Kinetics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Kinetics
study of reaction rates
stoichiometry- deals with amount of reactant & products
Collision Theory
molecules must collide to react
in order for a reaction to occur, there have to be effective collisions
sufficient energy
proper orientation
collide
energy of collision > activation energy
Activation energy (Ea)
energy reactants need to overcome (energy difference between the reactant and transition state)
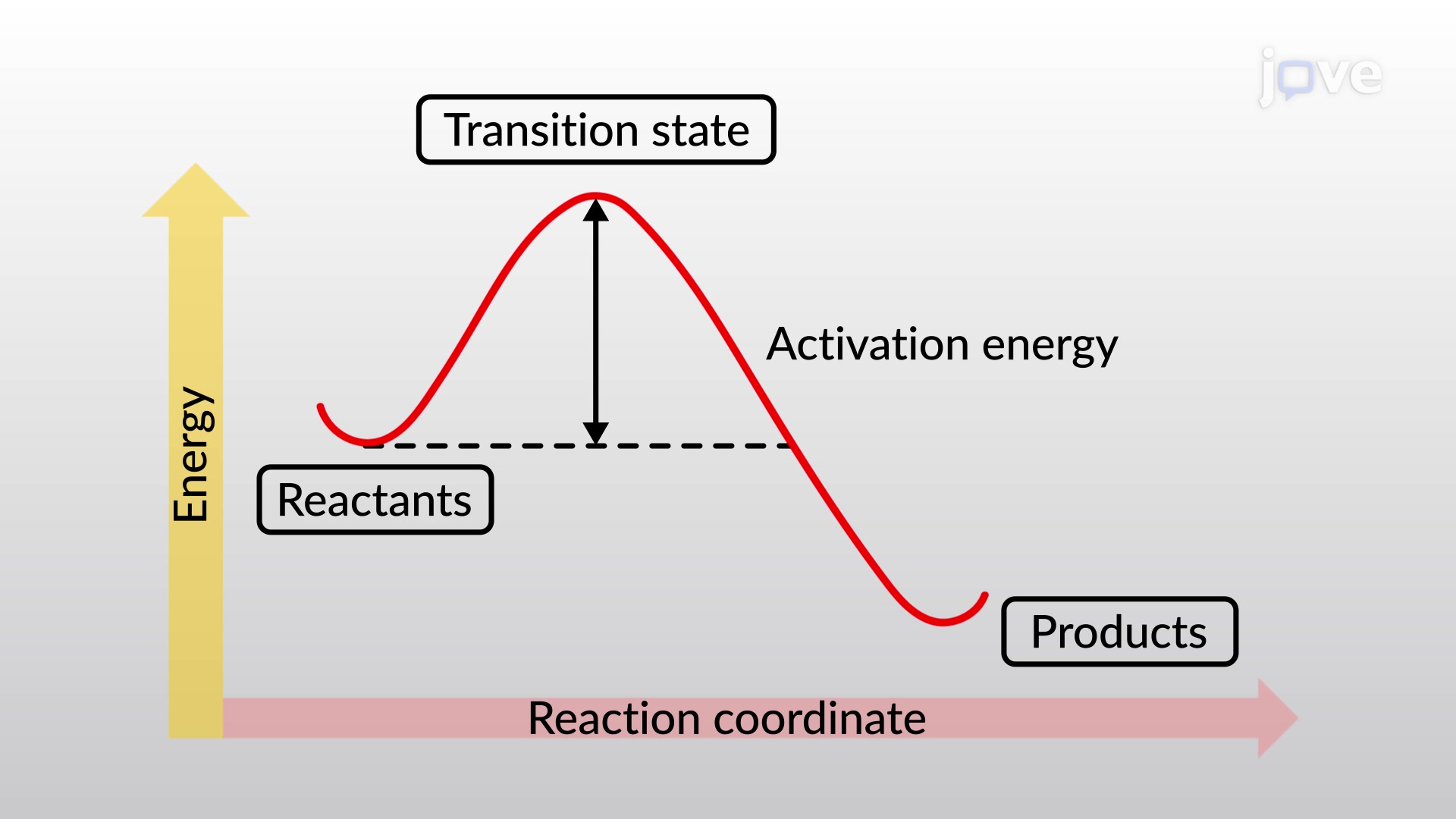
Activated complex (transition state)
arrangements of atoms found at the top of the potential energy state
unstable- bonds breaking + forming
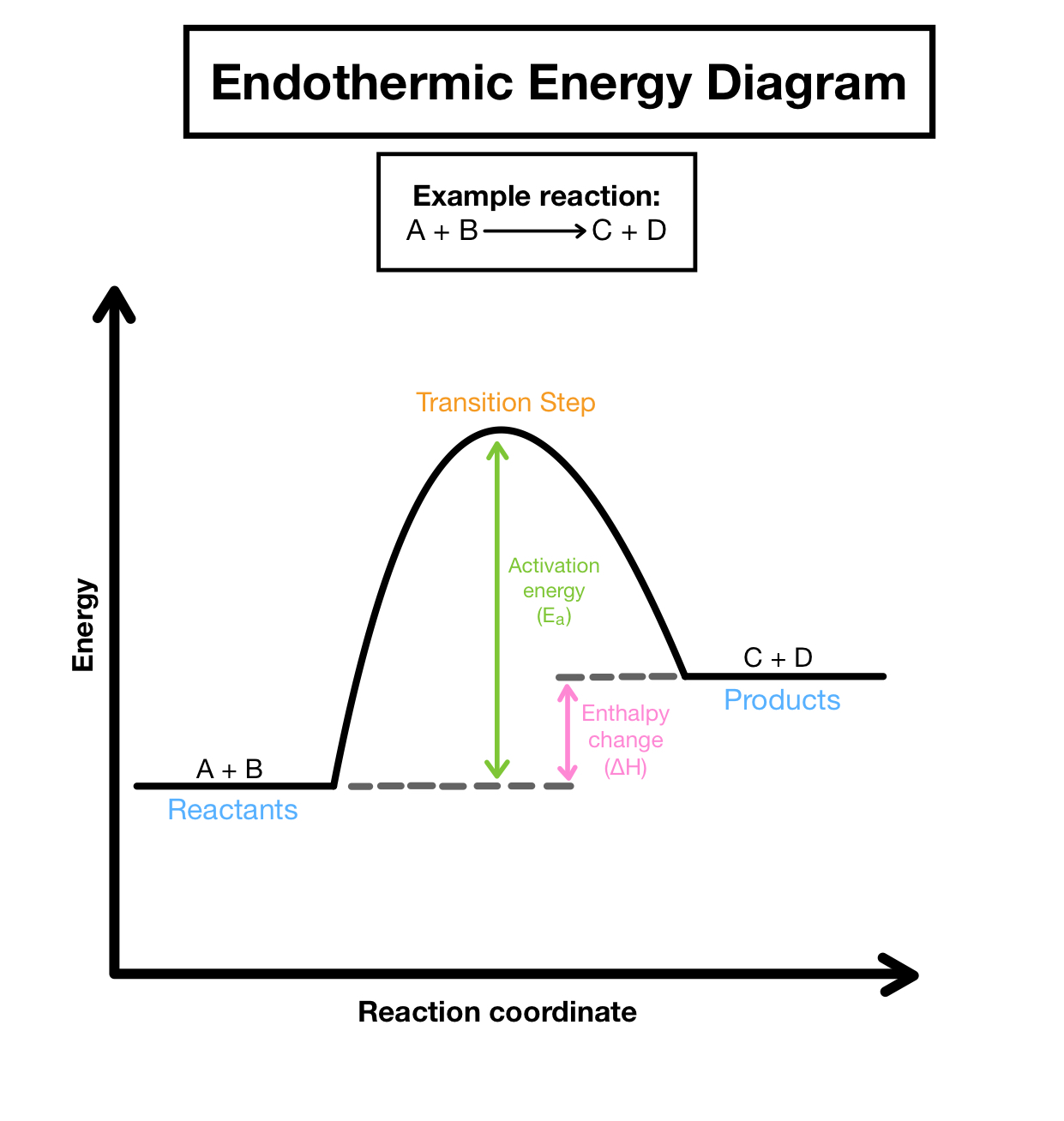
endo v exo
endo- product above reactant (+)
exo- product below reactant (-)
y- potential energy
x- reaction progress
ways to increase rate of reaction
stir mix
increase concentration (mol/L) (aq or gas)
increase surface area (s, l)
heat/ increase temperature
add a catalyst
speed up reaction, not reaction, not consumed
lowering activation energy by providing a new pathway- changing mechanism
Acid- base catalyst
takes reactant either adds or takes protons away to speed up chemical reaction
homogenous catalyst
surface catalyst (heterogenous catalyst)
made up metal ( more SA- more active sites)
increase number of successful collisions
reaction intermediate
providing active site on their surface, gases absorbed onto metal
metal breaks bonds
both molecules migrate towards each other
form products (saturated mlc so can’t bind to metal and leaves)
enzyme
homogenuous
reaction intermediates- short lived species that is formed then consumed during multi step chem reaction
speed up chem reaction, lower activation energy
binds substrate to active site
homogenous catalyst
esterification: use to make flavorings
reaction rate
change in concentration of a reactant/product per unit time
rate= (concentration A at t2 - concentration A at t1)/ t2 - t1
rate= Δ [A] / Δt
if concentration decrease with time then negative
instaneous rate
value of reaction rate at a particular time
slope of tangent line= change in y/ change in x
first- order half life
half- life is constant
explain why unlikely that reaction occurs in a single elementary step
unlikely that 4 molecules would all collide at the exact same moment, with the proper orientation and sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier
what does increase temperature do
adds energy which increase collisions, with lower temp. there isn’t sufficient energy for high collisions
activation energy
as activation energy increase the reaction rate decrease, need to overcome greater barrier
Ea= Eac - Er
molecularity
molecularity greater than bimolecular has a very low probablity of occuring
termolecular occur less than bimolecular
equilibrium
some reactions are reversible
we use double arrow
at equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the reverse reaction
rate forward= rate reversed
don’t want intermediate to show in rate law expression
equilibrium steps
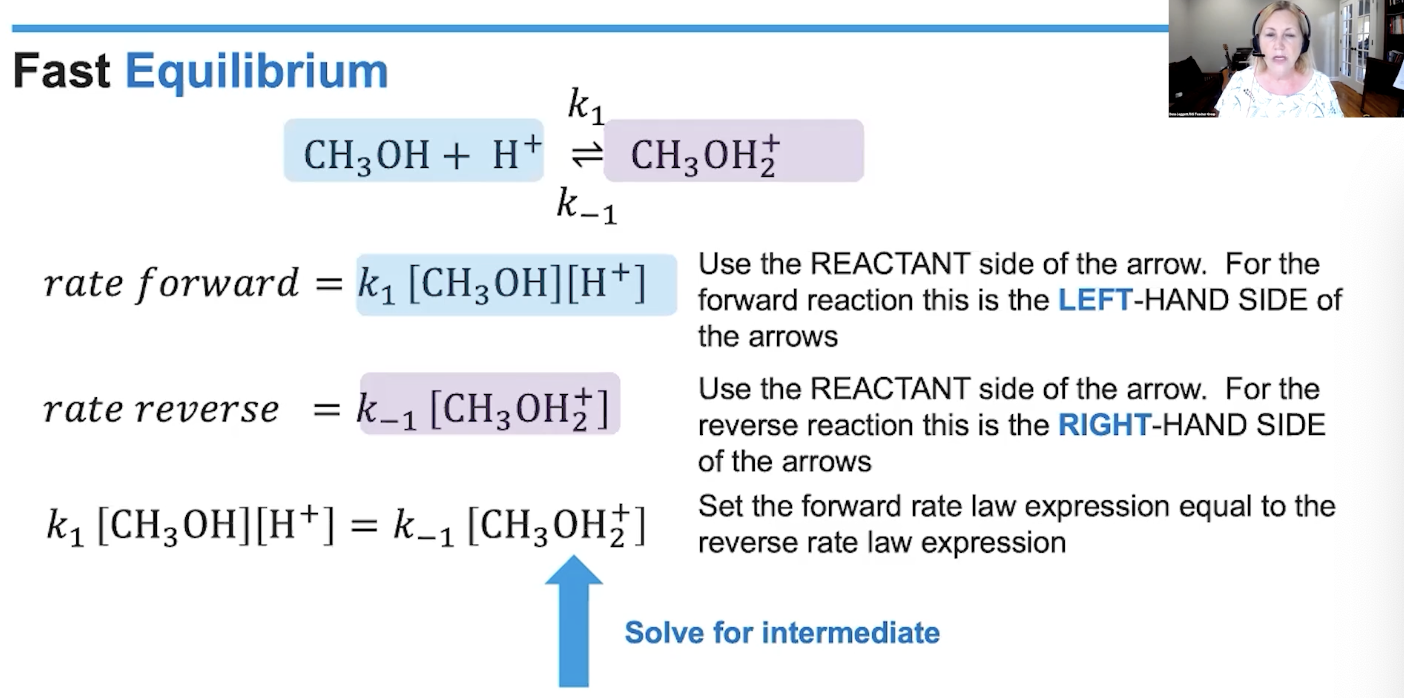
how do you know how many steps from reaction profile
number of peaks shows steps
largest activation peak is the slow step