Magnetism
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is a transformer?
A transformer is an electrical device that changes the voltage of an alternating current (AC) using electromagnetic induction.
How does a transformer change voltage?
An alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, creating a changing magnetic field.
This magnetic field passes through the iron core to the secondary coil.
The changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary coil (by the generator effect).
If the secondary coil is part of a closed circuit, an AC current flows.
(This only works with AC because a changing magnetic field is needed to induce a current)
What does the iron core do in a transformer?
The iron core strengthens and channels the magnetic field between the coils, ensuring efficient energy transfer.
What is the difference between step-up and step-down transformers?
Step-up transformers: Increase voltage (more turns on secondary coil).
Step-down transformers: Decrease voltage (fewer turns on secondary coil).
(Used in the National Grid to reduce energy loss in power transmission.)
What is the transformer equation?
Vs/Vp = Ns/Np
Where:
Vₛ = Voltage in secondary coil (V)
Vₚ = Voltage in primary coil (V)
Nₛ = Number of turns in secondary coil
Nₚ = Number of turns in primary coil
(The ratio of voltages equals the ratio of turns.)
What equation links power in an ideal transformer?
VpIp=VsIs
Where:
Vₚ & Iₚ = Voltage and current in primary coil
Vₛ & Iₛ = Voltage and current in secondary coil
(In an ideal transformer, power is conserved: power in = power out.)
Why are step-up and step-down transformers used in the National Grid?
Step-up transformers increase voltage to reduce current.
Lower current means less energy lost as heat in power lines.
Step-down transformers reduce voltage for safe home use (230V in the UK).
Why do transformers only work with AC and not DC?
AC constantly changes direction, creating a changing magnetic field.
A changing field is needed to induce voltage in the secondary coil.
DC (direct current) does not change direction, so no voltage is induced.
What is the generator effect?
The generator effect is when a changing magnetic field induces a potential difference (voltage) in a conductor, which can cause a current to flow if the circuit is complete.
so if the wire stops moving there is no induced pD as there’s no longer a change in magnetic field
How can a voltage be induced in a conductor?
A voltage is induced when:
A wire or coil of wire moves through a magnetic field.
A magnet moves into or out of a coil.
The magnetic field around a coil changes (e.g., alternating magnetic field).
(The wire must cut through magnetic field lines.)
What increases the size of the induced voltage?
Increasing the speed of movement
Using a stronger magnetic field
Increasing the number of turns in the coil
Using a longer coil of wire
How can you reverse the direction of the induced voltage?
Move the wire in the opposite direction
Reverse the poles of the magnet
How can you determine the direction of the induced voltage?
Use Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule:
Thumb = Motion of conductor
First Finger = Magnetic field (North to South)
Second Finger = Induced current (Positive to Negative)
How does an alternator generate electricity?
A coil rotates in a magnetic field.
The changing field induces an alternating current (AC).
A slip ring commutator allows the current to change direction every half-turn, maintaining AC output.
carbon brushes provide a good electrical connection between the coil and the external circuit
How does a dynamo generate electricity?
A coil rotates in a magnetic field.
A split-ring commutator ensures the current always flows in the same direction, producing DC output.
What effect does an induced current have on the magnetic field?
Lenz’s Law states that the induced current produces a magnetic field that opposes the change that caused it.
What is the energy transfer in a generator?
Kinetic energy (movement of coil/magnet) → Electrical energy (induced current)
Some energy is wasted as heat due to resistance in the wires.
What is a microphone?
A microphone is a device that converts sound energy into electrical energy using the generator effect.
How does a microphone convert sound into an electrical signal?
Sound waves hit a diaphragm (thin sheet inside the microphone).
The diaphragm vibrates with the sound waves.
The diaphragm is attached to a coil of wire, which moves inside a magnetic field.
The movement of the coil cuts through the magnetic field, inducing a potential difference (voltage) via the generator effect.
The alternating voltage is sent to an amplifier, then a speaker or recording device.
What is the motor effect?
The motor effect occurs when a current-carrying wire experiences a force due to the interaction between its magnetic field and an external magnetic field.
Why does the motor effect happen?
A current-carrying wire generates its own magnetic field, which interacts with an external magnetic field, causing a force on the wire.
When does the motor effect happen?
The wire must be in a magnetic field and perpendicular (or at an angle) to the field lines. No force acts if the wire is parallel to the field.
How can you predict the direction of the force in the motor effect?
Use Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule:
Thumb = Force (Motion)
First Finger = Magnetic Field (North to South)
Second Finger = Current (Positive to Negative)
How does changing the direction of the current or magnetic field affect the force?
Reversing the current reverses the force’s direction.
Reversing the magnetic field also reverses the force’s direction.
What affects the size of the force in the motor effect?
The force increases when:
Current increases
Magnetic field strength increases
The wire is at a 90° angle to the field
What is the equation to calculate the force on a current-carrying conductor?
F=BIL
Where:
F = Force (N)
B = Magnetic Flux Density (T, Tesla)
I = Current (A)
L = Length of wire in the field (m)
(Only applies when wire is perpendicular to the field!)
How can the direction of rotation of a motor be reversed?
Reverse the current
Reverse the magnetic field - by switching the poles
What is an electric motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into kinetic energy using the motor effect to produce rotation.
What causes an electric motor to rotate/how does it work?
When a current flows through a coil in a magnetic field, the motor effect produces opposite forces ( one acting down, the other acting upwards) on each side of the coil, making it rotate.
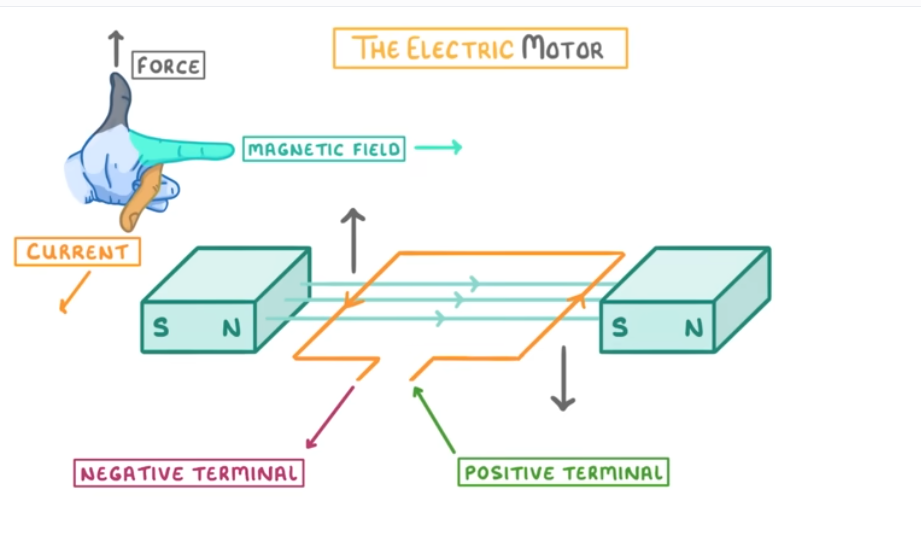
What is the function of the magnetic field in an electric motor?
The magnetic field interacts with the current in the coil, creating forces that cause the coil to spin.
How can you determine the direction of the force on the coil?
Use Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule:
Thumb = Direction of force (motion)
First Finger = Magnetic field (North to South)
Second Finger = Current (Positive to Negative)
(Each side of the coil experiences a force in opposite directions, making it rotate.)
Why do electric motors need a split-ring commutator?
The split-ring commutator:
Reverses the direction of the current every half-turn
Ensures the force always acts in the same direction
Keeps the motor spinning continuously
What can increase the speed of an electric motor?
Increase the current
Increase the strength of the magnetic field
Increase the number of turns in the coil
Use a stronger electromagnet
How can you change the direction of rotation of an electric motor?
Reverse the current direction
Reverse the magnetic field direction
What is the energy transfer in an electric motor?
Electrical energy (from the power source) → Kinetic energy (motor rotation)
Some energy is wasted as heat due to resistance in the wires.
What does the cone do in a loudspeaker?
The cone amplifies the vibrations of the coil, pushing air particles to create sound waves.
What is a loudspeaker?
A loudspeaker is a device that converts electrical energy into sound energy using the motor effect to create vibrations in a cone.
Describe how a loudspeaker produces sound.
1. An alternating current (AC) passes through a coil of wire.
2. The coil is placed inside a permanent magnet’s magnetic field.
3. The motor effect causes a force that moves the coil back and forth.
4. The coil is attached to a cone, which also moves.
5. The cone’s vibrations cause air particles to vibrate, producing sound waves.
Why must the current be alternating for a loudspeaker to work?
The alternating current (AC) continuously reverses direction, which makes the coil move back and forth, producing vibrations.
how to form a solenoid
loop a wire into a coil around an iron core
what is an electromagnet
a solenoid with an iron core
example of electromagnet irl
scrapyards and cranes when it’s switched on it’ll attract materials when it’s switched off it’ll drop materials
how to increase the strength of an electromagnet
- increase size of current flowing through the wire
- increase the number of turns in the coil in a given length ( keeping length the same)
- reducing length of wire whilst maintaining the same number of turns
- adding an iron core through the centre of the coils ( the iron core will become an induced magnet, the magnetic field produced from both the solenoid and the iron core will create a much stronger magnet overall
What happens when a current flows through a wire?
A magnetic field is created around the wire in concentric circles.
How can you determine the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire?
Use the Right-Hand Thumb Rule:
Thumb = direction of current
Fingers = direction of magnetic field lines
What affects the strength of the magnetic field around a wire?
Larger current = stronger field
Closer to the wire = stronger field
What is a solenoid?
A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a strong, uniform magnetic field when current flows through it.
What does the magnetic field around a solenoid look like?
Inside the solenoid = Strong, uniform, like a bar magnet
Outside the solenoid = Similar to a bar magnet’s field
How can you make the magnetic field of a solenoid stronger?
Increase current
Add more coils (turns of wire)
Use a soft iron core (makes an electromagnet)
How is an electromagnet different from a permanent magnet?
Electromagnets can be turned on and off
Strength of an electromagnet can be changed
Electromagnets require an electric current
Where are electromagnets used?
Electric bells
Scrapyard cranes (lifting heavy metals)
Magnetic door locks
MRI scanners
How does increasing the current affect the magnetic field?
How can you determine the north and south poles of a solenoid?
if current is flowing clockwise it’s the south pole, if it’s anticlockwise it’s the north pole
soft magnetic materials
materials thatlose their induced magnetism quickly
hard magnetic materials
materials that lose their induced magnetism slowly even after the magnetic field has been removed they retain their magnetism for some time
What is a magnet?
A magnet is an object that produces a magnetic field and can attract or repel certain materials
Which materials are magnetic?
Only iron, nickel, cobalt, and some of their alloys are magnetic.
What is a magnetic field?
A magnetic field is the region around a magnet where magnetic forces act on other materials or magnets.
What do magnetic field lines show?
They show the direction and strength of the magnetic field. Lines closer together indicate a stronger field.
What is the direction of a magnetic field?
Magnetic field lines always point from the north pole to the south pole outside the magnet.
What are permanent magnets?
Permanent magnets always produce a magnetic field and cannot be easily demagnetized (e.g., bar magnets, fridge magnets).
What are induced magnets?
Induced magnets are materials that become temporarily magnetized when placed in a magnetic field.
What happens to an induced magnet when removed from a magnetic field?
It loses its magnetism.
What happens when two like poles or opposite poles are brought close?
Like poles (N-N or S-S) repel
Opposite poles (N-S) attract
Why does a compass point north?
A compass needle aligns with the Earth's magnetic field, as the Earth has a magnetic north and south pole.
how are the poles like in a magnetic material
the poles are all aligned in the same direction
how are the poles like in a non magnetic material
the poles aren’t aligned so then the magnetic fields cancel each other out and the substance is non magnetic
the force between a magnetic material and a magnet is always ______ a _______ force is only ever experienced between two magnets
attractive, repulsive\
what happens when a magnetic material becomes magnetised
the poles shift their alignment in response so if it’s exposed to the north pole of the magnet the magnetic material will have an induced south pole
where will a uniform magnetic field be produced
in the gap between two opposite poles howeevr outside the gap the field won’t be uniform
what is a uniform magnetic field
a field that has the same strength and direction at every point
describe how to plot a magentic field
place a magnet on top of a piece of paper and draw a dot at one end of the magnet in the corner
place the plotting compass next to the dot and use a pencil to draw a new dot at the other side of the compass needle
move the compass so that it points away from the new dot and repeat the process above
repeat the process until there is a chain of dots and connect with a smooth curve