CIS 230 Exam One Reynolds
1/199
Earn XP
Description and Tags
200 terms and vocab
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
deployment
Configuring hardware and system software is an activity of the UP __________ discipline.
design or architectural design
Selecting hardware, network components, and system software is an activity of the UP __________ discipline.
business modeling
During the __________ and requirements UP disciplines, the business, its environment, and user requirements are defined and modeled.
white paper
A technology brief found on a vendor or manufacturer Web site is often called a __________.
IEEE Computer Society
Computer- and network-related standards can be found in the digital library of the __________.
technology architecture
The term __________ includes several other types of computer-related architecture including computer, network, and software architecture.
mainframes
One type or class of larger servers includes ____________, which are generally optimized for data storage and I/O capability.
register
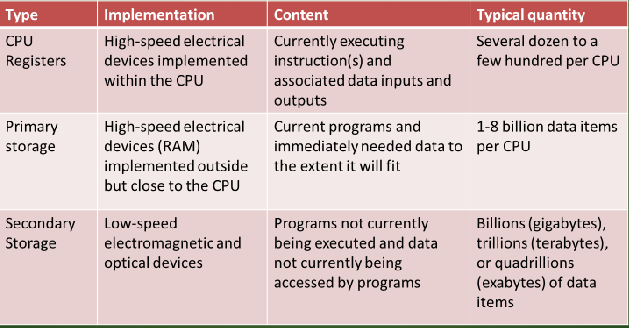
A(n) ____________ is a storage location implemented in the CPU.
primary storage
The term ____________ refers to storage devices, not located in the CPU, that hold instructions and data of currently running programs.
algorithm
A problem-solving procedure that requires executing one or more comparison and branch instructions is called a(n) ____________.
instruction
A(n) ____________ is a command to the CPU to perform one processing function on one or more data inputs.
secondary storage
The term ____________ describes the collection of storage devices that hold large quantities of data for long periods.
server
A(n) ____________ is a computer that manages shared resources and allows other computers to access them through a network.
formula
A program that solves a(n) ____________ requires no branching instructions.
supercomputer
A(n) ____________ typically uses the latest and most expensive technology.
cluster
A(n) ____________ is a group of similar or identical computers, connected by a high-speed network, that cooperate to provide services or run a shared application.
grid
A(n) ____________ is a group of dissimilar computer systems, connected by a high-speed network, that cooperate to provide services or run an application.
general-purpose
A CPU is a(n) ____________ processor capable of performing many different tasks simply by changing the program.
system bus
The __________ enables the CPU, primary storage, and secondary storage devices to communicate. (definition from quiz)
programming language
Most programs are written in a(n) ____________, such as FORTRAN or Java, which is then translated into equivalent CPU instructions.
network
A(n) ____________ consists of hardware and software components that enable multiple users and computers to share information, software, and hardware resources.
virtualization
____________ is a technique that enables a single computer to host multiple virtual machines.
Grosch’s Law
____________ says that larger computer classes are more cost-efficient than smaller ones - a statement that doesn't accurately describe modern computing hardware.
operating system
A(n) ____________ is the most common type of system software.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
WWW resources are identified and accessed by a(n) ____________.
volatility
Key characteristics that distinguish primary and secondary storage include cost, capacity, speed, and ____________.
floating-point
__________ notation encodes a real number as a mantissa multiplied by a power (exponent) of 2.
hexadecimal
Assembly (machine) language programs for most computers use __________ notation to represent memory address values.
data structure
A(n) __________ is a data item composed of multiple primitive data items.
EBCDIC
In older IBM mainframe computers, characters were encoded according to the __________ coding scheme.
pointer
A(n) __________ is the address of another data item or structure.
radix point
In a positional numbering system, the __________ separates digits representing whole number quantities from digits representing fractional quantities.
string
A(n) __________ is an array of characters.
segmented memory model
Most Intel CPUs use the _____________ , in which each memory address is represented by two integers.
linked list
A set of data items that can be accessed in a specified order by using pointers is called a(n) __________ or an index.
byte
A(n) __________ contains 8 bits.
singly linked list
A(n) __________ list stores one pointer with each list element.
array
A(n) __________ is a sequence of primitive data elements stored in sequential storage locations.
record
A(n) __________ is a data structure composed of other data structures or primitive data elements, commonly used as a unit of input and output to and from files or databases.
Boolean
A(n) __________ data item can contain only the values true or false.
index
A(n) __________ is an array of data items, each of which contains a key value and a pointer to another data item.
Unicode
Unlike ASCII and EBCDIC, __________ is a 16-bit or 32-bit character coding table.
least significant bit
The__________ is the bit of lowest magnitude in a byte or bit string.
Overflow
__________ occurs when the result of an arithmetic operation exceeds the number of bits available to store it.
class
A(n) __________ is a data structure containing both static data and methods.
object
A(n) __________ is one instance or variable of a class.
Resistance
__________ generates heat in electrical devices.
Gallium arsenide
__________ is a semiconducting material with optical properties.
transistor
A(n) __________ is an electrical switch built of semiconducting materials.
heat sink
A(n) __________ improves heat dissipation by providing a thermal mass and a large thermal transfer surface.
hertz (Hz)
One __________ is one cycle per second.
instruction register
When an instruction is first fetched from memory, it’s placed in the __________ and then decoded to extract its components.
gate
A(n) __________ is an electrical circuit that implements a Boolean or other primitive processing function on single bit inputs.
microprocessor
A microchip containing all the components of a CPU is called a(n) __________.
instruction pointer
The address of the next instruction to be fetched by the CPU is held in the __________.
load
The contents of a memory location are copied to a register while performing a(n) __________ operation.
integrated circuit, microchip
A(n) __________ or __________ contains multiple transistors or gates in a single sealed package.
RISC
A(n) __________ processor limits the number and type of complex instructions.
MOVE
A(n) __________ instruction copies data from one memory location to another.
wait states
The CPU incurs one or more __________ when it is idle, pending the completion of an operation by another device in the computer system.
word
A(n) __________ is the number of bits the CPU processes simultaneously. It also describes the size of a single register.
program status word (PSW)
In many CPUs, a register called the __________ stores bit flags representing CPU and program status, including those representing processing errors and the results of comparison operations.
operands
The components of an instruction are its op code and one or more __________.
Moore’s Law
__________ predicts that transistor density will double every two years or less.
benchmark
A(n) __________ is a measure of CPU or computer system performance when performing specific tasks.
pipelining
__________ is a CPU design technique in which instruction execution is divided into multiple stages and different instructions can execute in different stages simultaneously.
Systems architecture
structure, interaction, and technology of computer or
information system components
Computer architecture
Architecture of a single computer system or a group
of cooperating computer systems
Information architecture
Architecture of data or information—for example,
a database schema or the structure of a document archive
Network architecture
Architecture of a computer network including wired
and wireless connections, network-specific hardware such as routers, and related communication protocols and software
Software architecture
Architecture of a program, software subsystem, or software system
Technology architecture
Combination of all of the architectures with specific emphasis on issues such as performance, reliability, compatibility, and extensibility**
system development life cycle (SDLC)
Information system development follows a _________________.
The _____________ is the most commonly-used SDLC today
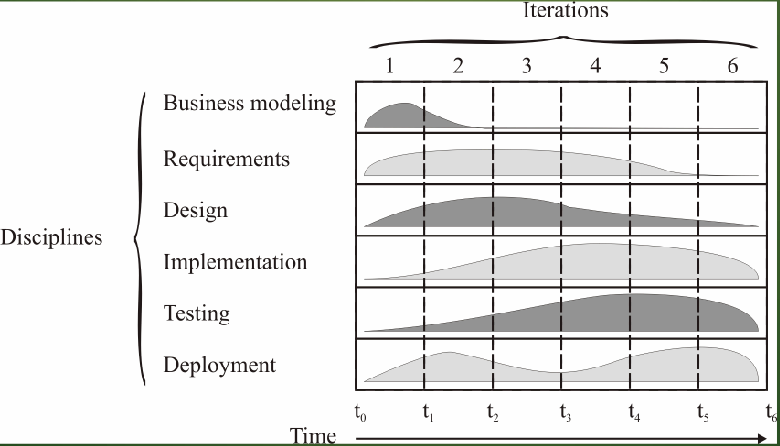
Unified Process (UP)
Discipline
A set of related activities of similar type and skill requirements
Iteration
A relatively short time duration during which a mix of UP activities are performed to produce one or more specific deliverables
UP DISCIPLINES AND ITERATIONS CHART
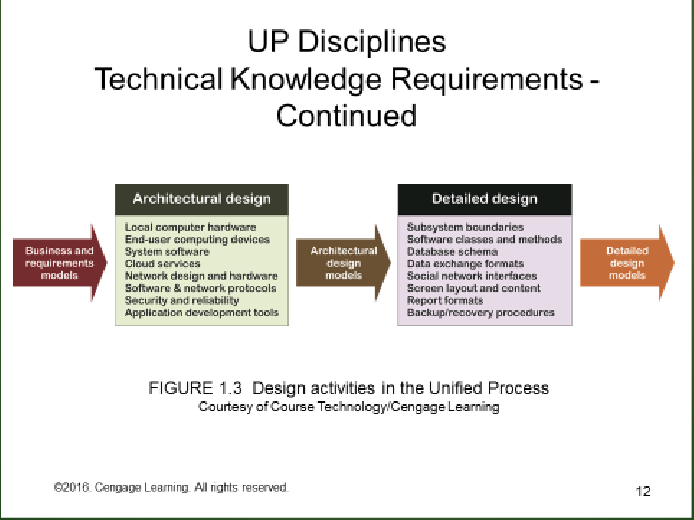
UP DISCIPLINES TECHNICAL CHART
automated computation device
An ____________can:
– Accept numeric inputs
– Perform computational functions
– Communicate results
Summarized as input – process - output
Complexity, Reliability, Speed
3 shortcomings of mechanical computing are _______________.
Optics
________ is gradually supplanting electricity (and it’s cousin, magnetism) in various areas of systems architecture
qubit
Quantum particles can exist in multiple states at the same time
processor
A ___________ is a device that can perform the following functions:
• Computation (+, ‒, ×, ÷)
• Comparison (<, =, >, ≠, ≤, ≥)
• Data movement among memory, mass storage, and I/O devices
instruction
An __________ is a command to a processor to perform a specific function (e.g.,
addition) on specific data input(s)
Program(s)
A stored set of instructions for performing a specific task, such as calculating payroll or generating reports. _________ are executed by processors.
general-purpose processor
_____________ read its program instructions from a storage device;
The content of the storage device can be changed, thus
changing the program and the function performed by it
special-purpose processor
____________ either:
1) uses program storage that can’t be altered (e.g., read-only
memory)
2) Has a single program “wired” into it
formula
is a complex mathematical relationship that can be
“solved” with a specific sequence of instructions
condition
_____________ is a numerical comparison used in a processing task to determine if the result is true or false
logic instructions
the instructions that implement comparison and branching are sometimes called ______________.
Speed, volatility, cost per bit
Different mixes of data characteristics drive the need for a variety of storage and technologies, each tailored to cost-effectively match the data characteristics with appropriate device characteristics such as: _______ , _______ , _________
COMPUTER CHART
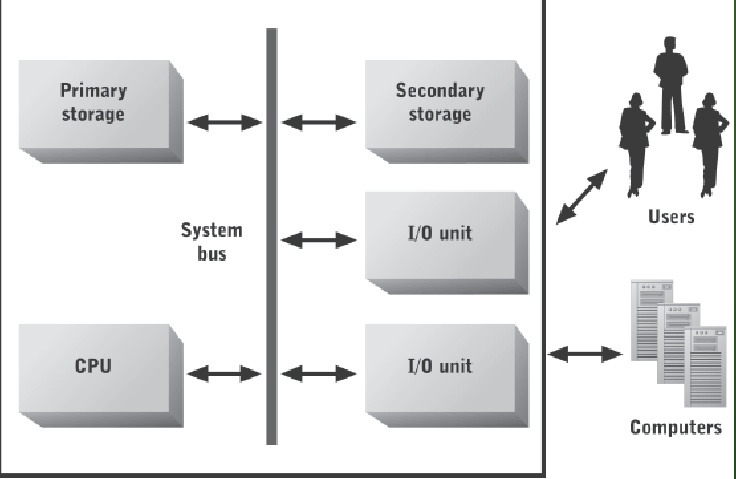
INSIDE THE CPU
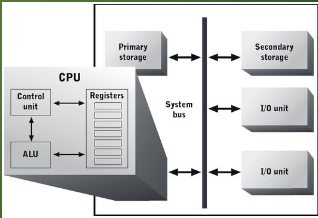
Arithmetic-logic unit (ALU)
Performs computation and logic instructions
Registers
Internal storage locations – each holds one data
item. Also hold inputs to and outputs from the ALU.
Control unit
Moves data among registers and other computer
system storage locations. Also accesses program instructions and either executes them (data movement) or directs the ALU to
execute them (computation and logic instructions).
Primary storage
______________ is also called, main memory or just memory, are areas of
high-speed storage that:
1) Holds programs currently being executed
2) Holds data inputs needed (or expected to be needed) immediately by executing programs
3) Is implemented outside the CPU, but is “close” to the CPU to improve access speed
4) Is implemented using “fast” device technology to improve access speed
5) Is volatile (loses its content when power is lost)
Random Access Memory (RAM)
In modern computers, primary storage is implemented with _____________. Contents can be moved to/from the CPU in a few nanoseconds. Capacity is normally a few gigabytes (billion data items) per CPU
Secondary storage
________________ hold large quantities of data and programs (typically hundreds of billions to a few quadrillions of data items)
1) Is non-volatile (holds content indefinitely)
2) Is much cheaper per bit than primary storage
3) Is much slower than primary storage
STORAGE COMPARISON SUMMARY