Chapter 11 | Intermolecular Forces
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Intermolecular forces
Attractive forces between molecules
Intramolecular forces
Hold atoms together in a molecule
Measure of intermolecular force
Boiling point
Melting point
Vaporization
Fusion
Sublimation
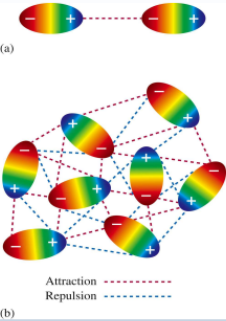
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Attractive forces between polar molecules
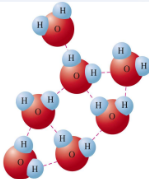
Hydrogen Bonding
Between the hydrogen atom in a polar F-H, O-H, or N-H bond and an electronegative O, N, or F atom
Have anomalously high boiling points (specific heat, heat of vaporization) and are more viscous
London Dispersion Forces
Attractive forces arise due to temporary dipoles induced in atoms or molecules
Polarizability
How easy the electron distribution in the atom or molecule can be distorted. Increases with number of electrons
Intermolecular force strength ranking
Ion-Ion > Ion-dipole > Hydrogen bond > Dipole-dipole > London dispersion
Surface Tension
Energy or work required to increase the surface area of a liquid
Viscosity
A liquids resistance to flow