PMP Module 8 Lead the Project Team - Part 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is quality?
The degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfills requirements.
What is Cost of Quality (CoQ)?
All costs incurred over the life of the product by investment in preventing nonconformance to requirements, appraisal of the product or service for conformance to requirements, and failure to meet requirements.
Money spent to avoid failure: prevention costs (training, equipment), appraisals (testing, inspections)
Money spent after: internal failure costs (rework, scrap), external failure costs (liabilities)
What is a quality management plan?
A component of the project or program management plan that describes how applicable policies, procedures, and guidelines will be implemented to achieve the quality objectives
What is a quality policy?
The basic principles that should govern the organization’s actions as it implements its system for quality management.
What are quality standards vs regulations?
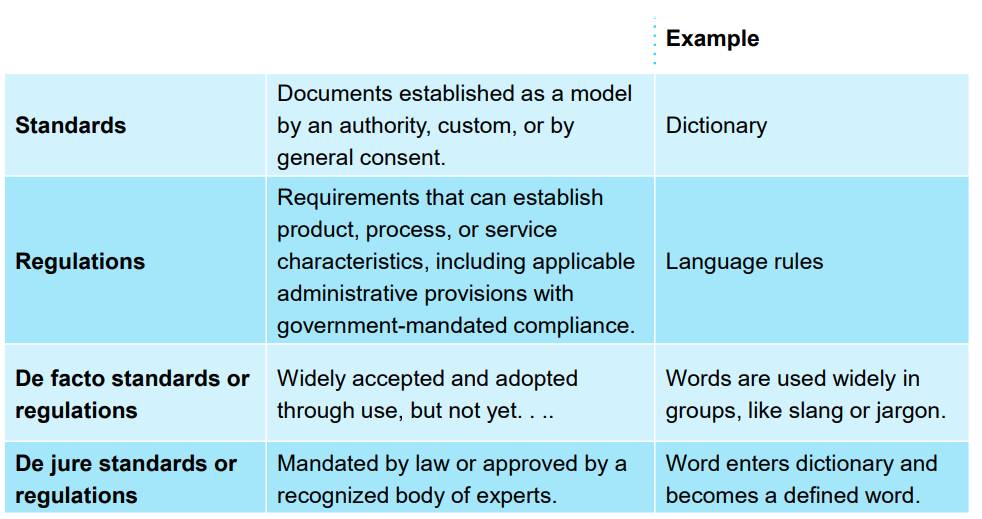
Define metrics
Metrics measure desired quality attributes for your product or project through testing, use of tools, processes.
Include a tolerance level that factors in what the customer will accept and describe the desired quality level in the acceptance criteria and DoD
Name some Quality Methods for Continuous Improvement
Six Sigma (aka Lean Six Sigma) – DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) – focus on removing waste
Kaizen – “change for better/improve”
(PDCA) Plan – Do – Check – Act – Shewhart/Deming
Agile methods - Scrum, Kanban, Crystal Methods (software), etc
What is an integrated project management plan?
An integrated view of all plans: The scope, schedule, budget, resources, quality and risk plans must support desired outcomes
What is a change management plan?
A component of the project management plan that establishes the Change Control Board, documents the extent of its authority, and describes how the change control system will be implemented
Define change request?
Request for change sent to upper management or the Change Control Board (CCB) for its evaluation and approval
What is active listening?
A communication technique that involves acknowledging the speaker’s message and the recipient clarifying the message to confirm that what was heard matches the message that the sender intended.
What are communications styles assessment?
A technique to identify the preferred communication method, format, and content for stakeholders for planned communication activities.
What are the leadership styles?
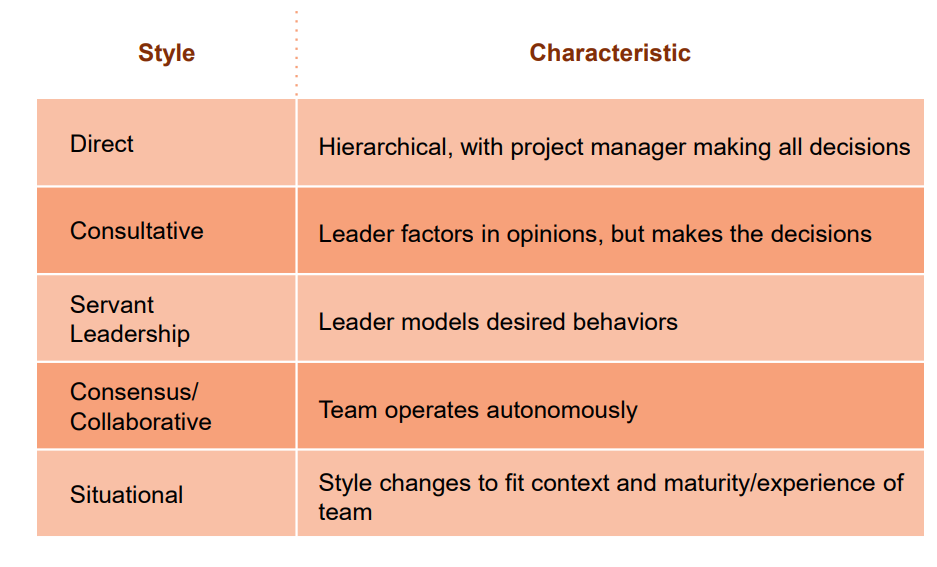
Difference between leadership and management?
Leadership - Guiding the team by using discussion and an exchange of ideas
Management - Directing actions using a prescribed set of behaviors
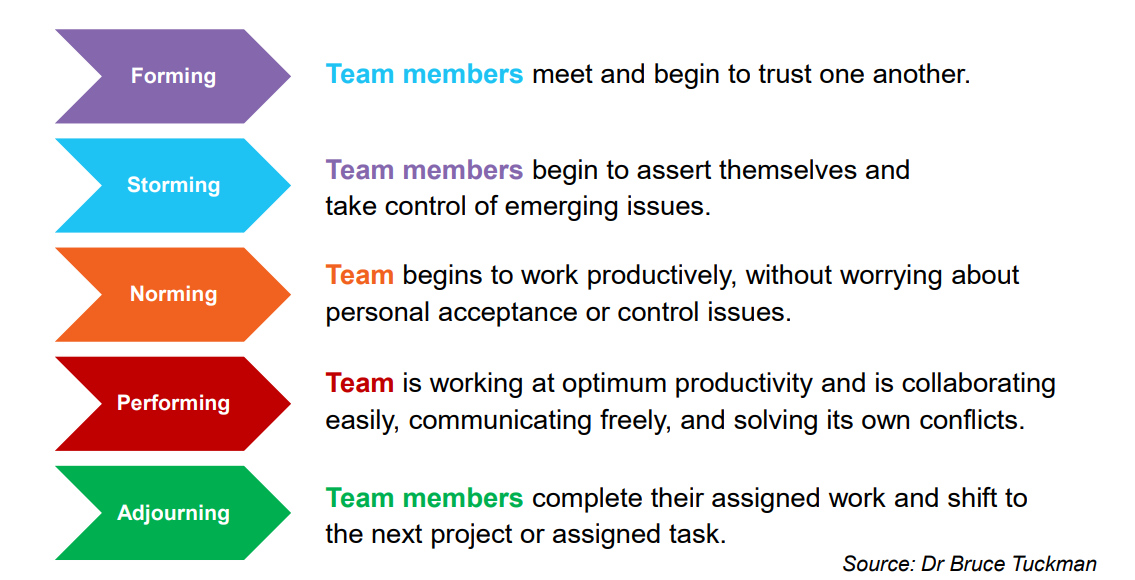
What are the Tuckman Stages of Team Development?
Forming, Storming, Norming, Performing, Adjourning
What is transparency?
Transparency: One of the three pillars of empirical process (transparency, inspection, and adaptability) that promotes real-time, accurate progress on every aspect of the project.
What are the two Work Information Management Systems?
Project Management Information System (PMIS)
Gather, integrate and share project data
Ensure consistency in collection and reporting
Ex. Microsoft Project
Artifacts Management Systems
Store and maintain project artifacts
Ex. Google drive, MS Teams
What are information radiators?
The generic term for visual displays placed in a visible location so everyone can quickly see the latest information
How can we maintain artifacts?
Configuration management plan
A component of the project management plan that describes how to identify and account for project artifacts under configuration control and how to record and report changes to them
Configuration management system - A collection of procedures used to track project artifacts and monitor and control changes to these artifacts
What is version control?
A system that records changes to a file, in a way that allows users to retrieve previous changes made to it
For each update, include: • A new version number • A date/time stamp • Name of user who made the changes
What is psychological safety?
Being able to show and employ oneself without fear of negative consequences of status, career, or self-worth—we should be comfortable being ourselves in our work setting.
What are 4 motivational theories and approaches?
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory
McGregor’s Theory X and Y
McClelland’s Achievement Motivation Theory
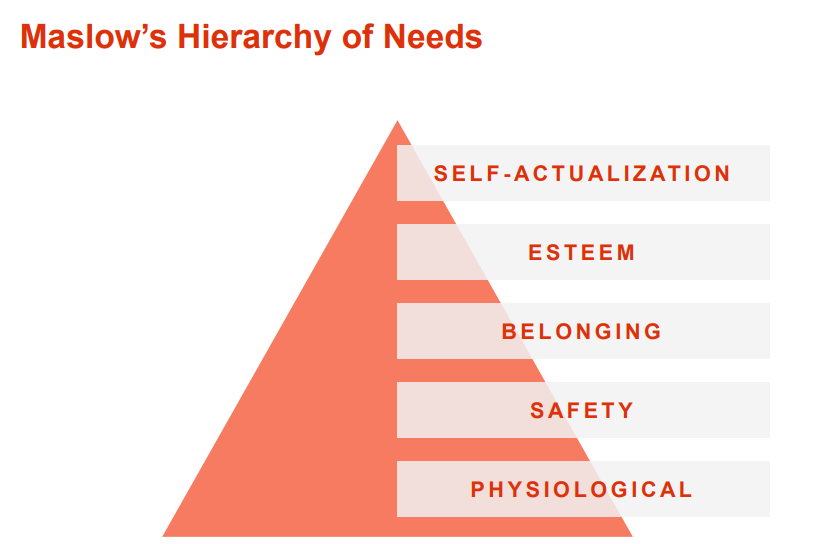
What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs?
A theory of psychology explaining human motivation based on the pursuit of different levels of needs. The theory states that humans are motivated to fulfill their needs in a hierarchical order. This order begins with the most basic needs before moving on to more advanced needs. The ultimate goal, according to this theory, is to reach the fifth level of the hierarchy: self-actualization
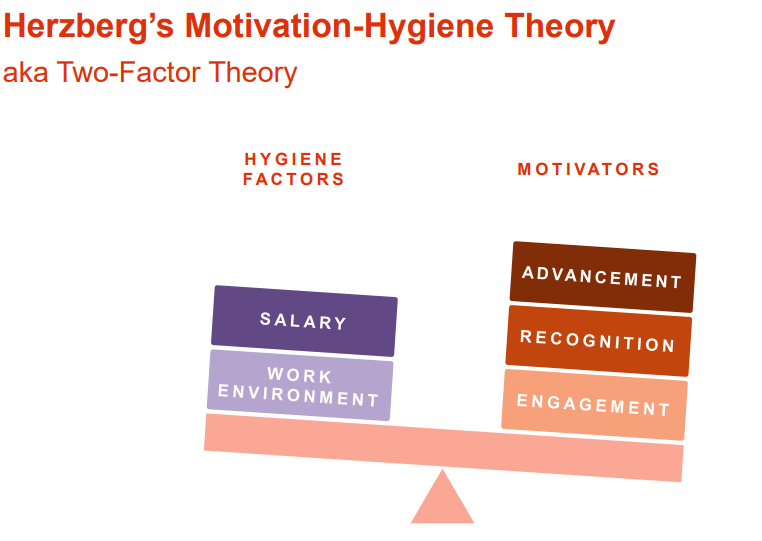
What is Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory?
In 1959, behavioral scientist Frederick Herzberg proposed that ‘hygiene’ or environmental factors can cause workers to feel satisfied or unsatisfied with their job and this factor affects their performance.
The theory also proposes that a worker’s independent drive associated with motivation also affects performance and that workers respond to feelings of connection with their work. Therefore, leaders should encourage workers to accept more authority as well as promote feedback.
Also known as Two Factor Theory, Herzberg’s Motivation Theory, and The Dual Structure Theory.
What is McGregor’s Theory X and Y?
Theory X (authoritarian): Refers to Theory X by Douglas McGregor which proposes that managers micro-manage their employees or team members because they assume their workers are unmotivated and dislike work.
Theory Y (Participative): Refers to Theory Y by Douglas McGregor which proposes that managers have an optimistic and positive opinion of their employees or team members, so this type of manager encourages a more collaborative, trust-based relationship between employees.
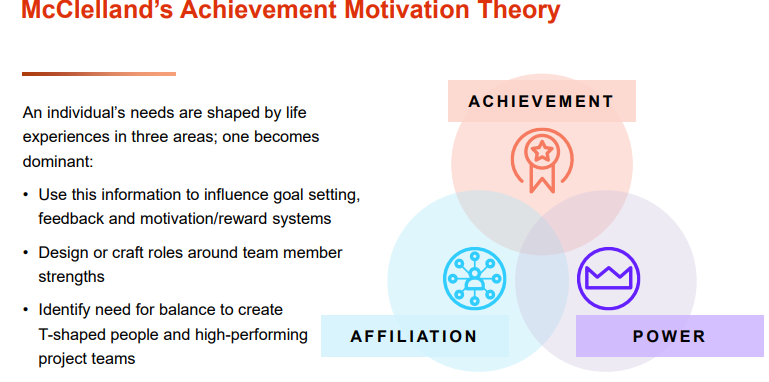
What is McClelland’s Achievement Motivation Theory?
A human motivation theory which states that every person has one of three main driving motivators: the needs for achievement, affiliation, or power. Those with a strong need for affiliation don't like to stand out or take risk, and they value relationships above anything else.
What are rewards vs recognitions?
Rewards are tangible, consumable items. For a specific outcome or achievement. used to motivate. NEVER reward without recognition!
Recognition are intangible experiential event. acknowledge person’s behaviour rather than an outcome. use to increase feelings of appreciation, can be given without reward.
How is decision-making done as a team?
Team charter identifies decision-making and conflict resolution criteria
Teams establish their own norms or Way of Working (WoW) for making decisions and conflict resolution
Teams always try to achieve consensus
Define consensus: Group decision technique in which the group agrees to support an outcome even if the individuals do not agree with the decision
What are some decision-making methods?
Voting (consensus-driven, based on data)
Multicriteria decision analysis (data-driven)
Autocratic decision making (leadership-driven, based on data)

What are three ways of voting in the voting method?
UNANIMITY Everyone agrees on a single course of action. Useful in project teams with great cohesion. Example: Delphi technique
MAJORITY Decision reached with > 50% of group support
Create groups of an uneven number of participants to ensure decisions are made and avoid tie votes/draws!
PLURALITY Decision reached with largest block in a group deciding, even if majority is not achieved. Use this method when more than two options are nominated. (AKA option with the most votes like our political system. Candidate did not get 50% of the vote, but the highest among the options)
What are other voting methods in the agile methods to reach consensus?
Fist of Five: using fingers to agreeing to disagreeing
Planning poker: assigning value for decision making
Dot Voting: when you give a series of dots to people and put dots against what is important. can put more than one dot on an item
Roman voting (thumbs): Thumbs up, down, and sideways (not sure)
Polling: online polling or raising people hands etc