OIA1004 TISSUES: THE LIVING FABRICS
1/35
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are the four basic tissue types in the body?
Epithelial (covering/lining), connective (support), muscle (movement), and nervous (coordination).
What are the general characteristics of epithelial tissue?
Tightly packed cells with little intercellular matrix, attached to a basement membrane, non-vascular, and high mitotic rate.
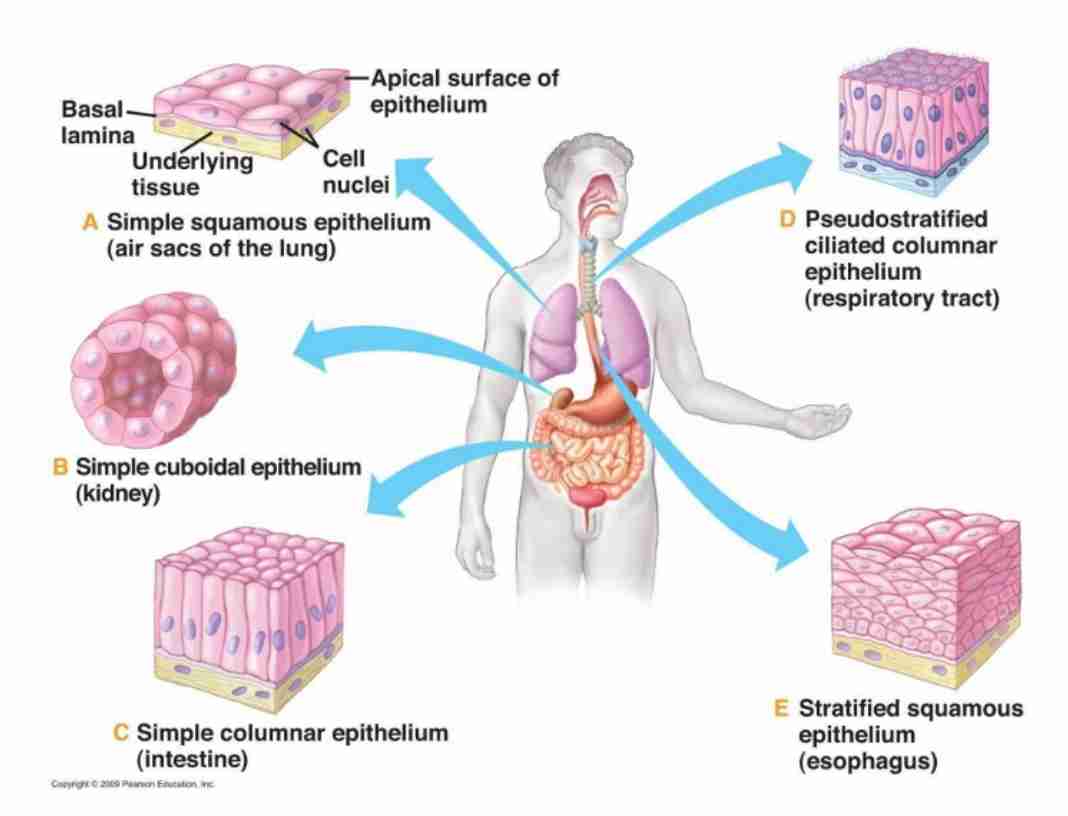
Name three functions of epithelial tissue.
Protection, secretion, and absorption.
What are classifications of glandar tissues?
Simple (unbranched duct), compound (repeated branching pattern, part of secretory portion), tubular (terminal secretory portion in tube form) & acinar (terminal secretory portion in form of sac/flask like).
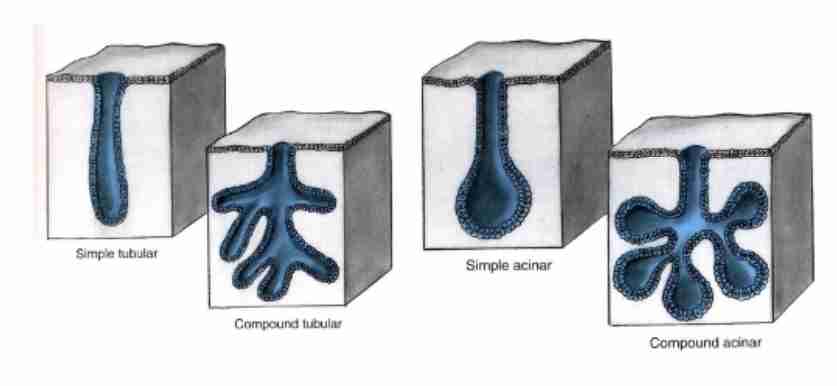
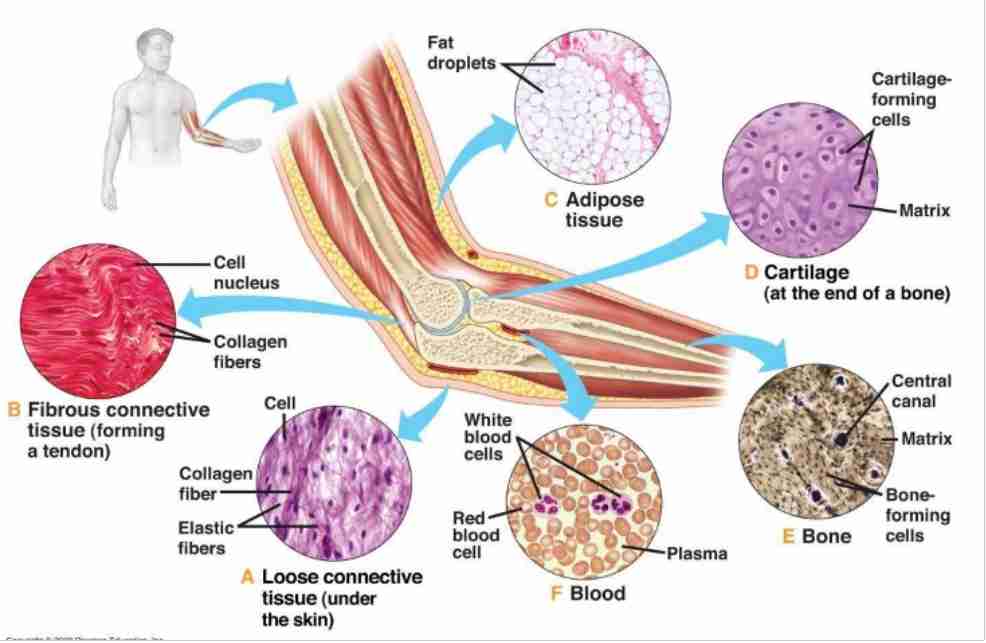
What are connective tissues responsible for?
Binding, anchoring, and supporting various cells, tissues, and organs.
What components make up connective tissue?
Cells (e.g., fibroblasts, macrophages) and extracellular matrix (fibers like collagen, elastic, and reticular).
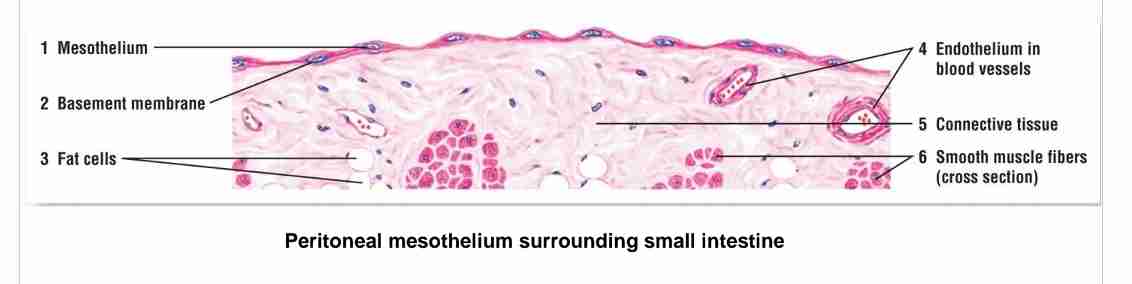
What is simple squamous epithelium, and where is it found?
A single layer of flat cells, found in mesothelium (external surface of digestive organs, lungs & heart) and endothelium (blood vessels). Function: filtration, diffusion, transport, secretion & reduce fiction.
What is the function of simple cuboidal epithelium?
Protection, transport, and absorption in excretory ducts and kidney tubules (lined w/ microvilli)
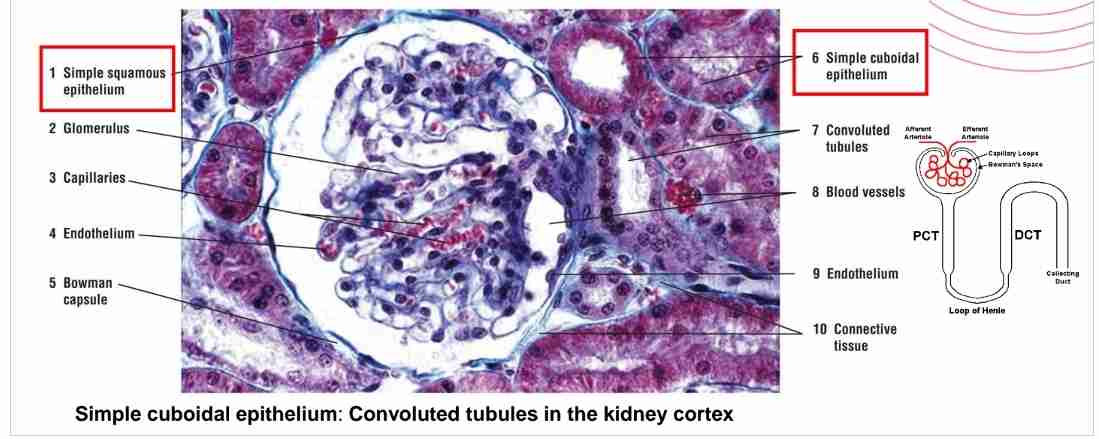
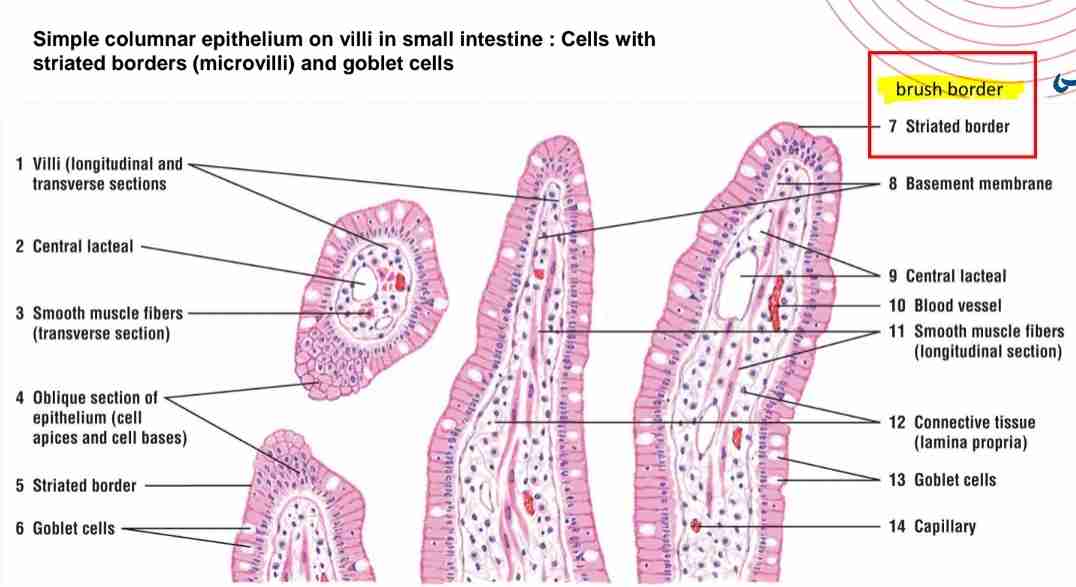
Where is simple columnar epithelium found?
Tall cells lining the stomach, intestines, and uterine tubes, often with microvilli or cilia.

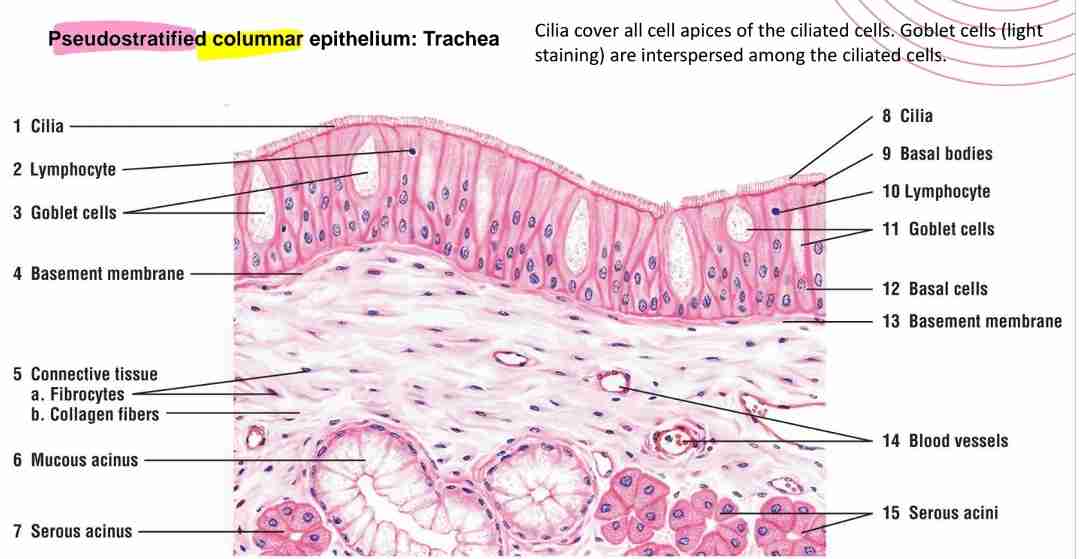
What is the main feature of pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
Single layer of cells that attach to basement membrane, not all cells reach surface. Cilliated cells interspersed among mucus-secreting cells and lines respiratory passages (e.g., trachea) & lumina of epipidymis & vas deferans.
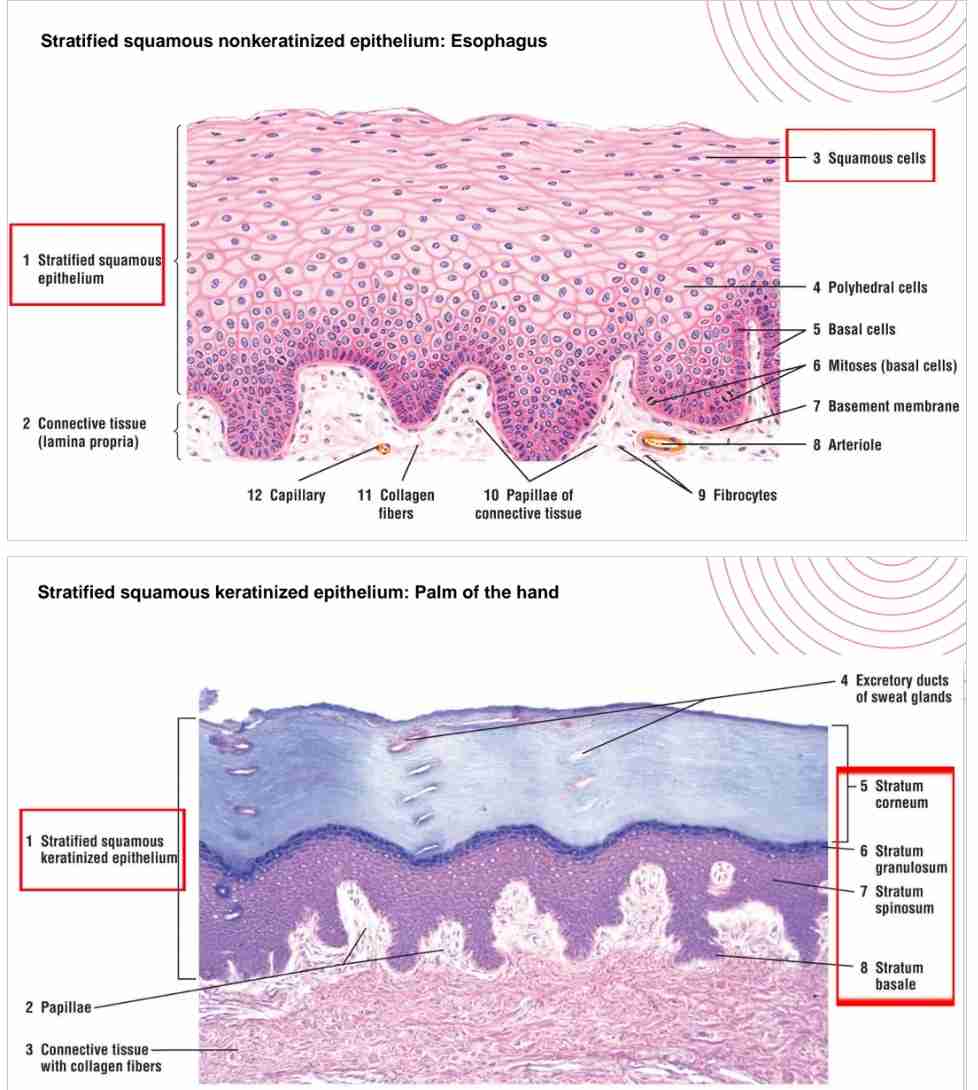
How does stratified squamous epithelium differ between keratinized and non-keratinized types?
Keratinized epithelium has dead, keratin-filled surface cells (e.g., skin), while non-keratinized covers moist cavities (e.g., mouth, vagina).
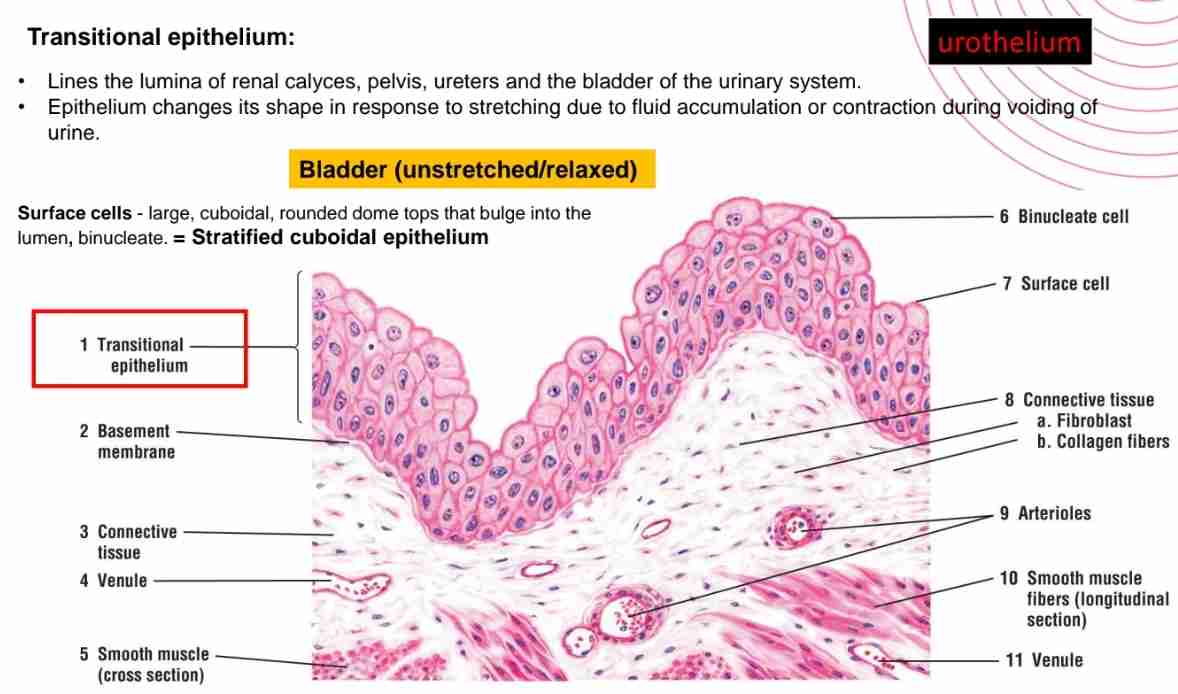
What are the main features of transitional epithelium?
Lines lumina of ureters & bladder of urinary system and epithelium changes it’s shape in response to stretching due to fluid accumulation/ contraction during excretion.
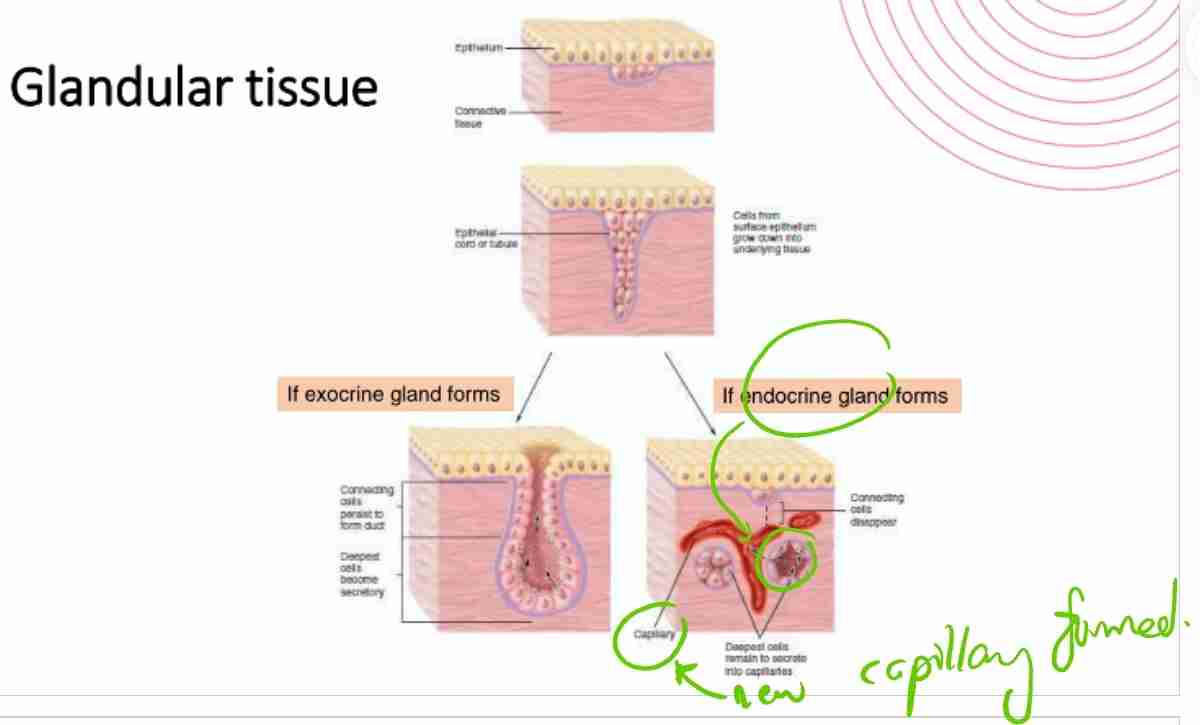
What differs between formation of exocrine and endocrine glands?
Exocrine (connecting cells persists to form duct where deepest cells become secretory) & endocrine (connecting cells disappear & deepest cells remain to secrete into capillaries).
What are types of glandar tissues?
Simple tubular (intestinal in large intestine & rectum); simple branched tubular (gastric in stomach); simple coiled tubular (sweat); compound acinar (mammary glands contains enlarged alveoli w/ excretory ducts); compound tubuloacinar (salivary)
What are functions of connective tissues?
binds, anchors & supports various tissues
provide gel-like medium for exchange nutrient, O2 & metabolic waste
protect & defend body against invasion & foreign bodies
What are the two types of connective tissue proper?
Loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue.
Where is loose connective tissue found?
Beneath epithelial layers and around blood vessels.
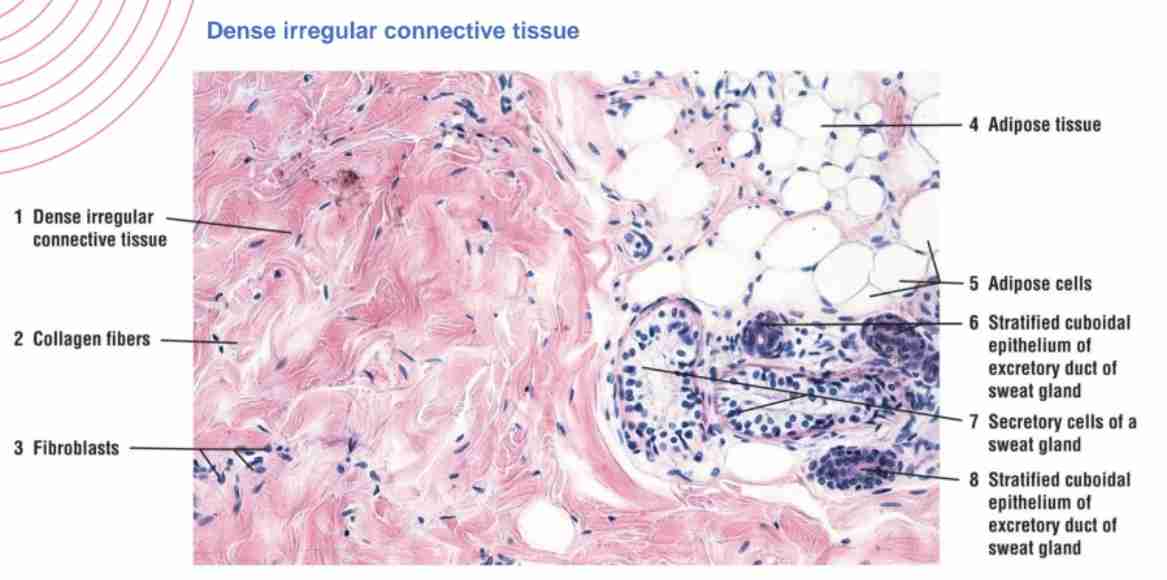
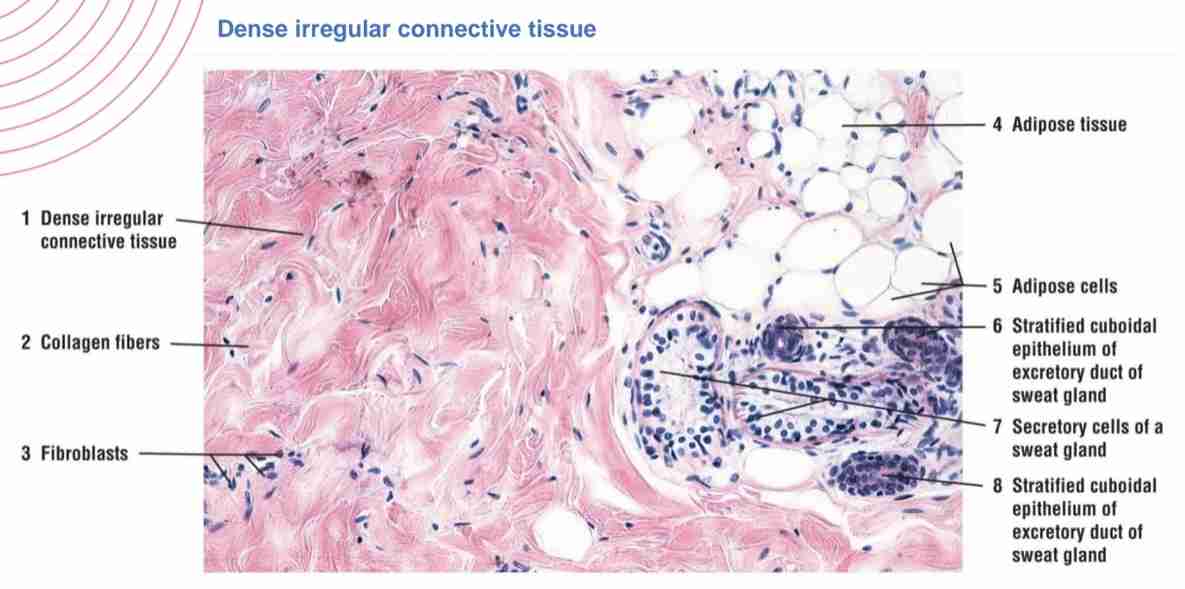
What is the main function of dense irregular connective tissue?
Concentrated in areas where need resistantce to forces from different directions (dermis of skin, capsules of organs).
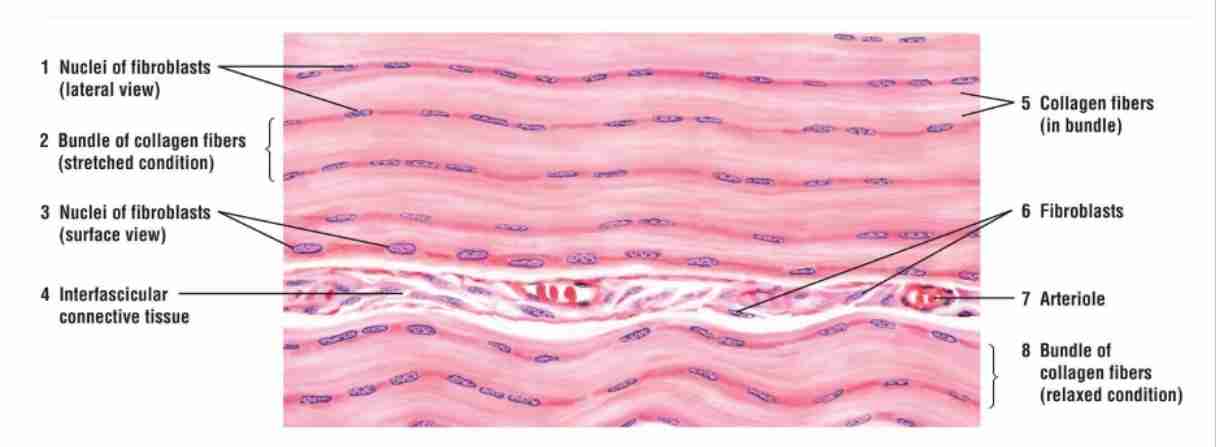
What is the main function of dense regular connective tissue?
Providing tensile strength, found in tendons and ligaments.
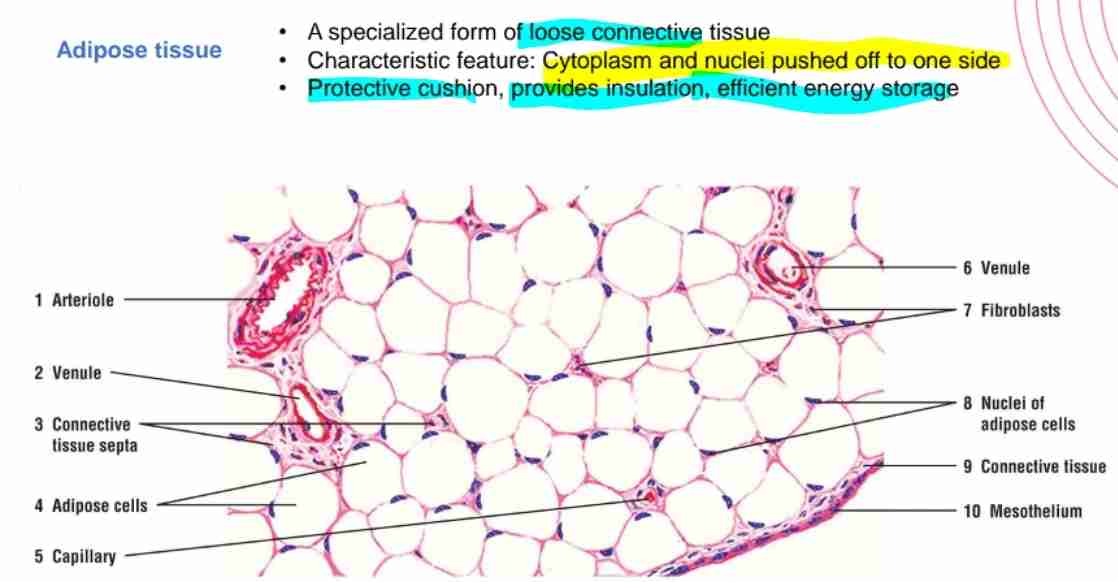
What is adipose tissue, and its primary role?
A specialized loose connective tissue w/ cytoplasm & nuclei pushed off one side: for energy storage, insulation, and cushioning.
Name the three types of cartilage.
Hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage.
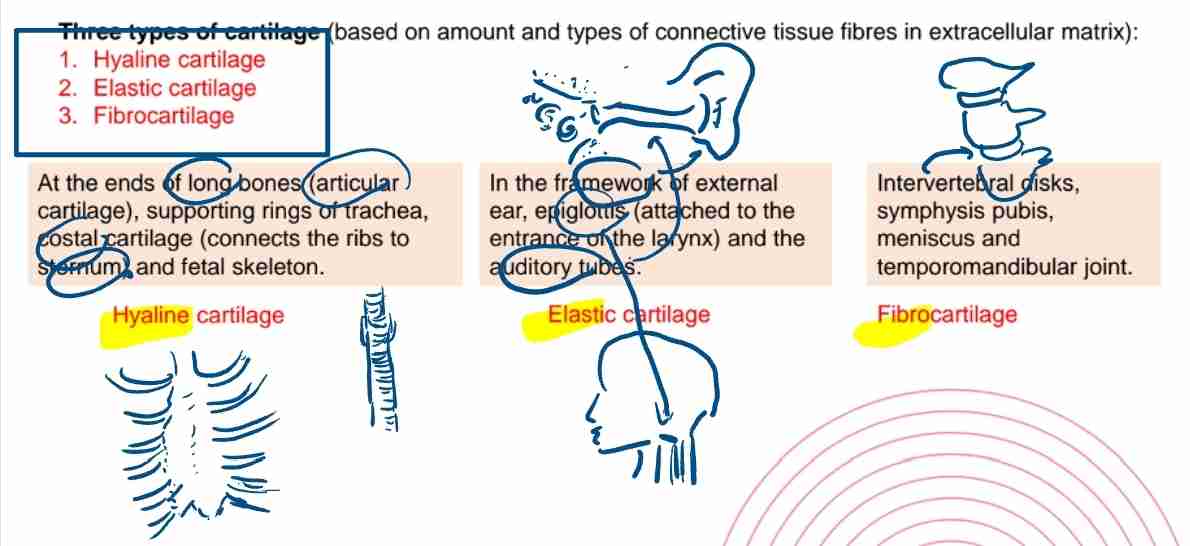
Where is hyaline cartilage found?
At the ends of long bones, trachea, and costal cartilage.
What makes elastic cartilage unique?
Its elasticity due to elastin fibers, found in the ear and epiglottis.
Where is fibrocartilage located?
Intervertebral discs and the pubic symphysis.
What is the primary function of bone tissue?
Support, protection, and storage of calcium and phosphorus.
What is unique about blood as connective tissue?
It has a liquid matrix (plasma) and functions in transport, defense, and homeostasis.
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
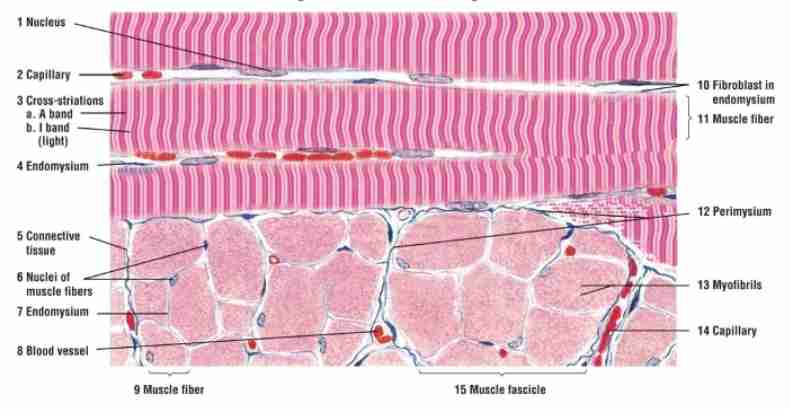
What is the key feature of skeletal muscle?
Voluntary control, multinucleated cells, and striations.
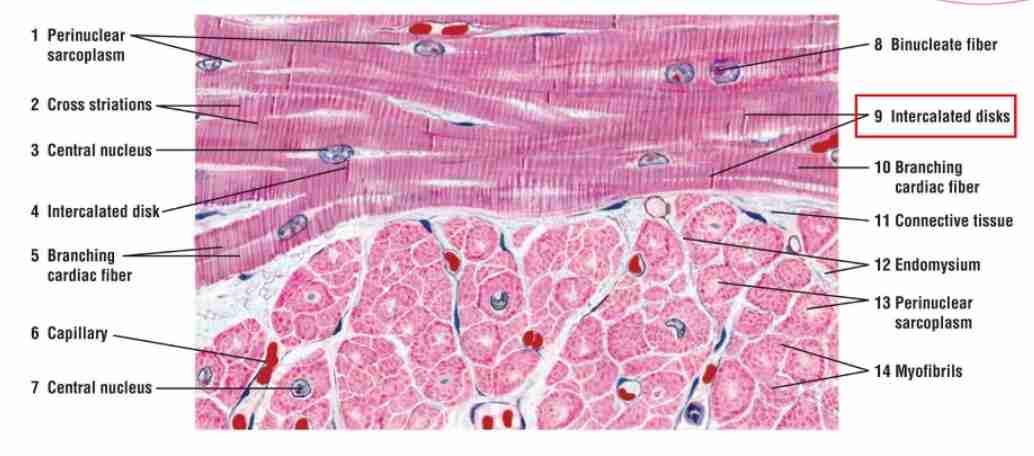
How does cardiac muscle differ from skeletal muscle?
It has involuntary control, one or two nuclei per cell, and intercalated discs.
Where is smooth muscle found?
In the walls of hollow organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels.
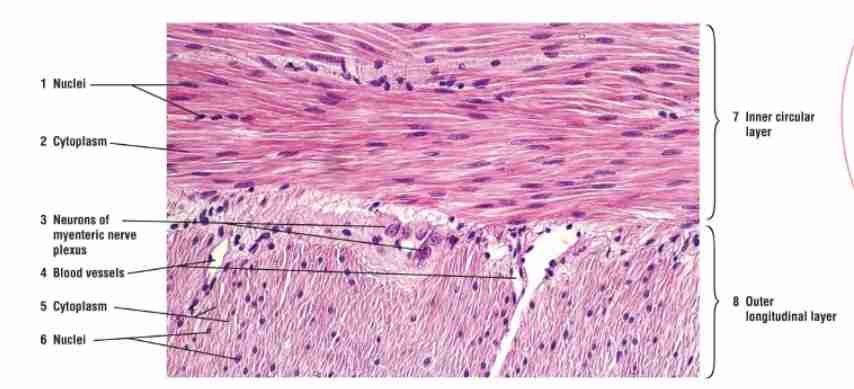
What is the function of smooth muscle?
Propelling substances through organs by rhythmic contractions.
What is the primary function of nervous tissue?
Communication and coordination through electrical impulses.
Name the two main cell types in nervous tissue.
Neurons (transmit signals) and glial cells (support neurons).
What is the role of myelinating glial cells in the CNS and PNS?
Oligodendrocytes myelinate axons in the CNS; Schwann cells in the PNS.
What is the function of astrocytes?
Formation of the blood-brain barrier and nutrient support for neurons.
Where is ependymal tissue found?
Lining the ventricular cavities and central canal of the spinal cord.