PDA IB Lecture 4: Introduction to Pharmacodynamics
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Pharmacodynamics
describe the effects of a drug on the body
- related to its mechanism(s) of action
- relationship between the drug concentration (or dose) and effect
Pharmacodynamics are typically described in ___________ terms in order to determine ____________________________ for patients
- quantitative terms
- appropriate dose ranges
For a drug to elicit a specific effect, the drug has to...
bind to its target/receptor
Drug
substance that interacts with a biological system/receptor to produce a physiologic effect
T/F: Most drugs are chemicals, but not all chemicals are drugs
TRUE
Agonist are drugs that....
mimic physiological activity
Antagonists have no ______________, but block an __________
- stimulatory action
- agonist
Receptor
macromolecule or component of a cell or organism that interacts with drug/ligand to initiate a chain of events leading to the drug's observed effects
Ligands
molecules that bind to a receptor (drugs, hormones, neurotransmitters)
What forms the most important class of receptors?
Proteins
(not ALL dug targets are proteins)
Can other cellular constituents server as therapeutic agents?
Yes, not every drug target is a protein or receptor
(ex: regulatory proteins, enzymes, transport proteins, structural proteins)
Actions of Drugs NOT Mediated by Receptors****
- neutralization of gastric acid by base
- increasing osmolarity of fluids
- cholesterol binding resins
- EDTA chelating agent
Some drugs act by simple mechanisms related to their....
chemical or physical properties
T/F: All drug targets are a protein/receptor
FALSE
not all
Receptors are specialized on transmission of information because they.... (2)
- recognize and bind to their ligand
- this binding propagates its regulatory signal into target cell
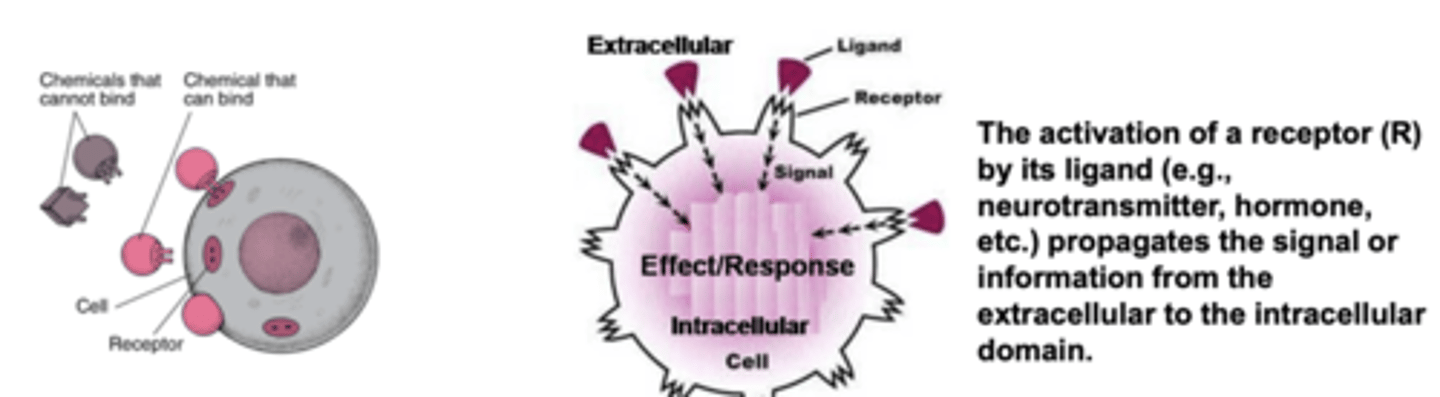
Drug-Receptor Interaction:
- The binding can be ________ and ___________
- A ligand may _________ or _________ a receptor
- Activation may __________ or ________ a particular cell function
- Each ligand may interact with __________________
- specific and reversible
- activate or inactivate
- increase or decrease
- multiple receptor subtypes
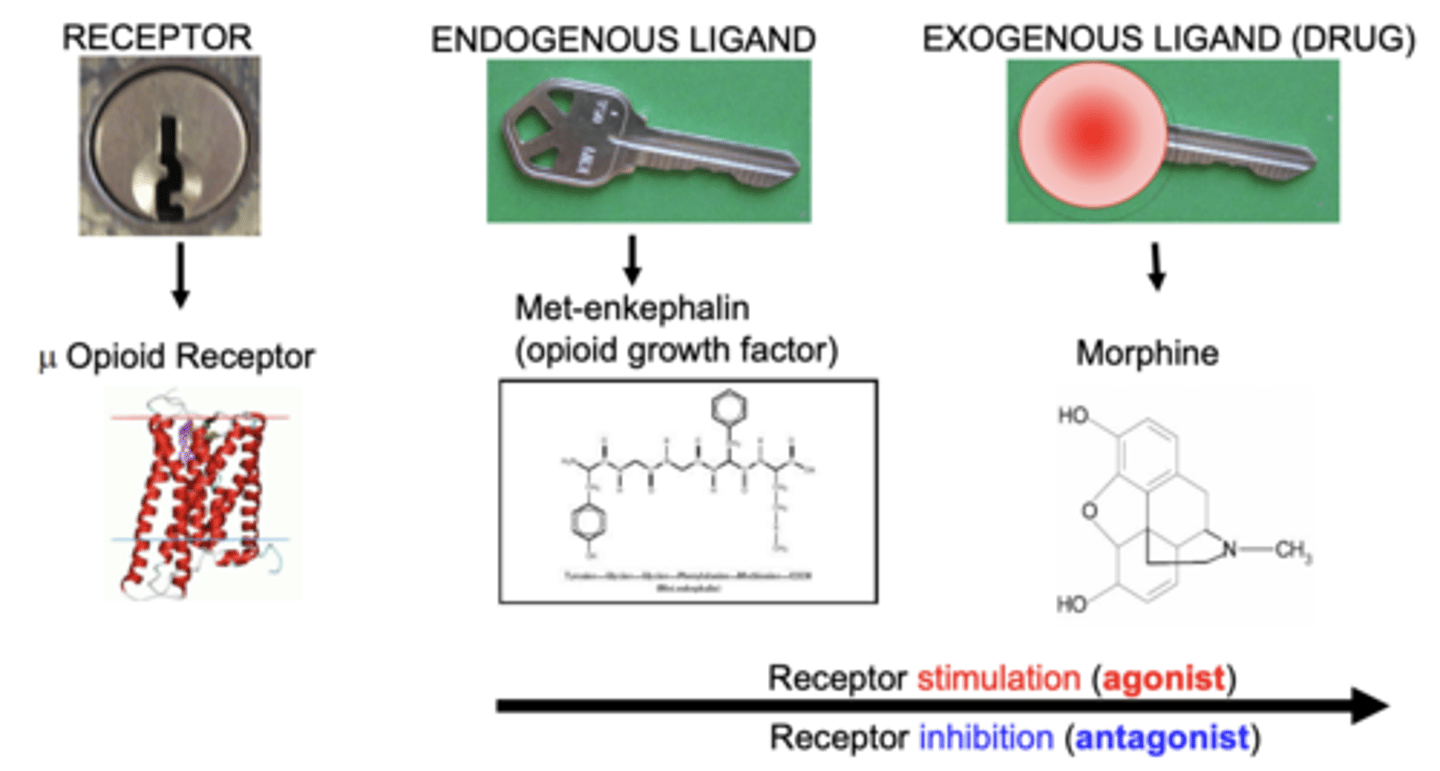
Receptor stimulation
agonist
Receptor inhibition
antagonist
Reversible drug-receptor interaction (2)
- most interactions are reversible between a drug and target
- drug disengages after a while and the receptor or enzyme resumes normal function
Irreversible drug-receptor interaction (3)
- after binding, the ligand reacts with the functional groups of the receptor
- ligand becomes covalently bound to receptor
- synthesis of new receptor protein may be needed to generate a receptor free of an irreversible blocker
The binding of a drug to a receptor is determined by the following forces: (5)
- Hydrogen bonds
- Ionic bonds
- Van der Waals forces
- Covalent bonds
- Hydrophobic interactions
Which binding forces are reversible? (4)***
- hydrogen bonds
- ionic bonds
- van der waals forces
- hydrophobic interactions
Which binding forces are irreversible?***
- covalent bonds
Receptor Properties (5)***
- binding affinity and intrinsic activity
- selectivity
- up- and down-regulation
- clustering
- desensitization
Binding affinity
A measure of the attraction force between the receptor and the drug
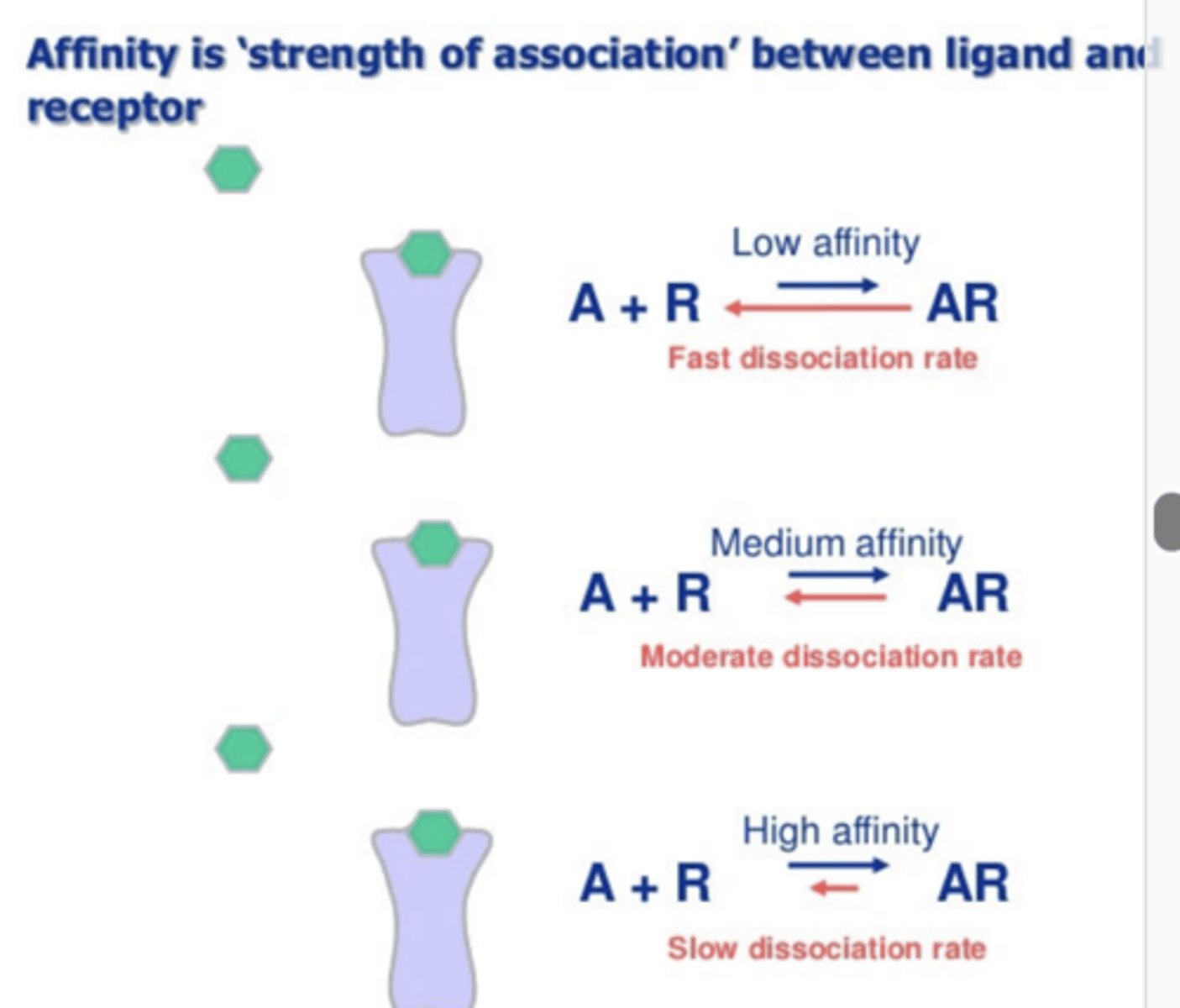
What does the affinity of a drug for a receptor determine?
the concentration required to form a significant number of drug-receptor complexes, and ultimately the magnitude of the response
- High-affinity ligand binding results from...
- Results in.....
greater attractive forces between the ligand and its receptor
- results in a higher occupancy of the receptor by its ligand compared to low-affinity ligands
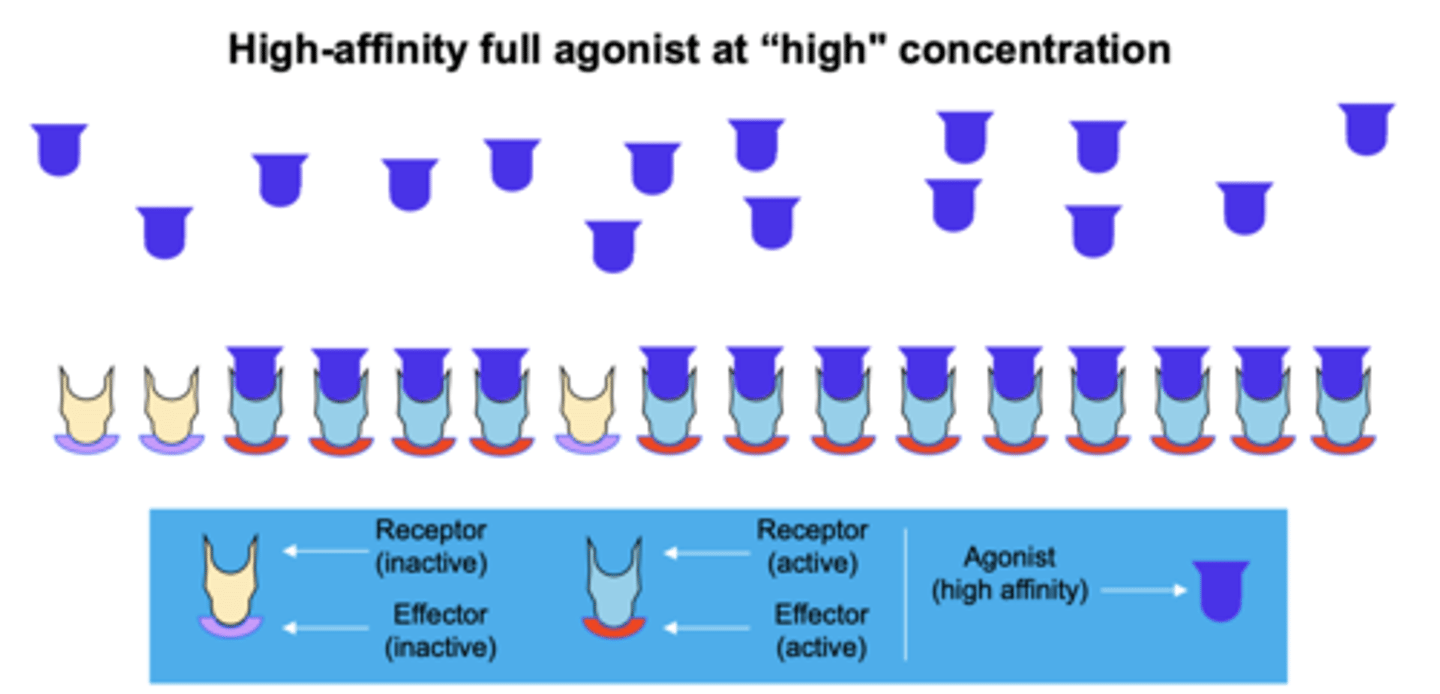
- Low-affinity ligand binding involves less....
- Results in...
- less attractive force
- results in a lower occupancy of the receptor by its ligand compared to high-affinity ligand
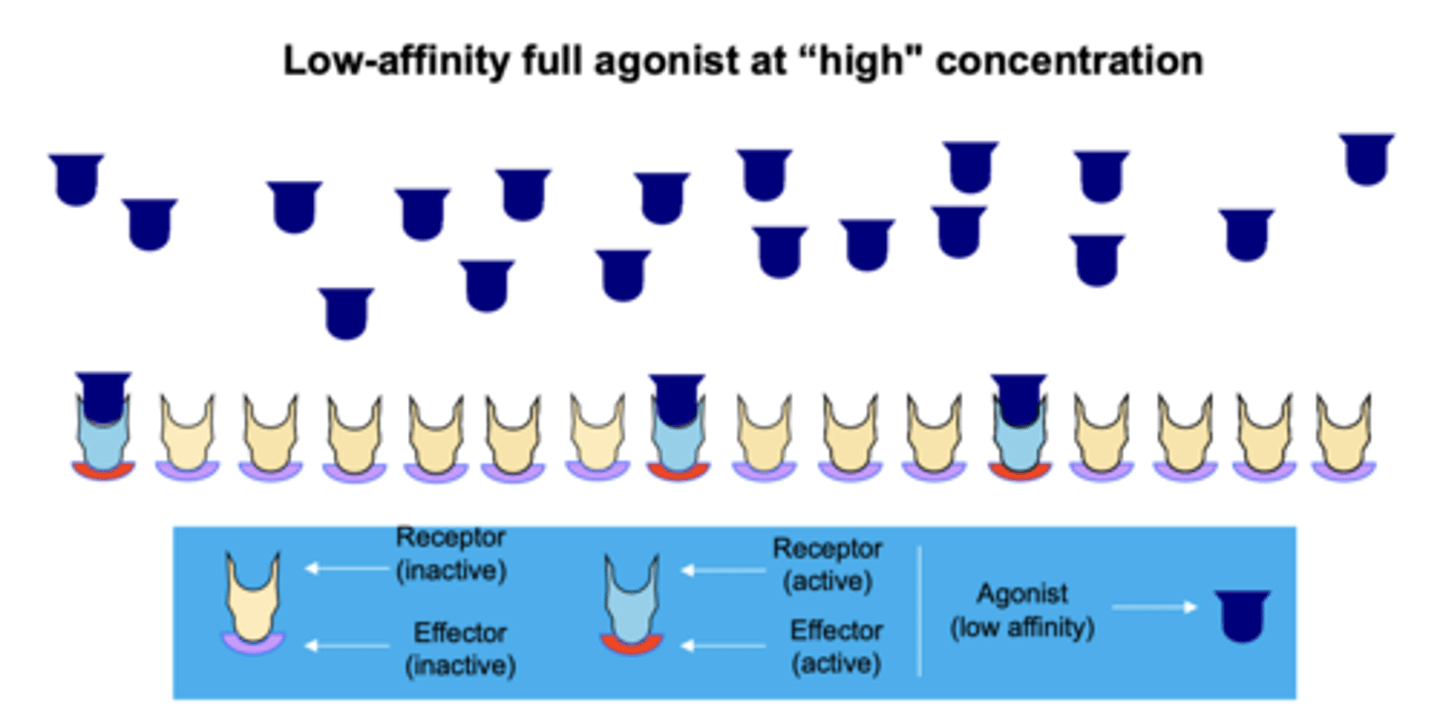
Intrinsic activity (IA) and efficacy refer to...
the ability of a drug-receptor complex to produce a maximum functional response
Intrinsic activity is a measure of...
the ability of a drug to generate an effect
A drug's action is affected by... (2)
- the degree of attraction (affinity) with the receptor
- ability to produce an effect
Drugs vary in their __________ and ________________
affinity and intrinsic activity
Agonists must have both......
great affinity and intrinsic activity
(must bind to their receptors, and be capable of producing effect in target area)
Antagonists must ________________, but they have little or no _______________
- bind effectively
- intrinsic activity
A full agonist would have an intrinsic activity of:
1
An antagonist would have an intrinsic activity of:
0
Partial agonists would have an intrinsic activity of:
in between (1 and 0)
Receptor selectivity refers to the....
extent/ability to which a drug binds with a particular receptor (target) rather than others
Selectivity is a measure of....
the ability of the drug to solely interact with its intended target
What features of a drug determine whether it will bind to a particular receptor?
the molecular features of a drug (size, shape, hydrophobicity, flexibility, electrical charge)
A drug's selectivity can often be explained by....
how selectively it attaches to receptors
Selective ligands tend to bind to...
very limited kinds of receptors
Non-selective ligands bind to...
several types of receptors
- tend to have more adverse effects
Do selective ligands or non-selective ligands tend to have more adverse effects?
non-selective ligands tend to have more adverse effects
What is the site of drug action determined by?
What does it not necessarily depend on?
location and functional capacity of its receptors
- does not necessarily depend on drug distribution
Widespread receptors have....
widespread effect
Localized receptors have...
localized effect
Morphine - opioid receptor agonist sites (4)
brain, spinal cord, peripheral neurons, and digestive tract
Digoxin (Na+, K+m ATPase inhibitor) sites (2)
myelinated axons, brain
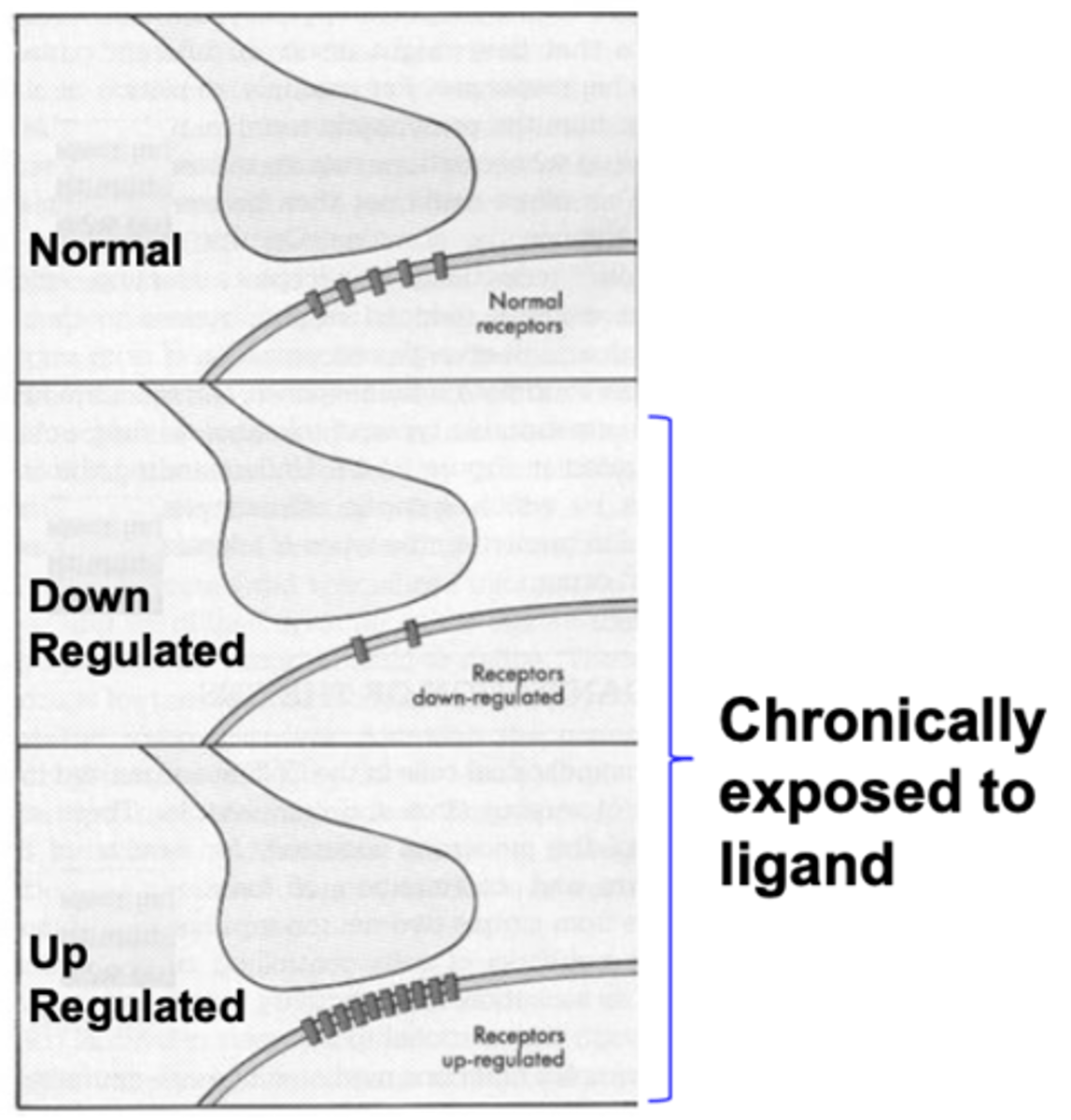
What is receptor density?
What can it be modified by?
- number of receptors per area
- can be modified by the ligand/drug-induced mechanisms of up or down regulation
Up-regulation
increase the number of receptors
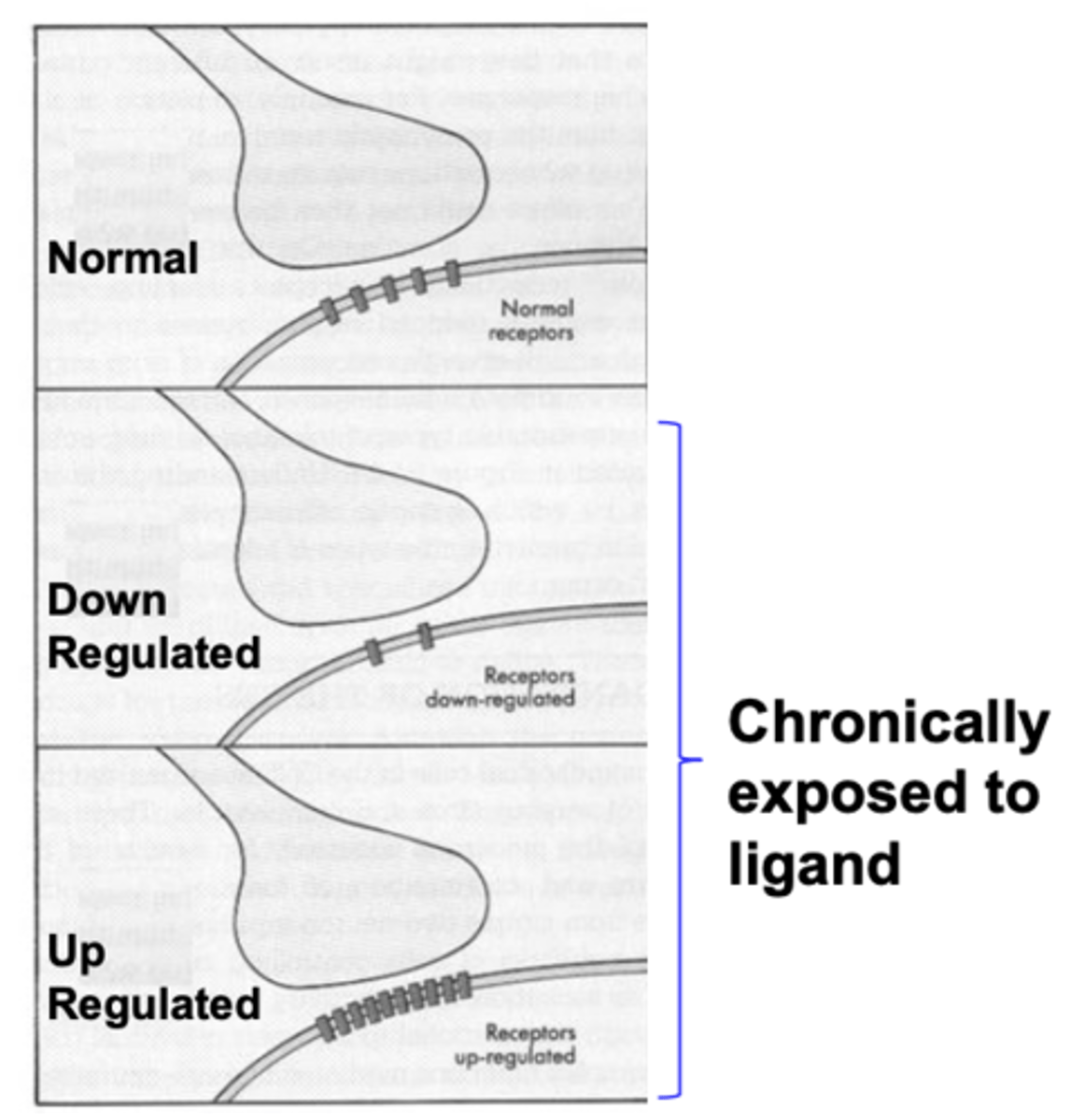
Down-regulation
decrease the number of receptors
Receptors may form ___________________ in response to ligands or electrical stimuli
clusters (group of receptors)
- often to amplify the sensitivity of a signaling response
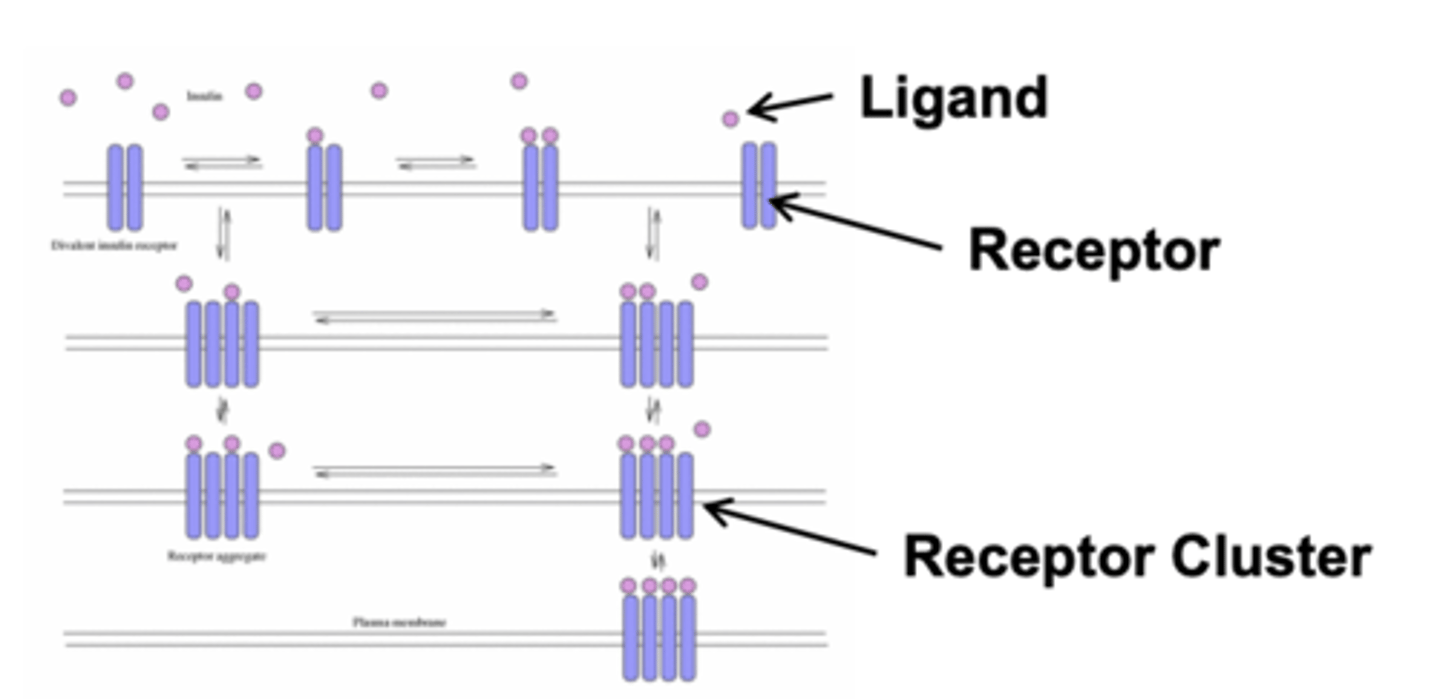
Interaction with extracellular multivalent ligands triggers....
cellular responses (immune T cells)
Receptor clustering mechanisms: (2)
- redistribution of existing receptors
- synthesis & insertion of new receptors at synapses
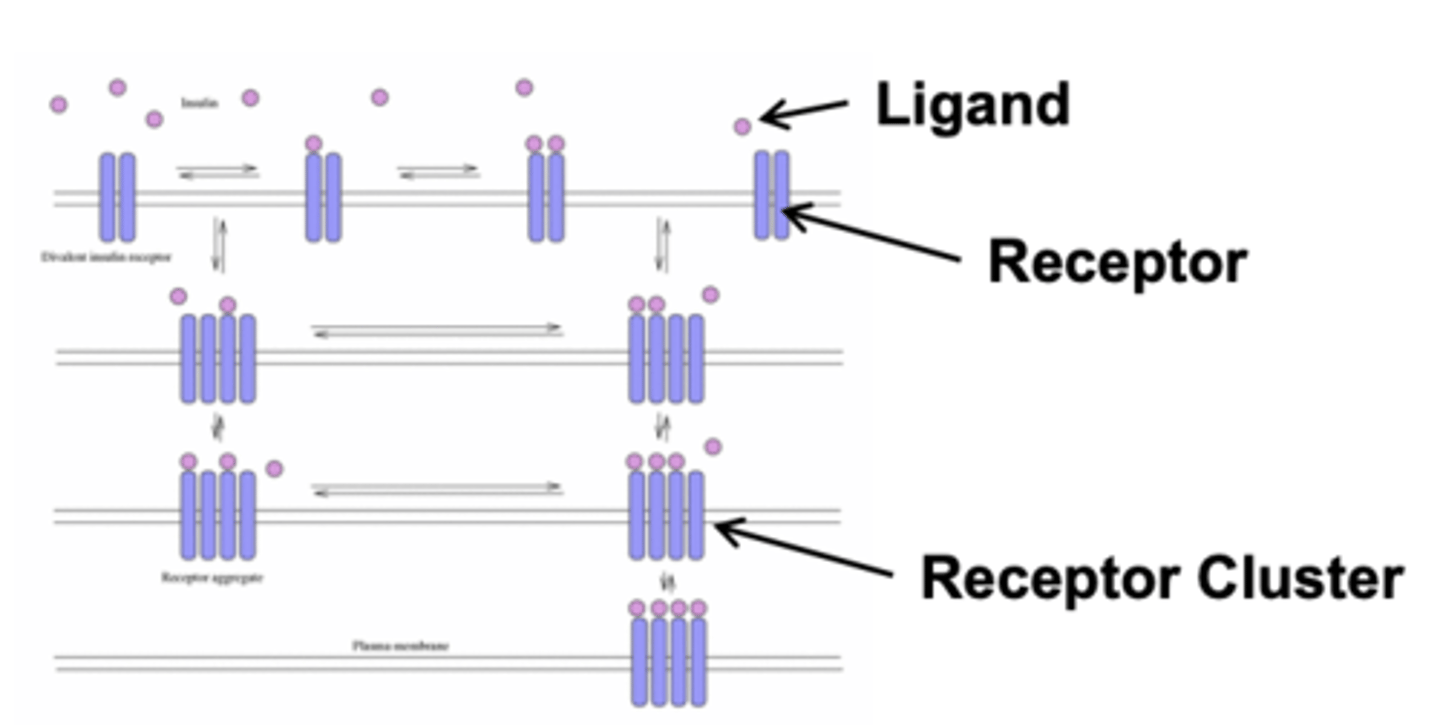
In the prolonged presence of an agonist, the receptor becomes.....
desensitized/inactivated (loss/decrease in response)
T/F: Desensitization is irreversible***
FALSE
it is a reversible mechanism***
- after removal of the drug for some time, the receptor can be activated by an agonist again
Receptors are almost always subject to....
feedback regulation by their own signaling outputs
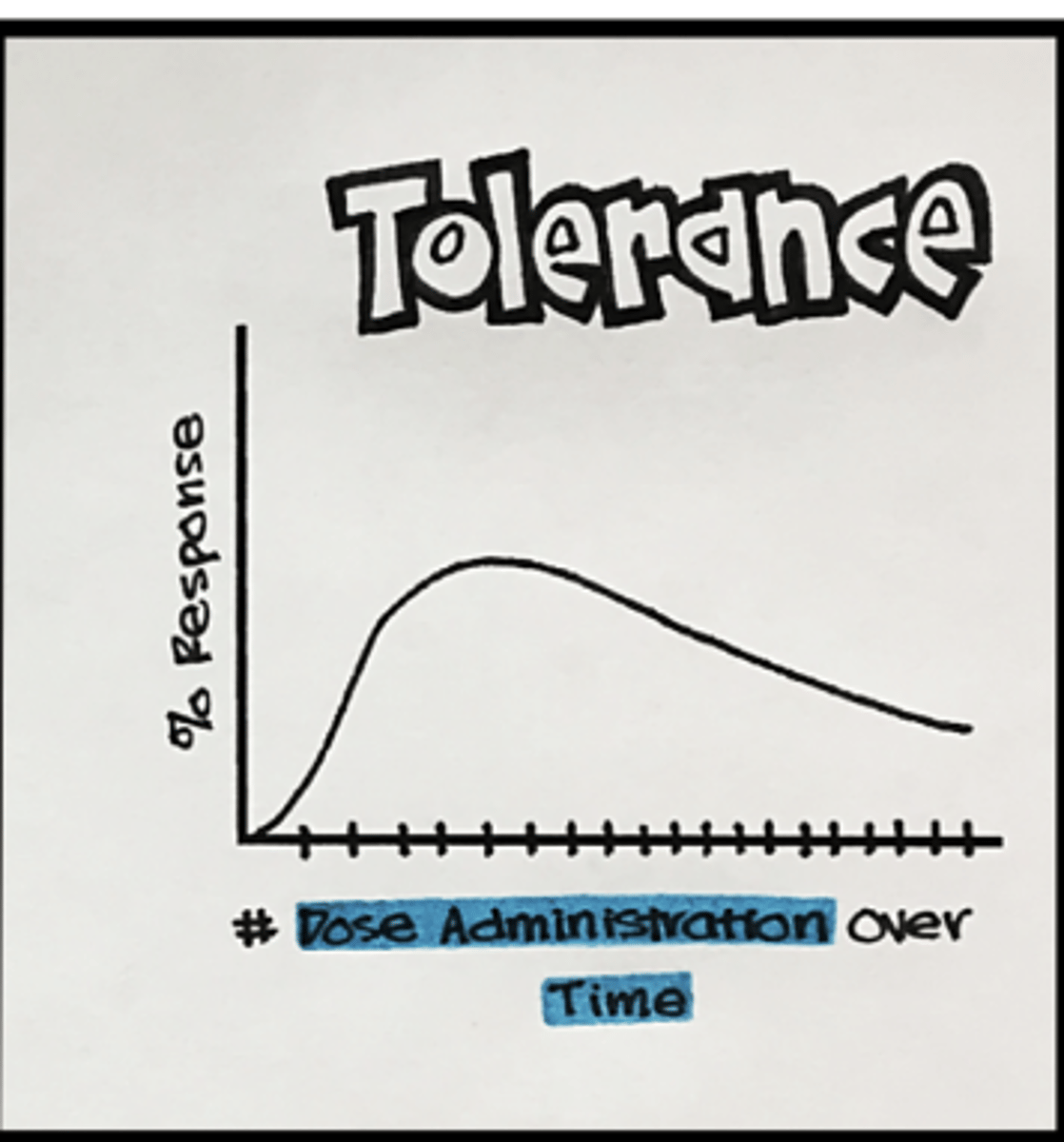
Desensitization: tolerance
reduction in response after repeated administration
- a gradual decreased response to a drug
- requires a higher dose to achieve same initial response
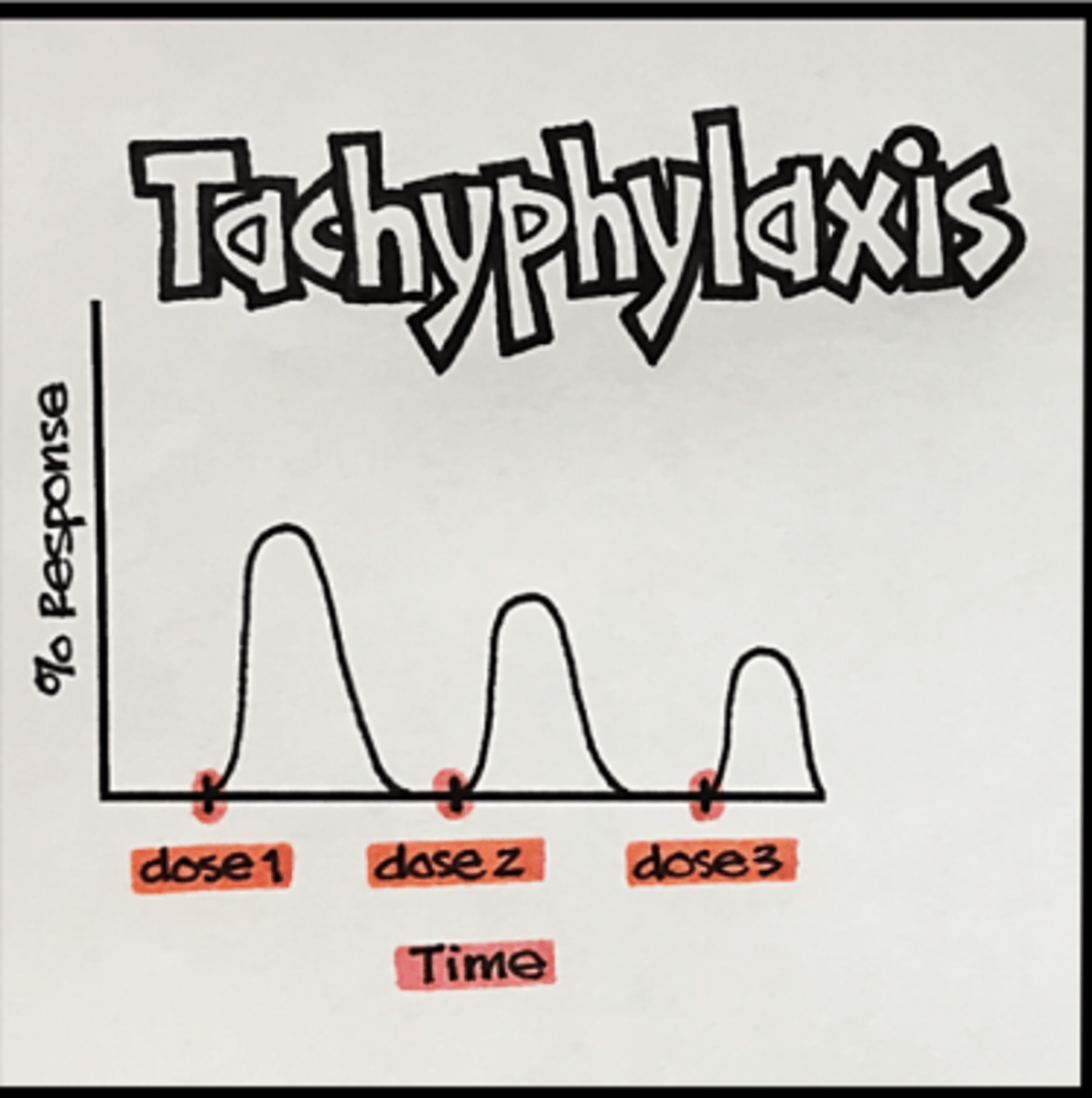
Desensitization: tachyphylaxis
rapid desensitization/loss of receptor's response to repeated doses over a short period of time (acute, sudden decrease)
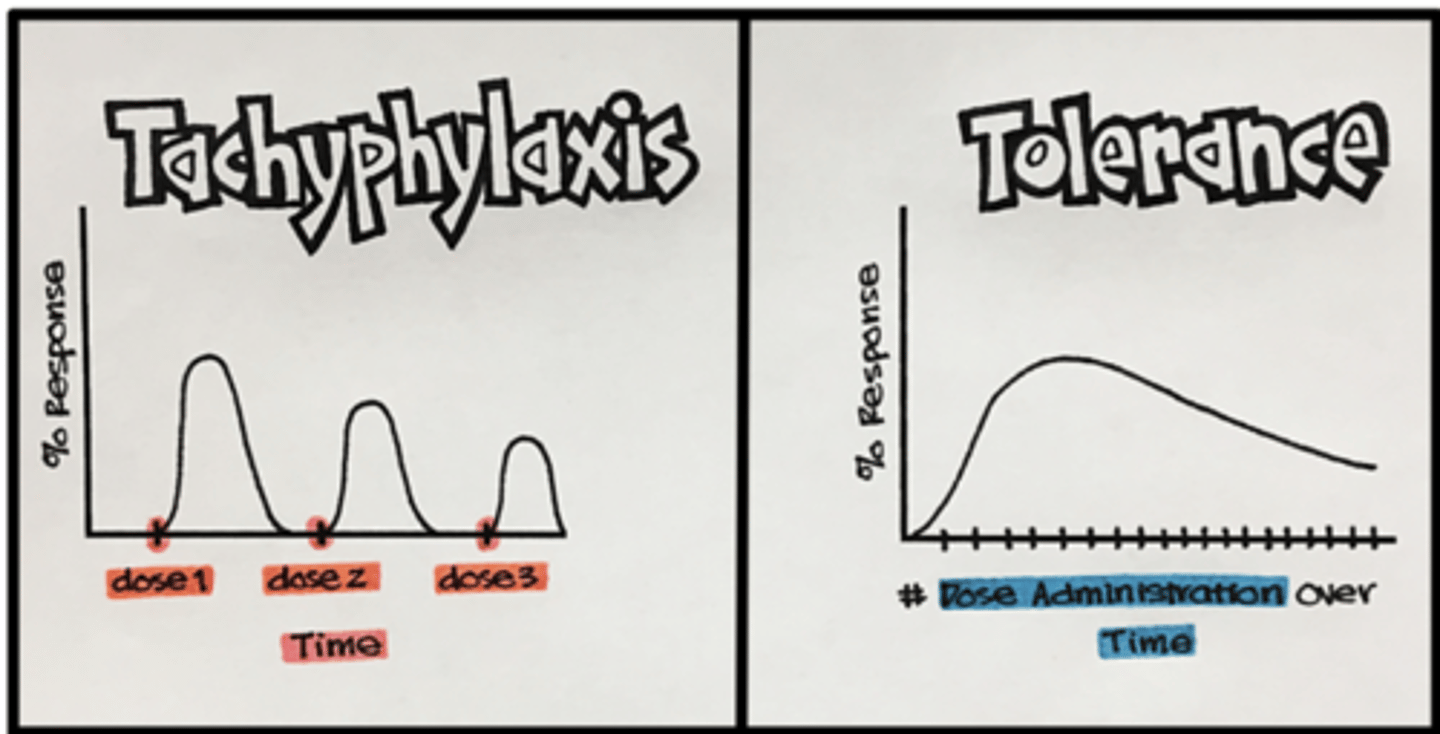
How is tolerance different from tachyphylaxis? (2)
tolerance develops over a long period of time, while tachyphylaxis is an acute event
- tolerance can be overcome by increasing the dose (unlike tachyphylaxis)
Mechanisms of desensitization (7)****
- modification of ______________
- intrinsic ____________________ changes
- modification of ________ surrounding ________
- productions of _______________ that inhibit the __________
- receptor _____________, ___________ or _____________
- ______________________ the expression of receptors
- ________________________ of mediators of ____________________
- modification of receptor subunits (phosphorylation, ribosylation, methylation, acylation)
- intrinsic conformational/shape changes
- modification of lipids surrounding receptor
- productions of messengers that inhibit the receptor
- receptor internalization, sequestration, or down regulation (for G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs))
- down regulating the expression of receptors
- loss/down regulation of mediators of downstream signal
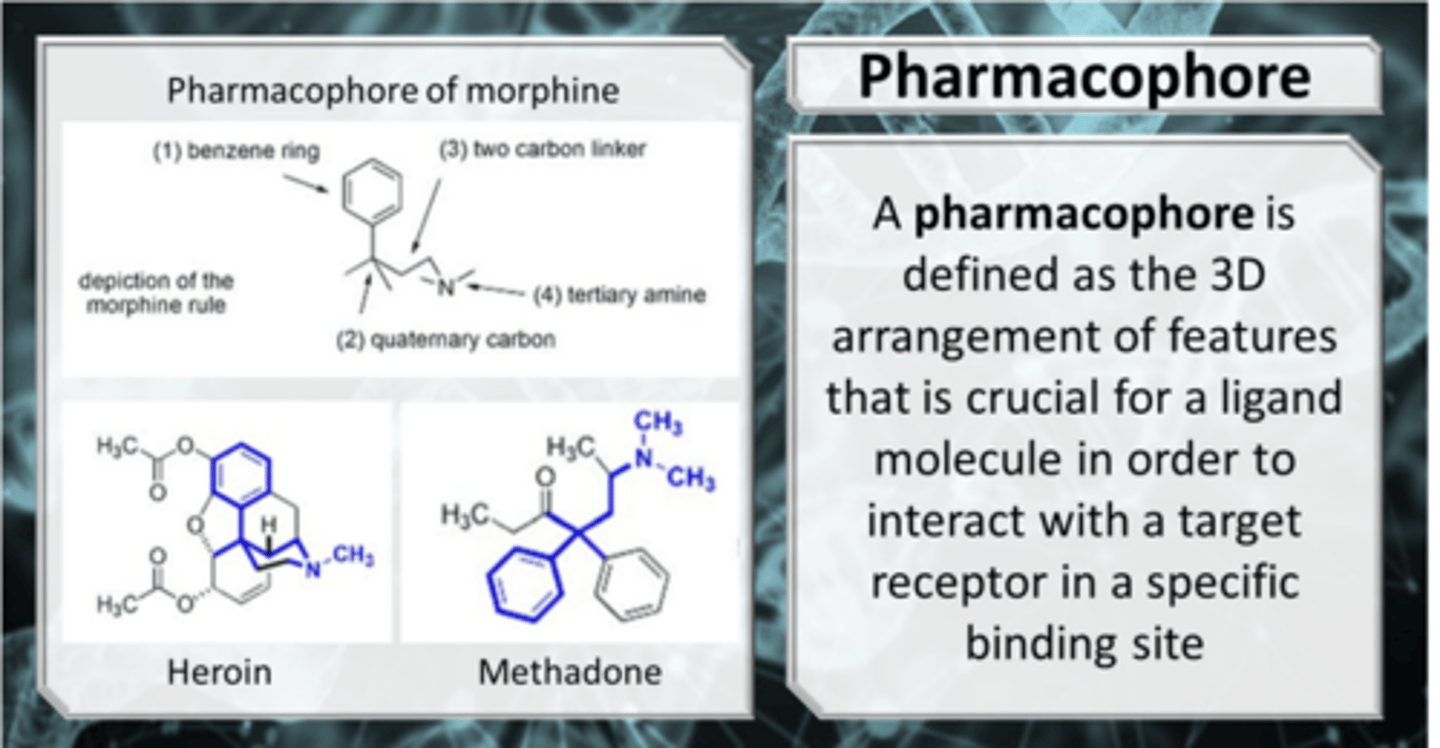
Pharmacophore
Set of structural features (chemistry) in a molecule that is:
- recognized at receptor site
- responsible for that molecule's pharmacological/biological activity
Most drug receptors are...
a. Small molecules with a molecular weight between 100 and 1000
b. Lipids arranged in a bilayer configuration
c. Proteins located on cell membranes or in the cytosol
d. DNA molecules
e. RNA molecules
c. Proteins located on cell membranes or in the cytosol
Receptors perform the following function/functions:
a. Ligand recognition
b. Signal transduction
c. Both ligand recognition and signal transduction
d. Disposal of agonists and antagonists
c. Both ligand recognition and signal transduction
Which of the following responses to sympathetic stimulation would prevent receptors from being coupled with G-proteins?
a. Sequestration
b. Down-regulation
c. Phosphorylation
d. Glucuronidation
c. Phosphorylation
What is true in relation to drug receptors?
a. All drugs act through specific receptors
b. All drug receptors are located on the surface of the target cells
c. Agonists induce a conformational change in the receptor
d. Partial agonists have low affinity for the receptor
c. Agonists induce a conformational change in the receptor