VESPR
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
VESPR
Molecules will adopt a shape that is lowest in energy
A low energy shape is one that minimizes the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) between adjacent atoms
What does this mean?
atoms try to spread out to reduce the "like charge repulsion" between outer electrons.
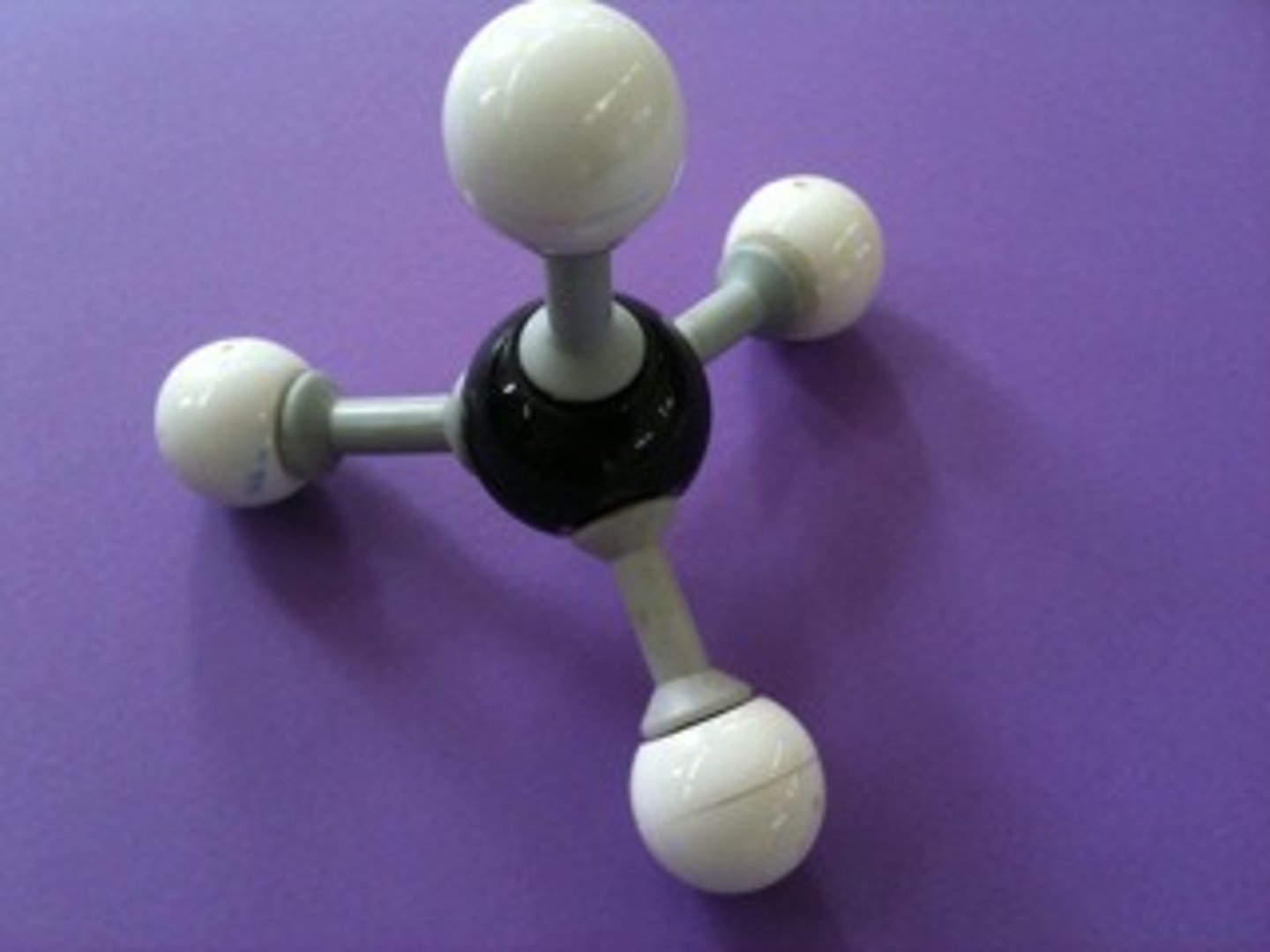
Methane CH4
This causes less repulsion between bonding pairs of electrons because they are 109.5 degrees apart

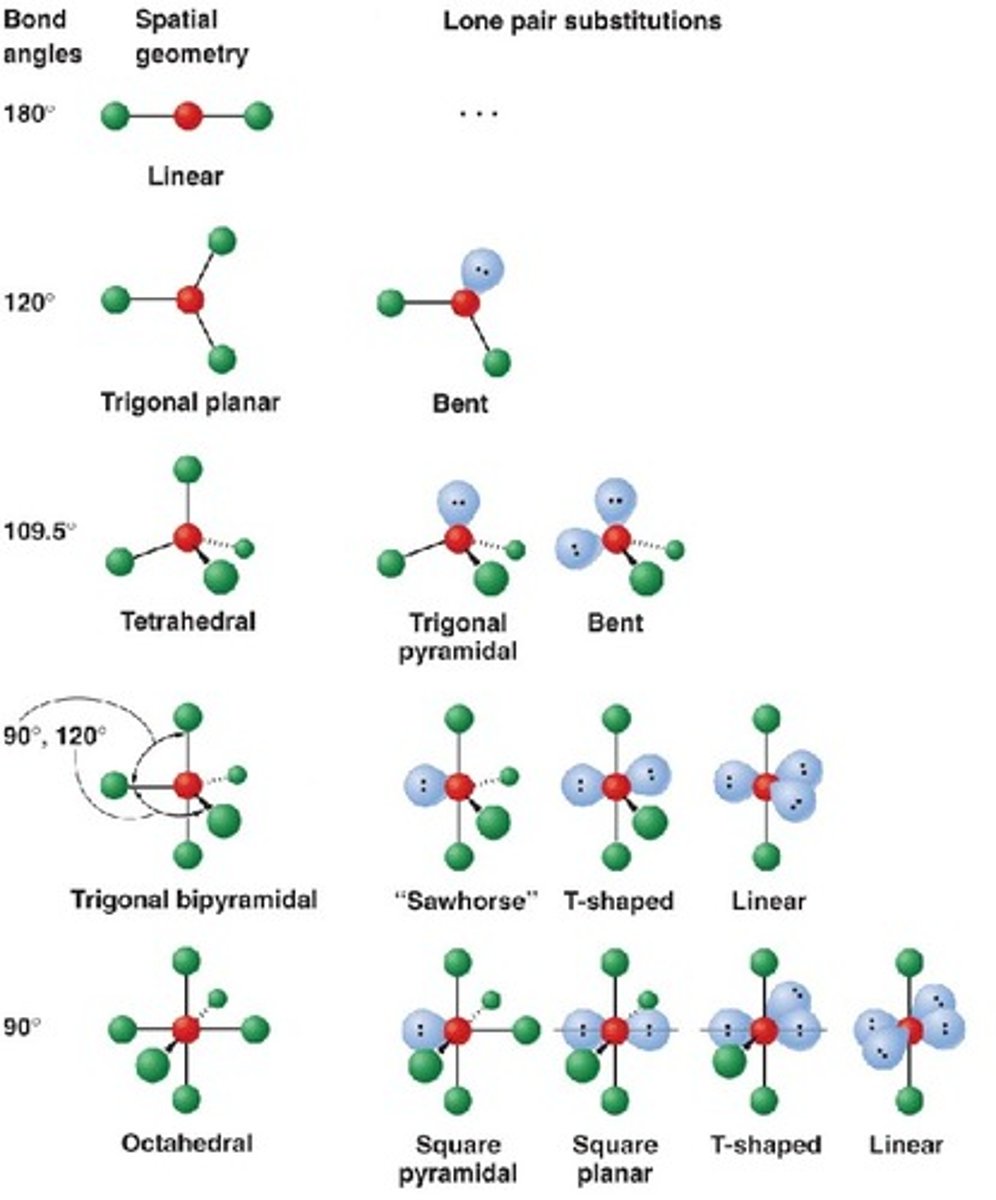
5 main shapes of molecular geometry
linear: 180 degrees
Trigonal Planar: 120 degress
Tetrahedral: 109.5
Trigonal Bipyramid: 90, the 120
Octahedral: 90
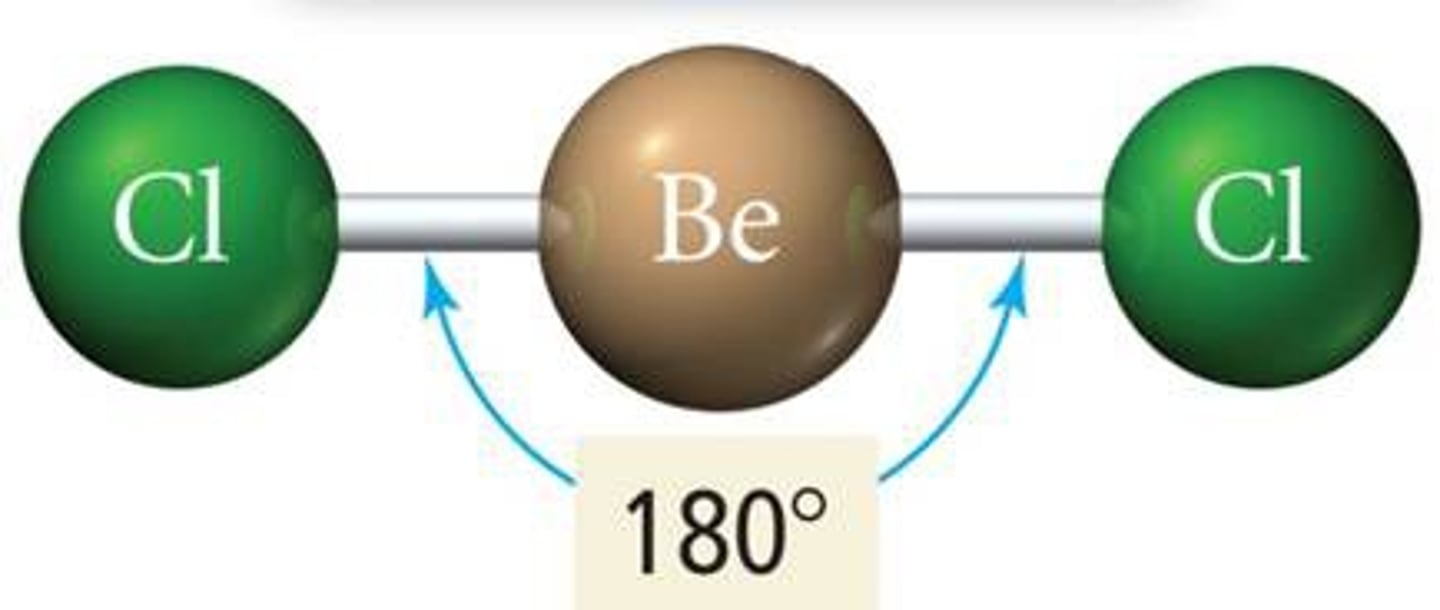
Linear molecular geometry
Bond Angle: 180
Molecular Geometry: linear
Domain (electron pair sites): 2
Number of bonding sites: 2
Number of lone pair electrons: 0
Trigonal Planar
Bond angle: 120
Molecular Geometry: trigonal planar
Domain: 3
Bonding Sites: 3
Lone pair: 0
Trigonal Planar (Bent)
Bond angle: 120
Molecular Geometry: trigonal planar
Domain: 3
Bonding Sites: 2
Lone pair: 1
Tetahedral
Bond angle: 109.5
Molecular Geometry: tetrahedral
Domain: 4
Bonding Sites:4
Lone pair: 0
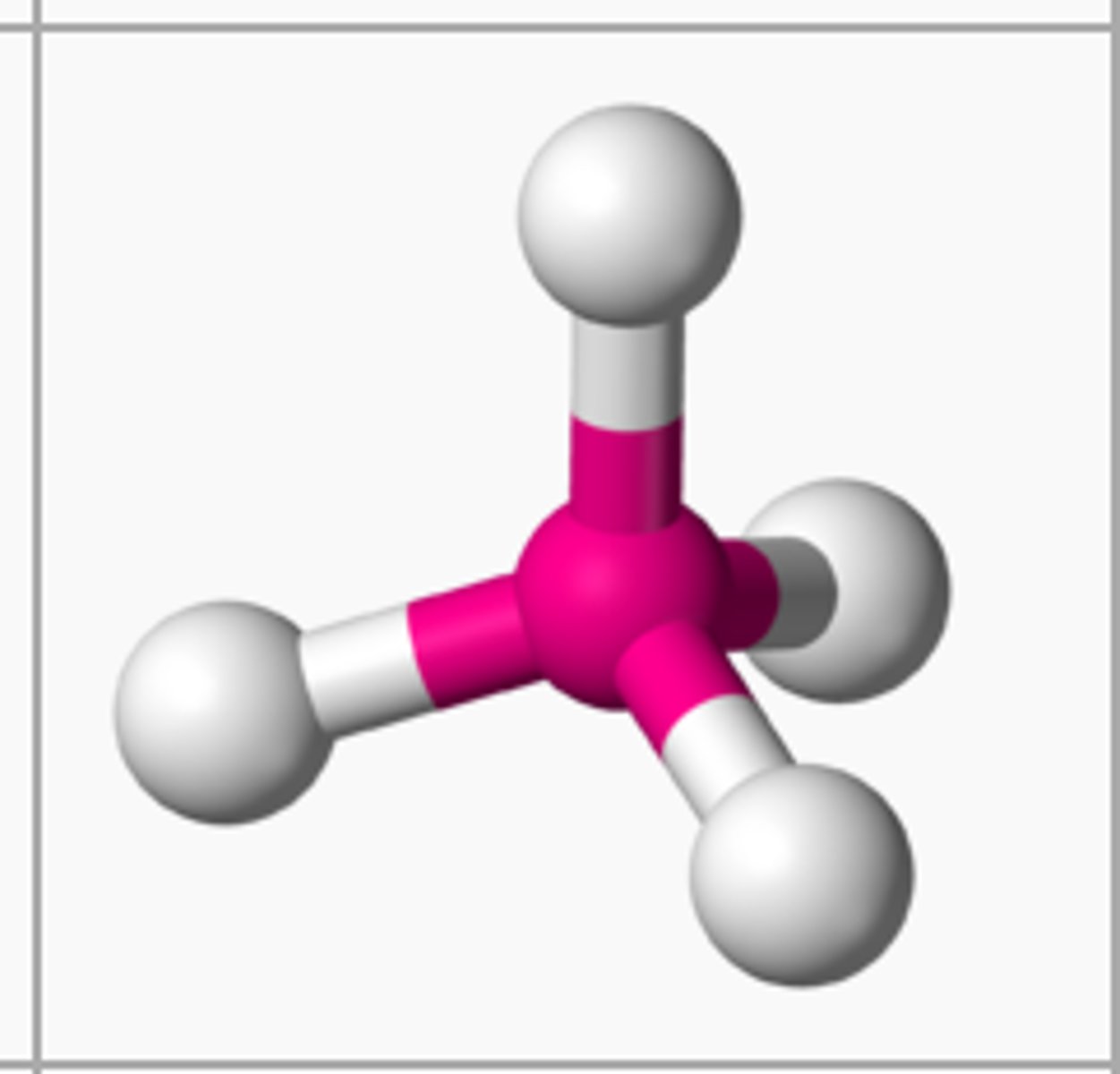
Tetrahedral (Bent)
Bond angle: 109.5
Molecular Geometry: tetrahedral
Domain: 4
Bonding Sites: 2
Lone pair: 2

Tetrahedral Trigonal Pyramidal
Bond angle: 109.5
Molecular Geometry: tetrahedral
Domain: 4
Bonding Sites: 3
Lone pair: 1
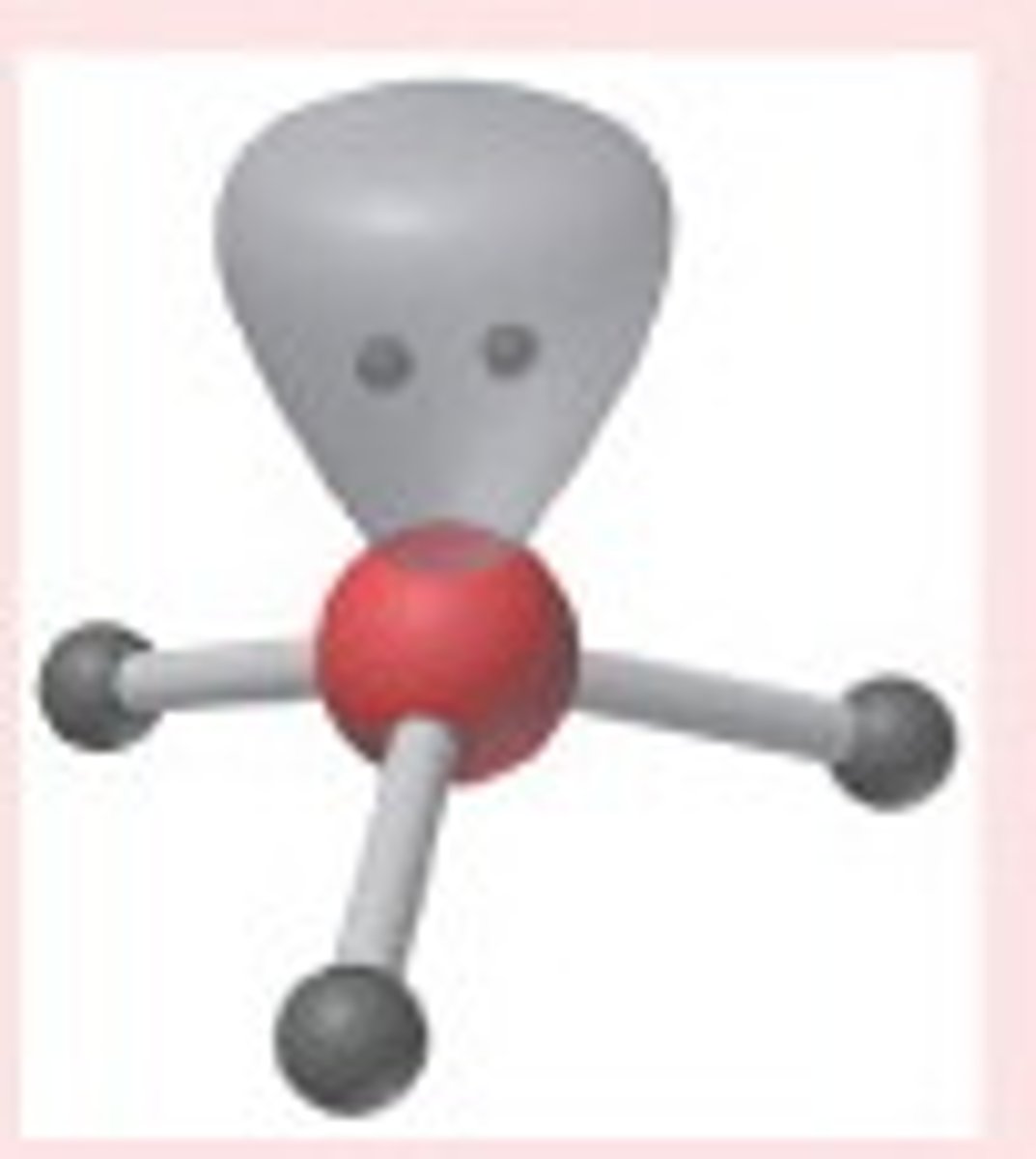
Trigonal Bipyramidal
Bond Angle: 120 +90
Molecular Geometry: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Domain: 5
Bonding Sites: 5
Lone pair: 0
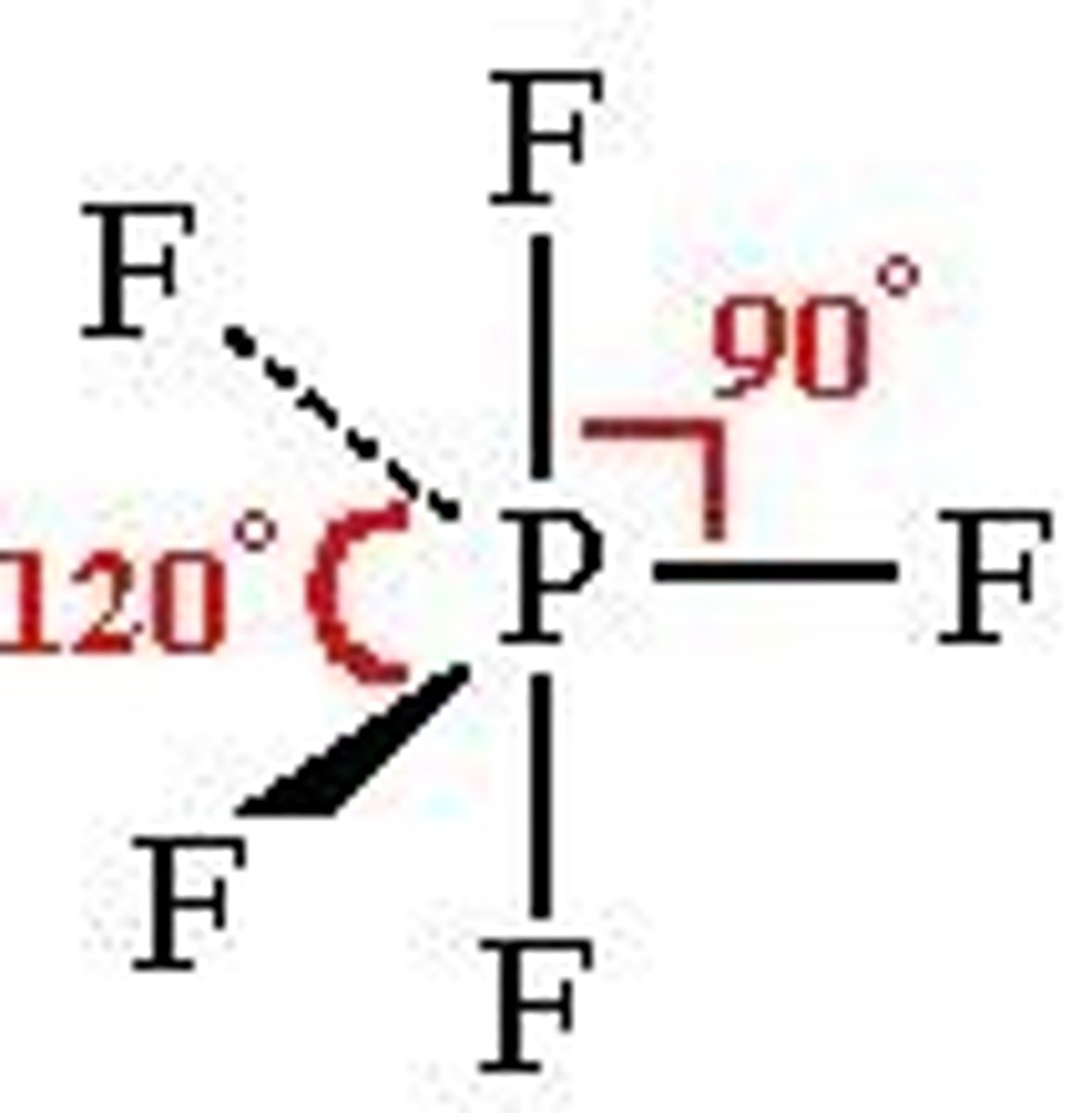
Trigonal Bipyramidal (Seesaw)
Bond Angle: 117 +90
Molecular Geometry: Seesaw
Domain: 5
Bonding Sites: 4
Lone pair: 1
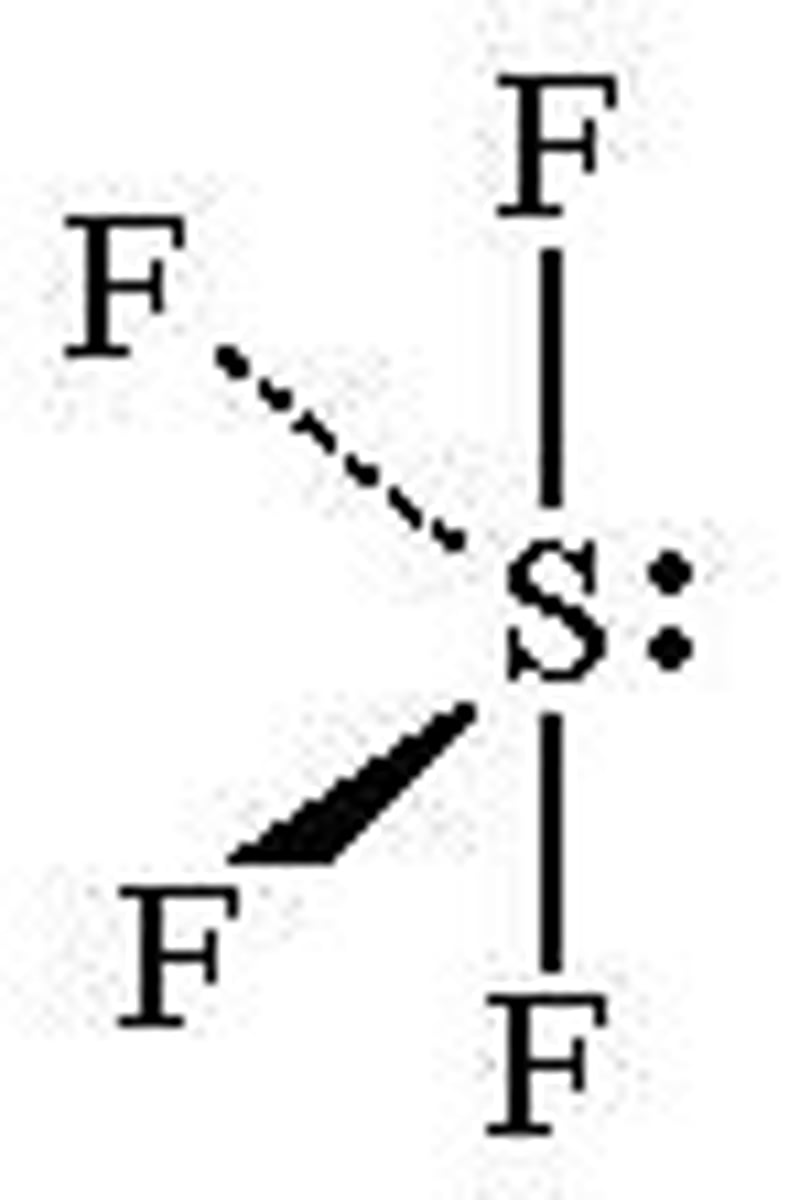
Trigonal Bipyramidal (T-Shaped)
Bond Angle: 90
Molecular Geometry: T-shaped
Domain: 5
Bonding Sites: 3
Lone pair: 2

Trigonal Bipyramidal (Linear)
Bond Angle: 120 +90
Molecular Geometry: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Domain: 5
Bonding Sites: 5
Lone pair: 0
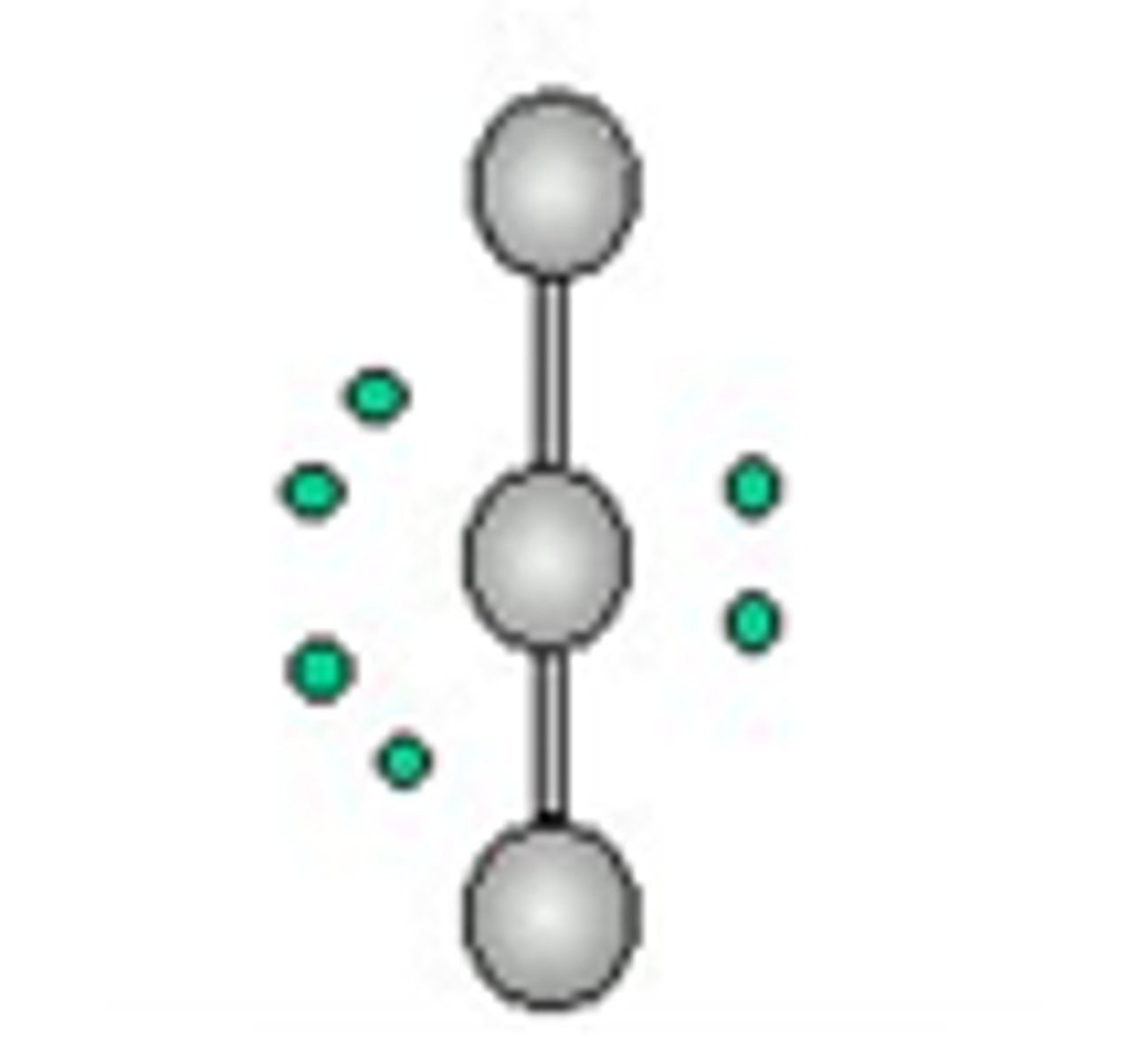
Octahedral
Bond Angle: 90
Molecular geometry: Octahedral
Domain: 6
Bonding sites: 6
Lone Pair: 0
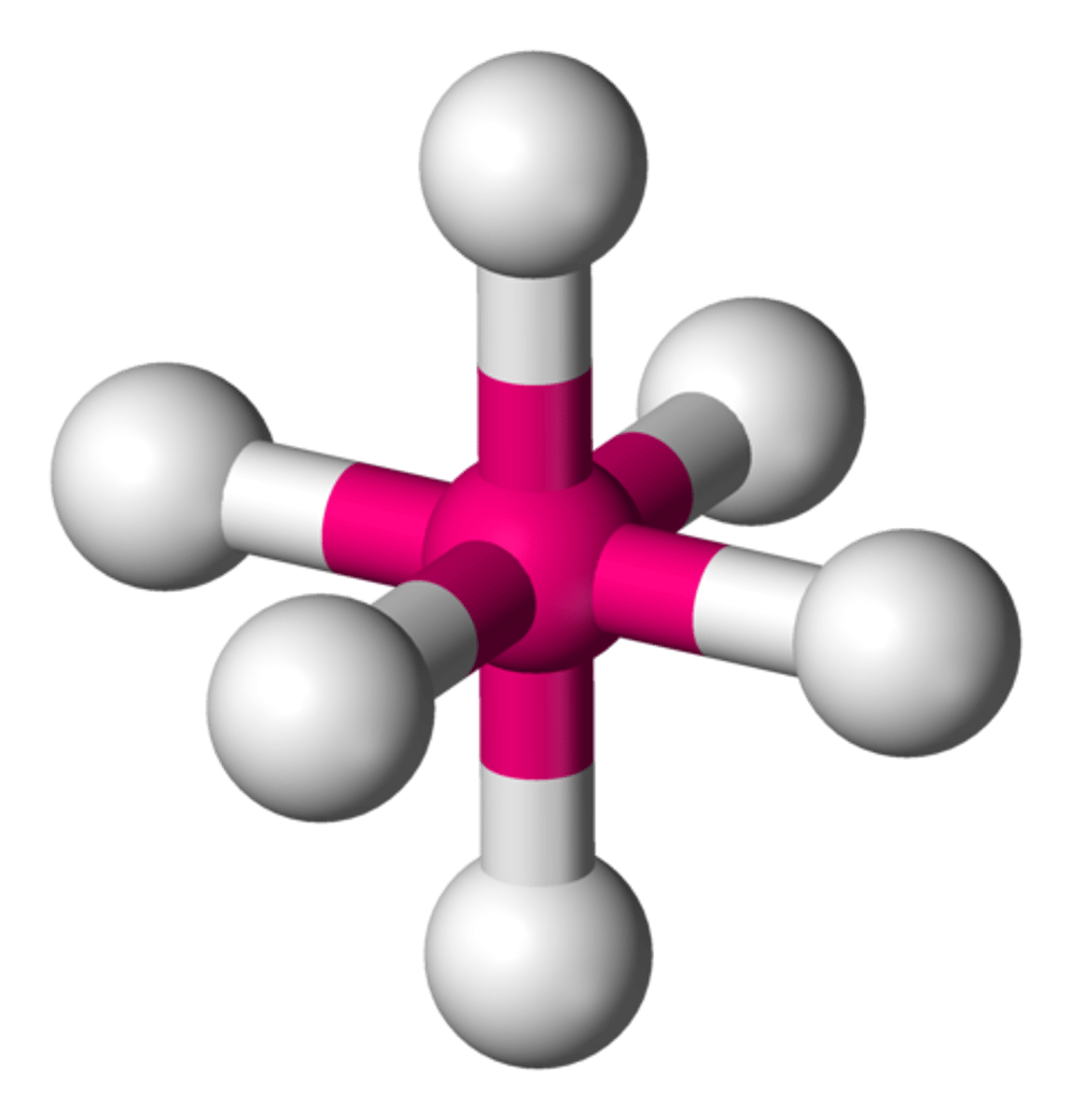
Square Pyramidal Octahedral
Bond Angle: 90
Molecular geometry: Square Pyramidal
Domain: 6
Bonding sites: 5
Lone Pair: 1

Square Planar Octahedral
Bond Angle: 90
Molecular geometry: square planar
Domain: 6
Bonding sites: 4
Lone Pair: 2
Steps for determining molecular geometry
1. draw Lewis dot structure
2. count number of bonds and lone pairs (domains)
Single,double, triple bonds and lone pair count as one domian
3. use chart to find shape
name of molecule is based on position of atoms (not domains)
Domain
region where electrons are likely to be, area of high electron concentration
bonds=bonding domains
lone pair=nonbonding domains
Domains (pt2)
negatively charged so they want to be as far apart. This minimizes :like charge repulsion" and is the lowest possible energy state
Lone pairs
take up more space than bonding pairs and thus push atoms farther away from each other
VESPR
"AXE"
A= central atom
X= number of atoms bonded to central atom (have subscript to state how many)
E= number of lone pair electrons on central atom (subscript)
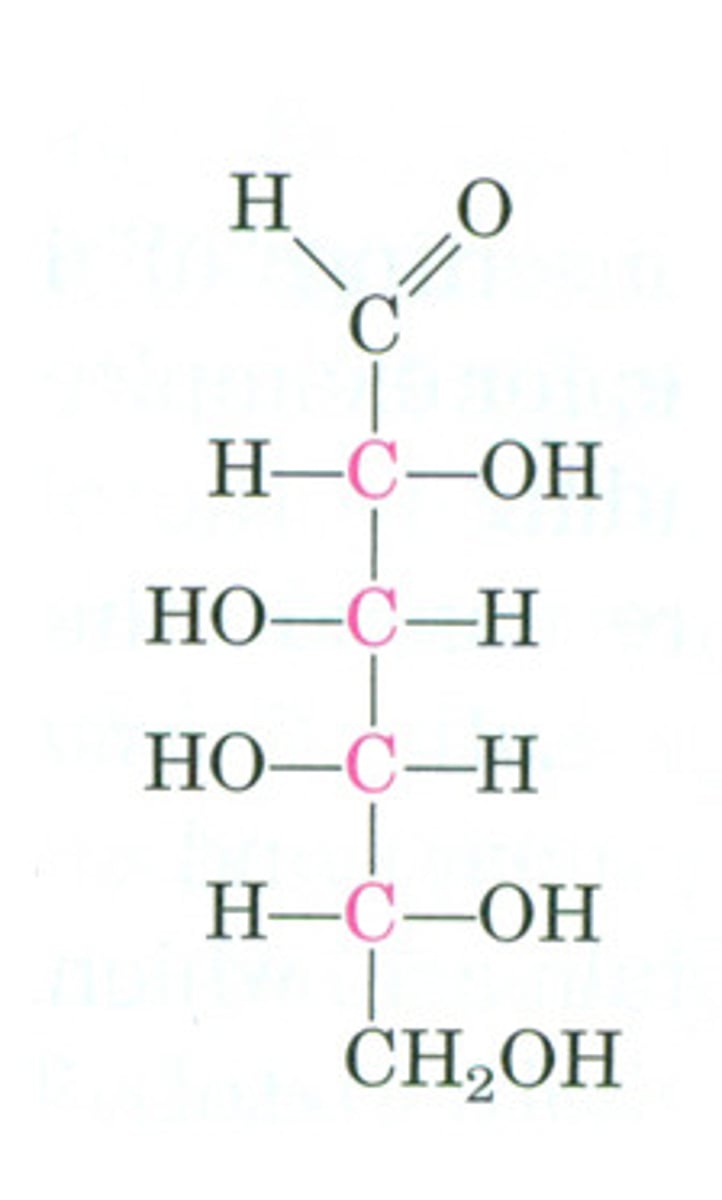
Fisher Projections
a way to make your Lewis structures seem 3D on paper
polar covalent
two atoms don't share electrons equally. Electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom which then one end of the molecule develops a partial negative charge b/c it has higher electron density
Dipole Moments
a molecule having an area of partial positive charge and area of partial negative
example: HCL

Dipole Moments (pt2)
ALL diatomic molecules with a polar bond have dipole moment
SOME polyatomic molecules with polar have dipole moment
(water does carbon dioxide doesn't it depends on molecular geometry)
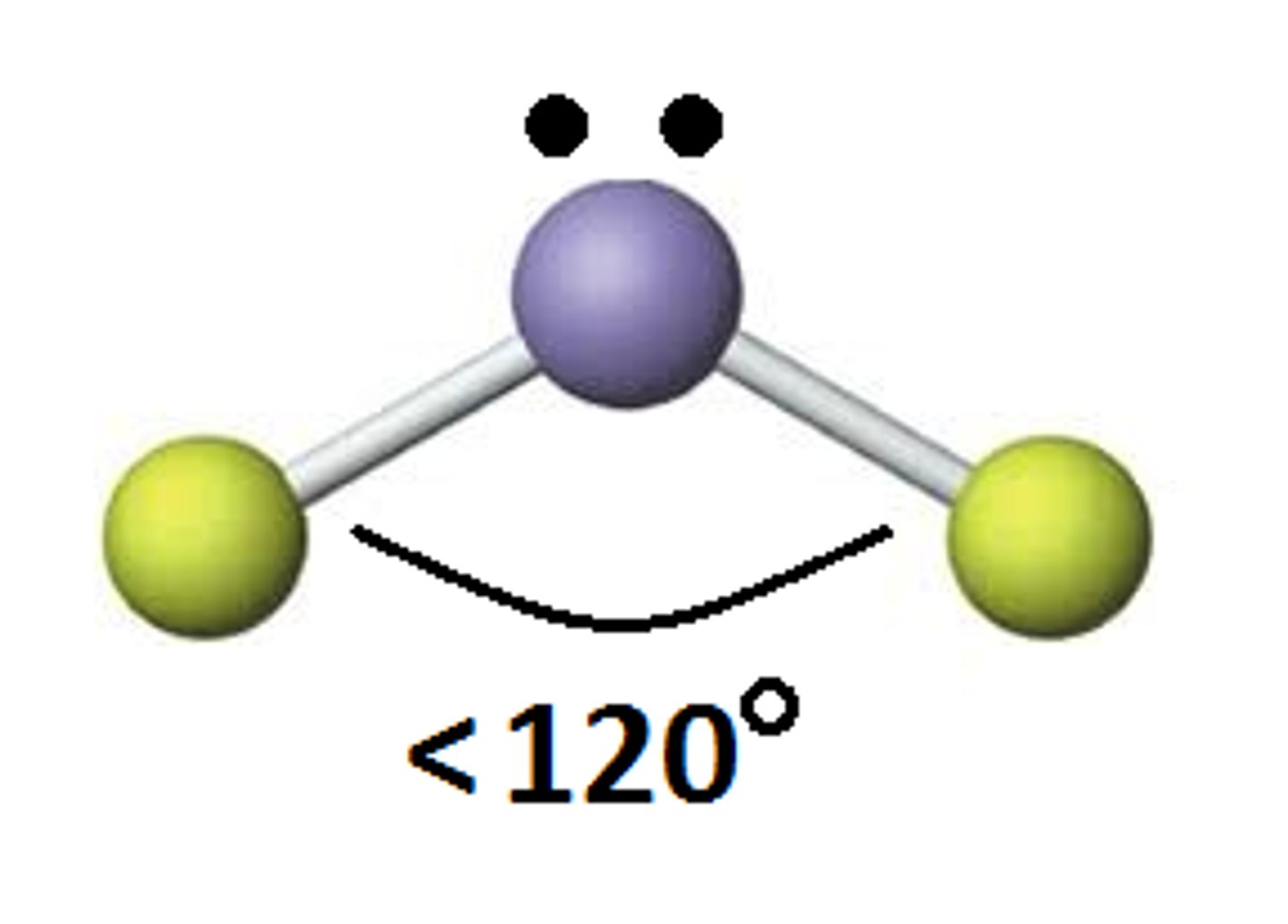
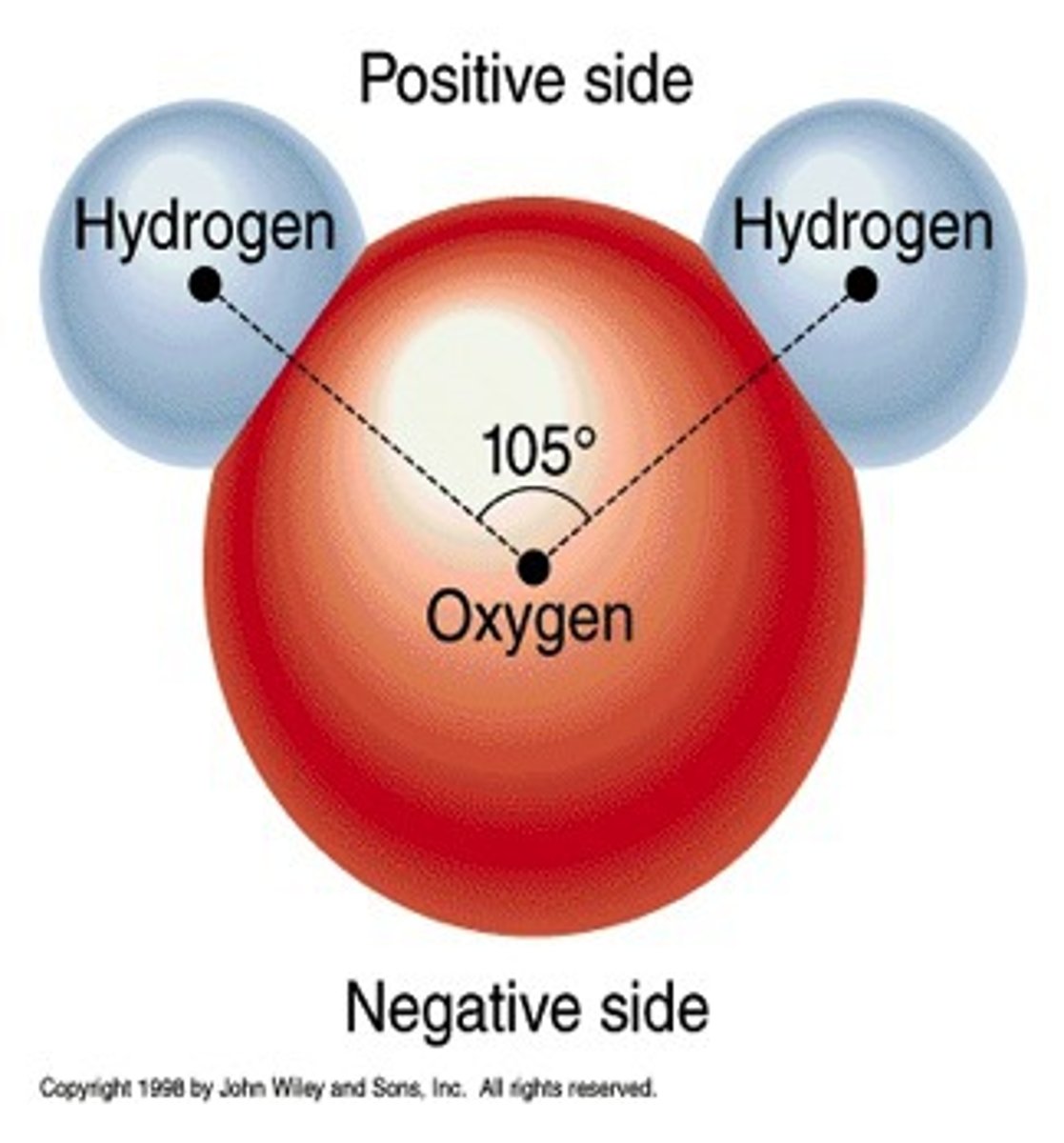
Water
Polar (H-O bonds)
geometry is "bent"
molecule is polar (has a dipole)
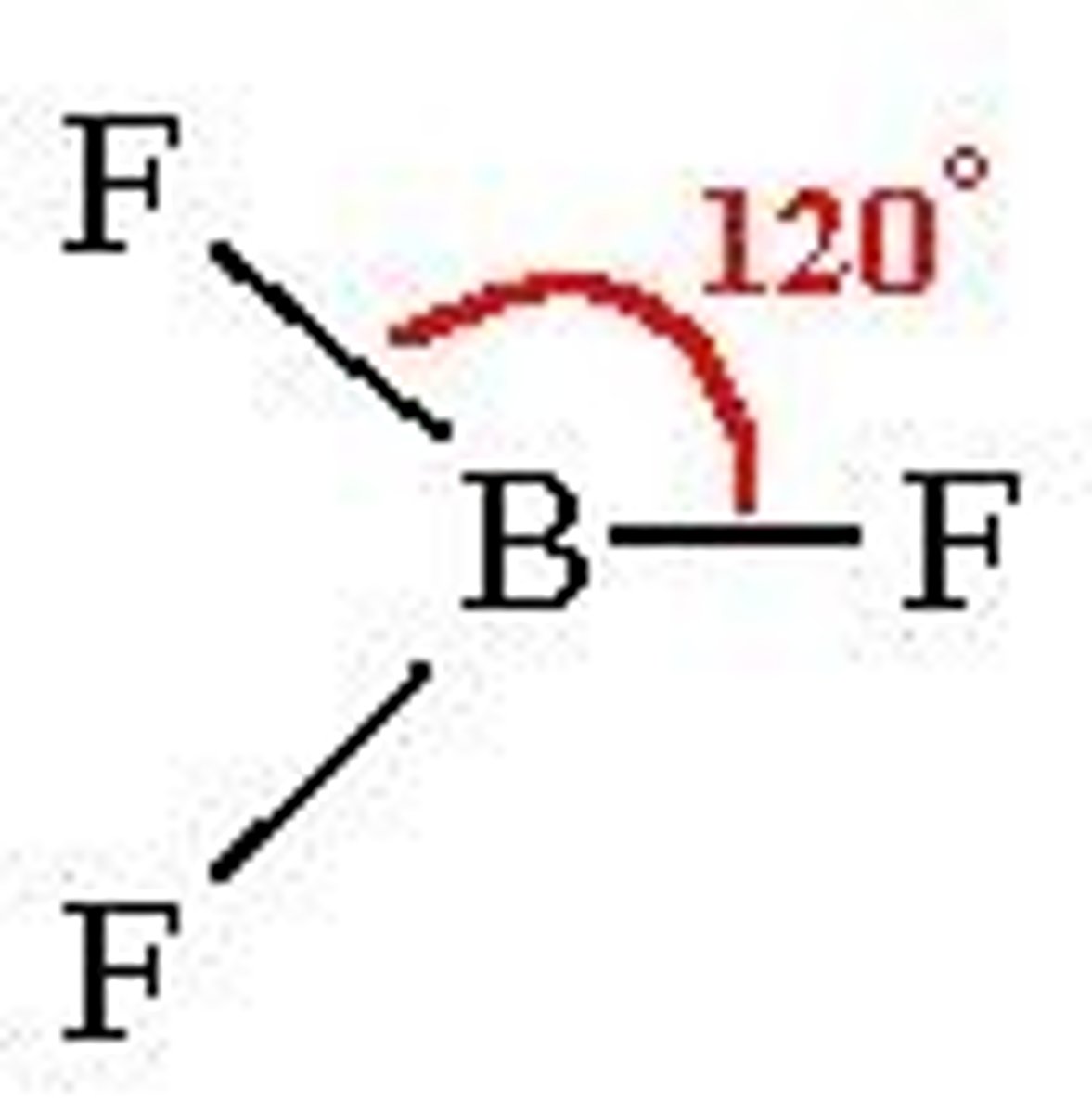
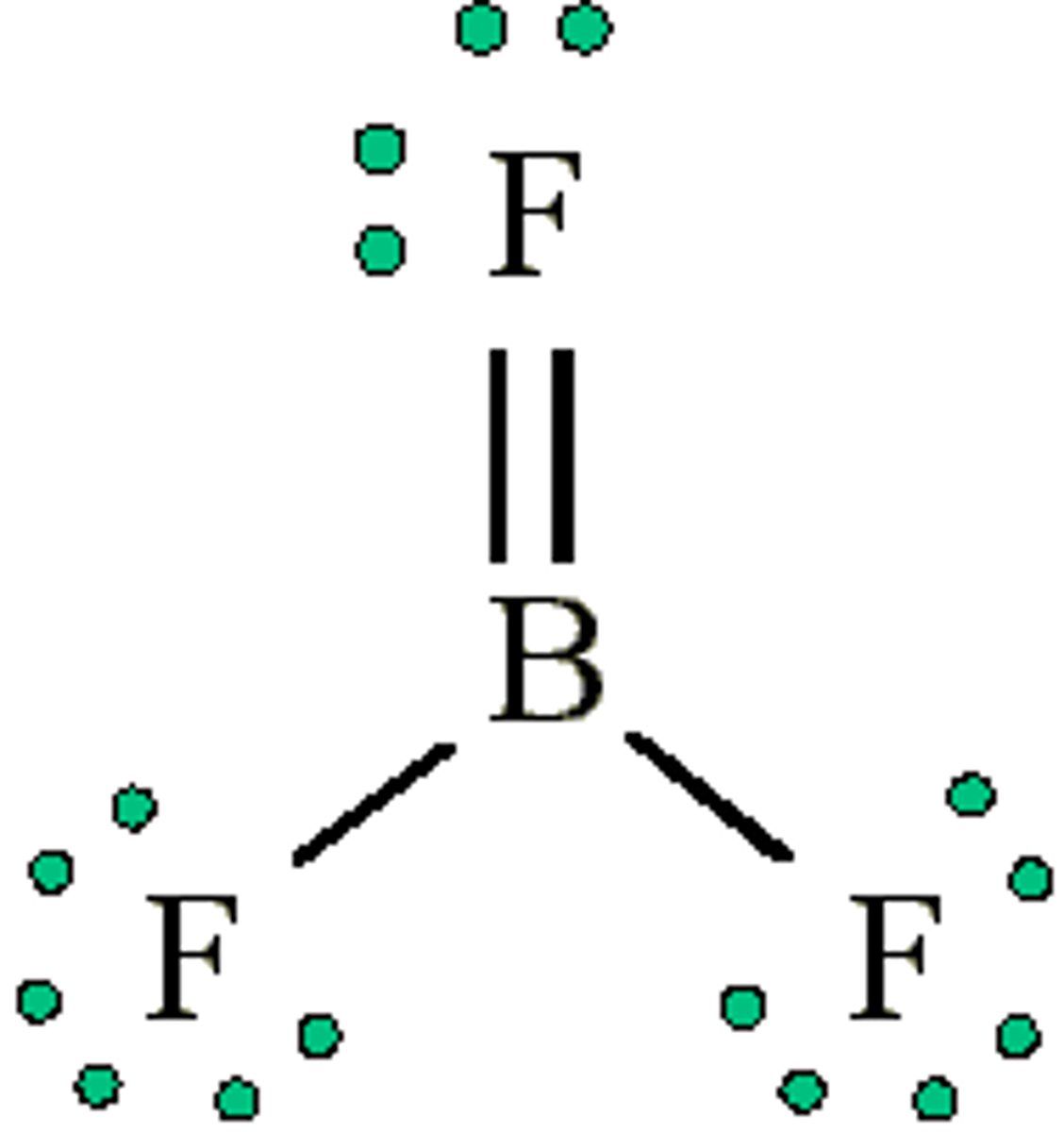
BF3 is non-polar
Has polar B-F bonds
geometry is "trigonal planar"
So the molecule is no polar (it doesn't have a dipole and all flourines "cancel")
"Like dissolves like"
Polar molecules dissolve in polar solvents
Nonpolar molecules dissolve in nonpolar solvents
polar and nonpolar dont mix
(oil: nonpolar, water:polar)
Hydrogen Bonds
bonds with N, O, F
bonding occurs b/w adjacent molecule covalent polar molecules
Dipole-Dipole
attractive forms between 2 opposite poles of 2 polar molecules
Dispersion
Because 2 nonpolar molecules attractive forces caused by movement of electrons
Create a temporary dipole