Producer and Consumer Behavior
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
income changes
pure income effect
price changes
income and substitution effects
normal goods
higher income = more consumption
inferior goods
higher income = less consumption
income effect
change in consumer choices resulting from change in income and purchasing power, holding price constant
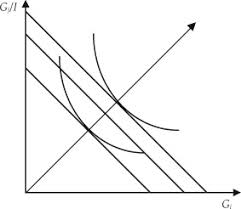
income expansion path (IEP)
curve that connects consumer’s optimal bundles at each income level
IEP positive slope
both goods normal
IEP negative slope
1 good inferior
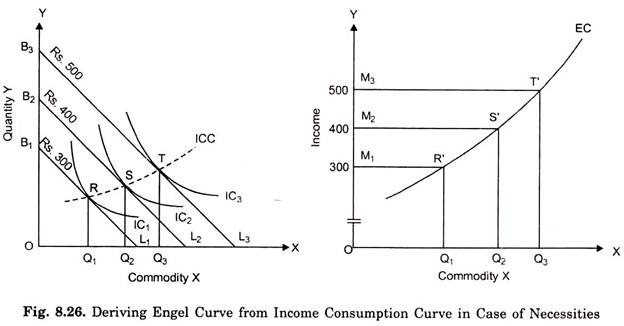
engel curve
shows relationship between quantity consumed and income; goods can transition from normal to inferior
positive engel slope
good is normal at that income level
negative engel slope
good is inferior at income level
deriving a demand curve
define relationship
change one price, observe changes in consumer choices
observed price = maximum willingness to pay for the last unit consumed
substitution effect
change in consumption resulting from a change in relative price of two goods
income effect
change in consumption resulting from a change in purchasing power of income
inferior good changes
increase in purchasing power = decrease consumption
decrease purchasing power = increase consumption
normal good changes
increase in purchasing power = increase consumption
decrease purchasing power = decrease consumption
total effect
substitution effect + income effect
isolating substitution effect
determine bundle of goods that would have been chosen at new price while maintaining utility experience before change in price; find where the new indifference curve would be parallel to new price/budget
isolating income effect
change in QD due to change in purchasing power after change in price (whatever is left after substitution effect)
purchasing power change on graph
BC1 to BC2
Income effect on graph
A’ to B
Substitution effect on graph
A to A’
market demand
horizontal sum of individuals’ demand curves
market quantity
sum of individuals’ quantity demanded at each price
production
process by which firms use inputs to create outputs
final goods
goods bought by consumers (bread)
intermediate goods
goods used to produce another good (wheat)
production function
mathematical relationship between inputs and how much output is made
production function equation
Q = KaL(1-a) ; a<=1
capital (K)
building, equipment
labor (L)
human resources
assumptions of production
firm produces 1 good
firm has already chosen the product to produce
only two inputs: capital and labor
capital fixed in short run, adjustable in long run
more inputs = more outputs
inputs are characterized by diminishing returns
firm can buy as much capital and labor as it wants to borrow
marginal product (MP)
additional unit of output using additional input (holding use of other input constant)
Marginal Product of Labor (MPL)
aQ(L,K)/aL
Marginal Product of Capital (MPK)
aQ(L,K)/aK
diminishing MPL
decline in output rate, not level; tends to happen in short run; doesn’t always have to diminish, only eventually
isoquant
“same quantity”; combinations of capital and labor that yield the same output
characteristics of isoquants
further from origin = higher output
can’t intersect
convex to origin
Slope of Isoquant
Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution
Marginal Rate of Technical Substitution
MRTSK,L= MPL / MPk
isocost
“same cost”; all input bundles that cost the same
W
wage; expense of labor
R
rent; cost of capital
Cost Equation
W*L + R*K
slope of cost
-W/R
cost minimizing condition
MPL / MPk = W/R
Marginal Product Per Dollar Labor
MPL / W
Marginal Product Per Dollar Capital
MPK / R
Returns to Scale
change in output when all inputs are increased in the same proportion
constant returns to scale
production increases proportionally to inputs
increasing returns to scale
changing inputs changes the outputs more than proportionally
decreasing returns to scale
changing inputs by the same proportion changes the output less than proportionally
firm expansion path
illustrates how the optimal mix of inputs varies with total output
total cost curve
firm’s cost of producing particular quantities
accounting cost
direct costs of operating a business
economic costs
accounting cost + opportunity cost
accounting profit
firm’s total revenue - accounting cost
economic profit
total revenue - economic cost
fixed cost
cost of fixed inputs, independent of output
variable cost
cost of inputs that vary with output
total cost
fixed cost + variable cost
average total cost
TC/Q
average fixed cost
FC/Q
Average variable cost
VC/Q
AFC curve
always declining
AVC & ATC Curves
U-shaped
marginal cost
additional cost of producing additional unit of output
MC
dTC/dQ (FULL DERIVATIVE)
MC < ATC
cost of producing one more unit is less than average cost; average cost falls with unit
MC > ATC
cost of producing one more unit is more than average cost; average cost rises with unit
MC = ATC
average is at minimum
economies of scale
cost rises more slowly than production
constant economies of scale
cost rises at same rate as production
diseconomies of scale
cost rises more quickly than production