science stars and global warming
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
define a star
a large ball of hot glowing plasma
define nuclear fusion
a high energy reaction in which two lighter atomic nuclei fuse to form a heavier nucleus
what do stars contain
hydrogen and helium
where does nuclear fusion occur and what is released in this reaction
in the core of stars , releases energy as electromagnetic radiation (light) and releases heat
apparent magnitude definition
a measure of how bright a star “appears” to be from early
absolute magnitude definition
measures a stars brightness if all stars are all the same distance
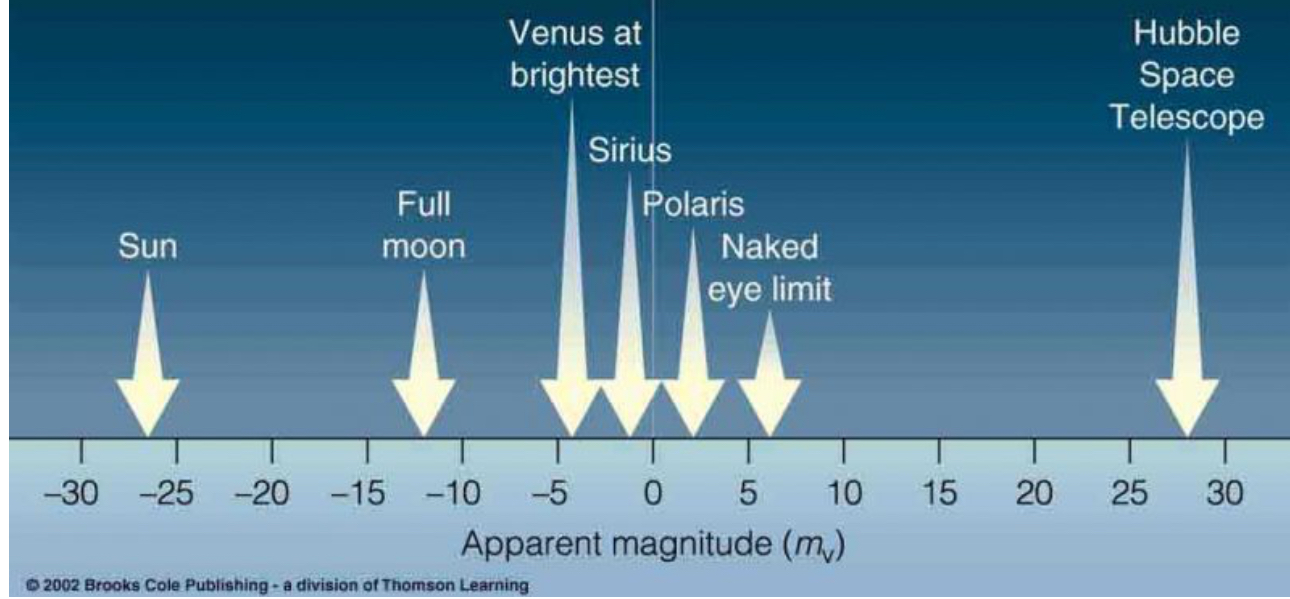
what is brighter sun or moon and why
sun bc the more negative the value the brighter the star
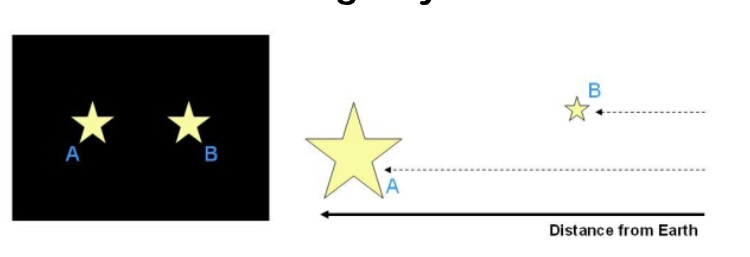
why does star A appear to be the same brightness as star B, despite star A being further away
A has a higher absolute magnitude, A and B have the same apparent magnitude
how do stars vary
size, mass, temperature, and brightness
how can we compare stars temperature
by analysing their colour, blue stars r hotter, red stars r colder
what’s the r hertzsprung russel diagram and what does it do
a method of displaying star data on a graph and shows the relationship between a stars brightness and temperature. it helps classify stars by showing where they r in their life cycle. it shows patterns in star types like main sequence stars, supergiants, giants, and white dwarfs
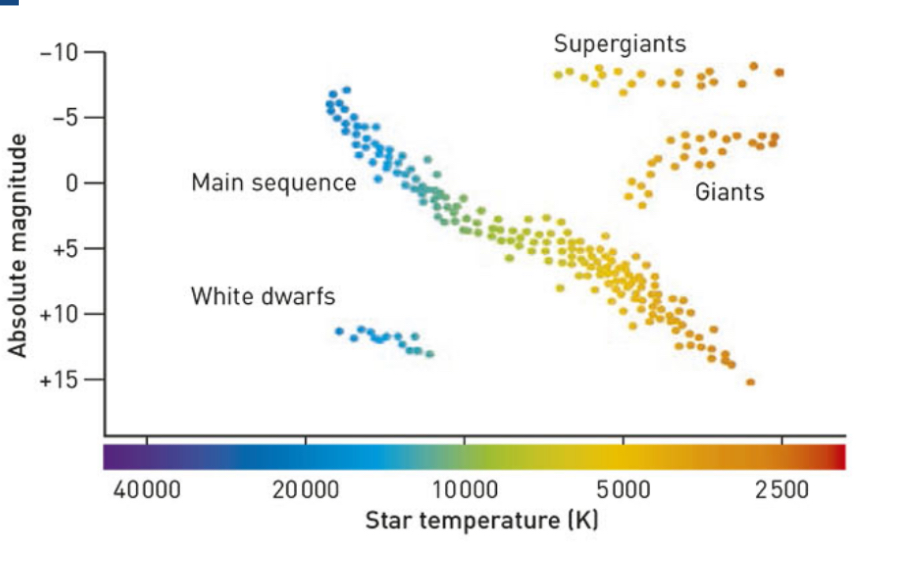
what trends do y observe on this hertzsprung russel diagram
most stars fall on a narrow band called the main sequence
define absolute magnitude
measures a stars brightness, if all stars are the same distance
define apparent magnitude
a measure of how bright a star “appears” to be from earth
draw a labelled diagram to show stellar parallax
where would u find the following on an HR(hertz spring russel) diagram:
white drawf
super giants
main sequence
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram, which compares temperature (left to right, hot to cool) and luminosity (bottom to top, dim to bright):
🌟1. Main Sequence
Location: From the top left to the bottom right (a diagonal line).
Includes most stars (like our Sun).
Hot, bright stars are at the top left; cool, dim ones at the bottom right.
🌟2. Supergiants
Location: At the top right.
Very cool but extremely bright because they are huge in size.
🌟3. White Dwarfs
Location: At the bottom left.
Very hot but dim because they are small and don’t produce much light.
free space yay keep going stay focused
explain where nuclear fusion occurs
Nuclear fusion happens in the cores of stars, where hydrogen atoms join to make helium and release energy.
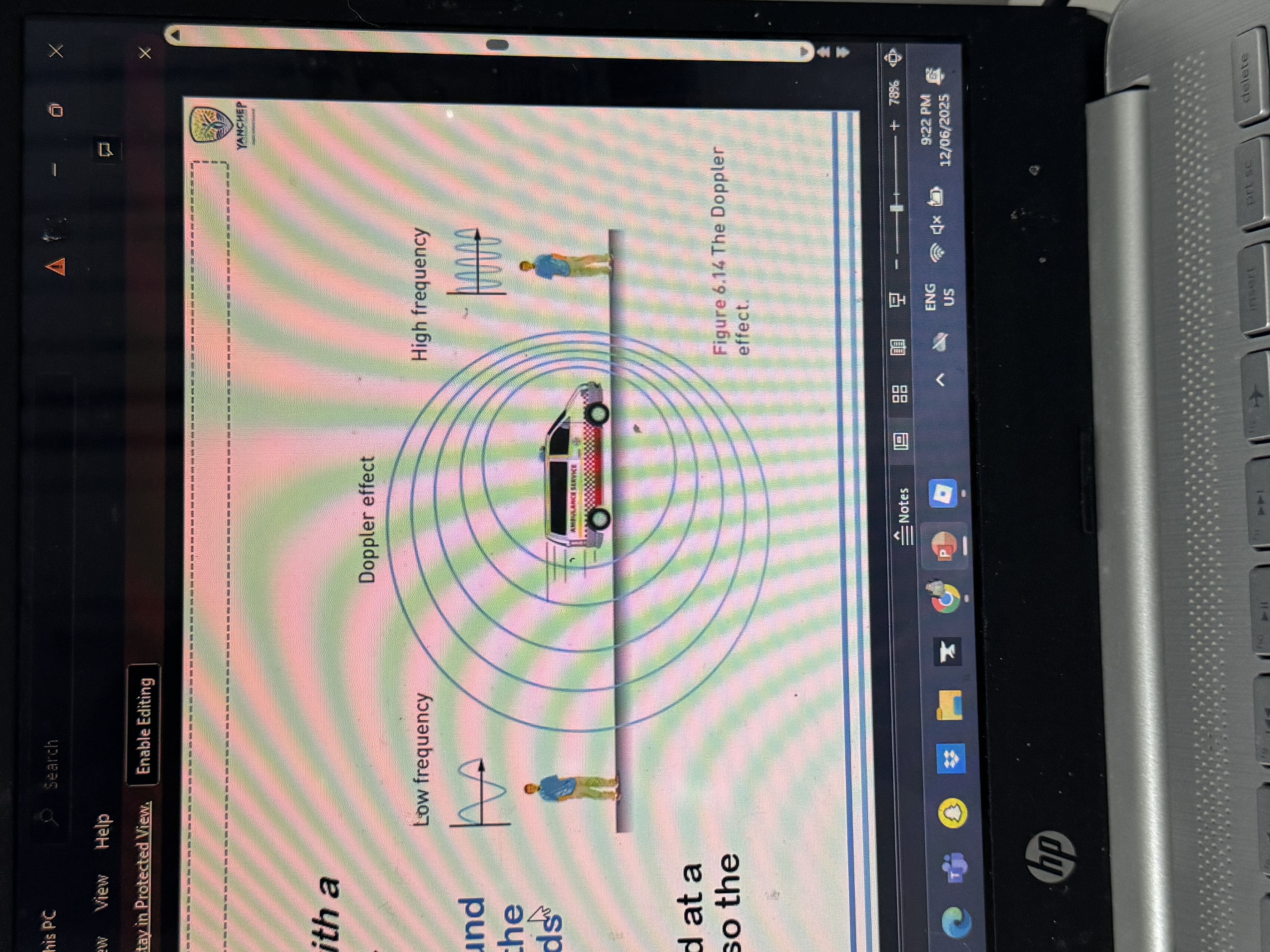
draw a diagram showing the doppler effect
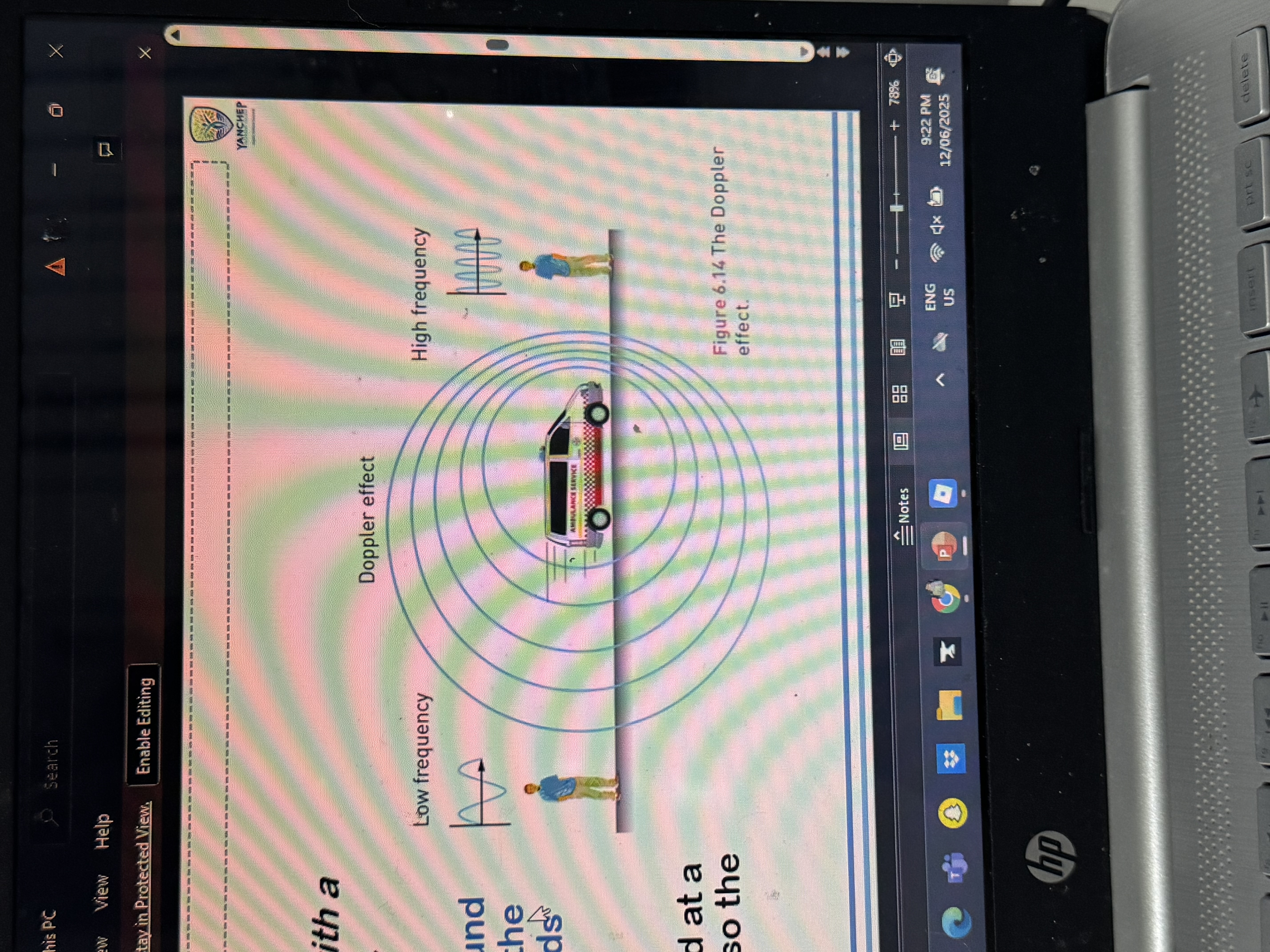
state the effect in the fréquence of sound where a car is coming towards u and going away from u
This is called the Doppler Effect.
🚗💨 When a car is
coming towards you
:
The sound waves are compressed
You hear a higher frequency (higher pitch)
🚗↘ When the car is
going away from you
:
The sound waves are stretched out
You hear a lower frequency (lower pitch)
free don’t give up
relate to the similarity of light and red shift: galaxies moving away from ours and galaxies moving towards ours
Redshift happens when a galaxy is moving away from us. The light waves it emits get stretched out, making the light appear more red (longer wavelength).
Blueshift happens when a galaxy is moving towards us. The light waves get compressed, making the light appear more blue (shorter wavelength).
So, both redshift and blueshift happen because of the Doppler effect — just like sound changes pitch when a car drives past you. For galaxies, the change in the light’s wavelength tells us if they are moving closer or farther away.
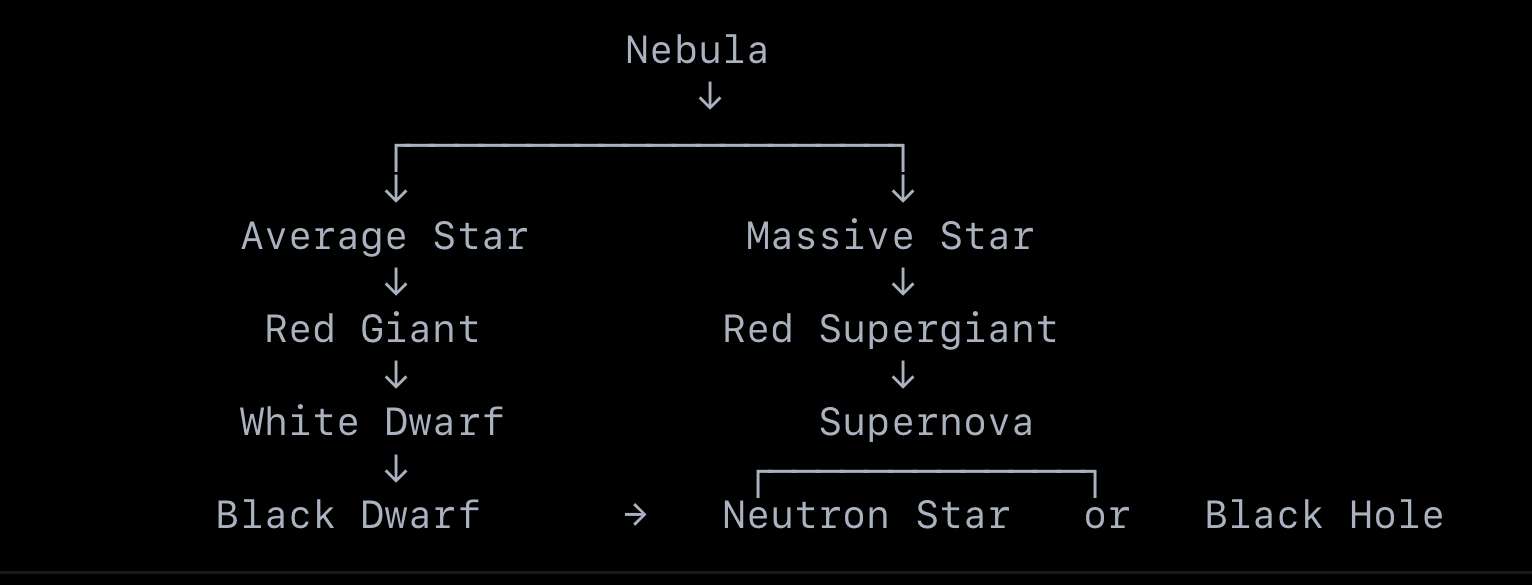
draw a flow chart to show the life cycle of a star
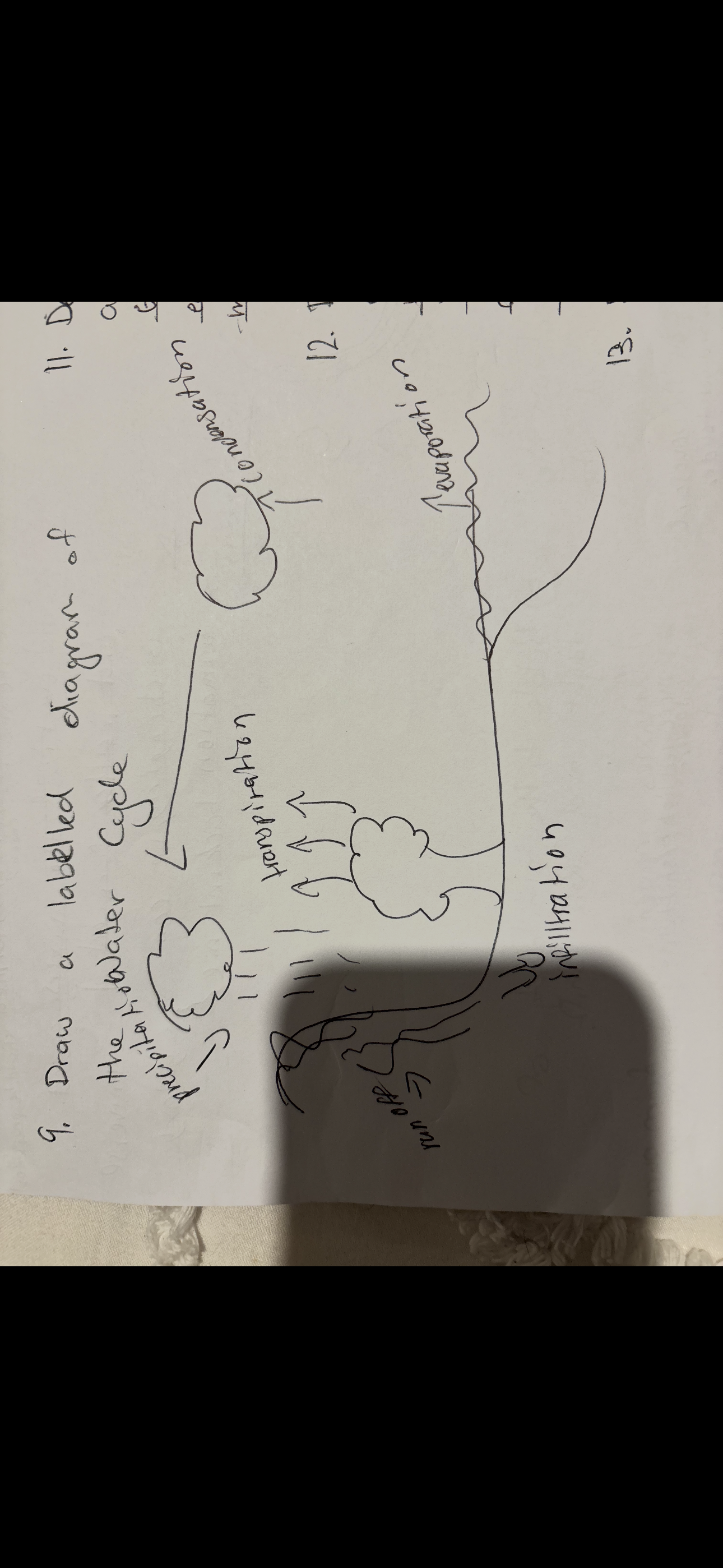
draw a labelled diagram of the water cycle
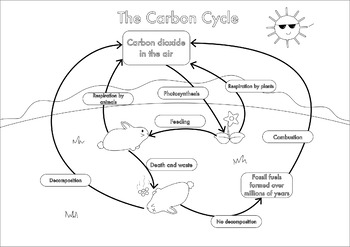
draw a labelled diagram of the carbon cycle
describe greeenhohse gases and give some examples
Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat. They let sunlight in but stop some of the heat from leaving the planet, kind of like a blanket. This process is called the greenhouse effect, and it helps keep Earth warm enough for life. But too many greenhouse gases can cause global warming. EG carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapour, ozone
describe the effects of the enhanced green house effect
Global warming
– Earth’s average temperature rises, causing long-term climate change.Melting ice caps and glaciers
– Leads to rising sea levels and loss of habitats (like for polar bears).More extreme weather
– Stronger storms, floods, droughts, and heatwaves become more common.Rising sea levels
– Causes flooding in coastal areas and small islands.Ecosystem damage
– Some animals and plants can’t adapt fast enough and may die out.Impact on food and water
– Droughts or floods affect crops and clean water supply.
discuss ways we can reduce our effects on the enhanced greenhouse effect
Use renewable energy
– Switching to solar, wind, or hydro power reduces carbon emissions from burning fossil fuels.Use public transport, walk, or bike
– Fewer cars on the road means less carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere.Reduce electricity use
– Turning off lights and using energy-efficient appliances lowers greenhouse gas production.Plant more trees
– Trees absorb carbon dioxide, helping to clean the air and cool the planet.Eat less meat
– Producing meat, especially beef, releases methane—a powerful greenhouse gas.Recycle and reduce waste
– Recycling uses less energy than making new products, and reducing waste cuts landfill gases.Buy local and sustainable products
– This lowers emissions from transport and supports eco-friendly farming or production methods.
describe the four spheres
Atmosphere
– The layer of gases surrounding Earth that we breathe and that controls weather and climate.Hydrosphere
– All the water on Earth, including oceans, rivers, lakes, and underground water.Lithosphere
– The solid, rocky outer part of the Earth including the crust and upper mantle, where landforms like mountains and soil exist.Biosphere
– All living things on Earth, including plants, animals, and humans, interacting with the other spheres.
propose a reason why a star with greater mass (eg rigel) could be smaller in size than a star with a lower mass (eg betelgeuse)
rigel is more dense than betelgeuse is.
betelgeuse is at a later stage in its life cycle and is shedding its outer layers. this makes it larger than rigel.
what gases do stars mostly contain
hydrogen and helium
what’s a light year
the distance light travels in one year (9.46 trillion km)
what is a stellar parallax
a change in the apparent position of a star against its background when viewed from two different positions
define galaxy
a group of stars held together by gravity
how fast does light travel
300,000km/s
why can we see stars and galaxies
light travels from them to earth over a period of time
how long does it take light from the sun to reach earth
about 8 minutes
what does parallax enable us to do
calculate distance between the earth and a star
respiration, combustion, consumption, and coal formation are processes found in the carbon cycle. State which sphere carbon starts in, and where it ends up.
respiration: biosphere to atmosphere
combustion: lithosphere to atmosphere
consumption: biosphere (plants) to biosphere (animals)
coal formation: biosphere to lithosphere
how are galaxies classified
by their shape: spiral elliptical and irregular
define nebula
a large cloud of gas and dust in space, often the site of star formation or the remnants of a stars explosion
define protostar
a young star that’s still gathering mass but has not yet started nuclear fusion
define supernovae
massive explosions that occur at the end of a stars life cycle
how does a protostar form
gravity pulls particles in a nebula closer together
how does a star die
the star runs out of elements to fuse
what do average sized stars form
red giants
what happens to an average sized star when it runs out of fuel
they form a white dwarf
what do massive stars (>8 time the mass of the sun) form
red supergiants
what happens after supergiants eventually result in a supernova
smaller supergiants will form a neutron star
larger supergiants will form a black hole
how is a star born
particles in space are attracted to each other by gravity. they form clouds which become nebulae when enough particles are in the same space. in nebulae, the particles collapse into protostars. the pressure involved raise the temperature to the point where nuclear fusion can occur. once this happens, a star is born.
how is a black dwarf formed
stars eventually run out of hydrogen, and start to fuse helium. stars doing this are red giants. once fusion stops they eject their outer layers as a planetary nebula. what is left behind is a white dwarf. a white dwarf will slowly cool until it becomes a black dwarf
what r the 3 pathways star can take as it runs out of fuel
1. Low-Mass Stars (like our Sun)
➡ White Dwarf
The star expands into a red giant.
It sheds its outer layers into space, forming a planetary nebula.
The hot, dense core that’s left becomes a white dwarf.
Then the white dwarf cools and becomes a black dwarf, making it stop glowing so technically becomes a black dwarf
2. Medium to High-Mass Stars
➡ Neutron Star
The star becomes a red supergiant.
It explodes in a powerful supernova.
The leftover core becomes a super-dense neutron star.
3. Very Massive Stars
➡ Black Hole
Also ends as a supernova.
If the remaining core is massive enough, it collapses into a black hole — a point with gravity so strong, not even light can escape.
what force causes to the particles of the universe to slowly move towards each other
gravity
which gas is the main component of a protostar
hydrogen
construct the equation for the fusion of deuterium and tritium
deuterium + tritium → helium + neutron + energy
name the stars that r 10 times as large as the sun or more
super giants
if a supernova occurs in a smaller star, recall what the star becomes
neutron star
FREE CARD U GOT THIS KEEP GOING
it a supernova occurs in a larger star, recall what the star becomes
black hole
process of the massive explosion called a supernova
stars which r much larger than our own are called supergiants
they begin life as blue supergiants and turn into red supergiants as they run out of hydrogen
their size means they can fuse heavier and heavier elements all the way to iron
eventually the star collapses under its own gravity, creating a massive explosion called a supernova
what is a fact about black holes
the biggest stars turn into them
black jokes have such great gravitational pulls that not even night can escape them
what do u do when drawing a line of best fit
ignore outliers
the line must reflect the trend (this could be curved)
the line must be balanced (approx equal number of points above and below
don’t force the line to pass thru specific points
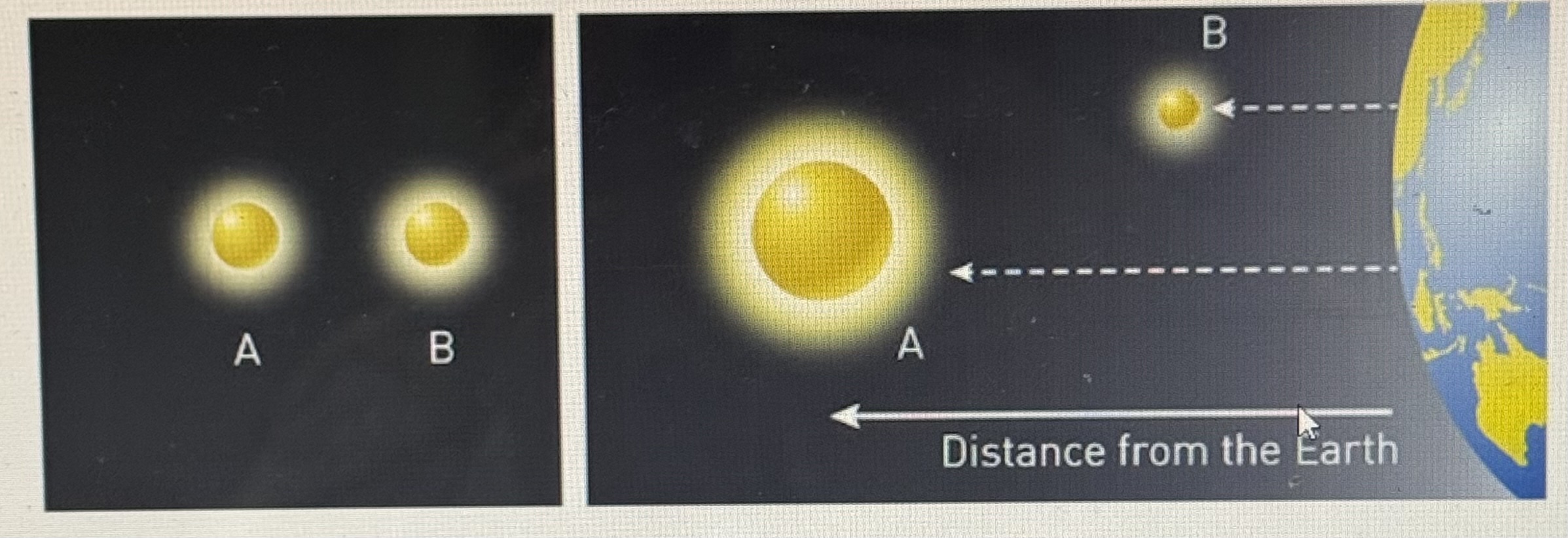
explain the phenomenon shown in the image below
star A and B have the same apparent brightness
star A has a larger absolute brightness
the two stars appear the same brightness from earth, as star A is much further away than star B
when stars form, interstellar hydrogen clouds undergo gravitational collapse and shrink . what do they form first?
a proto star
define quarks
fundamental particles that combine to form protons, neutrons , and other particles
what did edwin hubble discover in 1929
other galaxies were moving away from us. the further away the galaxy is the faster it’s moving away. he concluded that if u run the universe in reverse, everything must’ve come from a single point
what is the big bang theory
the universe came into existence from a single hot and dense point called a singularity
space expanded rapidly and silently from this point
over time, the universe cooled and matter formed. this includes the stars and planets in the universe we see (and are part of) today
provide evidence for the big bang theory
microwave background: radio antenna have picked up background noise, this is cosmic radiation from the big bang
mixtures of elements: the amount of hydrogen and heavier elements formed should be proportional to the amount of energy available. satellites have detected this
the universe is changing: when we examine distant galaxies, we’re looking back in time. we can see galaxy formation back in time
summarise the formation of the universe
1.
Big Bang (13.8 billion years ago)
The universe began as a tiny, hot, dense point and suddenly expanded.
2.
Cooling and Expansion
As it expanded, the universe cooled and formed simple particles.
3.
Formation of Atoms (about 380,000 years later)
Particles joined to form atoms (mainly hydrogen and helium); light could now travel.
4.
First Stars and Galaxies Form
Gravity formed the first stars and galaxies; stars began nuclear fusion.
5.
Creation of Heavier Elements
Big stars exploded (supernovae), spreading elements needed for life.
6.
Formation of Solar Systems (about 4.6 billion years ago)
Gas and dust formed new stars and planets—like our solar system.
what happened after the big bang
1 second — boiling soup of fundamental parked (electrons, quarks, etc)
3 seconds to 300,000 years — super hot fog
300,000 years — elemental particles combine to form atom
1 billion years — galaxy formation begins
3.5 billion years — dying stars produce heavier elements which will form new stars and planets
what does the big bang describe?
the formation of the universe — the beginning of the universe as a massive expansion from a hot , dense state
what observation supports the big bang theory
the universe is expanding, with galaxies moving away from each other, supports the big bang theory
what is the red shift
when the light spectrum is moved towards the red end
what’s the doppler effect
a change in frequency of a wave as the source and observer move towards or away from each other
how does light and sound travel
waves. light is transverse waves up and down. sound is longitudinal waves back and forth
describe the movement of the frequency of sound waves
frequency increases as source moves towards u - each wave is emitted at a point closer to u, so the waves bunch up
frequency decreases as source moves away from u - wfh eave is emitter at a point further from uc, so the waves spread out
what did edwin hubble examine in the 1920s
the spectra of light absorbed and emitted by galaxies. these spectra revealed info about the velocity of the galaxy
what did hubble notice about the spectra of light
lines were shifted in the red direction (red shift). this means light is reaching us with a lower frequency which suggests galaxies are moving away from us
why are distant galaxies travelling faster away from us
they have more red shifted spectra. this provides compelling t evidence for the BigBangTheory and has been used to determine that the expansion of the universe is accelerating
what is an absorption spectrum
the litht seen from a star that’s missing specific wavelengths
what’s an emission spectrum
the light emitted from an object that has absorbed light from somewhere else. it’s a collection of coloured bands
how to know if ur looking at an absorption spectrum or emission spectrum
Absorption = Rainbow with Missing Lines
Emission = Black with Bright Lines
draw a diagram demonstrating the doppler effect and label the sound wave frequencies
what’s a continuous spectrum
a complete rainbow with no dark lines or missing spots.