Week 2 - Charles Darwin development of theory of Natural selection
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what was darwins background (all his careers)
- failed med student
- studied naturaly theology under reverend john henslow to become a clergy man
- henslow introduced him to cpt. robert fitzroy of HMS Beagle who he joined on his 2 year maping voyage which turned out to be 5 years
- he then became a popular writer
what were darwins beleifs pre HMS beagle
- earth ~6000 yrs
- species were separetly and supernaturally created for a specific prupose
- species are unable to change
where were darwins major observations on the HMS beagle
1. south american manland
2. australia
3. galapagos island
what did darwin observe on the south amerocan mainlands
- animals/plants were very dif from europe but this was not due to climate (as nat theology would suggest) since they had v simmilar climate
- therfore, species (living or fossil) from one continent tend to be distinct even when conditions of another continent are similar
- simmilar species tend to geographically cluster
eg. found fossils that r simmilar to living armadillos in the same geographical location and no where else even w the same environtment
what did darwin see earthquakes doing in south america
raised the shoreline by several feet
theorized this was how mountains formed
what did darwin see during his andes expidition
Observed fossilized trees In sandstone (sedimentary rock) with No other vegetation
Darwin hypothesized:
Trees were once near the ocean, → became submerged in water → where they became fossilised. → Later earthquakes that occurred lifted the trees into the mountains
** showed how hutton and lyell were right: slow/subtle processes have dramatic effects over long periods of time
marsupials vs placental mammals
m - born small and underdeveloped so gestate in external pouch
p - born later and independant

what did darwin observe in austrailia
mammals were marsuial while everywhere else hes only seen placental mammals
however they were ecologically equivalent (unrelated species but addapted to simmilar habitats)
why did darwin thing there were marsupials in austrailia (2 theories)
1. austrailian environment is better suited for marsupials then placental (nat theo) - later disproved this
2. marsupials were the initial "starting poit" and then were modified into the european placentals (aka convergent evolution)
how was it tested if marsupials and placentals wwrre specifically made for their locations (special creation)
rabbits (placental mammals) were acc released in austraili by colonists
found: rabbbits wer able to thrive and proliferate (became invasive)
disproved natural theology theory since shows placental mammals are not unfit for 'marsupual" environments
what was darwins general conclusions from the galapagose islands
when small groups of individuals become idolated from their population they change over time --> these chnages can form new sub species or even a new species entirley
examples of darwns findings on the galapagos idlands
1. marine iguanas - similar to those on mainland ecuador but have adaptation for life in wter unique to galapagose
2. finches - 13 species all simmilar to mainland species (blueblack grassquit) but each w own distinct adaptadioni unique to their island --> diversity in sych a small group of bird suggest common anscetory)
3. tortoises - dif shells depending on which island
what was darwin not aware of on his travels (3)
1. theory of plate tectonics - continental plates r moving (5cm/year on avg)
2. egg-laying mammals evolved 220million years ago (duing pangea - allowing them to spread across the world)
3. marsupials and placentals both appears 120 million years ago in eurasia
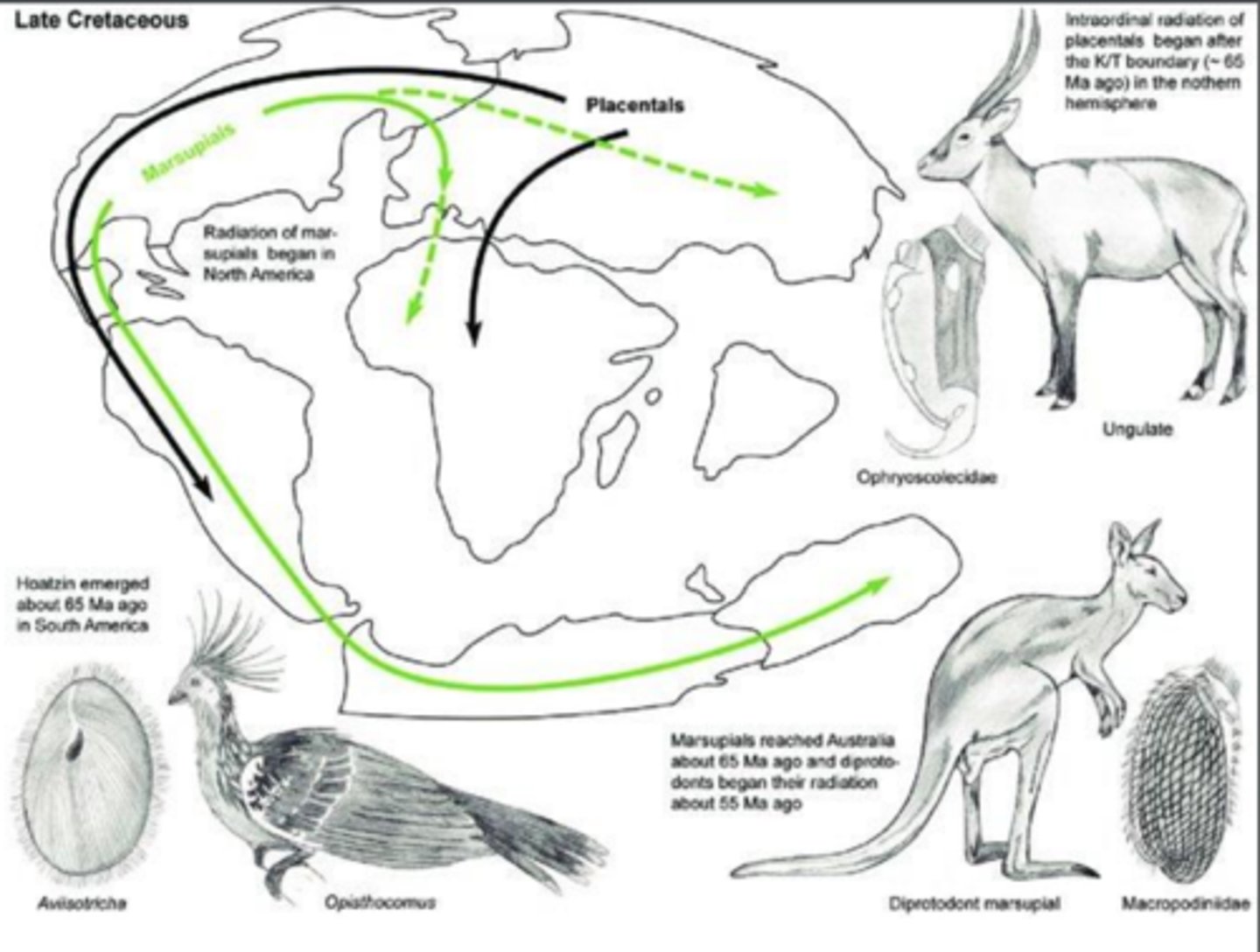
How did the marsupials and placental spread out from eurasia to the current distribution today?
marsupuials: eurasia → (via bering land bridge) north then south america → antarctica --> austrailia
placentals: didint follow. why?
hypothesis: temporari;y held bac bc of inland sea, onece sea dried they followed marsupuals path but austrailia was alr too isolatied
marsupials not in austrailia went extince (competition w placentals) and the ones in austrailia evolved to fill the same placental niches
darwins beleif post HBS beagle
species are NOT fixed and change over time (evolve)
what causes this change: he thoerized natural selection
what is fitness
ability to survive and reproduce fertile offspring
Artificial selection
Humans select individuals to breed that have desirable qualities --> create new breeds
domestication
the process of changing plants or animals to make them more useful to humans
popukar among rich to produce ectreme traits common with pigeons
also with agriculuture
Natural selection as per charles darwin
if we can artificially select for certeain traits why couldnt this happen naturally
- variant of trait in indivudial of a population give some increase fitness
- The individuals that survive (higher fitness) will leave behind more offspring which will inherit their traits
- leads to adaptive change of a population
natural selection is dependent on what
NS is dynamic,If the environment fluctuate so does the pressure on traits
Why did darwin keep silent after theorizing natural selection
challenged the church, special creation theory, other scientists and his wife
he wanted tonmake sure he was absolutley right by obsessivley collecting evidence before coming out w his theory
when was origin of species (darwins book finally released)
1859 - after sitting on it for 20 years finally prompted by letter from alfred russle wallace out of fear he woud be scoops - this is when he became a populr science writer
who was alfred russel wallace (dif bw his ideas and darwins)
- made a living from collectng specimens for collections (poor)
- from noticing differing island from each island of indonesia he naturally came up w the idea of NS and wrote a letter to darwin
*differnece whata wallance thought only environment was the selecting factor while darwin thoght other species were as well
what did darwin decide to do about the wallace dillema so he wouldnt get scooped
jointly presented walace and darwins findings to the linnean society (without wallaces knowledge but he was thankful)
but they didnt rlly care or understand or beleive it and it wasnt till book origin of species that evolutiion became more widley accepted
1859 Darwin origin of species
one of the best printed books in history - both praised and villified in the media
was written for the general public to understand includign A list of all his anecdotal evidence he gathered over the decades
this leads to darwin being known as the primary author of the theory of natural selection
what helped darwin understand the MECHANISM (cause) of evolution
the writings of TR malthus
all of darwins observations (1/5)
1. all species could technically geometrically increase if none of their offpsring died before reproducing (ideal conditions - geometric increase = by. contant factor eg x2 for bacterial cells w each reproduction
all of darwins observations (2 -3/5) + inference based on these
2. populations tend to remain stable in size
3. environmental resources are limited (food, nesting sites etc)
inference: individuals struggle for existence and only a fraction survive to reproduce
all of darwins observations (4 -5/5) + inference 2
4. no 2 individuals in a poplation are exactly alike
5. some of this variation is heritable (individuals tend to resemble their parents)
Inferences bases on bservations 4-5
inference 2 = survival partly depends on genetic make up (if u inherit traits that inc fitness ur more likely to leave more offsping = natural selection)
inference 3 = unequal ability to survive/reproduce causes gradual change in the makeup of populations (w individuals w favourable heritable traits progressibley becoming a greater percentage of the ppulation over time = evolution)
some subteties of natural selection
1. population is the smallest unit that can evolve
2. fitness is bility to reproduce relative to other in the population
3. NS only act on variation thats alr present
4. NS only act on variation thats heritable
5. natural selection is not progressive
1. population is the smallest unit that can evolve
population = group of interbreeding individuals in a given area
evolution = change in genetic makeup of a population over time
indiividuals CANNOT change their genetic makeup (lamark) eg. rabbits changing fur coulour depending on seasomn is not an evolutinoary change, their genetic makeup cannot change
2. fitness is bility to reproduce relative to other in the population
Survival is important, but only to allow reproduction
Fitness depends on the environment
Eg. polar bears have high fitness only in the arctic
3. NS only act on variation thats alr present
- NS Does not create new traits
- Natural selection (non-random) acts as an editor that eliminates unfit variants
- Does NOT create "perfect" organisms; can only work with variation already present
If NS doesnt cause variation/make new traits where does new variation arise from
variations arise from random processes:
1. mutation
2. crossing over
3. segregation & re-pairing of chromosomes during sexual reproduction (Mendel's 1st law)
4. NS only act on variation thats heritable (give example)
Acquired characteristics = not heritable
eg. polymedlia (six legged) frogs
1000s of these lower fitness frogs appeared died due to poor survival then reapearred a year later showing that NS had noteliminated them from the population
why? polymeilia was NOT GENETIC was caused by a parasite but there was no genetic differenced bw 4 and 6 legged frogs so polymelia was AQUIRED trait
5. natural selection is not progressive
- Changed in a population due to NS doesn't always lead to a more complex species
- The only goal of NS is survival and reproduction
- Some NS evolution even over simplify the organism to make it better fit
Eg. lizard cf. snake - Lizard is more complex But, snakes are descended from lizards - Lost legs as an adaptation for entering burrows