AP Biology: Speciation Final Exam
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Reproductive barriers
Biological features which prevent two populations from interbreeding. Can be prezygotic or postzygotic.
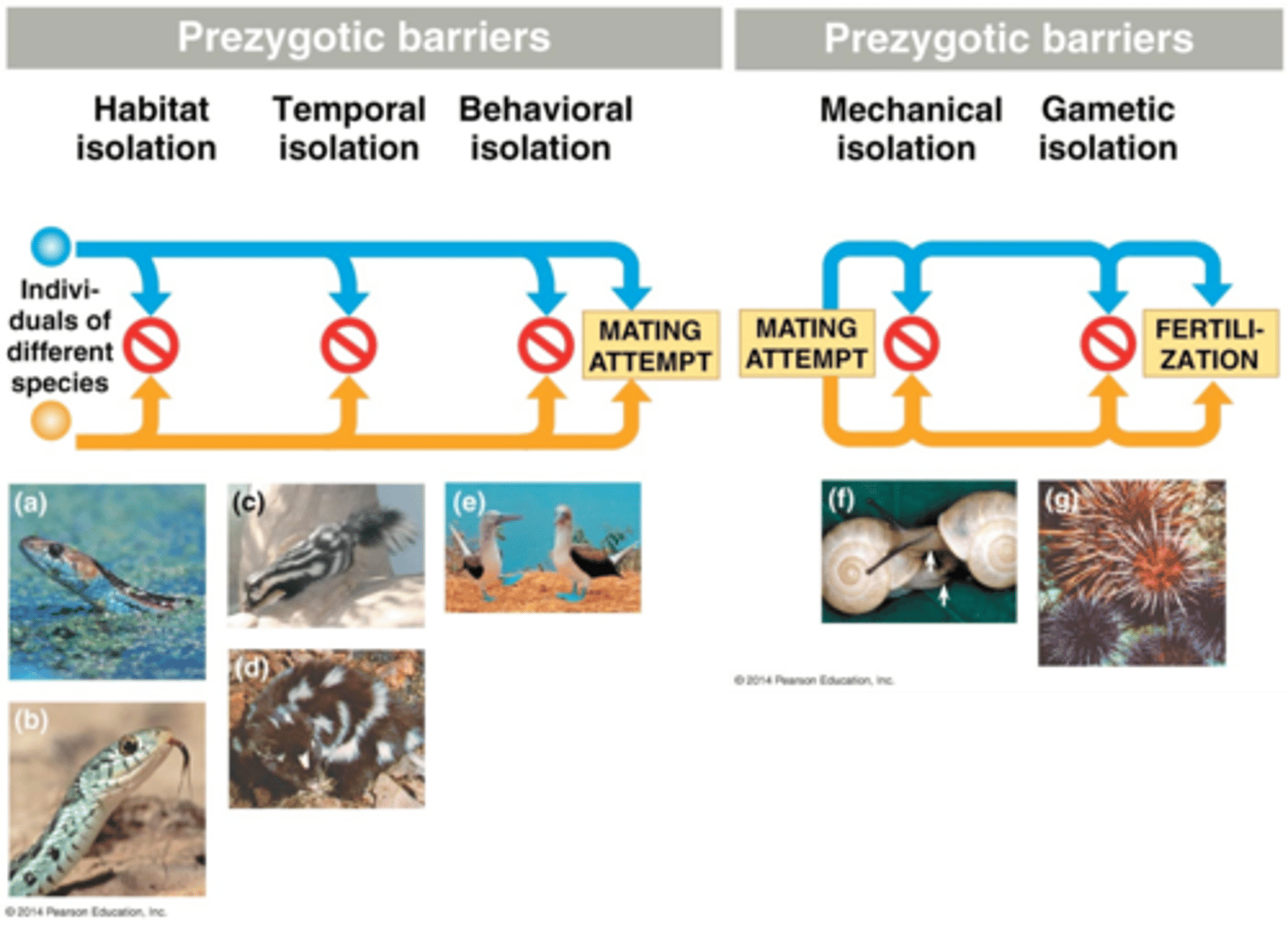
Prezygotic barriers
A type of reproductive barrier that prevents the male and female gametes from being able to combine into a zygote.
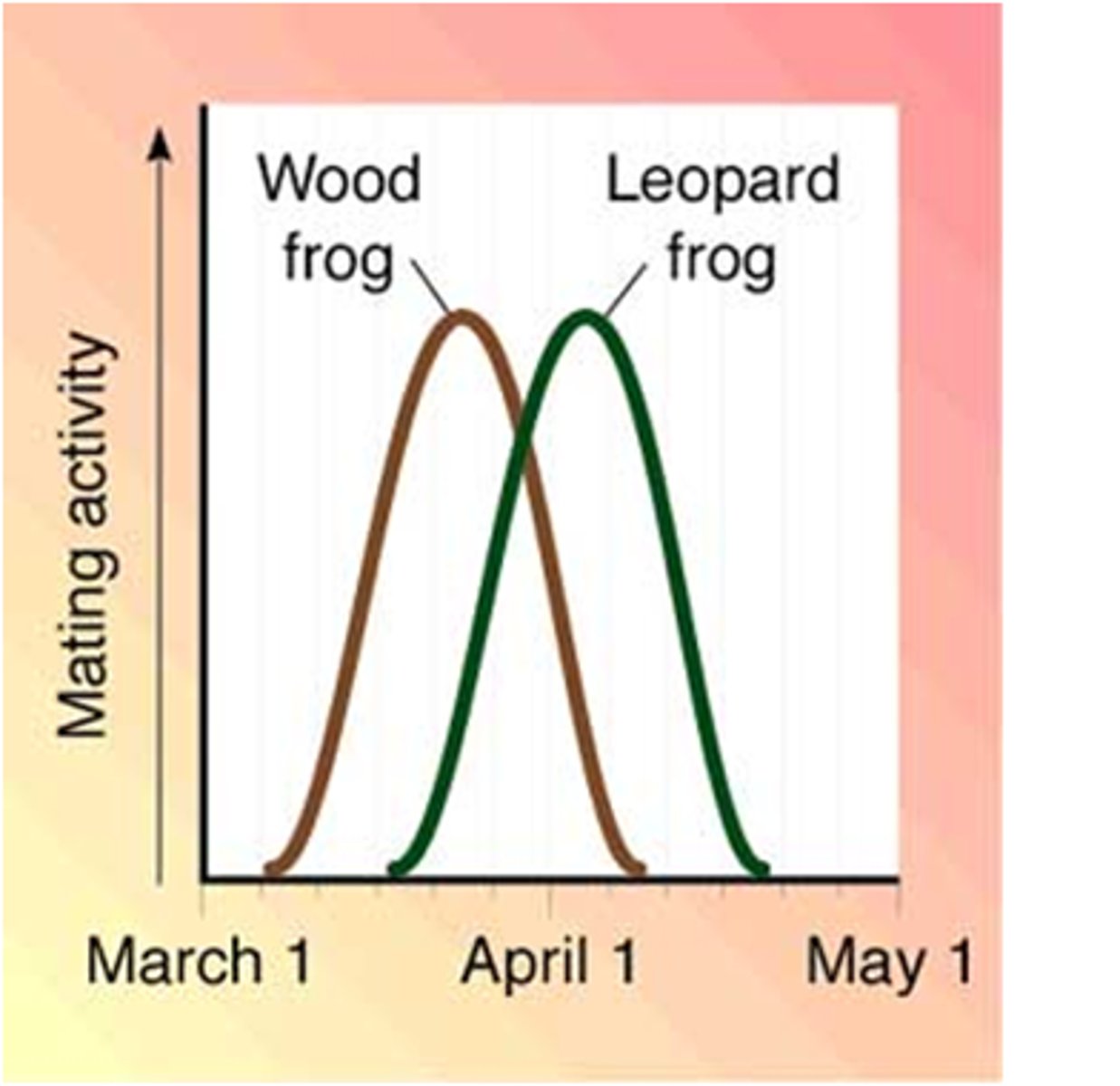
Temporal isolation
A type of prezygotic barrier in which species mating or flowering occurs at different seasons or times of day
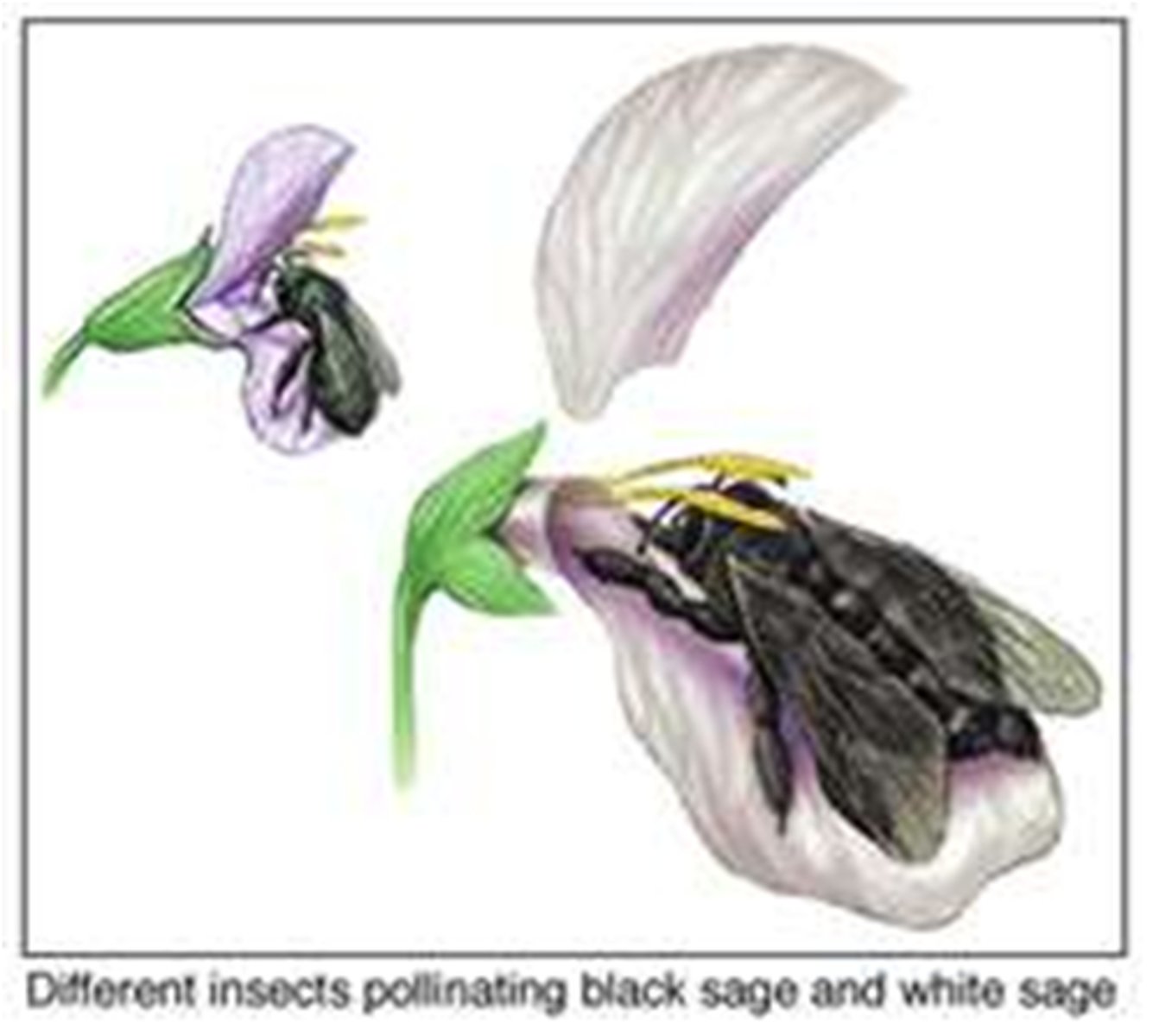
Habitat isolation
A type of prezygotic barrier in which two species live in the same general area but not in the same kind of place within that general area
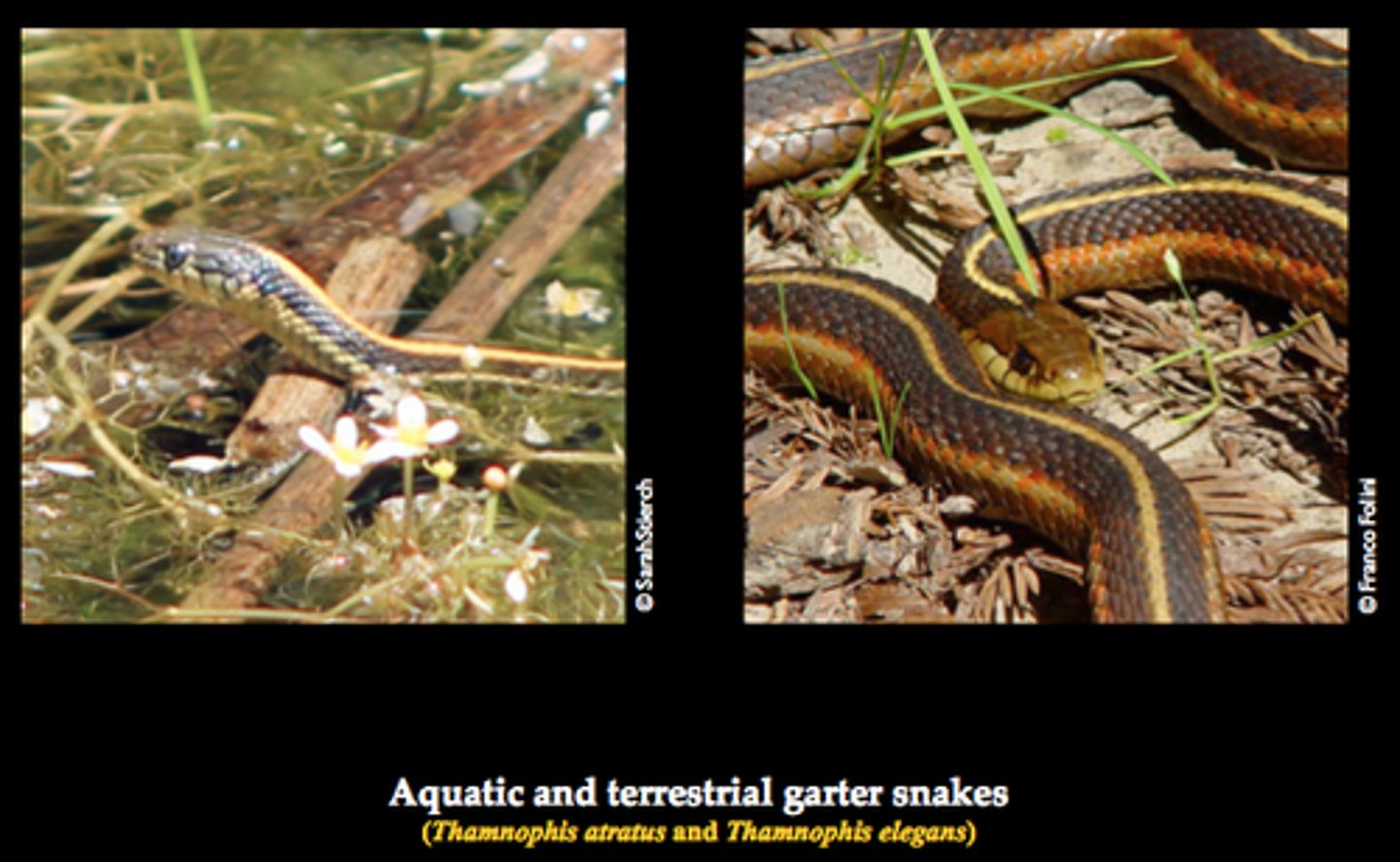

Behaviorial isolation
A type of Prezygotic barrier in which there is a little or no sexual attraction between different species. Usually caused by a difference in mating rituals or sexual preference.
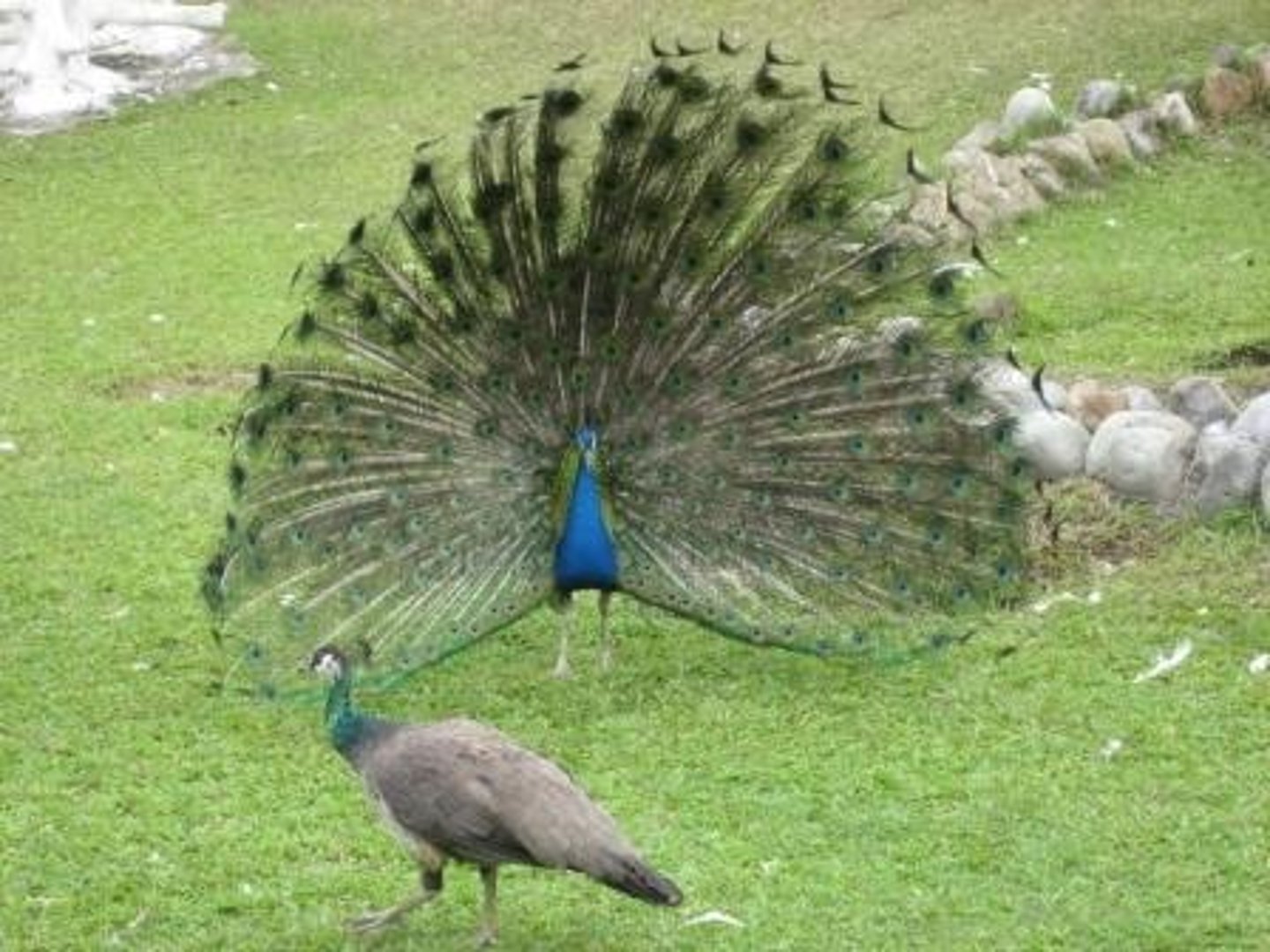

Mechanical isolation
A type of Prezygotic barrier which structural differences in genitalia of the animal or the flowers prevents sexual interaction or pollen transfer
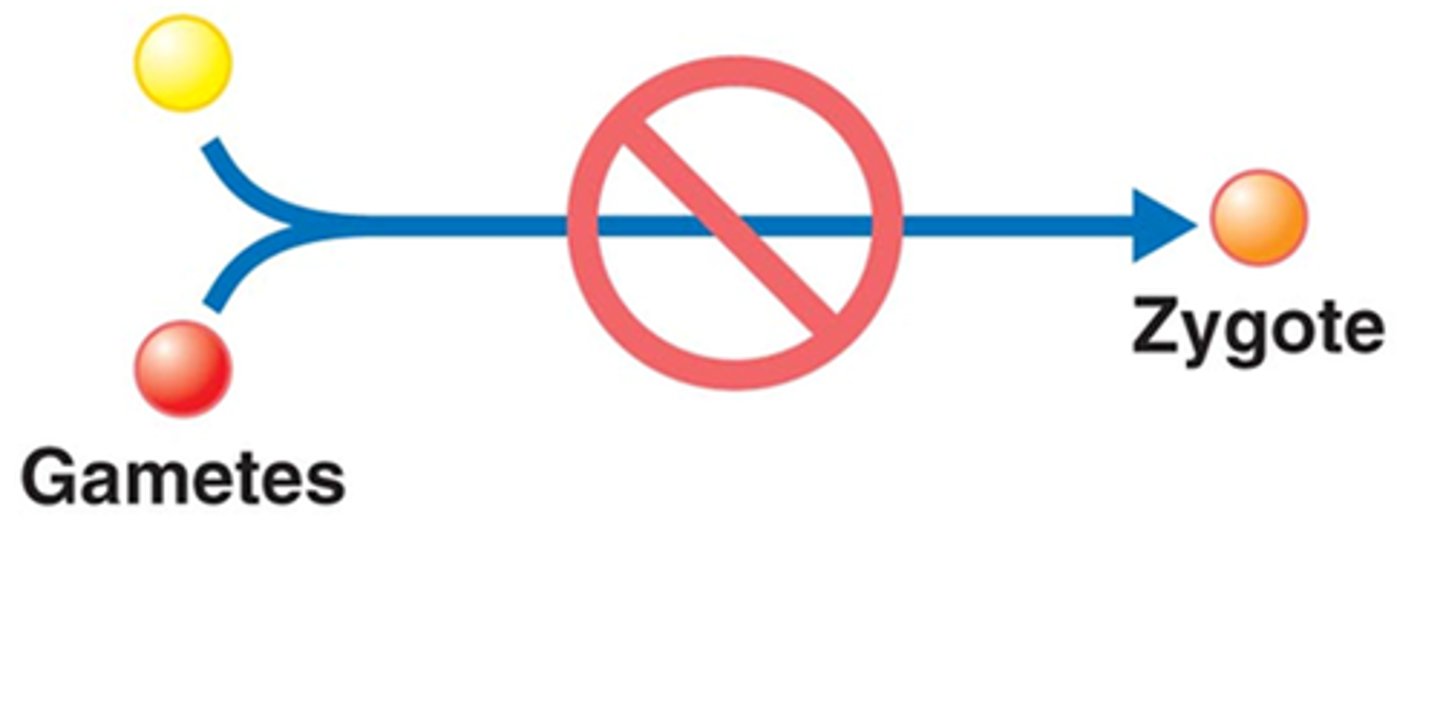
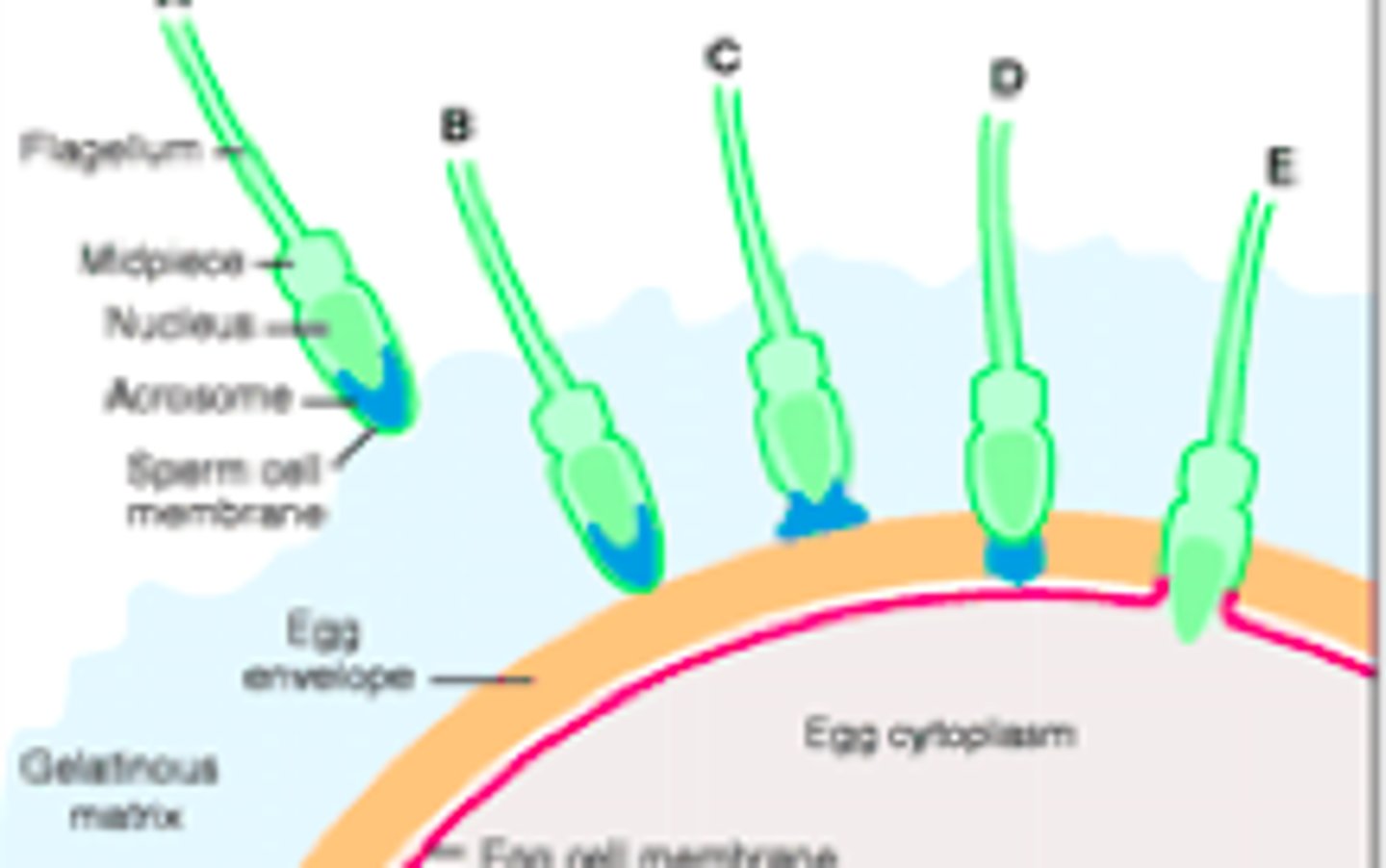
Gametic isolation
A type of prezygotic barrier in which a male and female from two different species may copulate (sexually interact) but the gametes don't unite to form a zygote
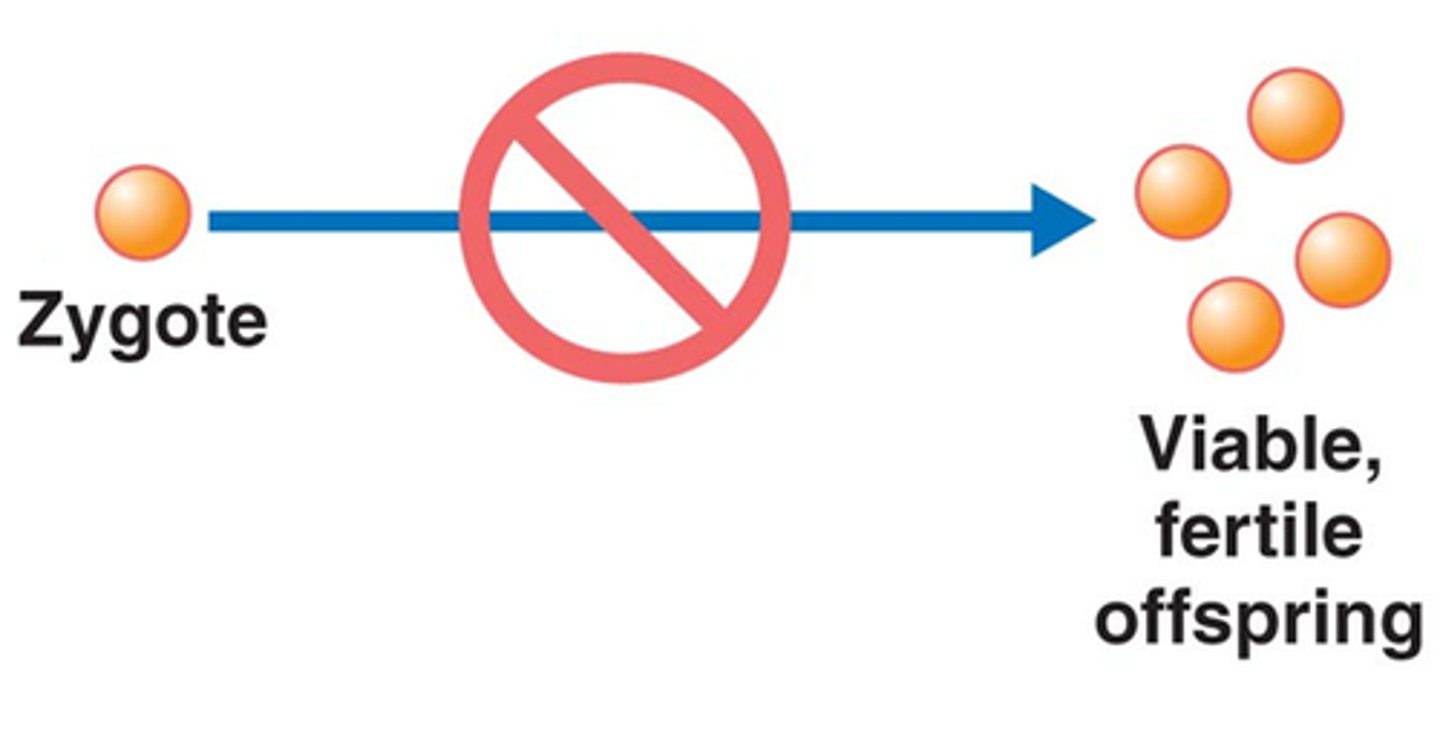
Postzygotic barriers
A type of reproductive barrier that allows two populations to sexually interact but prevents the development of a viable, fertile offspring
Hybrid inviability
A type of postzygotic barrier in which hybrids fail to develop or to reach sexual maturity
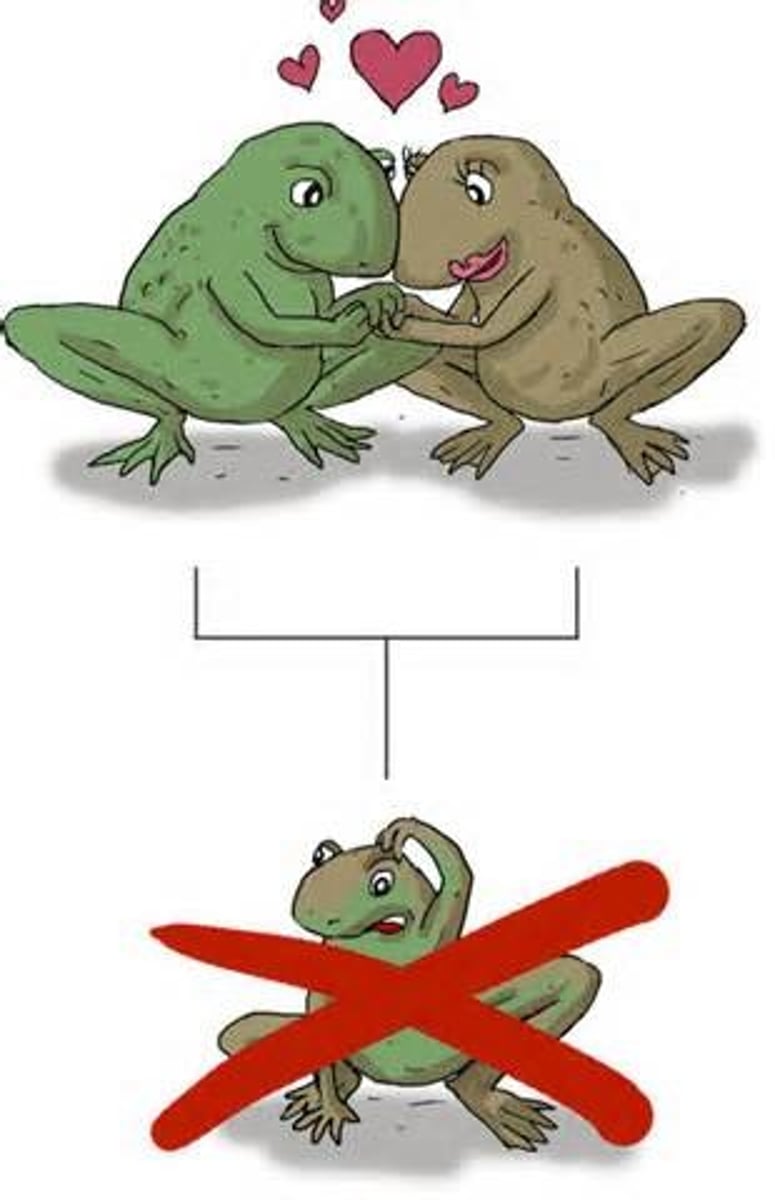
Hybrid sterility
A type of postzygotic barrier in which hybrids are able to survive but cannot reproduce.

Hybrid breakdown
A type of postzygotic barrier in which offspring of hybrids are weak and infertile

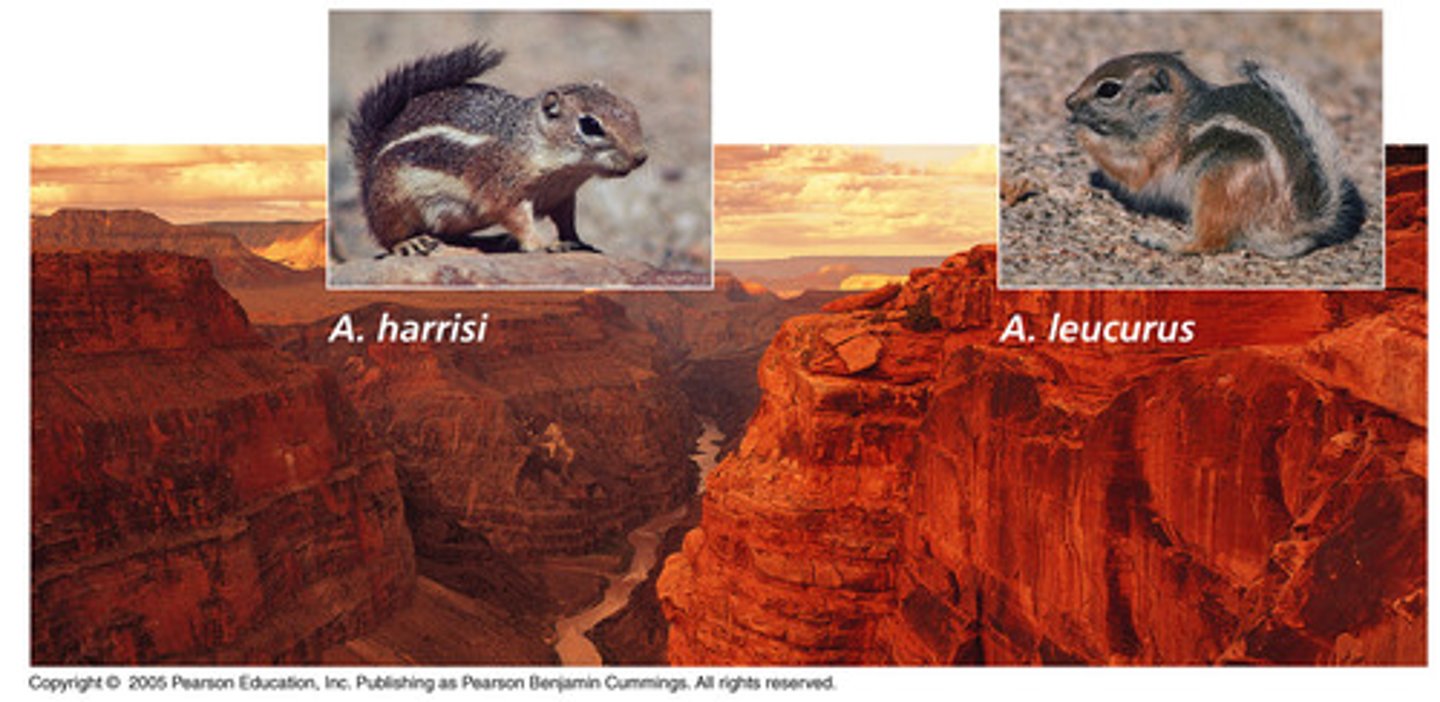
Allopatric speciation
Meaning "Different-homeland" The formation of a new species as a result of a population becoming isolated by a geographical barrier

Sympatric speciation
Meaning "Same-homeland" The formation of a new species even thought they are in the same geographical area
Gradualism
Evolution occurring slowly over time
Punctuated equilibrium
Evolution occurring through rapid, abrupt changes
Microevolution
Evolutionary change within populations
Gene Pool
Alleles of all genes in all individuals in a population
Gene Flow
Movement of alleles between populations
Reproductive Isolation
Incapable of interbreeding which indicates formation of a new species
Macroevolution
Evolution on a large scale which involves the splitting of one species into two or more species
Hybridization
Mating between two species
Adaptive radiation
A single ancestral species rapidly gives rise to a variety of new species as each adapts to a specific environment
Convergent Evolution
A biological trait evolves in two unrelated species because of exposure to similar environments
Analogous Traits
Example of Convergent Evolution
Homologous Structures
Structures in different species that are similar because of common ancestry.
Endosymbiosis
A theorized process in which early eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes.
Natural Selection
A process in which organisms with certain inherited characteristics are more likely to survive and reproduce than other organisms
Speciation
The formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.
Vestigial Structures
Are little or no importance to organism, but remain from an ancestor.