Anatomy Lecture-Exam 2 Content
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
How many carpal bones in each wrist and what are their names? What’s the mnemonic to remember them and where they are?
8 carpal bones
Scaphoid
Lunate
Triquetrum
Pisiform
Trapezium
Trapezoid
Capitate
Hamate
•“Sally Left the Party, To Take Cathy Home”
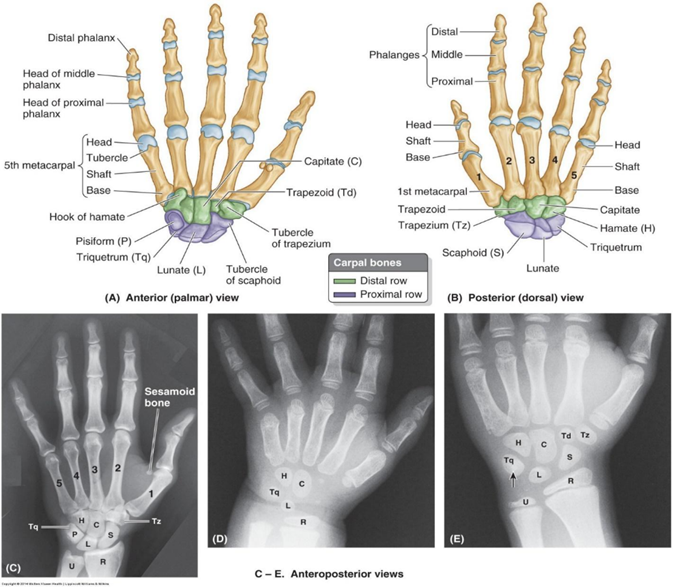
Which carpal bone is most commonly fractured?
scaphoid
Which carpal bone has a prominence that can be palpated deep to the hypothenar eminence?
hamate
Can you palpate the pisiform?
yes
anterior aspect of medial border of wrist (medial aspect of most distal wrist crease)
most mobile when wrist is flexed
Which carpal bone is the largest?
capitate (keystone)
How many metacarpals in each hand?
5
How many phalanges in each hand?
14
each finger has 3 except thumb, which has 2
On your hand, show me where sensation is supplied by the superficial radial nerve, the ulnar nerve, and the median nerve.
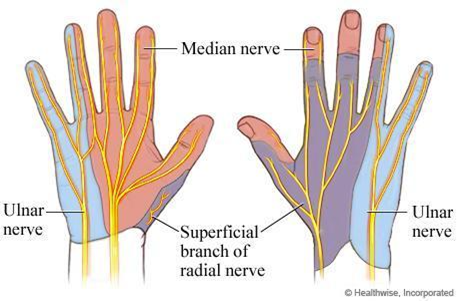
The ulnar artery and nerve pass __________ to the pisiform.
lateral
What is Guyon’s canal? Why is this structure important in batting sports, cycling and prolonged driving?
AKA Ulnar canal
Semi rigid longitudinal canal in the wrist that allows for passage of the ulnar artery and ulnar nerve into the hand
Spans over pisiform and hook of hamate
Entrapment of ulnar nerve in this canal can lead to tingling in the ring and little fingers before progressing to loss of sensation and/or impaired motor function of the intrinsic muscles of the hand (innervated by the ulnar n.)
Compression of ulnar n. more common in cyclists
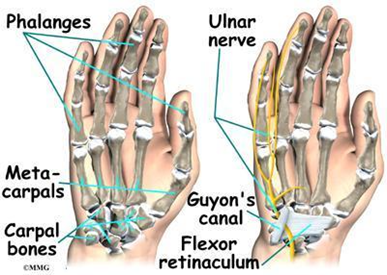
What does the flexor retinaculum have to do with the carpal tunnel?
What are the contents of the carpal tunnel?
Demonstrate the arrangement of the FDS tendons in the carpal tunnel. Visualize on cross-section, the arrangement of the tendons passing thru the carpal tunnel.
What structure forms the roof of the carpal tunnel?
What does palmaris longus insert upon? If there is a palmaris longus, there must be a palmaris brevis. Where is it? How many lumbricals in each hand? O, I, A, N of them.
What are the muscles of the thenar eminence?
adductor policis brevis
flexor pollicis brevis
opponens pollicis
Opponens pollicis: origin
Flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium
Opponens pollicis: insertion
Lateral side of 1st metacarpal
Opponens pollicis: action
To oppose thumb, it draws 1st metacarpal medially to center of palm and rotates it medially
Opponens pollicis: innervation
Recurrent branch of median nerve (C8, T1)
Abductor pollicis brevis: origin
Flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium
Abductor pollicis brevis: insertion
Lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb
Abductor pollicis brevis: action
Abducts thumb; helps oppose it
Abductor pollicis brevis: innervation
Recurrent branch of median nerve (C8, T1)
Flexor pollicis brevis: origin
Flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium
Flexor pollicis brevis: insertion
Lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb
Flexor pollicis brevis: action
flexes thumb
Flexor pollicis brevis: innervation
Recurrent branch of median nerve (C8, T1)
Adductor Pollicis: Origin
Oblique Head: Bases of 2nd and 3rd metacarpals, capitate, and adjacent carpals
Transverse Head: Anterior surface of shaft of 3rd metacarpal
Adductor Pollicis: Insertion
Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb
Adductor Pollicis: Action
Adducts thumb toward lateral border of palm
Where are the ulnar and radial collateral ligaments? What are the parts of the radial and ulnar collateral ligaments?
Radial collateral ligament extends from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and blends distally with the annular ligament of the radius
Ulnar collateral ligament extends from the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the coronoid process and olecranon of the ulna and consists of anterior cord, posterior cord, oblique band that deepens the socket for the trochlea of the humerus
Adductor Pollicis: Innervation
Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Abductor Digit Minimi: Origin
pisiform
Abductor Digit Minimi: Insertion
Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit
Abductor Digit Minimi: Action
Abducts 5th digit; assists in flexion of its proximal phalanx
Abductor Digit Minimi: Innervation
Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Flexor digiti minimi: Origin
Hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum
Flexor digiti minimi: Insertion
Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit
Flexor digiti minimi: Action
Flexes proximal phalanx of 5th digit
Flexor digiti minimi: Innervation
Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Opponens digiti minimi: origin
Hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum
Opponens digiti minimi: insertion
Medial border of 5th metacarpal
Opponens digiti minimi: action
Draws 5th metacarpal anterior and rotates it, bringing 5th digit into opposition with thumb
Opponens digiti minimi: innervation
Deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
In each hand, how many “layers” of interosseous muscles? How many interosseous muscles in each of these layers?
What is DAB and PAD?
DAB: Dorsal Interossei Muscles Abduct (Dorsal Abduct)
PAD: Palmar Adduct (middle finger does not have PAD because we use it as the midline)
How many arterial arches in each palm? What are they called?
What is a mallet (baseball) finger?
What do you suppose is “opened” to relieve compression on the median nerve in CTR surgery?
What small nerve needs to be carefully identified so that it is not accidentally cut in CTR surgery and the resulting deformity if it is injured is called what?
What are ulnar impaction?
What bones make up the true elbow? What parts of those bones?
Elbow joint = articulation of the distal humerus and the proximal ulna and radius
Humeroulnar joint = Trochlear notch of the ulna articulates with the trochlea of the humerus
Humeroradial joint = Head of the radius articulates with the capitulum of the humerus
Proximal radioulnar joint = The proximal articulation of the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna
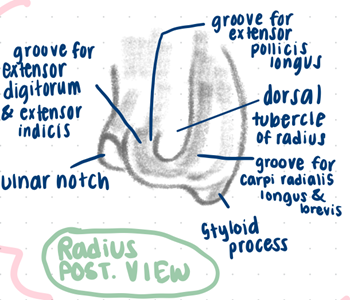
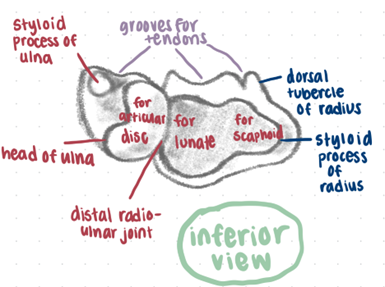
Bony features of radius and ulna
Radius:
head
radial tuberosity
interosseous border
pronator tubercle
ulnar notch
radial styloid process
Ulna:
olecranon
coronoid process
trochlear notch
radial notch
supinator crest
ulnar styloid process
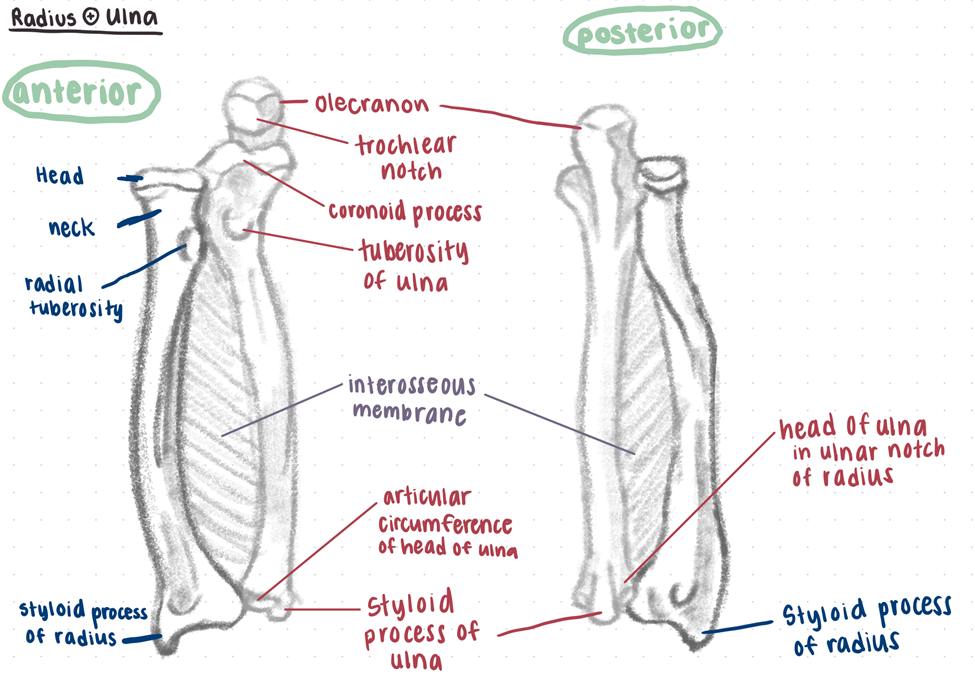
What motion do each of the ligaments of the elbow resist?
What are the 3 radioulnar (RU) joints?
Proximal radio ulnar joint: pivot type of synovial joint, allows movement of the head of the radius on the ula
Distal radio-ulnar joint: pivot synovial joint, the radius moves around the relatively fixed distal end of the ulna
What is the interosseous membrane?
A strong, fibrous membrane that firmly ties the forearm bones together, allowing for pronation and supination. It is also the proximal attachment for various deep forearm muscles
pronator teres origin
Ulnar head: coronoid process
Humeral head: medial epicondyle of humerus
pronator teres insertion
middle of convexity of lateral surface of radius
pronator teres action
Pronates and flexes forearm (at elbow)
pronator teres innervation
Median nerve (C6, C7)
flexor carpi radialis origin
Medial epicondyle of humerus
flexor carpi radialis insertion
Base of 2nd metacarpal
flexor carpi radialis action
Flexes and abducts hand (at wrist)
flexor carpi radialis innervation
Median nerve (C6, C7)
palmaris longus origin
Medial epicondyle of humerus
palmaris longus insertion
Distal half of flexor retinaculum and apex of palmar aponeurosis
palmaris longus action
Flexes hand (at wrist) and tenses palmar aponeurosis
palmaris longus innervation
Median nerve (C7, C8)
flexor carpi ulnaris origin
Humeral head: Medial epicondyle of humerus
Ulnar head: olecranon and posterior border of ulna (via aponeurosis)
flexor carpi ulnaris insertion
Pisiform, hook of hamate, 5th metacarpal
flexor carpi ulnaris action
Flexes and adducts hand (at wrist)
flexor carpi ulnaris innervation
Ulnar nerve (C7, C8)
flexor digitorum superficialis origin
Humero-ulnar head: medial epicondyle and coronoid process
Radial head: superior half of anterior border
flexor digitorum superficialis insertion
Shafts of middle phalanges of medial four digits
flexor digitorum superficialis action
Flexes middle phalanges at proximal interphalangeal joints of middle four digits; also flexes proximal phalanges at metacarpophalangeal joints
flexor digitorum superficialis innervation
Median nerve (C7, C8, T1)
flexor digitorum profundis origin
Proximal three quarters of medial and anterior surfaces of ulna and interosseous membrane
flexor digitorum profundis insertion
Medial part: bases of distal phalanges of 4th and 5th digits
Lateral part: bases of distal phalanges of 2nd and 3rd digits
flexor digitorum profundis action
Medial part: flexes distal phalanges 4 and 5 at interphalangeal joints
Lateral part: flexes distal phalanges 2 and 3 at distal interphalangeal joints
flexor digitorum profundis innervation
Medial part: ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
Lateral part: anterior interosseous nerve, from median nerve (C8, T1)
Flexor pollicis longus origin
Anterior surface of radius and adjacent interosseous membrane
Flexor pollicis longus insertion
Base of distal phalanx of thumb
Flexor pollicis longus action
Flexes phalanges of 1st digit (thumb)
Flexor pollicis longus innervation
anterior interosseous nerve, from median nerve (C8, T1)
pronator quadratus origin
Distal quarter of anterior surface of ulna
pronator quadratus insertion
Distal quarter of anterior surface of radius
pronator quadratus action
Pronates forearm; deep fibers bind radius and ulna together
pronator quadratus innervation
anterior interosseous nerve, from median nerve (C8, T1)
Forearm Flexors: superficial, intermediate, and deep group
Superficial:
pronator teres
flexor carpi radialis
palmaris longus
flexor carpi ulnaris
Intermediate:
flexor digitorum superficialis
flexor digitorum profundis
Deep:
flexor pollicis longus
pronator quadratus
The brachial A enters the cubital fossa and bifurcates into the _________ and __________ arteries.
radial, ulnar
Just above the wrist, ulnar A’s pulse can be felt _______________ to the flexor carpi ulnaris.
The radial A’s pulse, just above the wrist is felt ___________ to the flexor carpi radialis
Which muscles in the superficial and deep flexors of the forearm are NOT innervated by the Median N?
flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum profundus (medial part)
Which muscles does the ulnar nerve innervate in the forearm?
Flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum profundis (medial part)