Clinical Skills Lecture Final
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
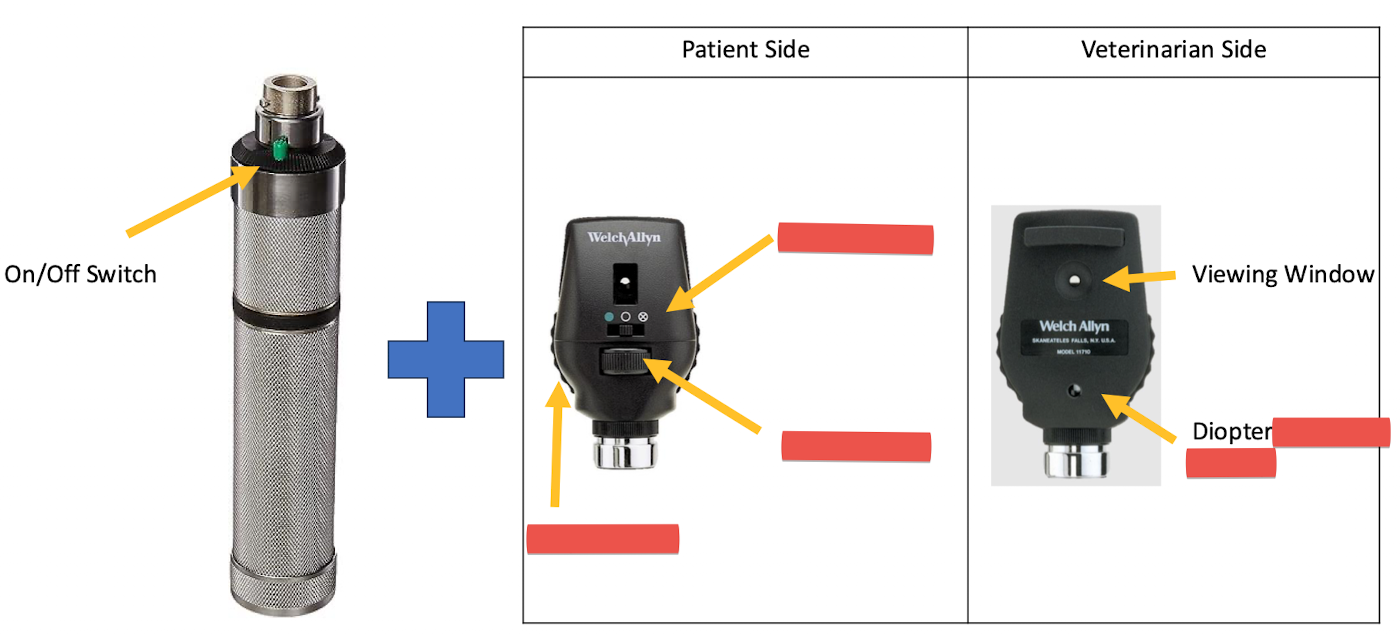
Name the equipment and label
Direct Opthalmoscope
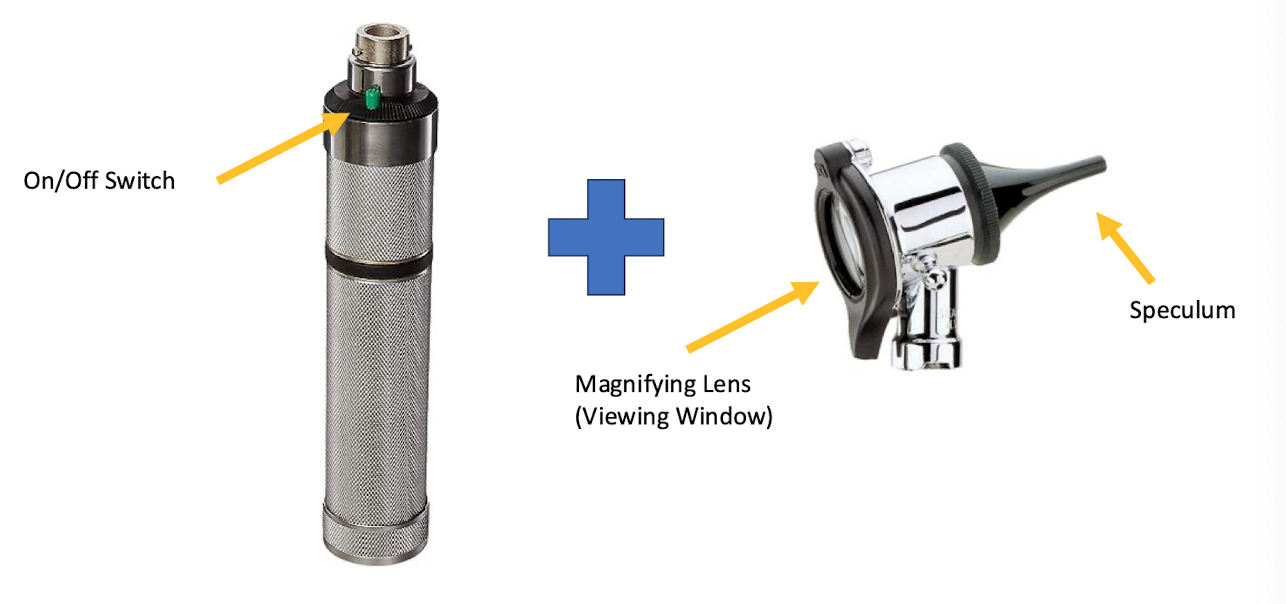

Name the piece of equipment
otoscope
______________:
• Is the animal alert or depressed?
• Is it responding to stimulus normally?
• What behavioural signals is the animal giving you
Mentation
Skin tent (________) = prolonged may
suggest dehydration
• Can be performed on top of head and over thorax
turgor
What is the normal heart rate for canines? Felines?
70-120bpm
100-200+bpm
Normal resp rate of dog?
10-30rpm
When listening to the lungs, you should listen to all lung fields for how many breaths?
2 breaths/location
what is a classical location for fleas/flea dirt?
base of tail
When should you get a rectal temp for small animals?
if ear temp is not taken or if concerned about precision
What is the normal canine temp? Feline?
canine: 37.9-39.9
feline: 38.1-39.2
What format should you use for medical records?
problem oriented medical records
true or false:
Problem oriented medical records are legal documents
True
What does SOAP stand for? What is in each?
Subjective data (signalment, history)
Objective data (physical exam)
Assessment (what does the data mean, create a problem list and rank severity, then rank ddx for each
Plan (for each problem, create a plan of action—diagnostic, therapeutic and client communication)
What does the acronym DAMNIT-VP stand for?

As new data is identified through the day, how is it added to the record?
via an addendum (record time, date and initials)
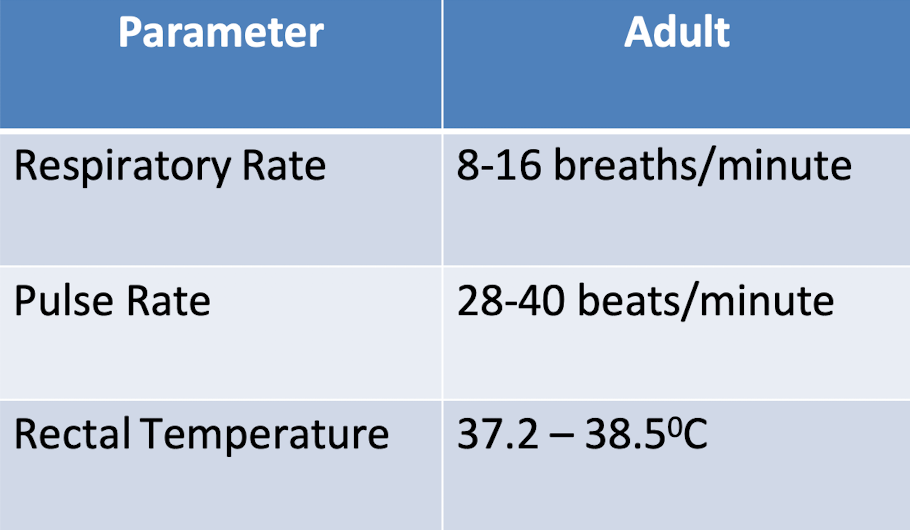
What is the normal ranges for TPR for an adult horse?
What side so you approach the horse?
from the left
Normal skin tent time in horses? Where can you do it?
<2s
neck or eyelid
Two areas to get an arterial pulse in horses?
Facial a.
Transverse facial a.
In the horse, what lymph nodes are the only palpable ones in normal state?
Mandibular nodes
___________________
masses of modified iridal tissue attached at the pupillary border. In herbivores only. Larger dorsally.
Corpora Nigra (or Granulae iridica)
In the equine exam, what two discrete structures are located at the dorsolateral aspect of the 3rd to 6th tracheal rings? Not visible in most horses. Palpable as firm movable structures.
Thyroid gland
True or false:
Normal jugular pulse of a horse extends 2/3 up the neck with the head in normal position.
False: 1/3
Which of the following structures can make it difficult to auscult the heart in equines?
Biceps
ribs
triceps
lung
triceps
Which of the following is ausculted on the right abdomen of the horse?
cecum
stomach
small colon
left dorsal colon
cecum
Average resp rate for a cow?
10-30 breaths per minute
Normal temp range for cow?
37.8-39.2
Average pulse rate for cow?
60-80b/min
How many rumen rolls should you hear in one minute in a cow?
1-2
In a cow, how many levels should you listen to lungs at?
3 levels for 2 resp cycles each
Two methods to check for abdominal pain in cows?
Wither’s pinch and xyphoid compression test
In a cow, how long is the ideal eyelid skin tent test for dehydration?
<3seconds
true or false: some lameness present as behaviour
true
What is one method to see if a behaviour is due to lameness or not?
2w trial of analgesia
What is the normal posture of a horse when standing?
should stand square in front and shift back and forth in the hindlimbs— any deviation from this is abnormal
When using equine hoof testers, an even squeeze must be applied only across the hoof wall and sole. Must be a _________ flinch/withdrawal
repeatable
True or false:
An equine should not move a way from the back palpation.
False: movement away is normal but excessive movement or evasion is not. Guarding or no movement is not normal.
What gait is used to look for symmetry in the equine lameness exam?
trot
What is the purpose of flexion tests during the equine dynamic exam? What joints are mainly flexed?
determine if this exacerbates the lameness.
hock and stifle
Does the equine head move up or down when the non-lame forelimb touches the ground?
down (often worse in a circle)
What is the main thing we look for when looking for hindlimb lameness?
hip hike: sometimes the lame leg has an upward motion of hip
What lameness scale?
Lameness is not perceptible under any circumstances.
0
Lameness scale?
Lameness is difficult to observe and is not consistently apparent, regardless of circumstances.
1
Lameness scale?
Lameness is consistently observable at a trot under all circumstances.
3
Lameness scale?
Lameness is obvious at a walk.
4
Lameness scale?
lameness is difficult to observe at a walk or when trotting in a straight line but apparent under certain circumstances.
2
Lameness scale?
lameness produces minimal weight bearing in motion and/or at rest or a complete inability to move.
5
At what point should you proceed with nerve or joint blocks during an equine lameness exam?
when lameness is consistent at a trot
What are 3 local blocks used to localize lower limb lameness?
palmar/plantar digital nerve block
abaxial nerve block
low 4 point
True or false:
it is always necessary to clip for equine nerve blocks
False: only in heavily feathered breeds
Which block would you use to block just the horse’s heal? You do this by blocking just above the collateral cartilages to avoid dorsal branches.
Palmar Plantar digital block
What block should be used to block the fetlock and below in equines?
Low 4 point
How long should you wait to evaluate perineural anesthesia in equines?
evaluate at 5-10 minutes and again at 15-20min
True or false:
Intra articular anesthesia needs aseptic preparation and injection.
True (5min with scrub, 90sec alcohol)
In birds, sitting very still, fluffed feathers, sitting on bottom of cage and eyes closed are all signs of _______.
stress
Visual exam of bird droppings is critical. What are the three normal components of bird droppings?
feces
urates (should always be white)
liquid urine
True or false: you should always obtain the weight of a bird during a physical.
true
Main thing to remember when handling small birds?
do not constrict the keel/thorax
__________
Located ventral and caudal to eye
Asymmetrical in nocturnal birds
ears
Where should you palpate to body condition score a bird?
keel (normal is 3/5)
What does a normal coelom feel like?
soft and slightly concave
Where is the uropygial/preen gland located?
just dorsal to tail feathers
What is the recommended humidity range for lab animals?
40-60%
What are two consequences of high humidity in lab animals? Low humidity?
High: resp problems, excessive soiling, fungus in cage
low: skin conditions like ring tail, resp conditions
When examining in reverse light cycle, use ________.
red lights
What is the average food and water consumption for mice?
eat 3-5g/d
water 6-7ml/d
Average weight of a lab mouse?
25-50g
How much should rats eat and drink per day?
Eat 5-6g/100g body weight
Drink 10-12ml/100g body weight
true or false: rodents are obligate nose breathers.
true
Average resp rate of lab rodent?
40-80bpm but can be 180-200 when distressed
What should you reference when assessing pain of rodent?
rat grimace scale where 2 is obvious and 0 is not present
When performing a physical exam on a rat/mouse, where should you start? Where should you spend a lot of time?
front to back
head
Red pigment (porphyrin) is normal in rat tears. When seen around eyes and nose, what are two things this indicates?
sign of stress and chromodacryorrhea
True or False:
Diarrhea in lab mice is not always significant.
False
What will you see when sexing a male mouse?
Open inguinal canals and see retractable testes and prominent scrotum.
male mice will have a _______________ found subcutaneously on ventrum cranial to prepuce.
coagulating gland
What is an indication of copulation in lab mice?
vaginal plug which contains secretions of vesicular gland and coagulating gland of male and remain in place for 10-15h.
What are three blood collection sites for lab animals?
lateral saphenous vein
lateral tail vein
submandibular vein
sheep kneeling down and eating may be a sign of ___________.
foot rot
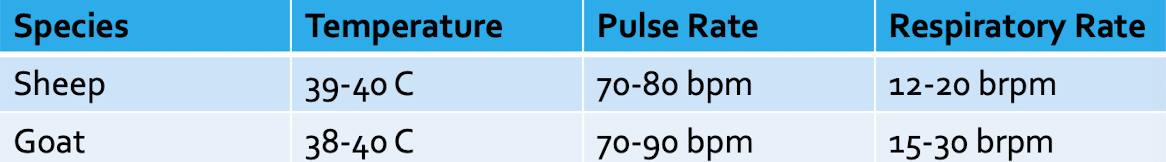
Average temp, pulse and resp rate for small ruminants?
True or false:
Small ruminants are stoic so noting even small abnormalities is necessary.
true
What are 2 defects in the abdominal wall that you should look for in a large animal?
abdominal wall ruptures and prepubic tendon rupture
Kicking, stretching, pawing and rolling can all be signs of _________ in large animals.
Abdominal pain
How often should you hear borborygmi?
Every 20-40sec
In a horse, what organs are you listening to in each of the 4 quadrants?
upper left: SI and large colon
lower left: large colon
upper right: cecum
right lower: large colon
_______________: rapid and firm push with fist to feel bump of solid, floating viscera on rebound.
Ballottement
___________: vigorously shake abdomen and listen with stethescope for splashing sounds.
Succussion
On a small animal’s abdomen, what can you palpate dorsally and caudally? Vetral and caudal?
colon/rectum
urinary bladder
Where can you palpate the intestines of a small animal?
mid abdomen
What kidney can you palpate in a small animal that is cranial to mid and dorsal to abdomen?
left kidney
Can you palpate the right kidney in small animals?
should be able to in cats, rarely in dogs
True or false:
You can easily be able to palpate the liver, stomach, pancreas, uterus, and lymph nodes.
false: all of these you can’t usually palpate
Abdominal effusion, fat, abdominal organ enlargment, and muscle laxity are all causes of ____________________.
abdominal distension
_____________ feels like a fluid wave.
abdominal effusions
In a large animal, what ICS do you auscultate when listening to the heart? What muscle is often in the way?
3rd-5th
triceps
What can you hear at the different areas for a cardiac auscultation?

What are the four heart sounds?
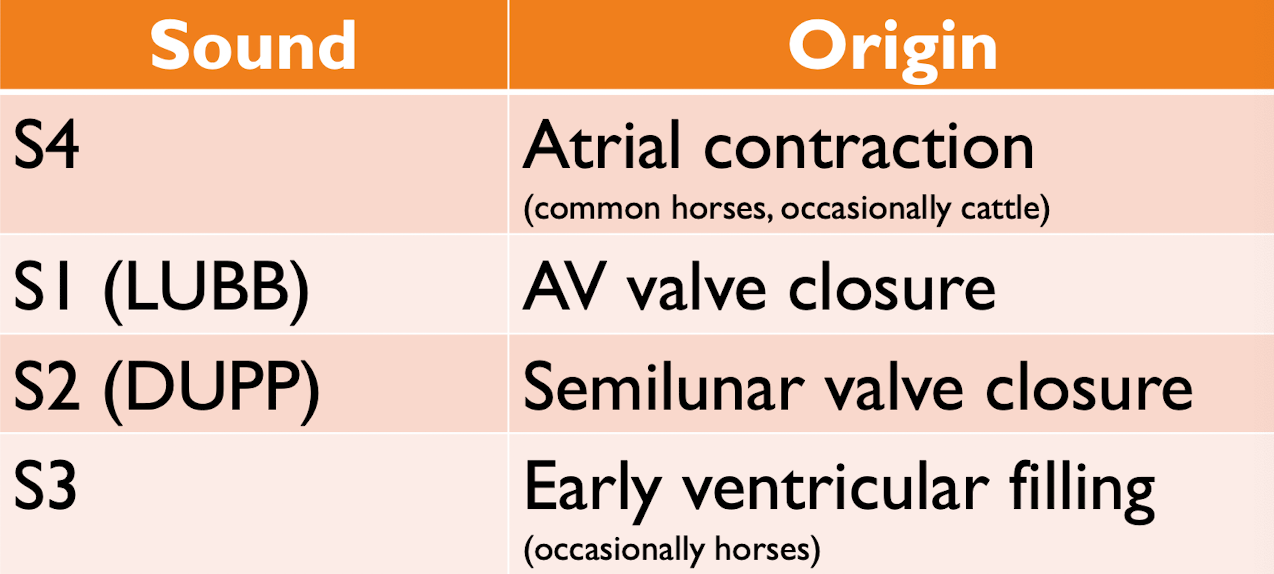
You should take the heart/pulse rates for atleast ___ seconds in large animals.
30
What could cause muffled heart sounds in large animals?
effusions
What could cause the abnormal heart sound of creaking new leather?
pericardial friction rubs