Chapter 11: Angular Kinematics of Human Movements
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is a relative angle?
the joint angle formed between two body segments
Compare the relative angle of the knee during sprinting vs distance running.
The relative angle at the knee tends to be smaller during sprinting than during distance running
What is an absolute angle?
the angular orientation of a body segment with respect to a fixed line of reference
reference lines are usually vertical or horizontal
Give an example of an absolute angle.
the angle of the thigh with respect to the vertical during a squat
the angle of one’s back with the wall when they go to pick something up
____ is the change in angular position
angular displacement
Angular Displacement
the angular distance from starting to finishing point

Angular displacement is the vector equivalent to _______.
angular distance
What are the units angular displacement is measured in?
degrees, radians, or rotations
Radian
the size of the angle formed at the center of the circle when the arc length is equal to the radius of the circle
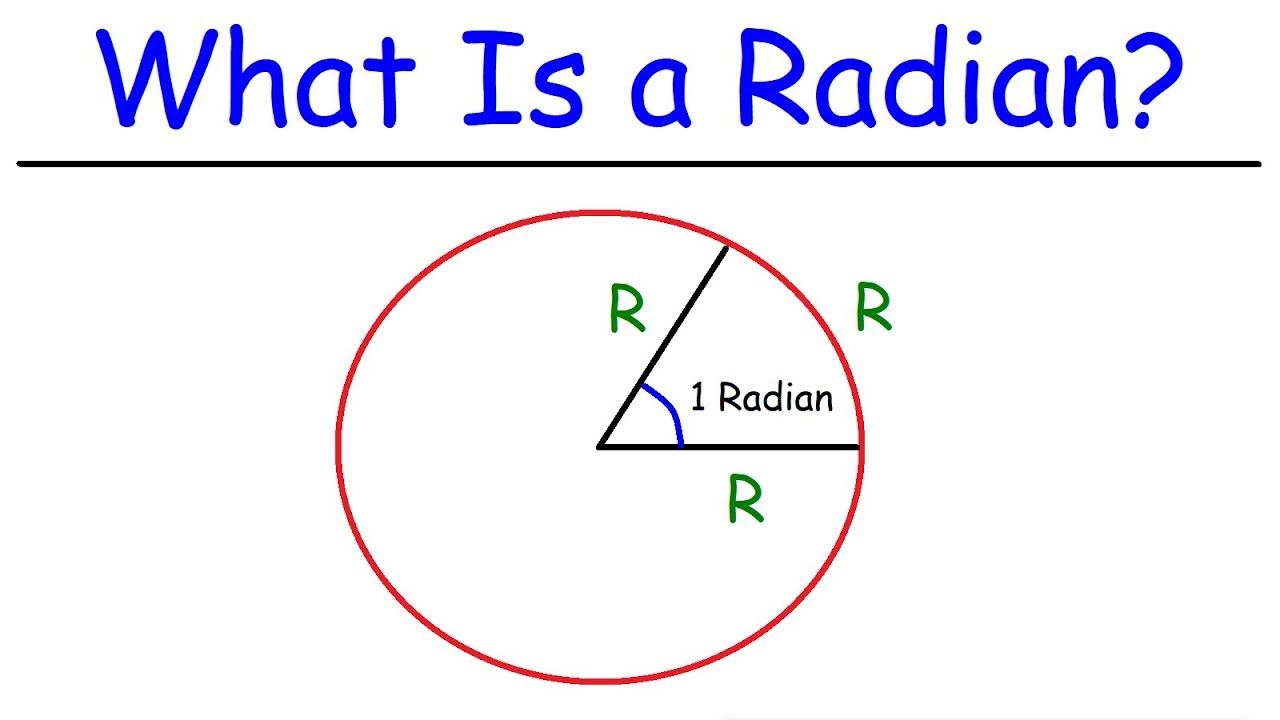
What is 90 degrees in radians and revolutions?
π/2 radians
¼ revolution
What is 180 degrees in radians and revolutions?
π radians
½ revolution
What is 270 degrees in radians and revolutions?
3π/2 radians
¾ revolutions
What is 360 degrees in radians and revolutions?
2π radians
1 revolution
Angular Velocity
the change in angular position over time
Angular velocity equation:
Angular velocity (ω) = angular displacement (θ) / time (t)
What units are angular velocity measured in?
degrees / s
radians / s
Angular Acceleration
the rate of change in angular velocity
Angular Acceleration equation
Angular acceleration (α) = change in angular velocity (Δω) / time (t)
What units are angular acceleration measured in?
degrees / s²
radians / s²
What is the relationship between linear and angular displacement?
the greater the radius of rotation ®, the greater the linear distance (s) traveled by a point on a rotating body
s = rΦ
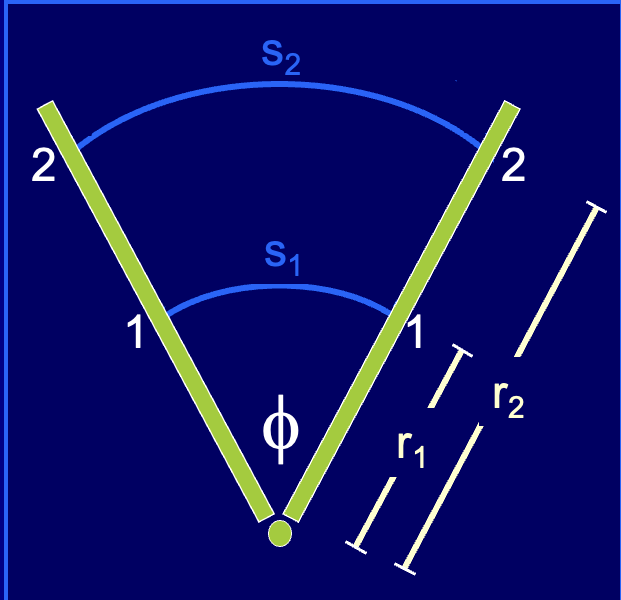
What is the relationship between linear and angular velocity?
since velocity is displacement over time, linear and angular velocity are related by the same factor that relates displacement: the radius of rotation ®
v = rω
What is the relationship between linear and angular acceleration?
the acceleration of a body in angular motion can be broken down into two perpendicular linear acceleration vectors
Tangential acceleration
the part of angular acceleration that acts along the tangent to the circular path, causing a change in speed
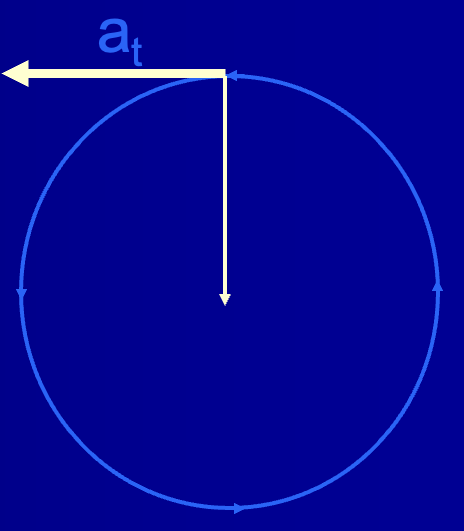
What does tangent mean?
tangent is a line that touches the circle and points in the direction the object is moving at that instant

Tangential acceleration represents what?
a change in linear speed
Equation for tangential acceleration:
at = (v2 -v1) / t
Radial acceleration
the vector of angular acceleration that is directed toward the center of curvature
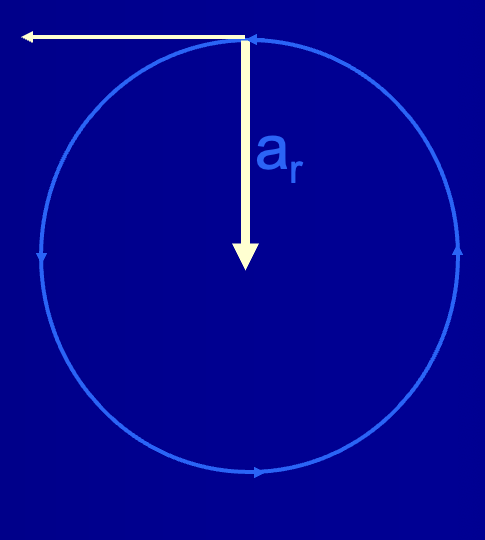
Equation for radial acceleration:
Angular acceleration (ar) = ω² t