antigen and antibodies
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Antigen or Immunogen
– molecule that generates an immune response; foreign molecular structures
Antigenicity
– ability of a molecule to be recognized by an antibody or lymphocyte
microbial antifen
bacterial antigen
viral antigen
other microbial antigen
Bacterial Antigens
The major components of bacterial surface are cell wall, capsule (K antigens), pili (F or K antigens), fimbriae and flagella (H antigens)
Cell wall of gram-positive organisms is largely composed of peptidoglycan but in gram-negative organisms, the layer of peptidoglycan is thin covered by an outer membrane consisting of lipopolysaccharides
The lipopolysaccharides in these organisms are mostly associated to the antigenicity of gram-negative bacteria
Bacterial lipopolysaccharides in gram-negative bacteria are also called endotoxins
Other bacterial antigens include:
i. Porins
heat-shock proteins
exotoxins – highly immunogenic proteins and stimulate the production of antibodies called antitoxins; when treated with formaldehyde. It will lose its toxicity but retains its antigenicity and thus it will modified and called toxoids
other bacterial antigen include
porin
heat shock protein
exotoxin
exotoxin
highly immunogenic proteins and stimulate the production of antibodies called antitoxins; when treated with formaldehyde.
It will lose its toxicity but retains its antigenicity and thus it will modified and called toxoids
toxoid
It will lose its toxicity but retains its antigenicity and thus it will modified
endotoxin
Bacterial lipopolysaccharides in gram-negative bacteria are also
K antigen
capsule
F or K antigen
pili
H antigen
fimbriae and flagella
gram-positive organisms
largely composed of peptidoglycan
gram-negative organisms
ayer of peptidoglycan is thin covered by an outer membrane consisting of lipopolysaccharides
viral protein
Can grow only inside living cells, thus, are “obligate”, intracellular parasites
Capsid proteins are good antigens and are highly capable of provoking antibody formation
Proteins in the virions act as antigens and trigger acquired immune response
Viral nucleic acid can be integrated into a cell’s genome. The viral genes code for new proteins, some of which are carried to the surface of infected cells and are then considered foreign and can provoke strong immune responses
capsid protein
good antigens and are highly capable of provoking antibody formation
Non-microbial Antigens
Some food may contain foreign molecules which may trigger an immune response and cause allergic reaction.
Inhaled dusts can contain fungal spores or pollen grains and enter the respiratory system. Snake bite or mosquito bite may inject foreign molecule
factors that signidicantly influence the antigenicity of a molecule
✓ Size
✓ Complexity
✓ Dose
✓ Route of administration
✓ Host genetics
✓ Chemical stability
✓ Foreignness
waht makes a good antigen
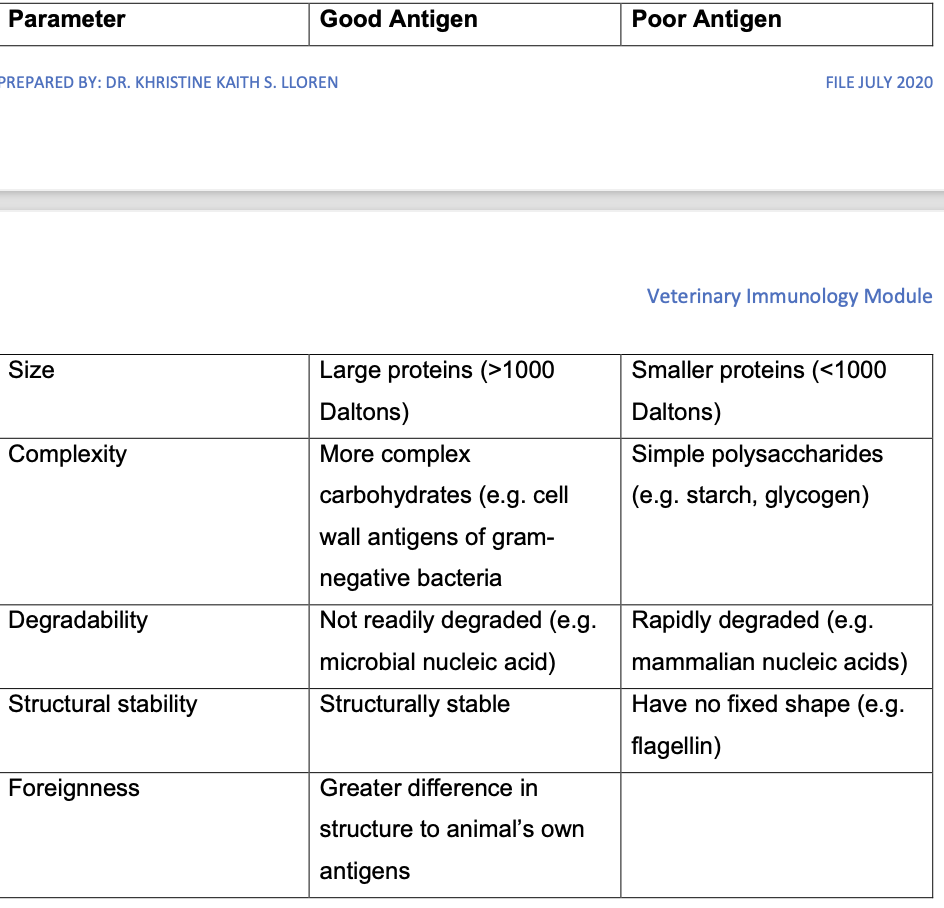
foreignness
however, not all foreign molecules can stimulate immune
response. (e.g. steel bone pins and plastic heart valves)
This is due to the molecular uniformity and inertness. These polymers cannot be degraded and processed by cells
Epitopes or antigenic determinants
These are sites on the surface of an antigen that stimulates a specific immune response
Many different epitopes may be recognized by the immune system, but some are much more immunogenic than others
Haptens
Small molecule that cannot initiate an immune response unless it is bound to an immunogenic carrier molecule
The antigenic molecule to which the haptens are attached is called the ‘carrier’
example of hapten
o Antibiotic penicillin (small nonimmunogenic molecule) → forms “penicilloyl” group when degraded in the body→bind to serum proteins such as albumin→penicilloyl-albumin complex→penicilloyl hapten→recognized as foreign epitope in some individuals → antibodies response and cause allergic reaction
o Resin of poison ivy plant called urushiol → binds to protein it comes in contact (e.g. skin proteins of person who rubs against the plant) → modified skin proteins→regarded as foreign→attacked my lymphocytes →allergic contact dermatitis
cross reactivity
There are instances that identical or similar epitopes can be found on apparently unrelated molecules.
Antibodies directed against one antigen may react unexpectedly with an unrelated antigen
Antibodies directed against a protein in one species may also react in a detectable manner with homologous or similar protein in another species
antibodies
Once B cell response is triggered, the receptors are shed into the surrounding fluid, where they act as antibodies
They bind to specific antigens and facilitates removal by phagocytes, activate complement and neutralize the activity of the antigen
They are glycoproteins called Immunoglobulins
Consists of two pairs of protein: the heavy and light chain linked together by disulfide bond
Antibodies monomers have a Y shape with an antigen-binding site at the end of each arm of the Y. The tail of the Y is the Fc region.
The antibody monomer is composed of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains; each chain forms several domains. The variable region contains the antigen binding site; the constant region encompasses the entire Fc region as well as part of the Fab regions.
two pairs of protein:
the heavy and light chain linked together by disulfide bond
Antibodies monomers
have a Y shape with an antigen-binding site at the end of each arm of the Y.
Fc region
The tail of the Y
immunoglobulin
they are glycoprotein
antibodies
function
o Primary: bind to antigen
o Neutralize bacterial toxin
o Prevent viral attachments to cells by forming bridge between phagocyte and invader
immunoglobulin classes
IgG
IgM
IgA
IgE
IgD
immunoglobulin variation
allotypes
idiotypes
Immunoglobulin G (IgG)
Highest concentrations in serum
Made and secreted by plasma cells in the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone
marrow
Plays the major role in antibody-mediated defense mechanisms
Consists of two identical light chains and two gamma heavy chains
Smallest antibody (can escape from the blood vessels more easily)
Major antibody of secondary immune response
Immunoglobulin M (IgM)
Also produced by plasma cells in the spleen, lymph nodes and bone marrow
Second highest concentration in serum
The major antibody produced during a primary immune response although it is also produced during secondary immune response
Considerably more efficient than IgG at complement activation, opsonization, neutralization of viruses and agglutination
Due to very large size, they rarely enter tissue fluids at sites of inflammation
Immunoglobulin A (IgA)
Secreted by plasma cells located under body surfaces (e.g. in the walls of intestine, respiratory tract, urinary system, skin and mammary gland
Main antibody on the mucosal surfaces of the body
Either pass through epithelial cells into external secretions or diffuse into the bloodstream
Prevents antigens adhering to body surfaces (important in protecting the intestinal, respiratory, and urogenital tracts, mammary gland and the eyes against microbial invasion
Does not opsonize antigens and does not activate the classical complement pathway
Secreted in milk of lactating dams
Immunoglobulin E (IgE)
• Also produced beneath body surfaces
• Typical Y-shaped, four-chain immunoglobulin with four constant domains in its
heavy chains
• Present in extremely low concentrations in serum
• Cannot simply bind and coat antigens but triggers acute inflammation by acting
as a signal transducing molecule (signaling molecule) and are found on the
surface of mast cell and basophil
• Has the shortest half-life (2-3 days)
• An important immune response to parasites
Immunoglobulin D (IgD)
Unique because it has not been detected in all mammals
It is present in primates, rodents, cattle, sheep, pigs and dogs
Absent in horses, rabbits and chickens
Present only in trace amounts
Can be destroyed by mild heat treatment like IgE
Allotypes
The inherited sequence variations in heavy chain genes of the immunoglobulin
Thus, immunoglobulins of one individual may differ from those of another
individual of the same species
Idiotypes
Results from the variations in the amino acid sequences within the variable domains on light and heavy chains
Differences associated with the antigen-binding region of an antibody
Monoclonal Antibodies
– antibodies specific for one antigen; produced by hybridoma (cell line derived by the fusion of a single normal B cell and an immortal B cell tumor line); widely use in research
Polyclonal Antibodies
– collection of antibodies from different B cells that recognize multiple epitopes on the same antigen
Affinity
- a measure of the binding strength between an antigenic determinant (epitope) and an antibody binding site (paratope)
Avidity
the total strength of all the interactions in an antibody-antigen complex which may have more than on bonding site; it is influenced by affinity as well as structural arrangements of epitope and variable regions of antibody
Antigen binding site
– part of an antibody that binds antigen
Anti-serum
– serum that contains a detectable number of antibody molecules that bind to a particular antigen
Diversity
– presence of large numbers of antibodies that bind different specificities
Domain
– a region found in molecules coded for by members of the immunoglobulin supergene family, which comprises approximately 110 amino acids
Fab (Fragment antigen binding)
– part of an antibody which contains the antigen binding site of the molecule composed of the variable regions of one light chain and one heavy chain
Fc (Fragment crystallizable)
– fragment of an antibody molecule lacking the antigen binding sites caused by papain digestion. It contains the constant regions of both the heavy chains from the hinge region to the carboxyl terminus of the molecules
Paratope
– part of an antibody molecule which makes contact with the antigenic determinant
Serum
– residual fluid when blood forms clot and is where antibodies can be found