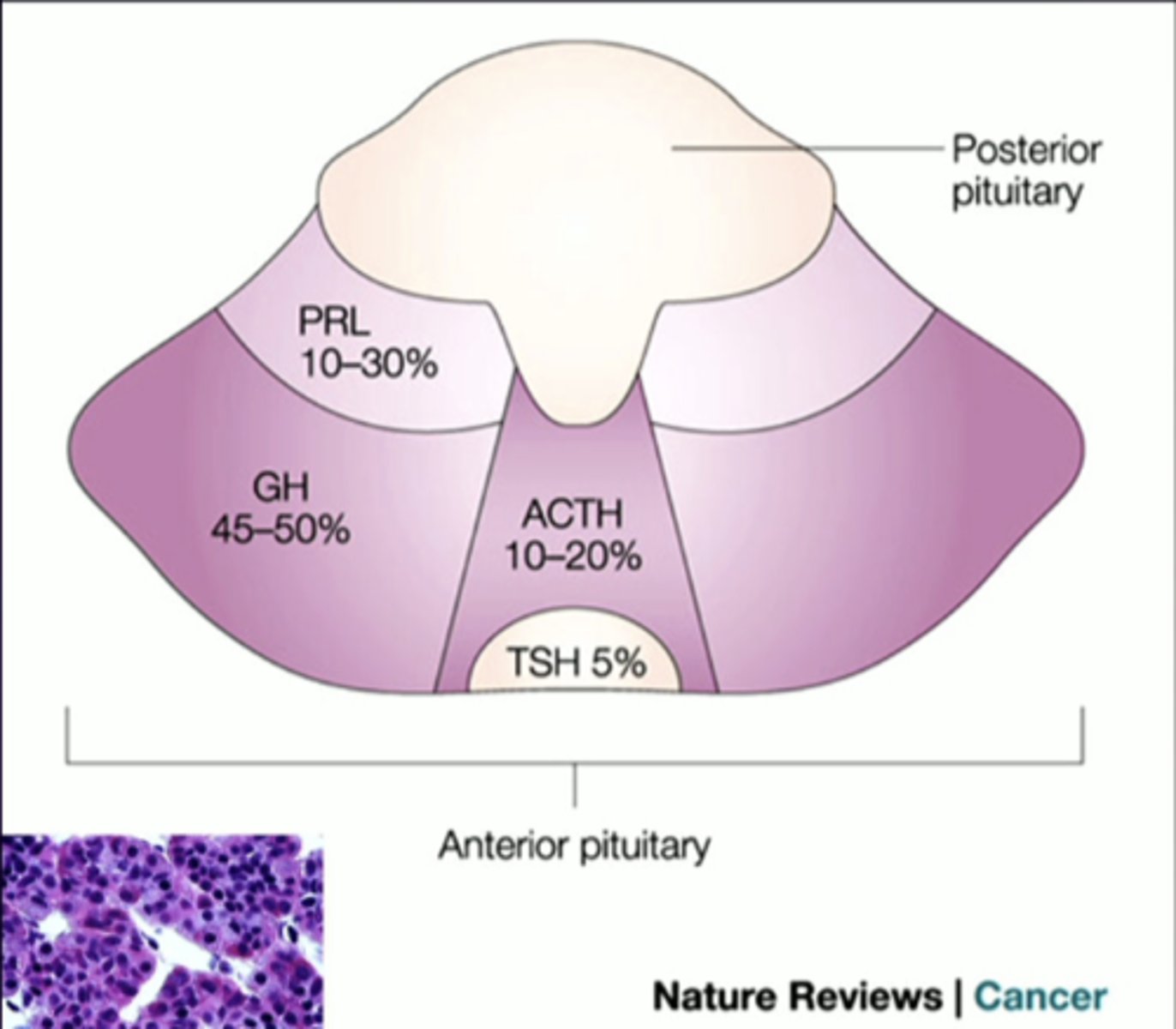
ACTH
anterior pituitary cell types (-trophs)
adrenocorticotropin
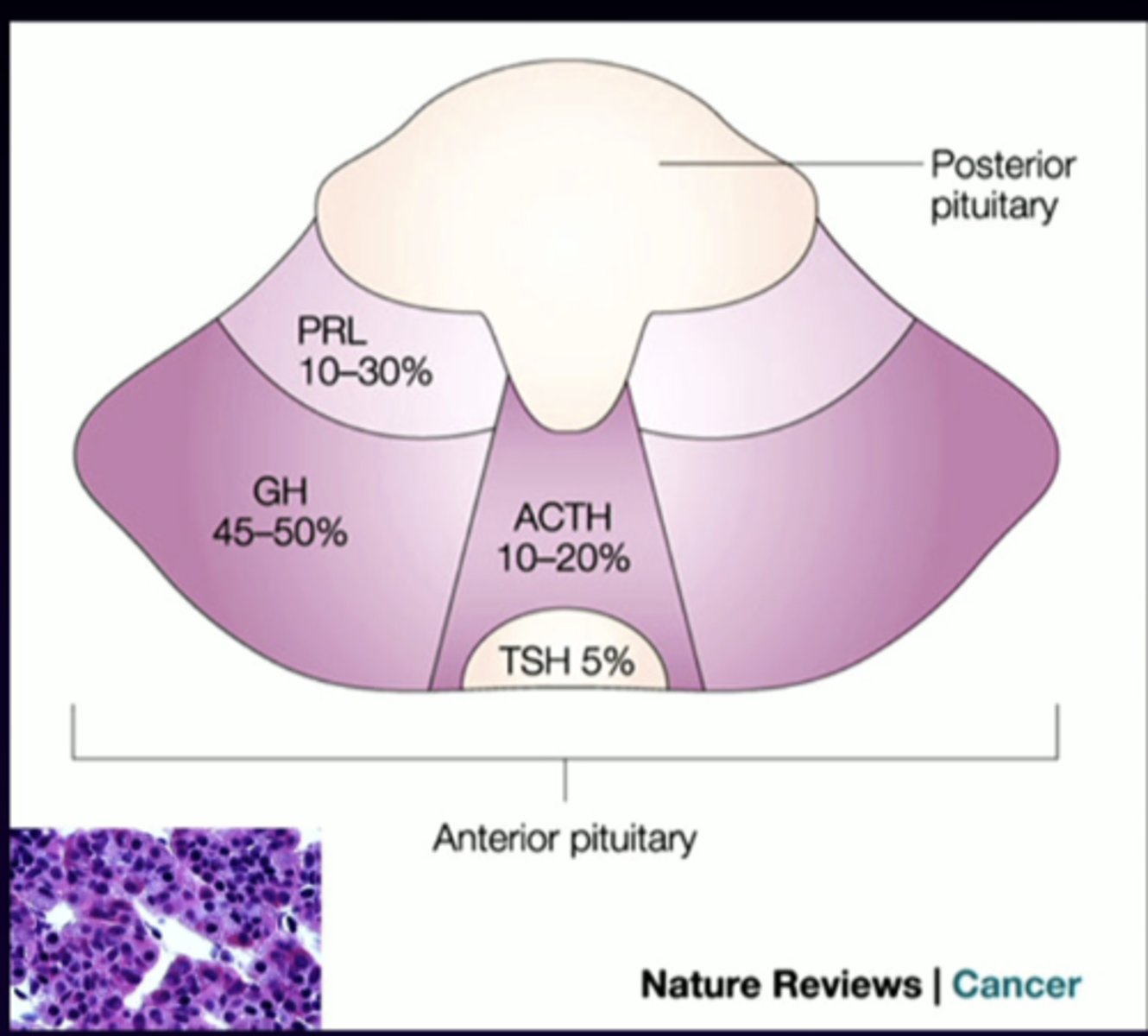
TSH
anterior pituitary cell types (-trophs)
thyroid-stimulating hormone
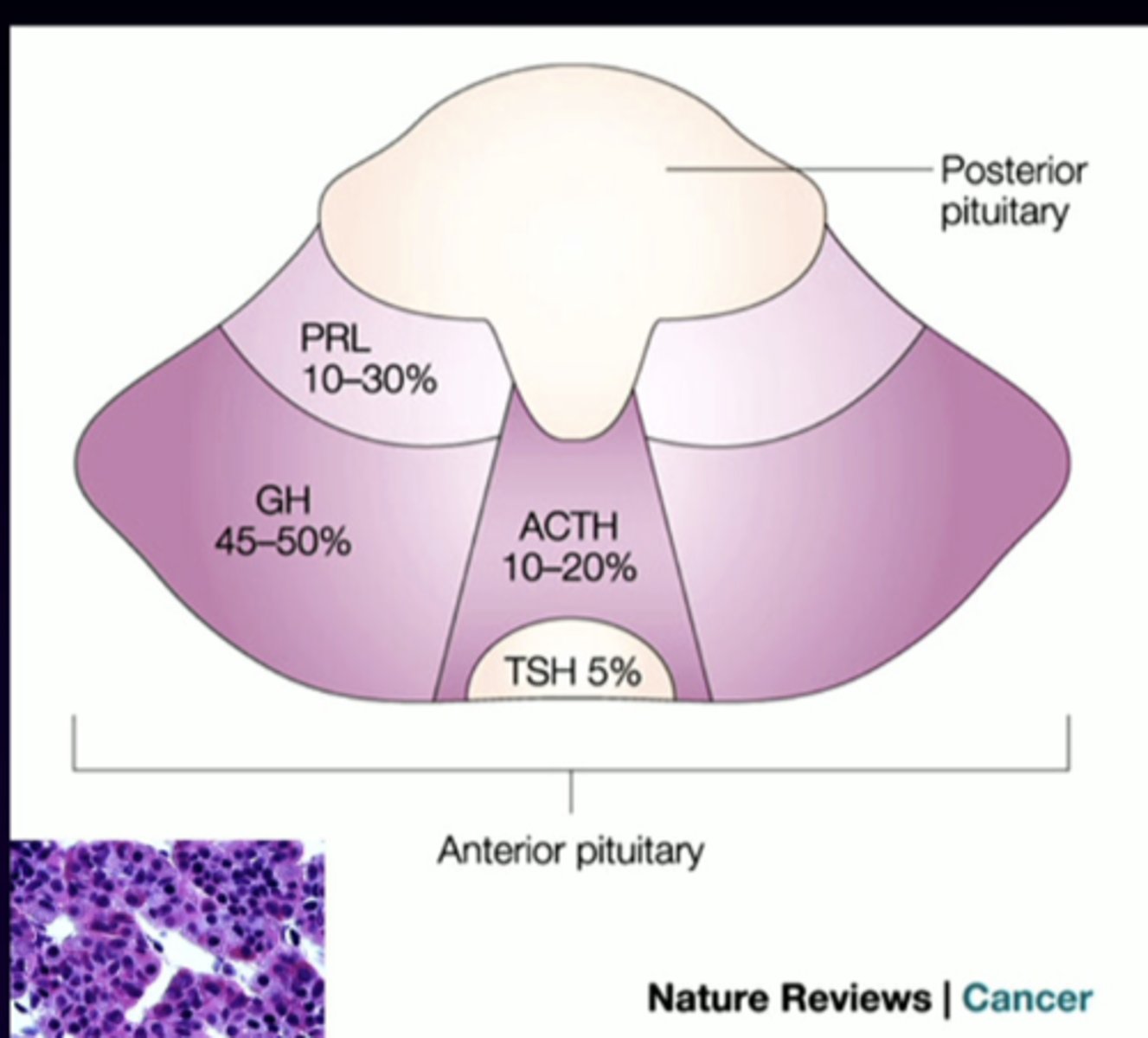
LH
anterior pituitary cell types (-trophs)
luteinizing hormone
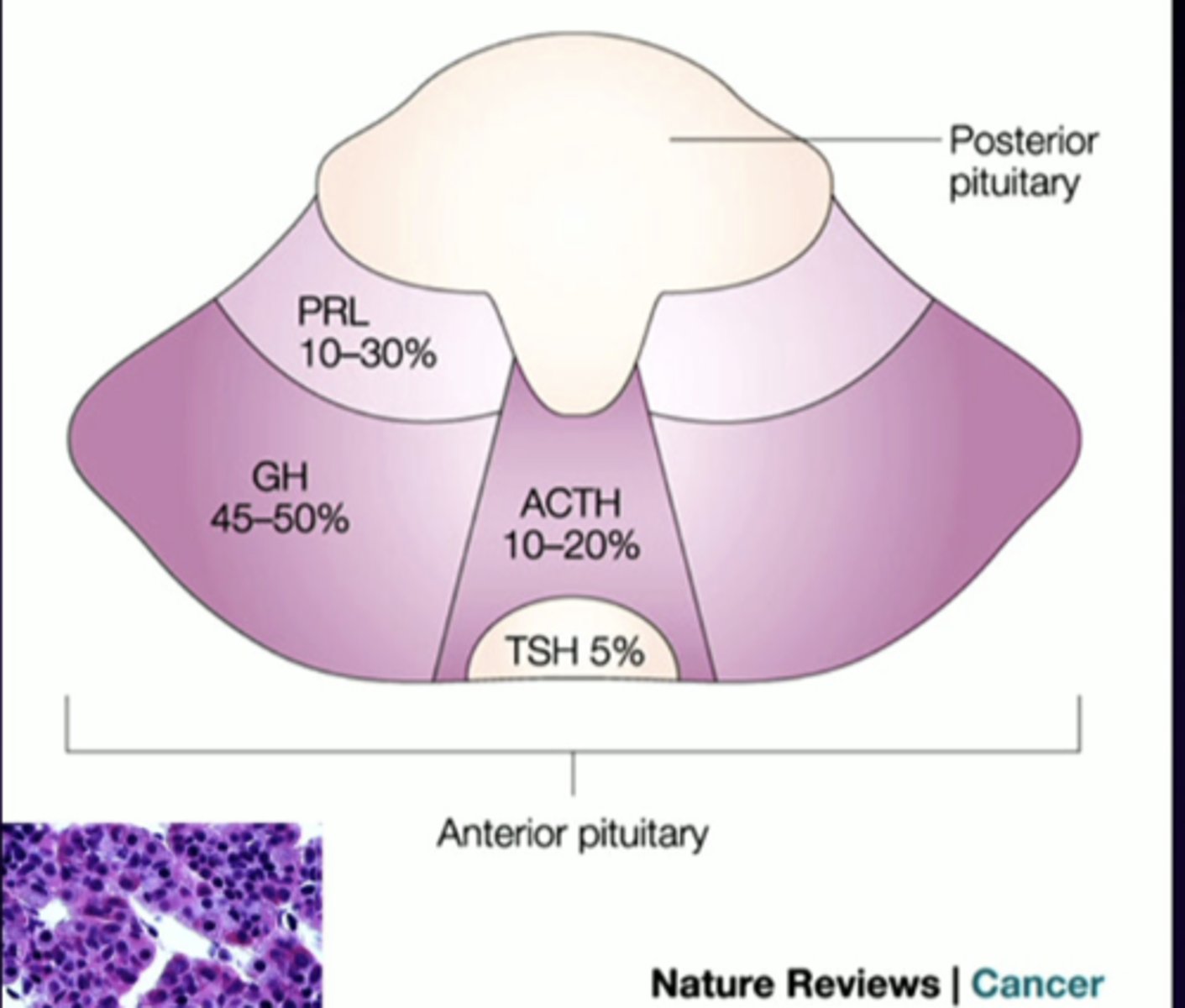
FSH
anterior pituitary cell types (-trophs)
follicle-stimulating hormone
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
secreted via gonadotrophs that are scattered throughout the anterior pituitary
corticotrophs (CRH)
includes ACTH and B-endorphin
thyrotrophs (TRH)
thyroid-stimulating hormone
gonadotroph (GnRH)
LH and FSH
somatotrophs (GHRH)
growth hormone
lactotrophs (dopamine)
prolactin (normally turned off)
releasing hormone
what does RH stand for
negative feedback loops are important because as you are activating these, you need to make sure you arent over-activating them
negative feedback loops are important because as you are activating these, you need to make sure you arent over activating them
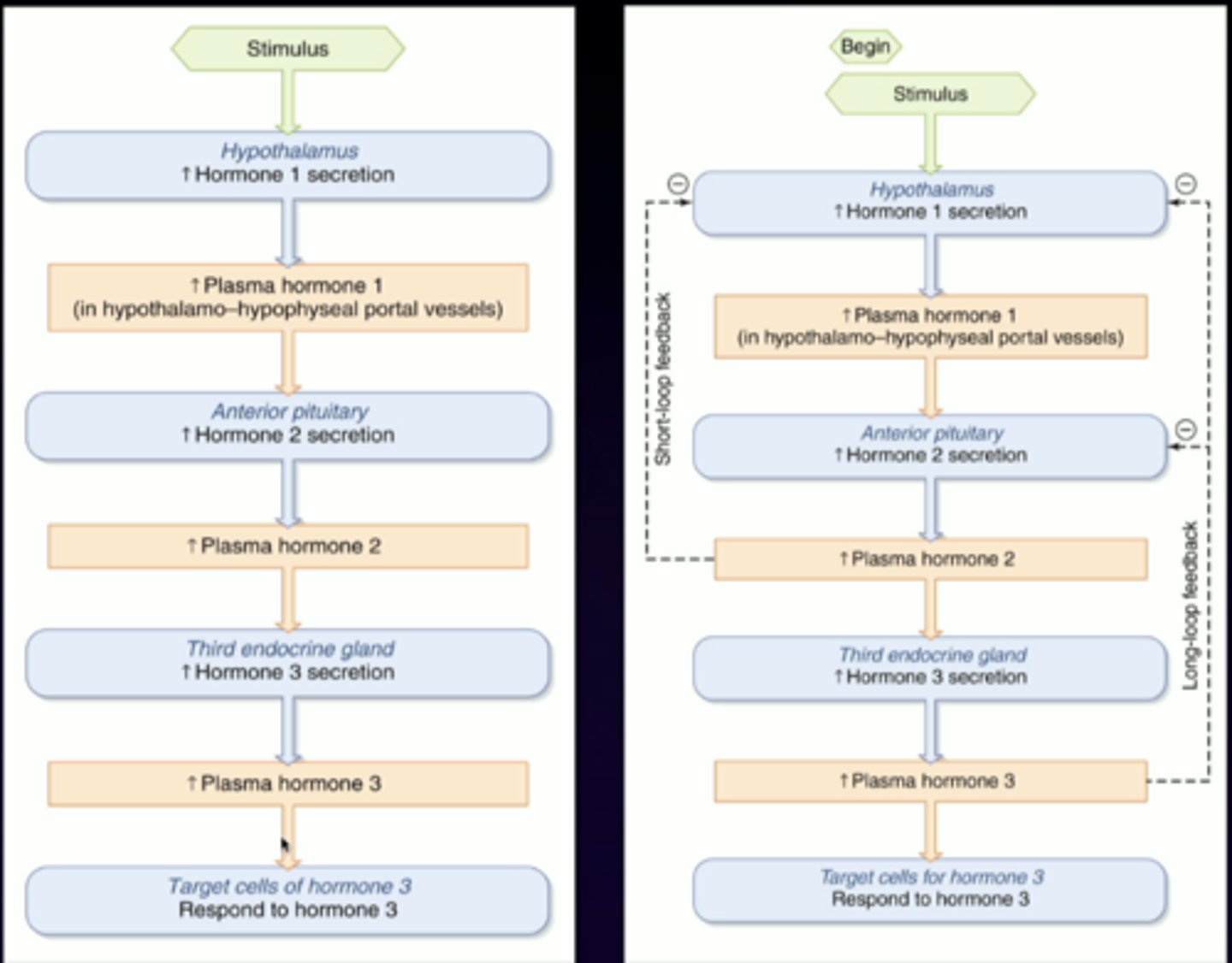
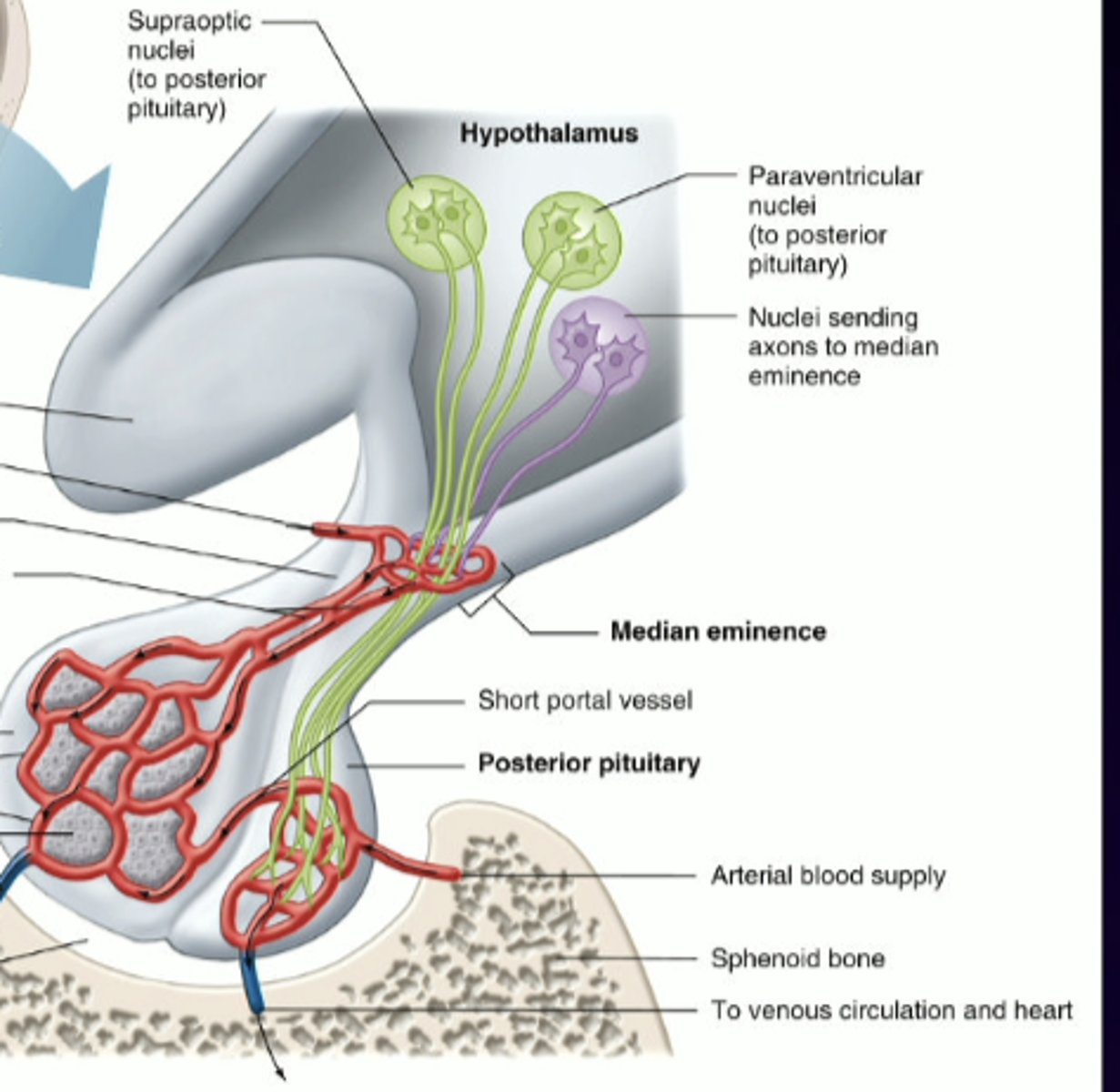
1. large, long, hypothalamic neurons releasing peptide hormones directly into the pituitary blood stream
describe this image in relation to the posterior pituitary

oxytocin and vasopressin
made in the hypothalamus and released in the posterior pituitary
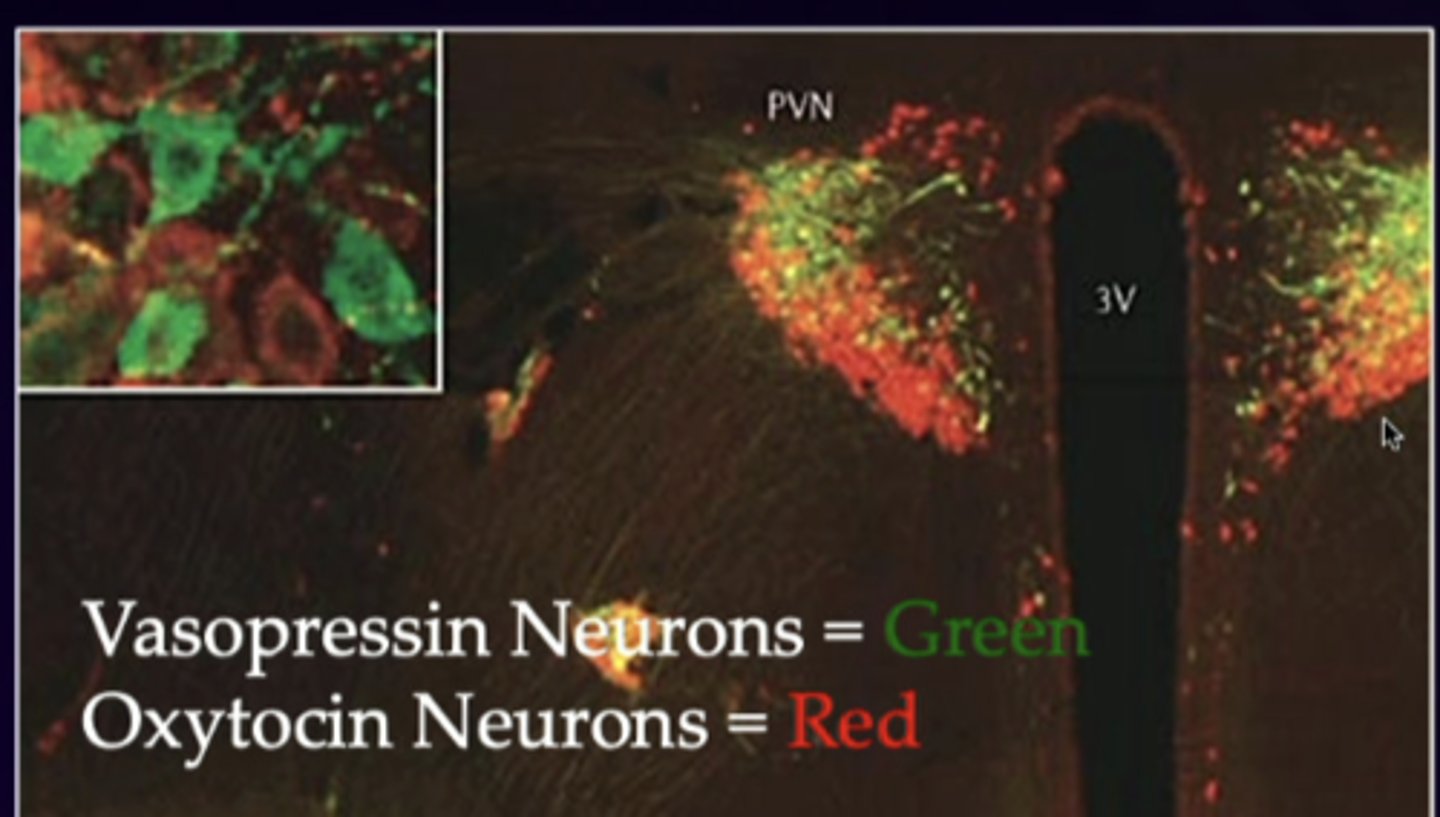
anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
arginine vesopressin (AVP) is equal to ...
uterus and mammary myoepithelial cells
what is the target organ/cell of oxytocin
V1R: smooth muscle cells
V2R: kidney collecting ducts
what is the target organ/cell of vasopressin
uterine contraction and milk ejection
what are the physiological effects of oxytocin
vasoconstriction and increased water retention (kidney collecting ducts)
what are the physiological effects of vasopressin
oxytocin
key part of birthing process and breastfeeding
the stretch of the cervix at the end of pregnancy
what is a mechanical stimuli that triggers oxytocin release in blood stream
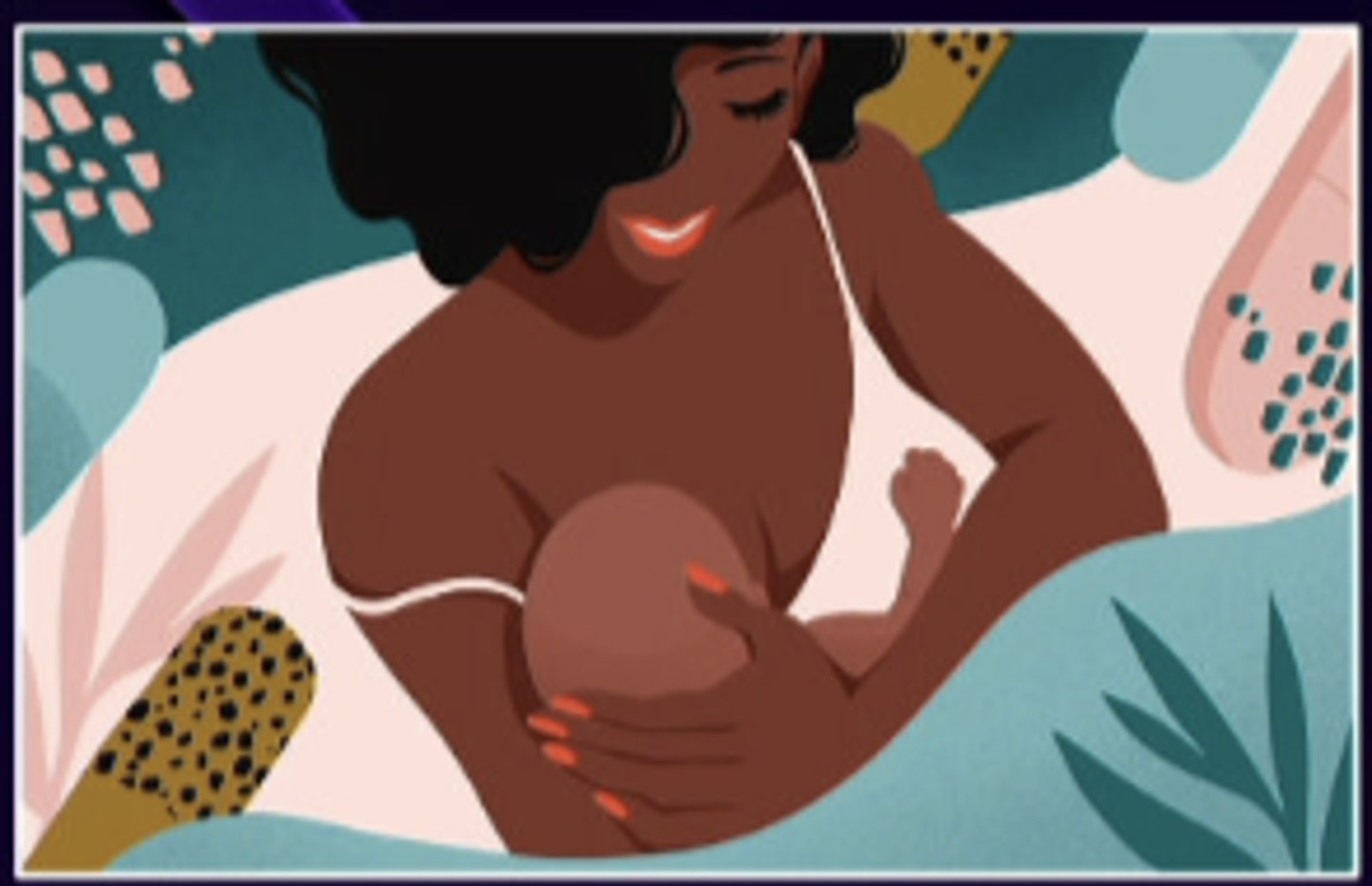
breastfeeding or breast pumping
what is a mechanical stimuli that triggers oxytocin release in blood stream

smooth muscle contraction
uterus and breast tissue
oxytocin increases...
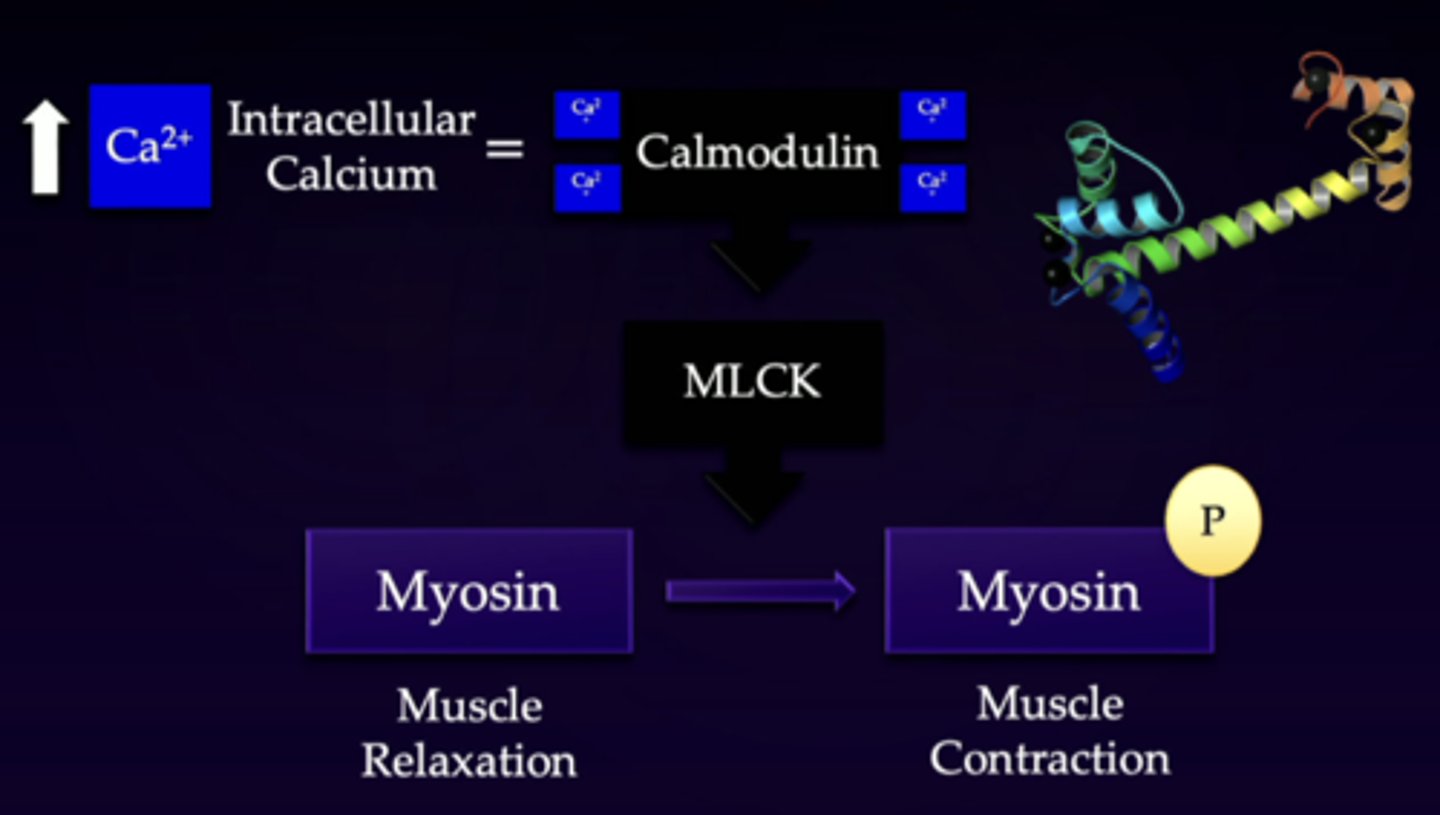
myosin light chain kinase
serves as a bridge between increased calcium levels and muscle contraction
kinase
going from inactive to active form through phosphorylation
1. intracellular calcium levels are being increased (need enough calcium for signaling)
2. if you have enough of this, you activate calmodulin
3. calmodulin then activates another protein in a MLCK chain (myosin light chain kinase)
4. then it makes the myosin active (muscle relaxation compared to muscle contraction)
what is this image showing
psychological modulation of oxytocin release
highly integrated with neuronal oxytocin signaling in central brain circuits

neurotransmitters
peptide hormones often act as .....
vasopressin release and vasoconstriction to increase blood pressure
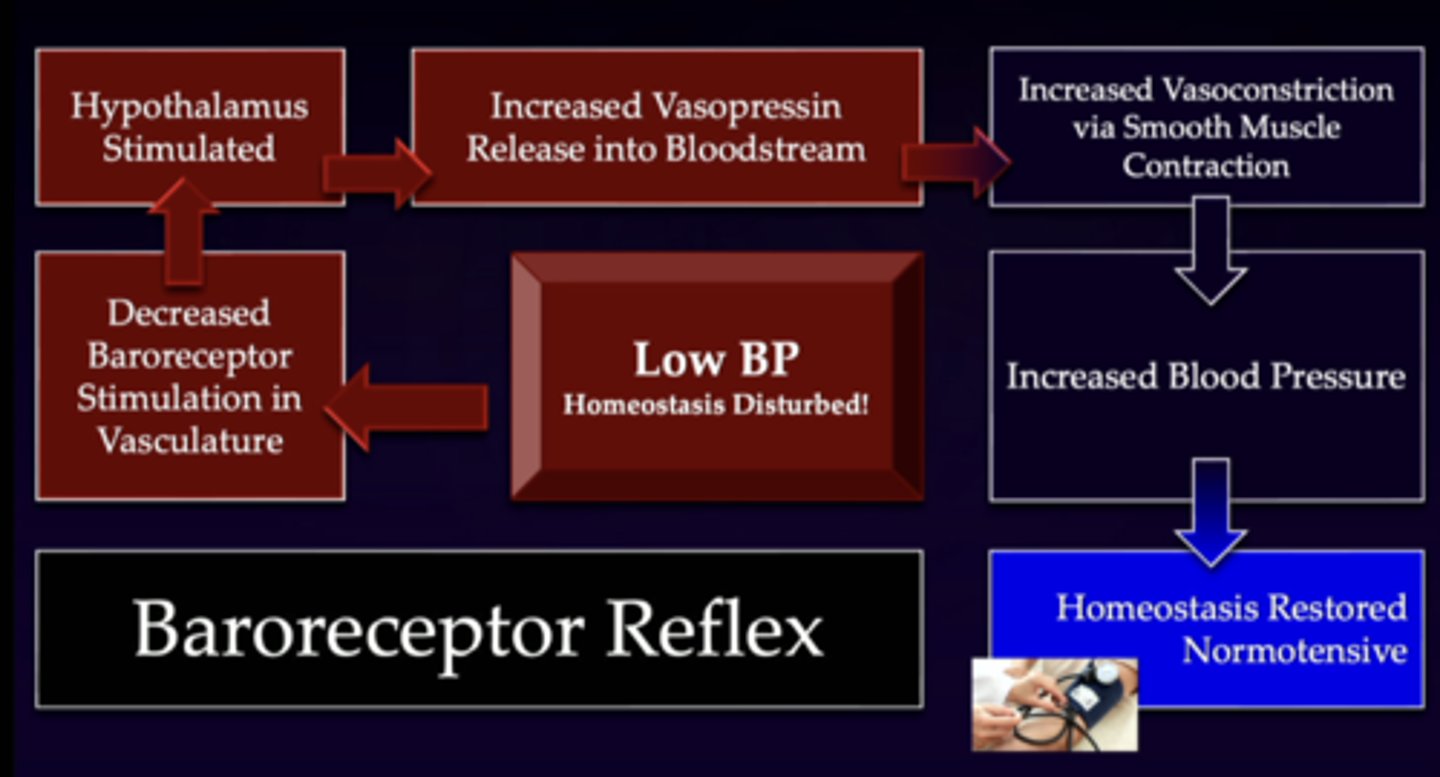
loss of vasculature baroreceptor stimulation leads to...
1. you have low blood pressure
2. baroreceptors sense this low blood pressure
3. baroreceptor sends signal to hypothalamus
4. hypothalamus releases vasopressin into blood stream through posterior pituitary system
5. through actions on V1A receptors, you have increases vasoconstriction and smooth muscle contraction
6. increase blood pressure
7. homeostasis is restored
***baroreceptor reflex
describe this image
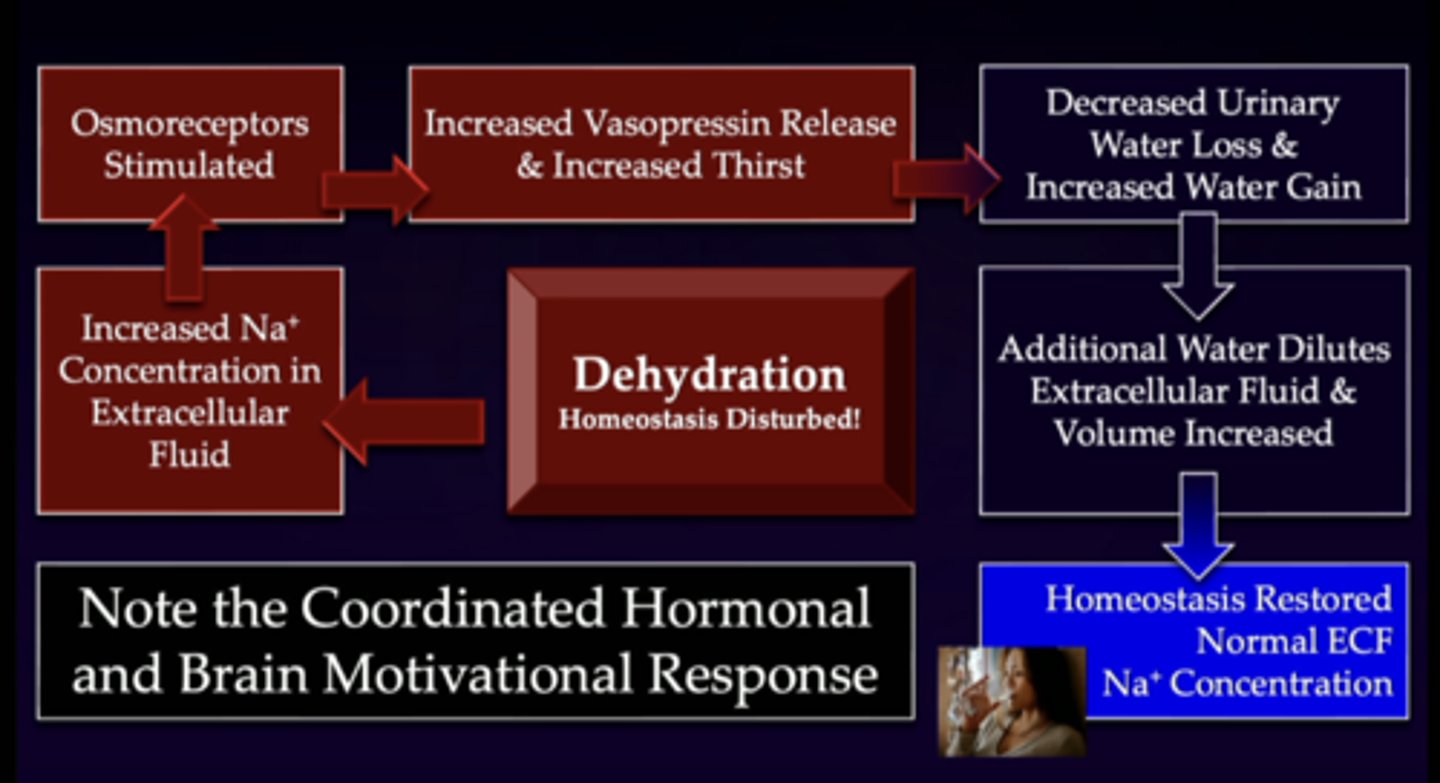
1. you are dehydrated
2. increase in sodium concentration in extracellular fluid
3. body senses it through this ^^
4. stimulates osmoreceptors
5. increases vasopressin release through posterior pituitary system
6. at the end of the day you have decreased urinary water loss and increased water gain
7. this additional water will dilute the ECF
8. homeostasis is restored
***note the coordinated hormonal and brain motivational response
describe this image
hypothalamic (brain) osmoreceptors
increased blood plasma osmolarity is detected by....
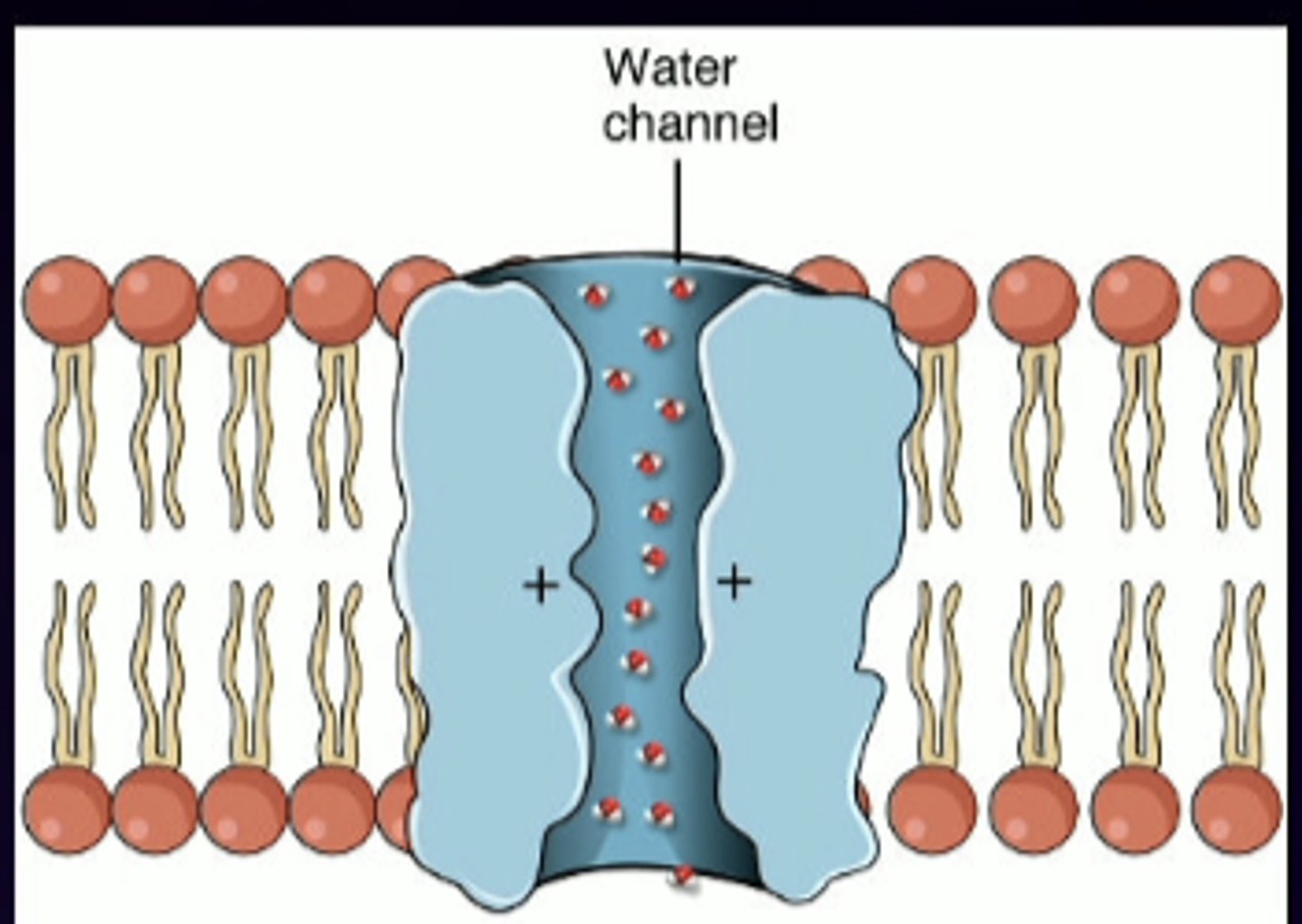
water channels
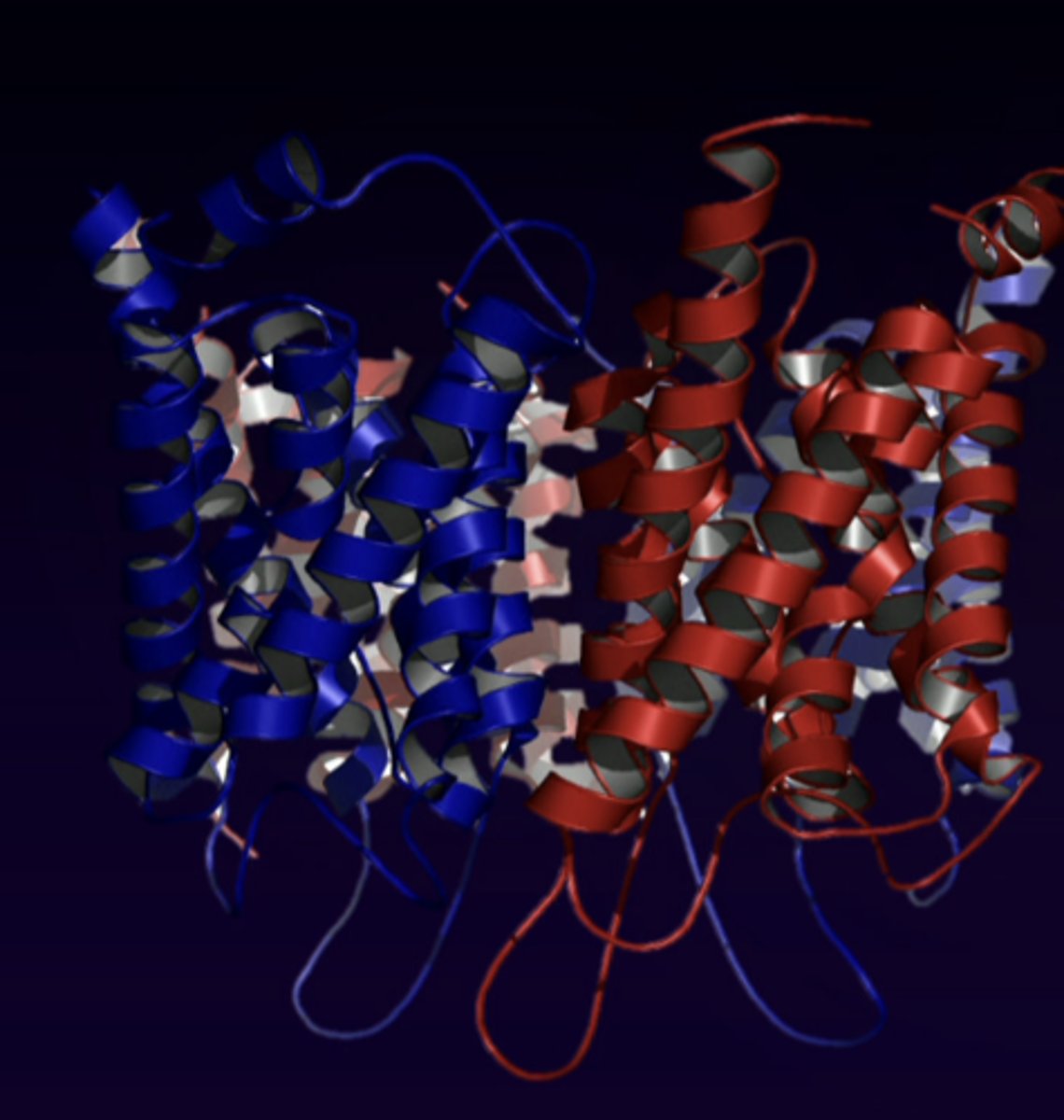
aquaporins are ...
retain water
vasopressin increases the levels of aquaporin in kidneys to...
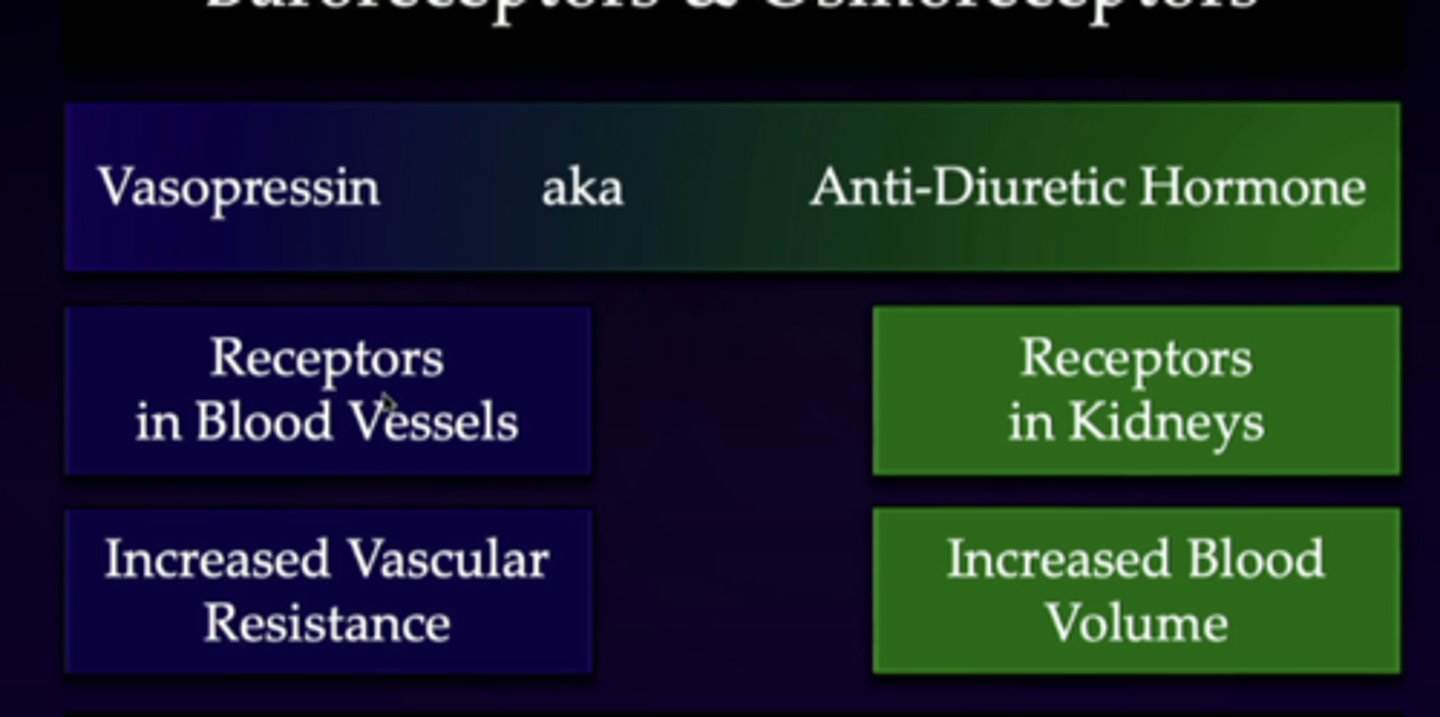
vasopressin
receptors in blood vessels
increased vascular resistance

anti-diuretic hormone
receptors in kidneys
increased blood volume
baroreceptors
located in vasculature
Osmoreceptors
located in hypothalamus
induction of labor via facilitation of uterine contractions
Pitocin is a synthetic version of the neuropeptide oxytocin, and thus can most readily be used for what purpose?