resp 4: lower resp alterations
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
chest trauma types
blunt trauma and penetrating trauma
blunt
chest strikes or is struck by an object
blunt trauma severe
rib/sternal fractures can lacerate lung tissue
shearing can cause laceration and tearing of aorta
chest compression: contusion, crush injury, or organ rupture
penetrating trauma
foreign object impales organ tissues and creates open wound through pleural space
eg knife, gunshots, etc
pneumothorax
what is it
what does it lead to/cause/detailed patho
air entering pleural cavity
normally, it is negative air pressure that reduces friction
air = positive pressure = partially or fully collapse
eventually causes dec lung volume
pneumothorax dx
cxr shows air or fluid in pleural space
pleural space = between the visceral pleura (covers the lungs) and the parietal pleura (lines the chest wall).
pneumothorax cms 3/4
small: Mild tachycardia and dyspnea
severe: respiratory distress
ausculation: Absent breath sounds over affected area
hyperresonance
classes/types of pneumothorax
spontaneous and iatrogenic
open and closed
tension
spontaneous pneumothorax
Rupture of blebs
air filled sacs located on the surface of the lungs
can be healthy or from resp concerns (copd, asthma, cf, pneumonia)
smoking, male, tall and thin, family hx, prevois medical hx
iatrogenic
Caused by puncture during medical procedures
eg biopsy, aspiration, tearing from ett, barotrauma from excess o2, etc
open vs closed pneumothorax
open: Air enters through an opening in the chest wall
penetrating trauma
Closed: No external wound
visceral lining is interrupted
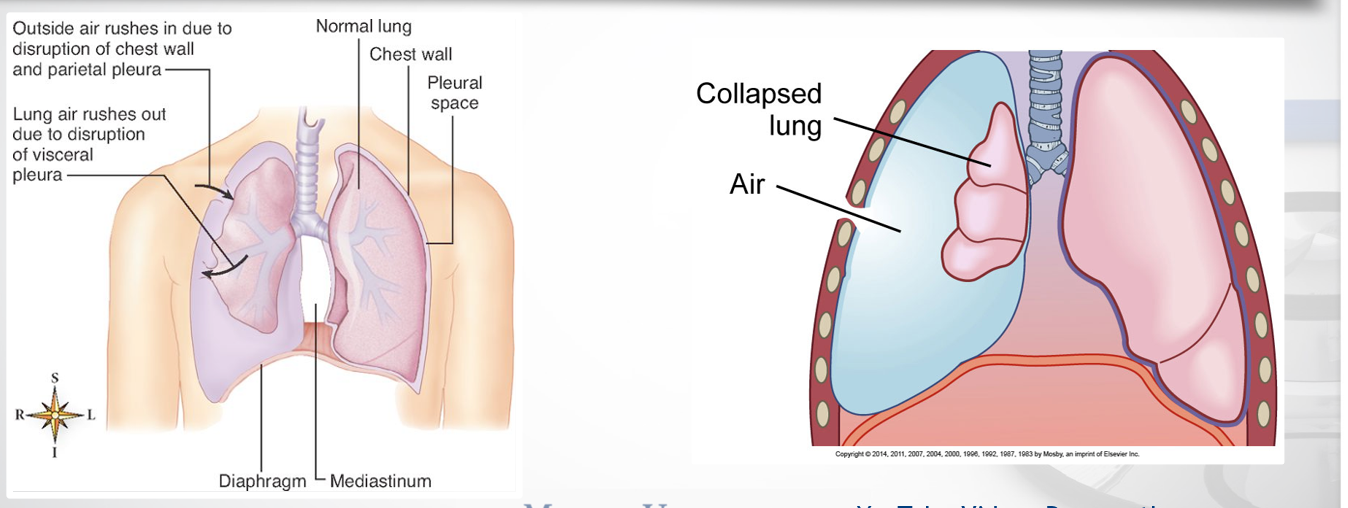
tension pneumothorax affects what systems
affects both resp and cardiac systems
cms of tension pneumothorax 7/8
mediastinal shift and tracheal deviation
dyspnea + tachypnea
marked tachycardia
dec/abs lung sounds on the affected side
neck vein distention
cyanosis
diaphoresis
tension complication/tx
death from prolonged hypoxemia/cardiac insufficiency
URGENT: needle decompression and chest tube insertion
Hemothorax, Hemopneumothorax, Chylothorax
def only
Hemothorax
Blood in pleural space
Hemopneumothorax
blood and air
Chylothorax
Lymphatic fluid in pleural space
chylothorax tx
Treat conservatively (chest drainage, bowel rest, dietary mods)
with meds
surgery (thoracic duct ligation) or pleurodesis
Penetrating chest wound dressing
emergency: vent/occlusive dressing secured on 3 sides
prevents air from entering lungs during inhalation
during exhalation, allows some air to escape
object in place?
do not remove until hcp
stabilize with bulky dressing
Pneumothorax/pneumothorax procedures/mgt: 5
interprofessional 3
stable? 1
repeated? 1
Thoracentesis
Chest tubes with water-seal drainage system
Pleurodesis
if : stable with minimum air> no tx needed
Surgery may be indicated for repeated spontaneous pneumothorax
thoracentesis
what is it
purposes
positioning
how much
Aspiration of intrapleural fluid
dx and therapeutic purposes
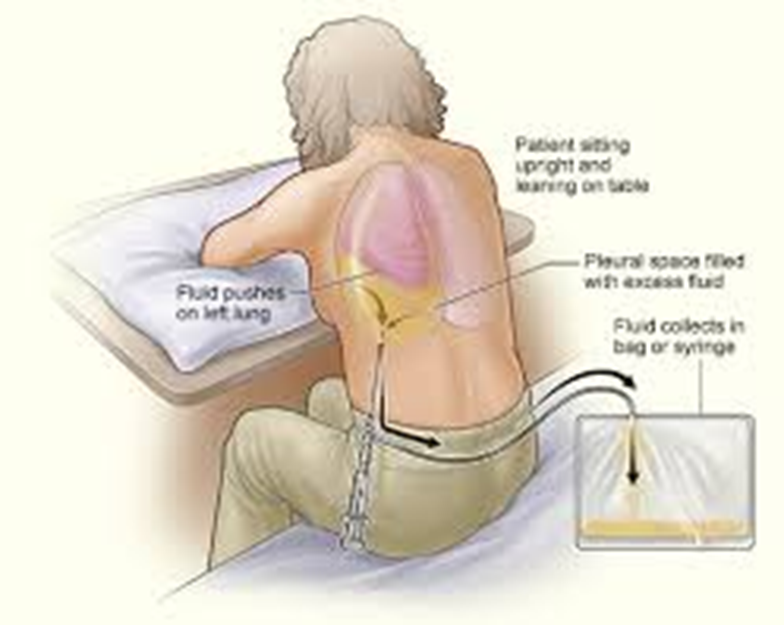
Only 1000-1200mL fluid removed
why only that much 3
too much = risk for hypoxemia/hypotension
also re-expansion pulm edema
after procedure 2
Chest x-ray/ Ultrasound for puncture site after for complications
monitor vitals (bp, pulse ox, and signs of resp distress)
chest tubes
role in pleural drainage
To remove air or fluid from pleural and/or mediastinal space
Reestablishes negative pressure = Lung re-expands
size
20 inches long
Various sizes (12F to 40F)
depends on pt condition and size
large: 36-40 blood
medium: 24-36: fluid
small: 12-24: air
chest tube insertion 6/7
where/locations
where is it inserted
pt position
bed? and why
after/during 2/3
usually in ER, OR, or pt bedside
arm above head of affected side
inserted in midaxillary area
elevate bed 30-60 deg to lower diaphragm and reduce injury
cxr after to confirm placement
monitor pt comfort and pain
chest tube drainage
-chambers
collection chamber (holds about 2l of water)
water seal
suction control/dry suction regulator

water seal 3
what it means/does 2
fill
corresponds w resp (tidaling)
allows air exit, not enter
fill with sterile water to 2 cm line
chest tube mgt 6
Prepare drainage unit as ordered
maintain patency of drainage system
observe tidaling
Observe for bubbling in water-seal chamber
Observe fluid levels in water-seal chamber
dressing care
drainage unit
wet suction: add sterile water to water-seal chamber (about 2 cm) and suction control chamber (20cm) as indicated or ordered
dry suction: add sterile water to fil line of air leak meter
maintain patency of drainage system
Keep tubing loosely coiled
Tape the connections for extra security
keep upright and below chest level at all times
tidaling
what does it mean
absent?
air fluctuations
rise with inhalation
fall with exhalation
absent?
drainage system is not functioning
lung is fully expanded
attached to suction
disconnect briefly and observe tidaling
bubbling
air leak or pt (bronchopleural leak)
clamp the tube at pt’s chest level
if it stops: air is coming from pt
continues: the unit may need to be replaced
dressing care
sterile occlusive dressing change
remove old dressing carefully = prevent removing unattached items
cleanse site and maintain asepsis
petroleum gauze preferred, then dressing on top
assessments for patient with a chest tube 5
Vital signs
lung sounds
pain
Drainage amount and color
Drainage site infection: culture
education/encourage
shoulder stiffness prevention
Encourage deep breathing
range-of-motion exercises
incentive spirometry
Milking or Stripping Chest Tube
yes or no
why
so what
Not recommended
Can increase intrapleural pressures and damage lungs
Position tubing so that drainage flows freely to negate need for milking or stripping
clamping
Never clamp routinely, only briefly for:
Changing drainage apparatus
Checking for air leaks
chest tube complications 3
Re-expansion pulmonary edema
Vasovagal response
Subcutaneous emphysema: air in tissue around insertion site
cracking felt on palpation
report these to hcp 5
Drainage > 100 mL or 200 ml/hr
Subcutaneous emphysema
Respiratory distress
diminished/absent breath sounds
chest drainage site infection
drainage/collection full
Change when full: do not empty
Measure fluid level
unit overturned 2
return to upright position
have patient exhale and cough
unit disconnected
immediate priority, activate water-seal system
immerse in 2 cm of sterile water
Do NOT EVER clamp (unless when removing)
risk vs benefit
atmospheric air in lungs vs air build up & tension pneumothorax
If accidentally removed
place occlusive dressing and secure with tape on 3 sides only.
removal or chest tube: when 3/4
when 2
what to do 1/2
When lungs re-expanded and drainage minimal
physician order
suction discontinued first
gravity drain for about 24 hours
nsn care for removal 5
Pain meds 30–60 min prior.
Valsalva maneuver during removal (hold breath and bear down)
Apply occlusive dressing before inhalation
Chest x-ray is done (recurrence)
check pneumothorax/effusion.
Monitor for respiratory distress (recurrence)