
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
The 'stuff' of the universe - anything that has mass and volume.
A characteristic or behaviour of a substance that may be observed when it undergoes a chemical change or reaction.
A reversible change that forms no new substances.
An irreversible change where bonds are broken/formed and new substances are created.
A mixture that is not evenly mixed, e.g. Curry
A mixture that is evenly mixed, where each part would have the same contents, e.g. sugar water
When energy is released from a substance, making the substance colder and the surroundings warmer. e.g. Freezing, condensation
When energy is absorbed into the substance, making the substance warmer, and the surroundings colder. e.g. melting, evaporation.
What are the properties of solids?
Rigid, fixed shape and volume, particles can only vibrate
What are the properties of a liquid?
Not rigid or fixed shape, fixed volume, particles can vibrate and rotate
What are the properties of gases?
Not rigid, fixed volume, or fixed shape, particles can vibrate, rotate and translate
A term used to describe a solution that has been dissolved in water, e.g. salt water.
What are the properties of Alkali Metals?
Low melting and boiling points, very soft and shiny form +1e cations, react violently with water
What are the properties of Alkali Earth Metals?
shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive, form +2e cations
Are ductile and malleable, conduct electricity and heat, and have high melting and boiling points. Exist in multiple oxidation states (usually +2)
These groups include metalloids and non-metals, which have varied properties such as low density, low melting points, and poor conductivity. Elements like carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and noble gases are included in these groups.
very reactive, highly toxic gases that form -1e anions. Diatonic - exist as two atoms
Very unreactive, colorless, odorless gases that exist as monatomic molecules. They have full valence electron shells, which contributes to their stability.
Atoms that have a positive or negative charge due to a loss or gain of electrons. This occurs in chemical reactions in order to fill or empty valence shells.
Metals typically form positive ions + (cations)
Non-metals typically form negative ions - (anions)
Formed when a positive cation and negative anion bond together. The two atoms often share a valence electron
Form crystals or crystal lattices, have higher melting/boiling points, are hard but brittle and conduct electricity when dissolved in water
The cation name goes first, then the anion
Cation name remains the same
-ide suffix is added to the end of the anion e.g. oxygen = oxide
What are Covalent Compounds?
A chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms
What are elements are covalent compounds formed between?
Covelant compounds form between two or more non-metal elements
How to name Covalent Compounds?
A prefix is used to indicate how many of the atom are present (e.g. mono). The second element takes the -ide suffix
What would P2O5 be named?
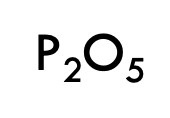
Diphosphorus Pentoxide
What are the properties of Covalent Compounds?
Low melting and boiling points, soft or brittle solid, poor conductivity
What are some ways to know a chemical reaction has taken place?
Gas formed, colour change, Solid Precipitates, Temperature change, change of smell
What is a combustion reaction?
a reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy in the form of light and heat.
What is the general formula for a combustion reaction?
Fuel + O2 → CO2 + H2O
What is a combination reaction?
A reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single new substance
What is the general formula for a combination reaction?
A + B → AB
What is a decomposition reaction?
A reaction in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
What is the general formula for a decomposition reaction?
AB → A + B
What is a displacement reaction?
A reaction in which the atom of the more reactive element displaces the less reactive element
What is the general formula for a single displacement reaction?
A + BC → AC + B
What is a double displacement reaction?
A reaction in which two reactants exchange ions to form two new compounds.
What do double displacement reactions typically form?
They typically form precipitates
What is the general formula for double displacement reactions?
AB + CD → AD + CB