Module 1 (Week 2) - Chapter 17: The Gains From International Trade
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Define open economy.
An economy that engages in international trade
Define closed economy.
An economy that does not engage in international trade
True or False: Without trade, everyone must be self-sufficient. With trade, people can specialize in what they do well and satisfy other needs by trading.
True
Define absolute advantage.
When one region can produce more of a particular good than another region using an equal quantity of resources
Fewer resources to produce one unit of a particular good
Define comparative advantage.
When one region can produce a particular good at a lower opportunity cost than another region
Having to give up less output of other goods
Gains from specialization and trade depend on the pattern of ______ advantage (not ______ advantage).
Gains from specialization and trade depend on the pattern of comparative advantage (not absolute advantage).
Whenever opportunity costs differ between countries, specialization can ______ the world’s production of both products.
Whenever opportunity costs differ between countries, specialization can increase the world’s production of both products.
World output ______ if countries specialize in the production of goods in which they have a comparative advantage.
World output increases if countries specialize in the production of goods in which they have a comparative advantage.
True or False: International trade leads to specialization in production and increased consumption possibilities.
True
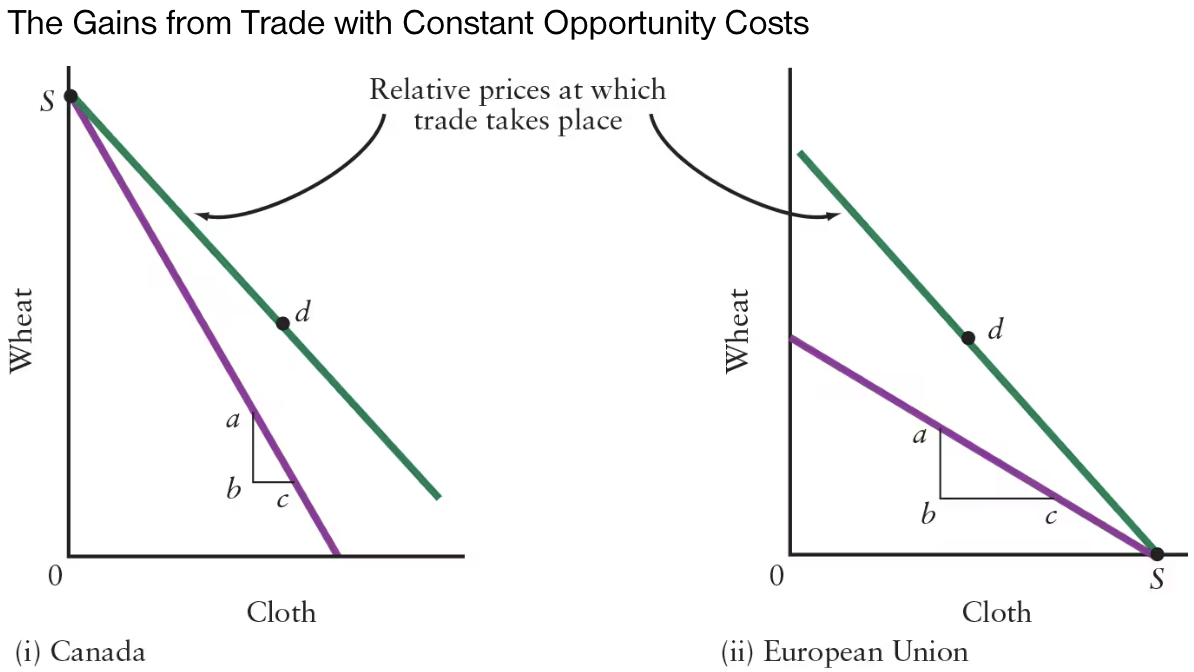
The difference in the slopes of the production possibilities boundaries reflects differences in ______.
The difference in the slopes of the production possibilities boundaries reflects differences in comparative advantage.
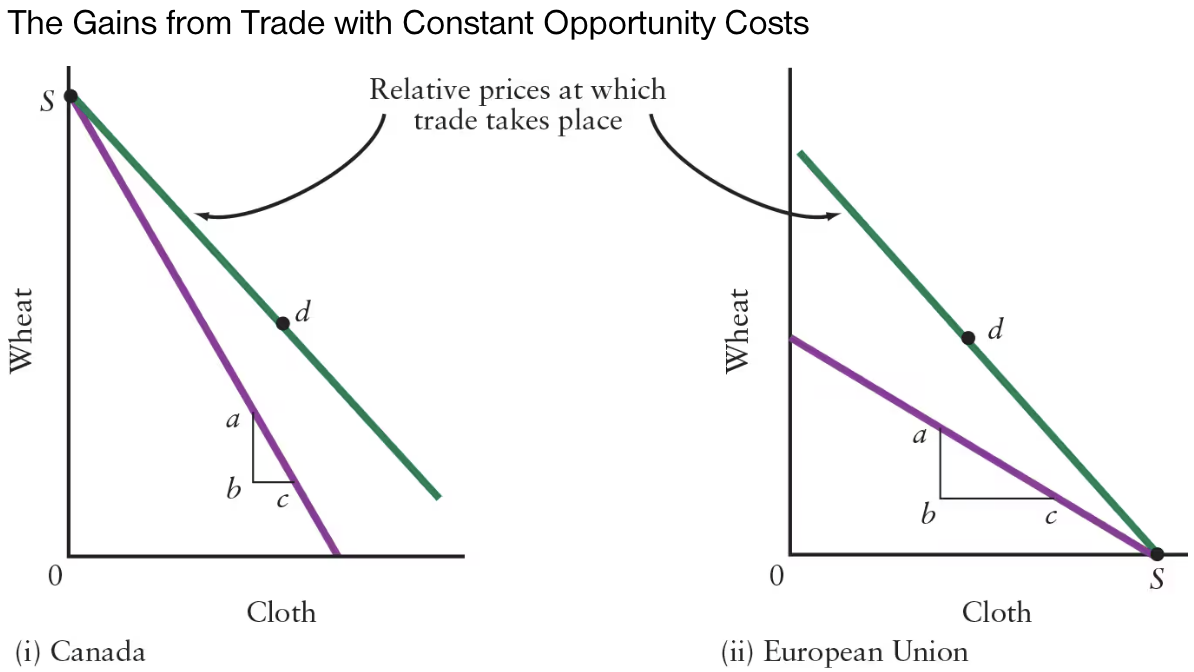
The opportunity cost of producing wheat in Canada is ______ than that in the EU.
The opportunity cost of producing wheat in Canada is less than that in the EU.
True or False: Without international trade, the production possibilities boundary is also the consumption possibilities boundary.
True
What are the 2 ways in which international trade leads to an expansion of goods consumed in the economy?
By allowing goods consumed to differ from goods produced
By allow a profitable change in the pattern of production
True or False: With international trade, consumption and production can be altered independently to reflect the relative values of goods in the international market.
True
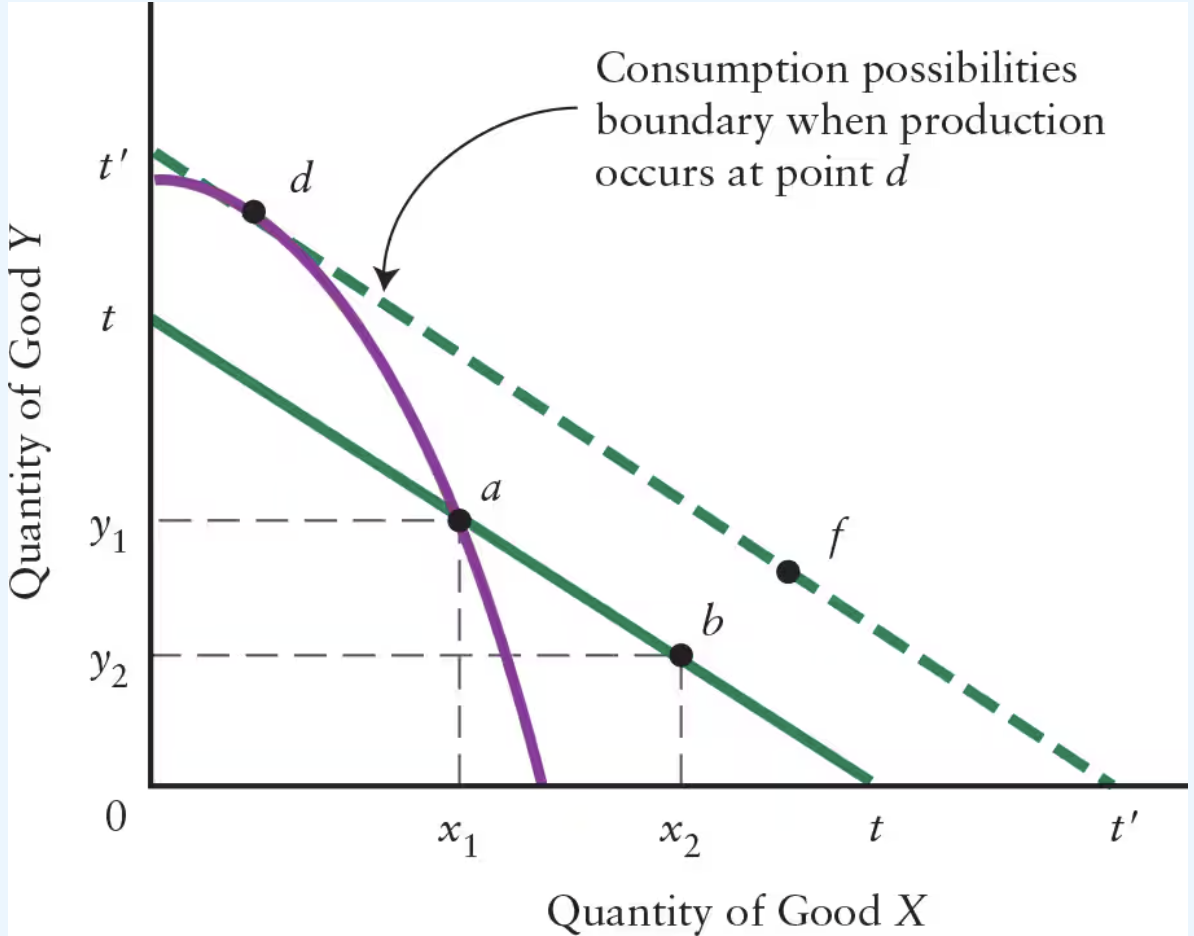
True or False: The benefits of moving from a no-trade position (point a) to a trading position (points b or f) are the gains from trade.
True
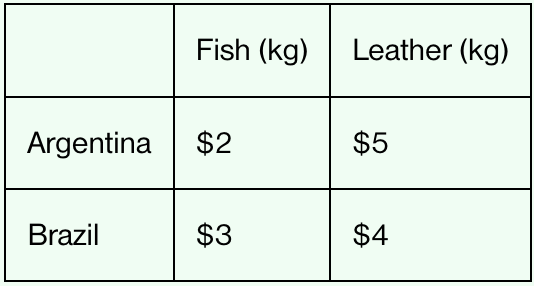
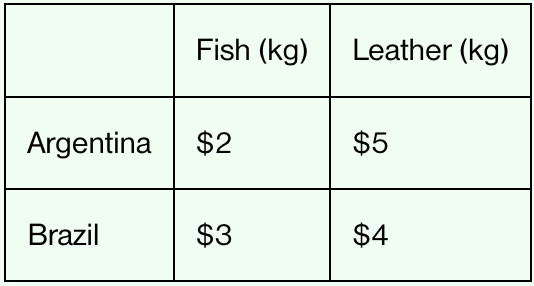
The table shows the total resource cost of producing 1 kilogram of each good in both countries. Which country has the absolute advantage in fish production?
Argentina
More efficient producer of fish
Total resource cost ($2) is less than Brazil’s ($3)
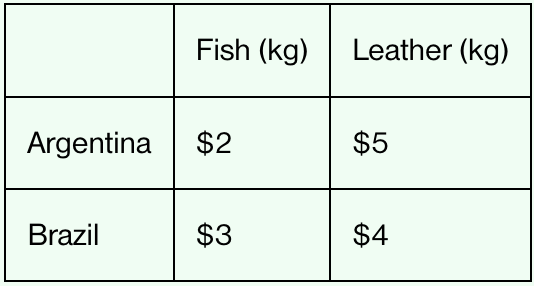
The table shows the total resource cost of producing 1 kilogram of each good in both countries. Which country has the absolute advantage in leather production?
Brazil
More efficient producer of leather
Total resource cost ($4) is less than Argentina’s ($5)
The table shows the total resource cost of producing 1 kilogram of each good in both countries. Which country has the comparative advantage in leather production?
Brazil
Lower opportunity cost for leather
In Argentina, 1 kilogram of leather costs 2.5 kilograms of fish
In Brazil, 1 kilogram of leather costs 1.33 kilograms of fish
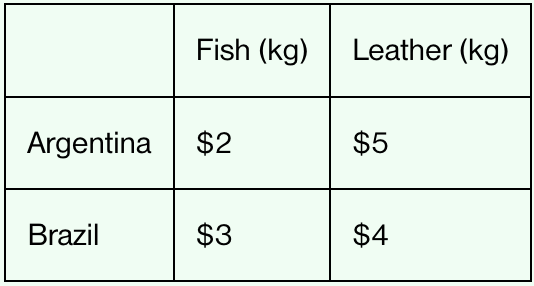
The table shows the total resource cost of producing 1 kilogram of each good in both countries. Which country has the comparative advantage in fish production?
Argentina
Lower opportunity cost for fish
In Brazil, 1 kilogram of fish costs 0.75 kilogram of leather
In Argentina, 1 kilogram of fish costs 0.4 kilogram of leather
In many industries, production costs ______ as the scale of production increases.
In many industries, production costs decrease as the scale of production increases.
Define intra-industry trade.
A result of scale economies in which different countries specialize in different versions of similar products to be traded
Trade of goods or services within the same industry
Define learning by doing.
As countries gain experience in particular tasks, workers and managers become more efficient in performance.
Increase in expertise leads to decrease in costs
A higher domestic price level will result in:
A) Lower export revenues
B) Lower imports
C) Higher export revenues
D) Higher imports
D) Higher imports
A higher domestic price level makes domestic goods more expensive relative to foreign goods
Exports will fall, and imports will rise
What are the 4 sources of comparative advantage?
Different factor endowments
Different climates
Human capital
Acquired comparative advantage
Explain the relationship between comparative advantage and different factor endowments.
Heckscher-Ohlin Theory: countries have comparative advantages in the production of goods that intensively use the factors of production with which they are abundantly endowed
Ex: Canada is abundantly endowed with forests
Comparative advantage in goods that use forest products (paper, raw lumber, wooden furniture)
Explain the relationship between comparative advantage and different climates.
The effects of sunshine, rainfall, average temperature, and other natural factors lead to different outputs in most agricultural goods
Explain the relationship between comparative advantage and human capital.
Human Capital: acquired skills
Ex: trade schools, mass-production techniques
Explain the relationship between comparative advantage and acquired comparative advantage.
Comparative advantages are dynamic (not static)
Current industries depend more on human capital than on fixed physical capital or natural resources
Define the law of one price.
National prices of tradable goods in different countries (net of taxes or tariffs) will differ by no more than the cost of transporting goods between countries
There is a single world price (after accounting for differences in transport costs)
Define world price.
The price at which quantity demanded worldwide is equal to quantity supplied worldwide
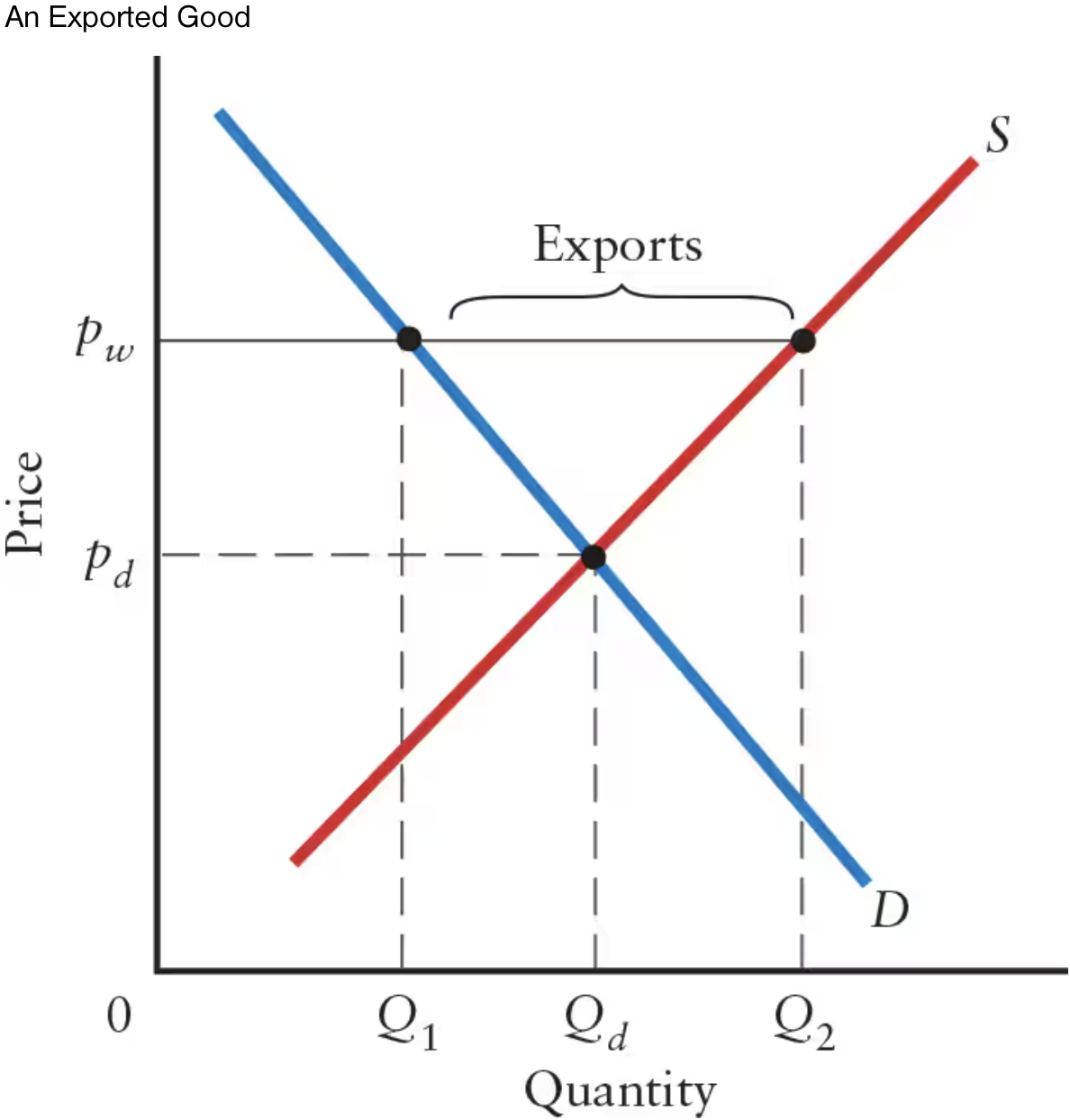
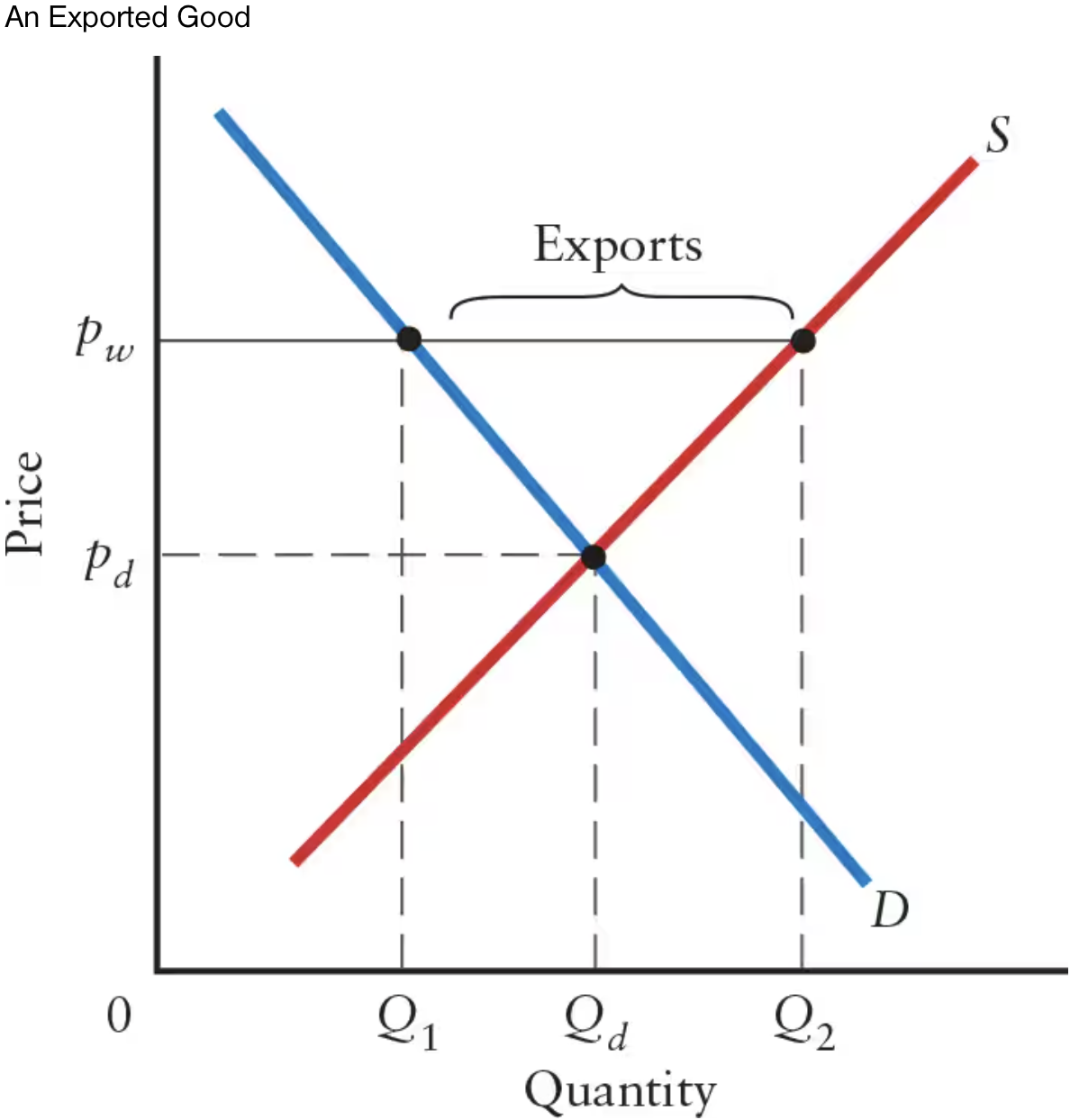
In this graph, what does the intersection of the demand and supply curves represent?
The intersection represents price and quantity in the domestic market when there is no foreign trade.
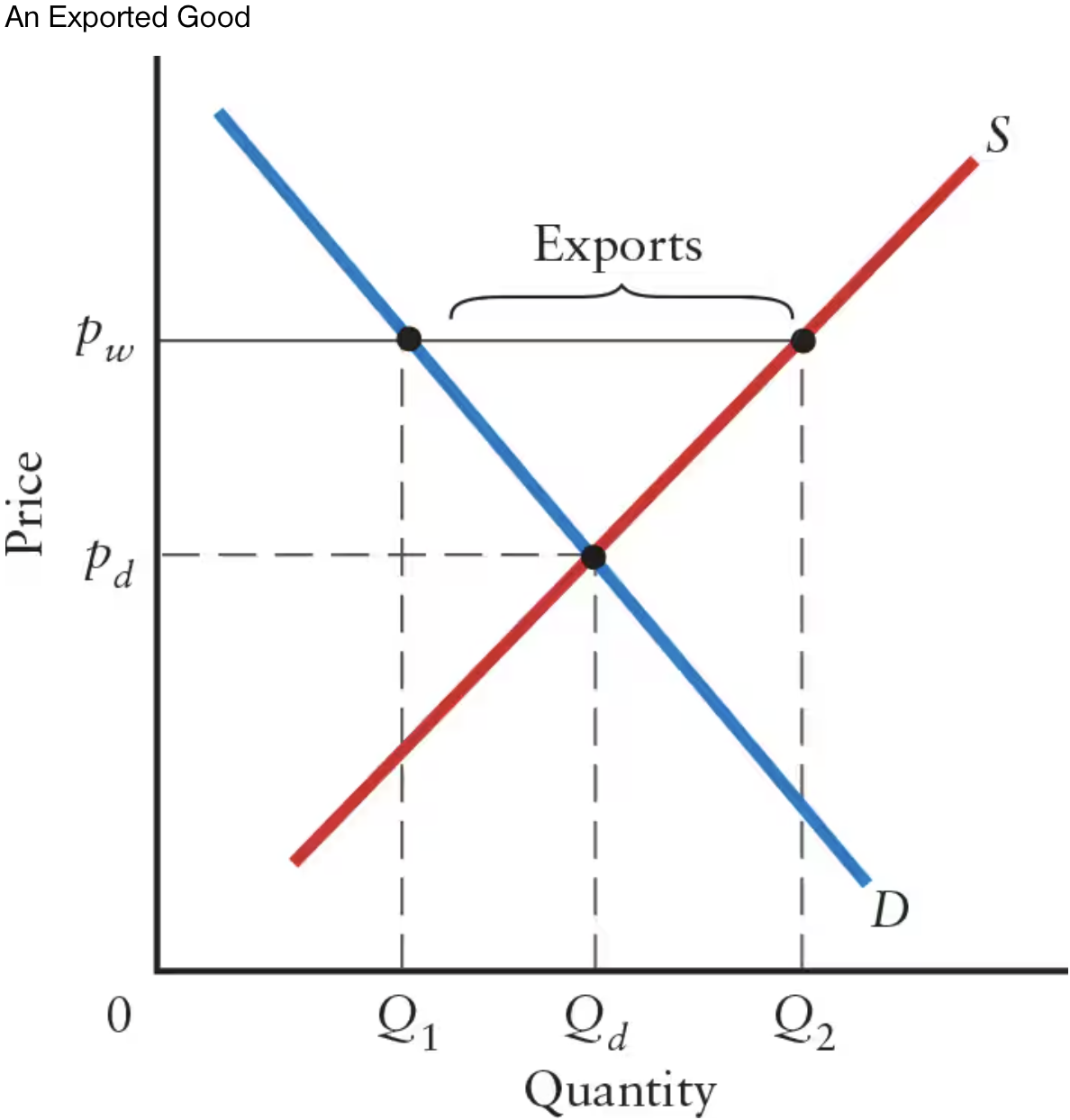
Exports occur whenever there is excess ______ domestically at the world price.
Exports occur whenever there is excess supply domestically at the world price.
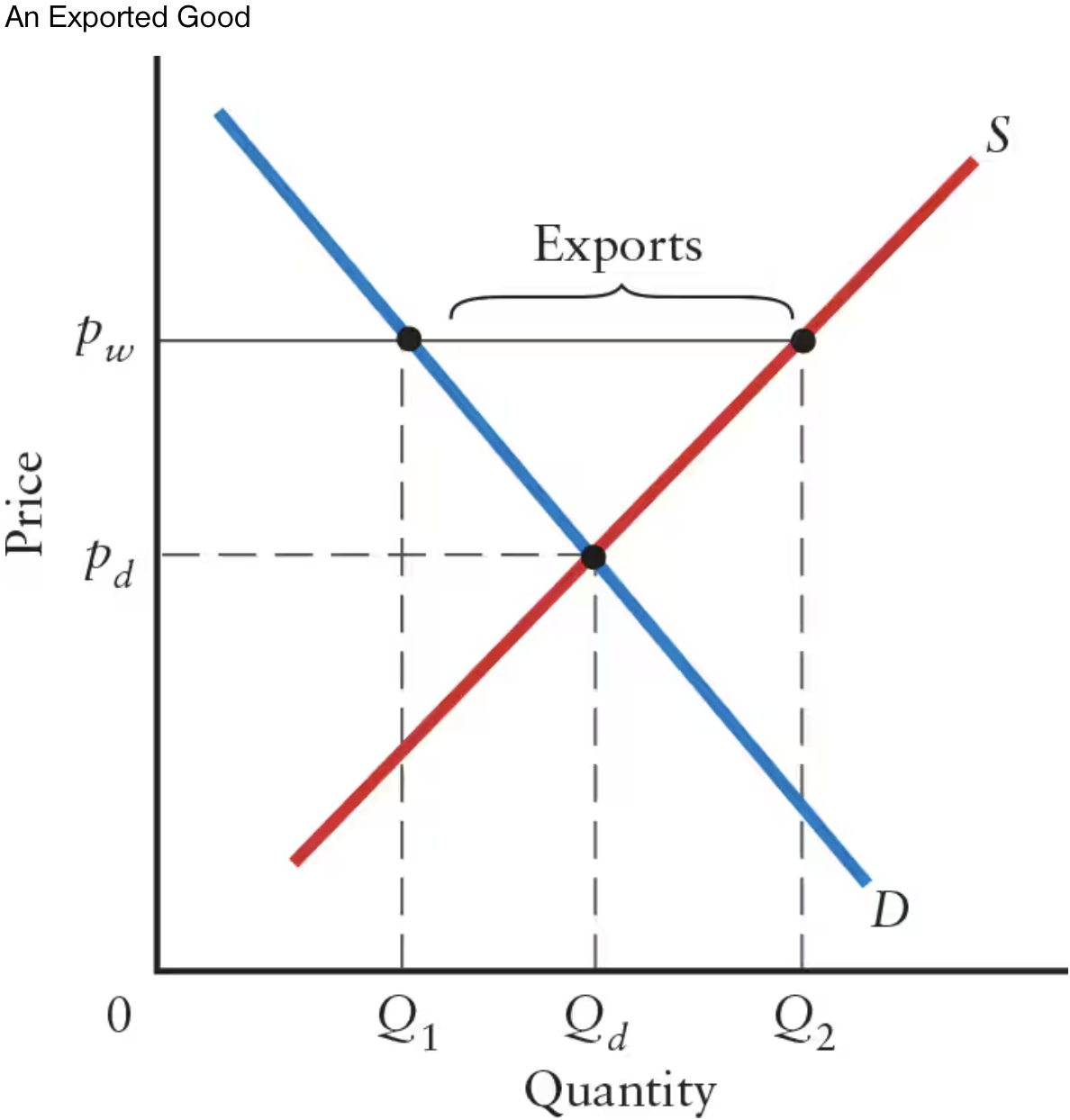
In this graph, the world price of pw is ______ than pd.
In this graph, the world price of pw is higher than pd.
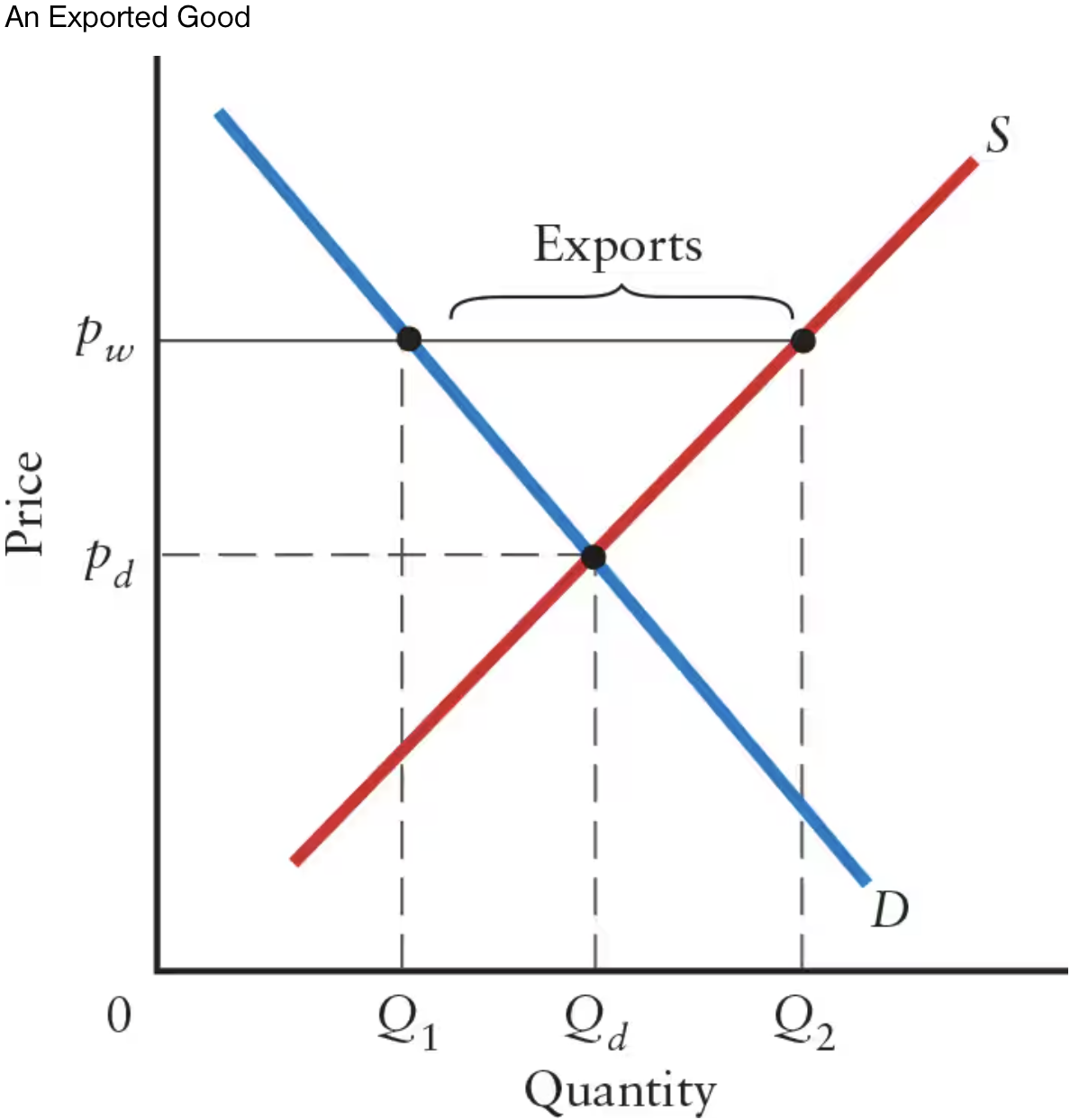
If the world price is higher than domestic price (pw > pd), there will be excess ______.
If the world price is higher than domestic price (pw > pd), there will be excess supply.
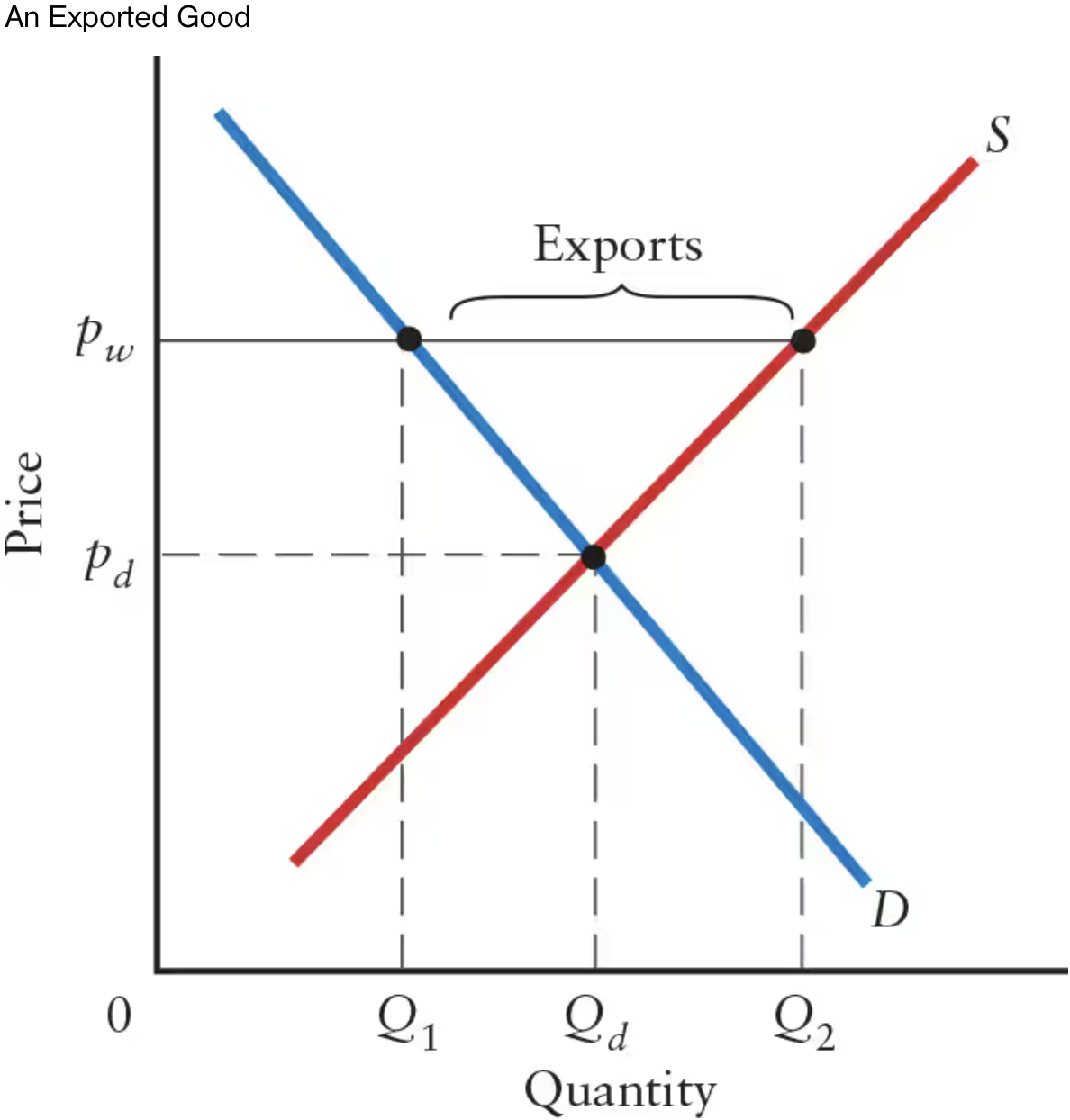
What is the equation for calculating exports at the world price?
Q2 — Q1
Q2 represents quantity supplied at the world price
Q1 represents quantity demanded at the world price
Countries export goods for which they are low-cost producers. That is, they export goods for which they have a ______.
Countries export goods for which they are low-cost producers. That is, they export goods for which they have a comparative advantage.
Imports occur whenever there is excess ______ domestically at the world price.
Imports occur whenever there is excess demand domestically at the world price.
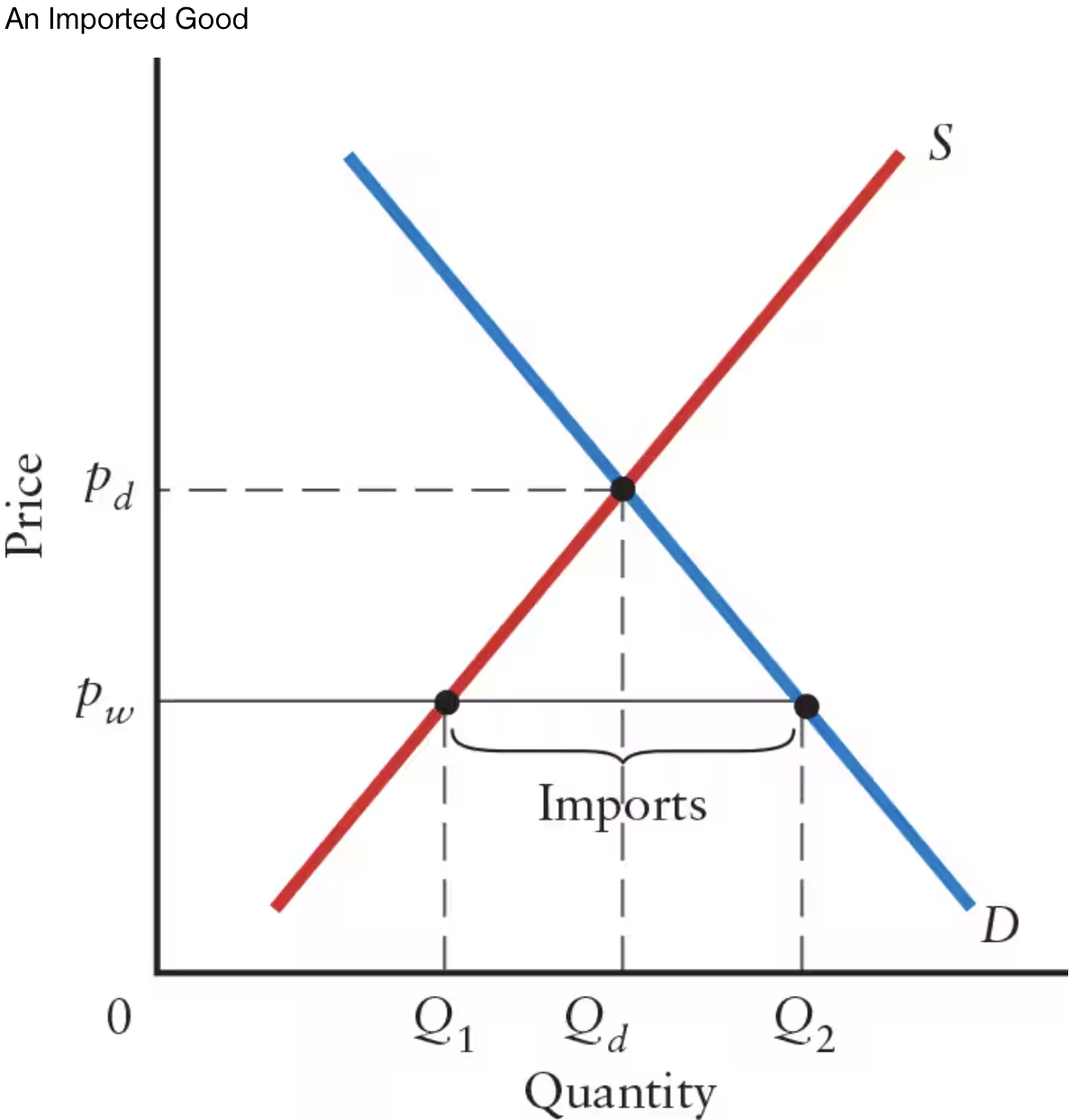
In this graph, the world price of pw is ____ than pd.
In this graph, the world price of pw is less than pd.
Countries import goods for which they are high-cost producers. That is, they import goods for which they have a ______.
Countries import goods for which they are high-cost producers. That is, they import goods for which they have a comparative disadvantage.
National comparative advantages are determined by differences in national ______.
National comparative advantages are determined by differences in national opportunity costs.
What are the 3 causes of decentralized production?
Scale economies allow firms to reduce costs by concentrating the production of individual components in different specialized factories
Differences in national wage rates
Low costs of communication and transportation
Allows for coordination of global supply chains at a low cost
Define terms of trade.
The ratio of export prices to import prices
Shows the quantity of imports that can be purchased per unit of exports sold
Explain the conditions in which a fall in the terms of trade can occur.
Rise in the price of imported goods
It will now take more exports to buy the same quantity of imports
Explain the conditions in which a rise in the terms of trade can occur.
Rise in the price of exported goods
It will now take fewer exports to buy the same quantity of imports
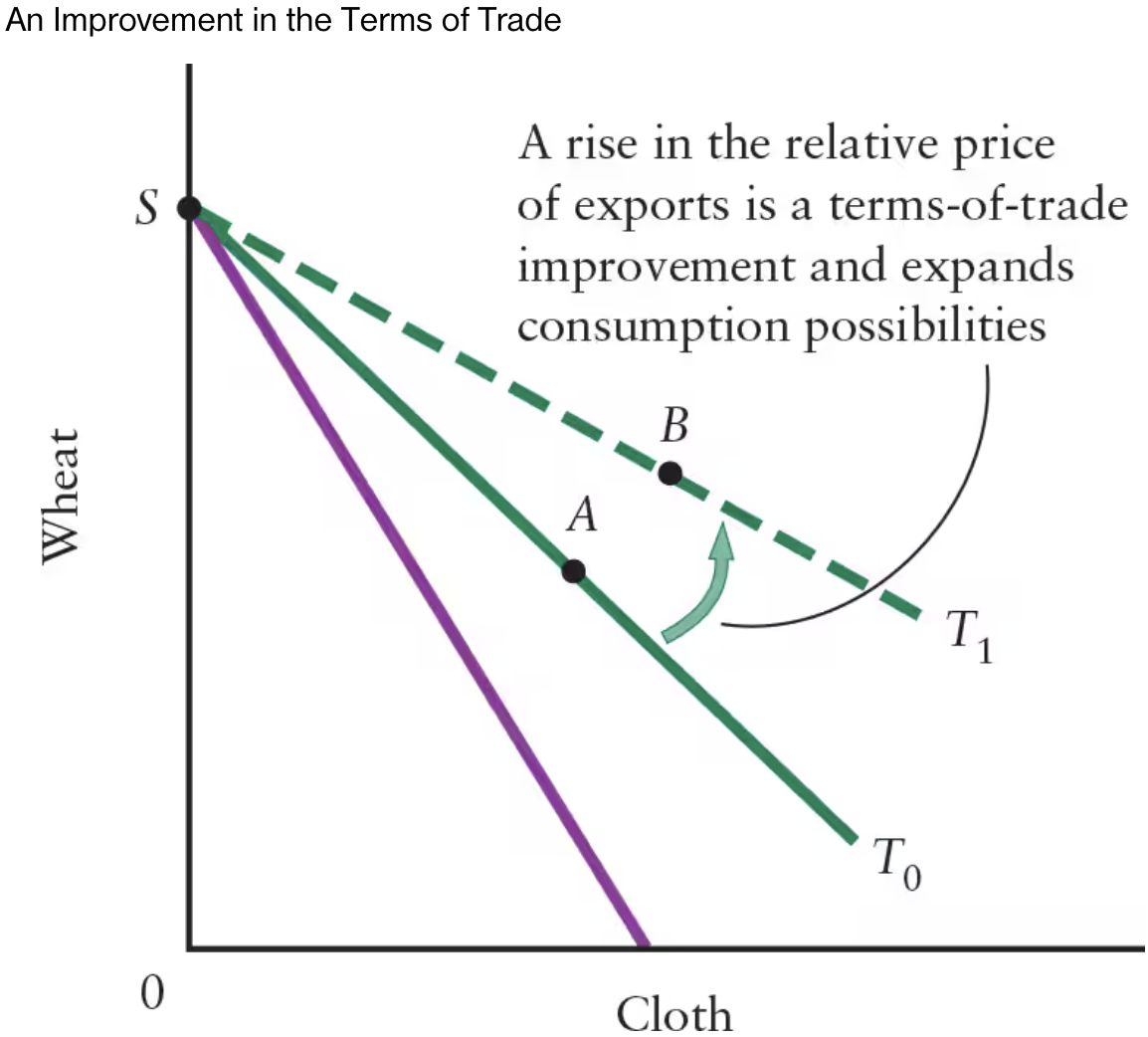
A steep production possibilities boundary indicates that only a small amount of ______ must be given up for more ______.
A steep production possibilities boundary indicates that only a small amount of cloth must be given up for more wheat.
Cloth is relatively expensive, and wheat is relatively cheap
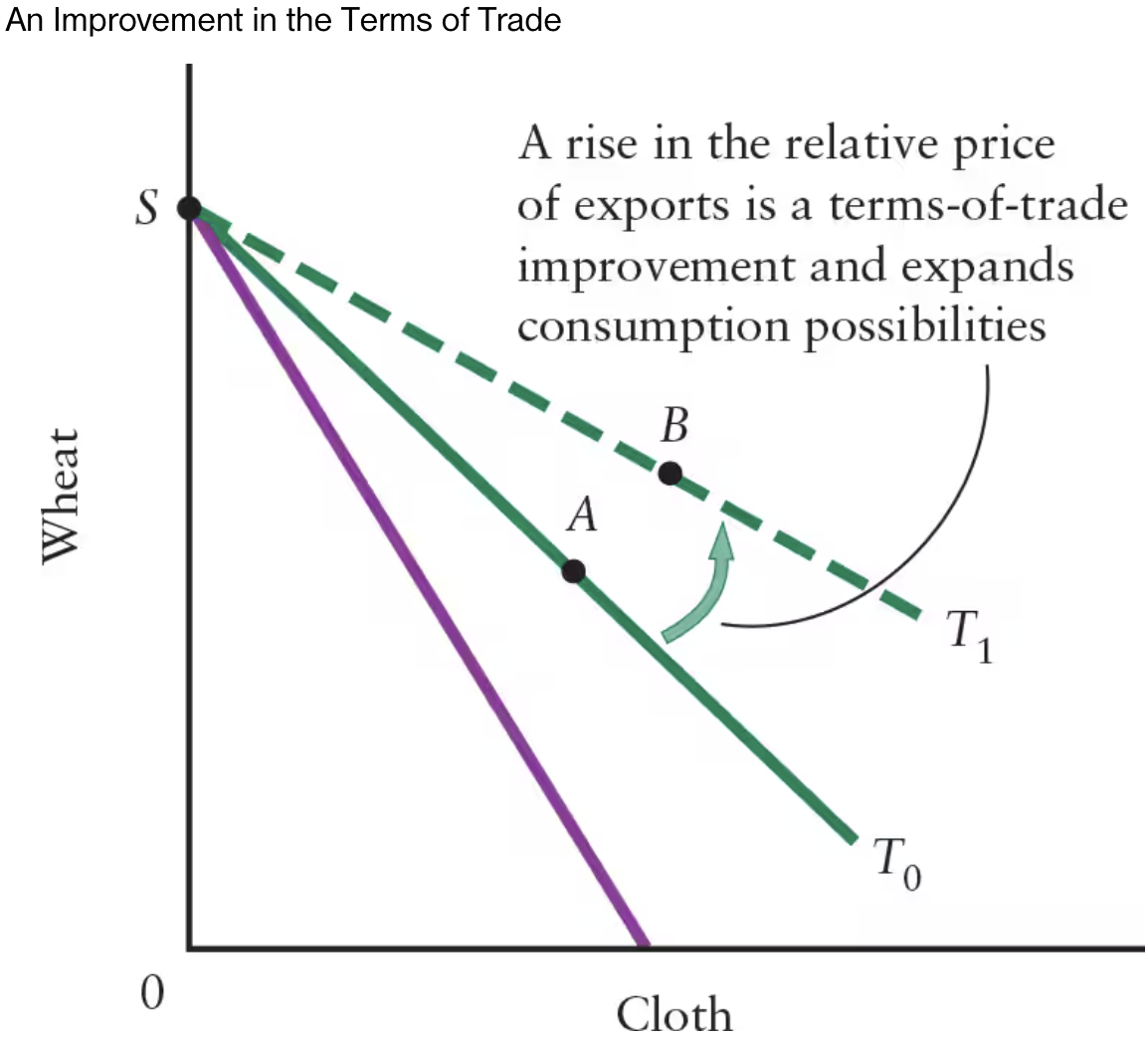
A flatter production possibilities boundary indicates that a larger amount of ______ must be given up for more ______.
A flatter production possibilities boundary indicates that a larger amount of cloth must be given up for more wheat.
Cloth is relatively cheap, and wheat is relatively expensive
True or False: Changes in the terms of trade lead to changes in a country’s consumption possibilities.
True
What is the formula for calculating a country’s terms of trade as an index number?
Terms of Trade = Index of Export Prices / Index of Import Prices X 100
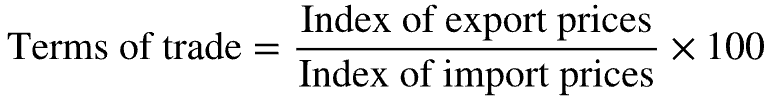
Define terms-of-trade improvement.
A rise in the terms-of-trade index number
Define terms-of-trade deterioration.
A decrease in the terms-of-trade index number
Which of the following is not a factor that can improve the terms of trade?
A) Appreciation of the local currency
B) Depreciation of a trade partner’s currency
C) Increase in international prices of the country’s exports
D) Presence of deflation in the country
D) Presence of deflation in the country
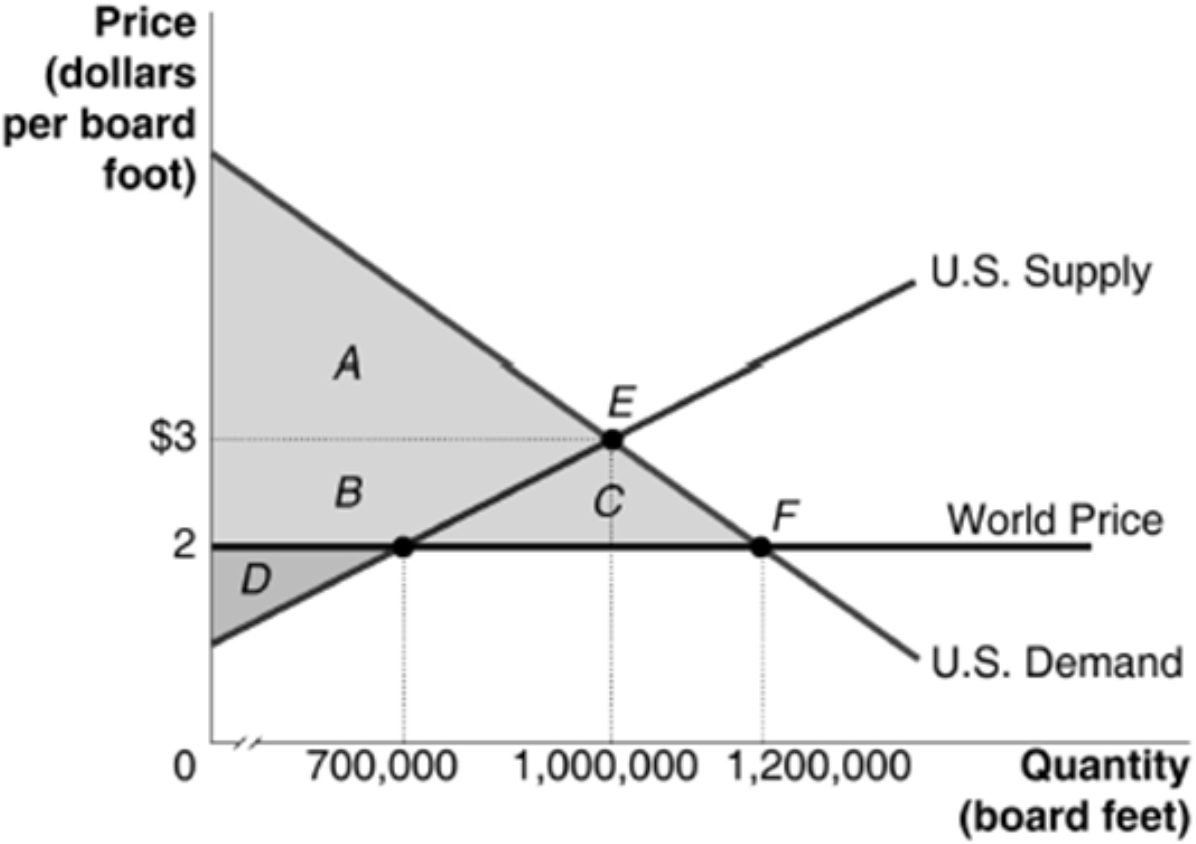
How many board feet of lumber will be imported if imports are allowed into the US?
A) 700,000
B) 1,000,000
C) 500,000
D) 1,200,000
C) 500,000
1,200,000 — 700,000 = 500,000
At $2 per board foot, domestic suppliers are willing and able to supply 700,000 board feet of lumber
However, demand for lumber at $2 per board foot is 1,200,000 board feet
Imports will make up the 500,000 board feet shortage
Comparative advantages:
A) Can be influenced only by free markets
B) Are fixed because of natural endowments
C) Can be influenced by governments
D) Are fixed because of the law of one price
C) Can be influenced by governments
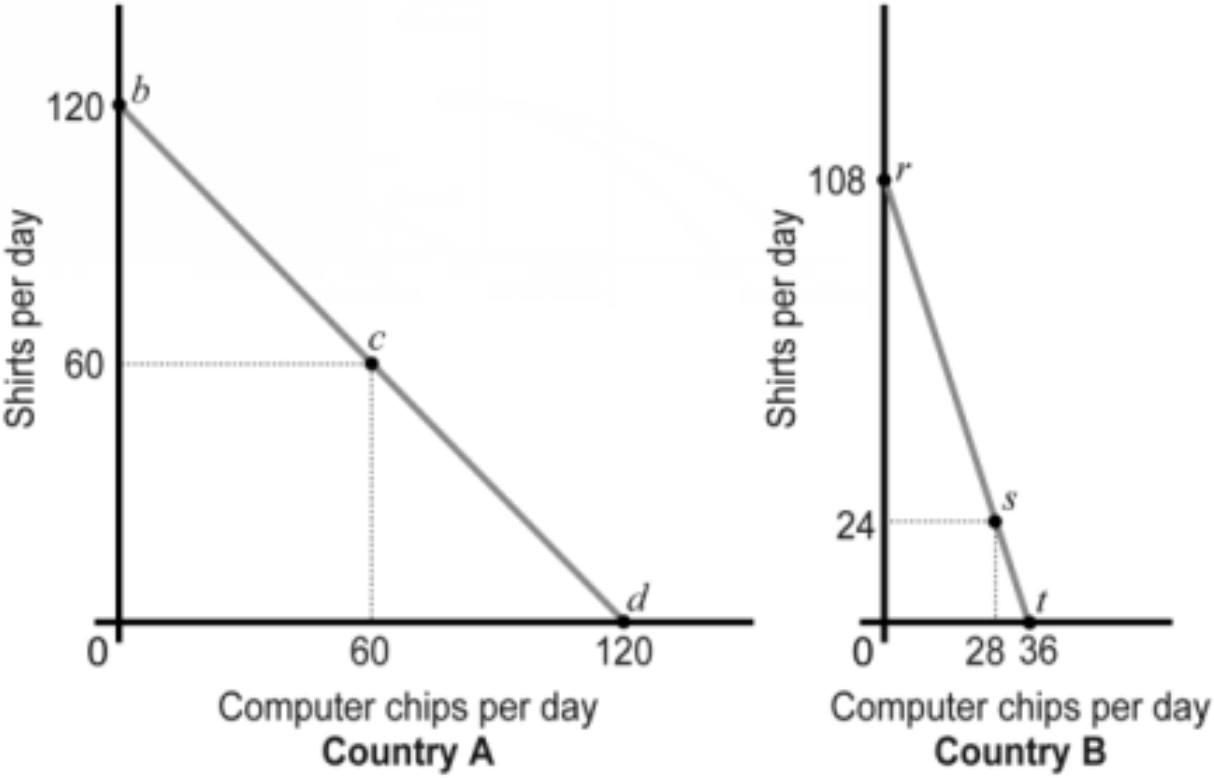
Which country has a comparative advantage in the production of shirts?
A) Both
B) Neither
C) Country A
D) Country B
D) Country B
Country with the lowest opportunity costs in shirt production will have a comparative advantage
Country A gives up the production of 1 computer chip to produce another shirt
Country B gives up 1/3 of a computer chip to produce another shirt
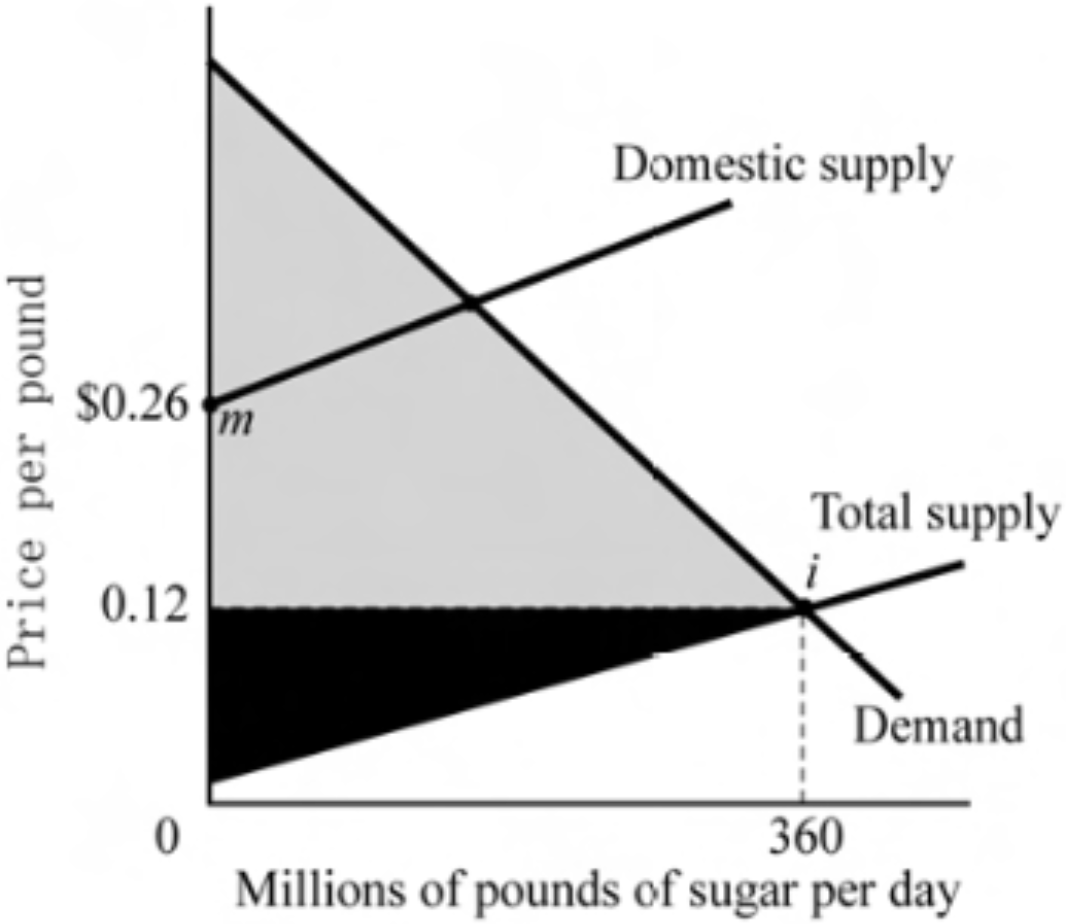
How much domestic sugar will be supplied at $0.12 under free trade?
A) 0 pounds
B) 360 million pounds
C) More than 360 million pounds
D) Between 100 and 300 million pounds
A) 0 pounds
Domestic suppliers are unwilling to supply any output at $0.12 per pound
They will not begin sugar production until the price reaches $0.26 per pound
If a country is exporting a product, we know that:
A) The country’s equilibrium price is higher than the international price
B) The country's equilibrium price is lower than the international price
C) The country's equilibrium quantity is higher than the international supply
D) The country's equilibrium quantity is lower than the international supply
B) The country's equilibrium price is lower than the international price
If a country is importing a product, we know that:
A) The country's equilibrium quantity is lower than the international supply
B) The country's equilibrium price is higher than the international price
C) The country's equilibrium quantity is higher than the international supply
D) The country's equilibrium price is lower than the international price
B) The country's equilibrium price is higher than the international price