FHCE 3200 exam 1 Study Guide
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:34 AM on 9/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
1
New cards
financial literacy
How well you can understand and use personal finance-related information
one of the most important predictors of
savings and investment success
and overall well-being.
one of the most important predictors of
savings and investment success
and overall well-being.
2
New cards
financial knowledge
the ability to understand personal finance information
3
New cards
financial risk tolerance
unwillingness to engage in financial endeavors that have uncertain outcomes.
4
New cards
key action steps to financial well-being
1. Keep good records
2. Spend less than you earn
3. Maintain appropriate insurance
4. Save money on a regular basis
2. Spend less than you earn
3. Maintain appropriate insurance
4. Save money on a regular basis
5
New cards
human capital
ability and willingness to work, learn, earn, and make wise decisions about how to save and invest money.
6
New cards
social capital
how well you are able to form connections with other people
7
New cards
Informal Social Capital
the interpersonal relationships you form with your family and close friends
8
New cards
Formal Social Capital
connect you with people in professional, recreational, leisure, and social communities
9
New cards
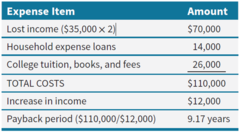
Calculate the Payback period
Total Costs/Increase in annual income
10
New cards
Risk
uncertainty associated with any physical, social, emotional, environmental, labor market, or financial activity
11
New cards
risk taking
doing something that involves the possibility of a gain or a loss
12
New cards
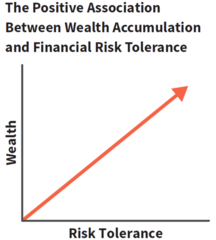
wealth creation and risk tolerance
In financial markets, the only way to accumulate a certain level of wealth is to take informed financial risks with your savings.
13
New cards
Identify the SMART goal process
Specific
Measurable
Attainable
Relevant
Timely
Measurable
Attainable
Relevant
Timely
14
New cards
Specific
Document the when, what, where, and how aspects of the goal
15
New cards
Measurable
Attach a quantifiable standard for achieving the goal
16
New cards
Attainable
Be realistic about whether you can achieve the goal
17
New cards
Relevant
Develop those financial goals that are crucial to improving your financial situation
18
New cards
Timely
Create a goal you can meet in a reasonable amount of time
19
New cards
Goal Time Horizons
time between creating a goal and achieving the goal
20
New cards
short-term time horizon
less than 1 year
21
New cards
long term time horizon
greater than 1 year
22
New cards
Past Oriented
based on memories, whether good or bad. Those who view past events negatively have the most trouble staying on their financial path
23
New cards
Present-Oriented
based on hedonistic perspective or fatalistic perspective
24
New cards
hedonistic perspective
doing things for pleasure, the experience, and excitement of the action
25
New cards
fatalistic perspective
unable to visualize a meaningful future
26
New cards
Future-Oriented
based on a calculation of the consequences of actions in terms of a future payoff
27
New cards
self-efficacy
how well you believe you can do something.
28
New cards
hyperbolic discounting
occurs when the value of future benefits is perceived to be lower than that of an alternative available right now.
29
New cards
Heuristics
•Based on past experiences
•Automatic and rarely used with forethought
•Can help you make quick decisions, however, they sometimes lead to problematic choices and outcomes
•Automatic and rarely used with forethought
•Can help you make quick decisions, however, they sometimes lead to problematic choices and outcomes
30
New cards
Status quo bias
the preference to keep things the way they are rather than change
31
New cards
loss-averse
characteristic of being very reluctant to do anything that might lead to loss
32
New cards
optimism bias
people believe that, compared with other people, they are more likely to experience positive events and less likely to experience negative events in the future
33
New cards
Confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
34
New cards
interior finance
refers to your knowledge, attitudes, perceptions, and abilities
35
New cards
exterior finance
the observable actions you take with money and the associated outcomes such as
Loan payment amounts
saving rates
cash flow management
net worth
Loan payment amounts
saving rates
cash flow management
net worth
36
New cards
Interest
the price paid for the use of borrowed money
Borrowed money you pay back with interest (loan)
Lended money you generate interest (savings, loaning)
Borrowed money you pay back with interest (loan)
Lended money you generate interest (savings, loaning)
37
New cards
True/False:
It can take up to 99 years to receive your federally insured money from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
It can take up to 99 years to receive your federally insured money from the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
False
38
New cards
BOTH Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) and National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) protect your deposit up to
$250,00
39
New cards
APR (Annual Percentage Rate)
annual sum of the periodic interest rates applied to the account, without considering the effect of compound growth.
40
New cards
APY (annual percentage yield)
The effective annual rate of return taking into account the effect of compounding interest.
41
New cards
APR Formula
periodic interest rate x number of periods in the year
42
New cards
APY Formula
[(1+Periodic Interest rate)^(number of periods in a year)]-1
43
New cards
Time Value of Money calculations
FV: Future Value
PV: Present value
N: # of periods
I/Y: Interest
PMT: a series of more than one payment or deposits
PV: Present value
N: # of periods
I/Y: Interest
PMT: a series of more than one payment or deposits
44
New cards
Time Vale of Money (TVM) formula
FV/(1+i)^N
45
New cards
future value of an annuity
the amount accumulated in the future when a series of payments is invested and accrues interest
46
New cards
Future value of an annuity formula
FVA=(PMT/i)[((1+i)^n)-1]
47
New cards
present value of an annuity
The amount at a present time that is equivalent to a series of payments and interest in the future.
48
New cards
Present Value of an Annuity formula
PVA=(PMT/i)(1-(1/[(1+i)^n]))
49
New cards
Amortized Payments
a payment of the same amount for a set number of months or years
50
New cards
Amortized Payments formula
Monthly Payment=PV((I × (1 + I)^N)/((1 + I)^N) - 1)
51
New cards
Future Value (FV)
how much current savings and investments will be worth at a certain date in the future
52
New cards
Present Value (PV)
Value today of a future amount
53
New cards
Annuity
a series of equal regular deposits
54
New cards
Rule of 72
The number of years it takes for a certain amount to double in value is equal to 72 divided by its annual rate of interest.
55
New cards
balance sheet
A financial statement that reports assets, liabilities, and owner's equity on a specific date.
56
New cards
Net Work formula
Assets-Liabilities=Owners equity (ALOE)
57
New cards
liquidity
How quickly and easily an asset can be converted into cash
58
New cards
fair market value
the price someone would realistically pay you to buy the asset
59
New cards
Appreciating Assets
assets that increase in value over time, for example, a house
60
New cards
depreciating assets
assets such as cars and computers, fall in value over time
61
New cards
short term liability
liability typically expected to be paid within one year or less
62
New cards
long-term liability
Liabilities with longer repayment schedule and would include student loans and money borrowed to purchase a house (i.e., a mortgage)
63
New cards
bad debt
borrow money to buy something that either goes down in value quickly or is consumed immediately.
64
New cards
good debt
The concept that sometimes it is worth taking on certain types of debt in order to generate income in the long run. Common examples include college education debt and real estate.
65
New cards
current ratio
current assets / current liabilities=1
66
New cards
debt ratio
total liabilities/total assets = 40%
67
New cards
savings ratio formula
total savings/total income=12% or higher
68
New cards
targeted saving rates based on age
69
New cards
Emergency Fund Ratio
cash and cash equivalents (Monetary Assets) / monthly non-discretionary cash flows(Necessary Expenses); benchmark = 3-6 months
70
New cards
consumer debt-to-income ratio
total consumer debt payments/total income = 15% or less
71
New cards
total debt to income ratio
Total debt payments/Total income=no more than 36% of income being used for debt payments
72
New cards
surplus
Income exceeds expenses
73
New cards
Sections of a budget
Income, Expenses, Surplus/Deficit (Profit/Loss)
74
New cards
deficit
Expenses exceeds income
75
New cards
Save More Tomorrow
Commit to putting half of every future raise towards your saving
76
New cards
Present Bias
A preference for choosing short term pleasures over long term investments
77
New cards
Income
broad term used to describe all sources of money obtained by individuals and households and can include:
•Allowances
•Public assistance
•Interest
•Dividends
•Social Security payments
•Allowances
•Public assistance
•Interest
•Dividends
•Social Security payments
78
New cards
Earnings
just one form of income:
•Compensation received for services performed for an employer
•Compensation received for services performed for an employer
79
New cards
Wage
•what an employer pays an employee to work
•usually based on an hourly rate
•usually based on an hourly rate
80
New cards
Salary
•payment for work for a set period of time
•usually an annual amount
•usually an annual amount
81
New cards
commission
•payment based on the sale of a product or service
82
New cards
Bonus
•an extra payment usually based on performance
83
New cards
Overtime
working more than 40 hours in one week. gets paid 1.5x regular wage
84
New cards
Six steps for creating a financial plan
1.Set a Financial Goal
2.Know Your Starting Point
3.Determine Your Financial Score
4.Determine Your Financial Capacity
5.Know Your Time Horizon
6.Formalize and Implement Your Financial Plan
2.Know Your Starting Point
3.Determine Your Financial Score
4.Determine Your Financial Capacity
5.Know Your Time Horizon
6.Formalize and Implement Your Financial Plan
85
New cards
Sole Proprietorship
unlimited liability, limited access to resources, easy start-up, sole receiver of profit
86
New cards
General Partnership
A partnership in which all owners share in operating the business and in assuming liability for the business's debts. unlimited liability
87
New cards
Limited Partnership
general partner manages the business and one or more limited partners invest money in the business
88
New cards
Limited liability partnership
•Partners are not liable for actions of other partners, but are liable for the general obligations of the business
89
New cards
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A legal entity that is not taxable itself and distributes the profits to its owners, but shields personal assets from business debt like a corporation.
90
New cards
Corporation
A business owned by stockholders who share in its profits but are not personally responsible for its debts.
Very effective at limiting liability, but also expensive to form and maintain
Very effective at limiting liability, but also expensive to form and maintain
91
New cards
Earned Income
money from work primarily through the labor market.
•Salaries, wages, commissions, or bonuses
•Salaries, wages, commissions, or bonuses
92
New cards
Unearned Income
money from non-labor sources.
•Interest from savings accounts
•Dividends
•Capital gains
•Monetary gifts
•Government benefits
•Money received by inheritance
•Proceeds from savings bonds
•Interest from savings accounts
•Dividends
•Capital gains
•Monetary gifts
•Government benefits
•Money received by inheritance
•Proceeds from savings bonds
93
New cards
capital assets
almost everything you own or use for personal or investment purposes, according to the IRS
•Your home
•Your car
•Investments like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds
•Ownership interest in a small business you started
•Rental or other real estate you own
•Your home
•Your car
•Investments like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds
•Ownership interest in a small business you started
•Rental or other real estate you own
94
New cards
Calculate capital gain
Calculating steps:
Selling Price
- Basis (Purchase price)
- Selling costs
= Realized Capital Gain
Selling Price
- Basis (Purchase price)
- Selling costs
= Realized Capital Gain
95
New cards
Calculate capital loss
Original Price - Price Sold at