AP Biology- Unit 7 Natural Selection
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
EVERYTHING you need to know to understand unit 7 of AP Biology, Natural Selection!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Evolution
change in genetic makeup of pop over time
Natural Selection
organisms w/ adaptations best suited for that environment
-greater chance of survival + reproduction
-pass adaptations to subsequent generations
Competition
organisms v. organisms for limited resources
-space, food, mates, nutrients, light
Phenotype: how competitive an organism is
-Ex. Male Giraffes w/ longer necks are more favorable to female giraffes
This is competition for Mates
Genetic Variation
genetic differences in population
Increase w/ mutations+sexual reproduction
Increase population of organisms will survive under changing environmental conditions
Adaptations
Traits providing advantage in environment
-greater chance of reproduction
Selective Pressure
biotic+abiotic factors influencing survivability
-disease, climate, food availability
-changing env. → dif selective pressures
Ex. Dark colored moths fav after soot from industrial solution
after Clean Air Act → lighter phenotype favored
Fitness
Reproductive success over generations
ex. insecticide resistance in insects increase their fitness
Artificial Selection
Humans select desirable traits in other species
-selectively breed individuals w certain traits
-result in phenotypes that would not otherwise exist in nature
→ more OR less genetic diversity
Convergent Evolution
Similar environmental conditions select similar traits in different populations/species
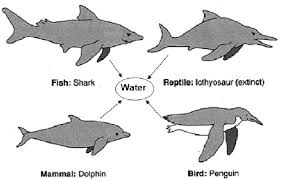
Analogous Structures
Similar traits in related/unrelated species
ex. Aquatic env. → streamlined bodies in vertebrates (birds/fish)
Genetic Drift
Nonselective process
Random Change in allele frequency
-Natural disasters (fires, volcanos, eruptions)
Founder Effect
Random process reducing genetic variation in small pop
-Separation from a larger pop
-Migration and geological events isolate populations
Genetic makeup of founder pop dif from original
Bottleneck Effect
ex. of genetic drift
-size of pop. severely reduced
-result of environmental disaster, hunting
Gene Flow/Migration
movement of individuals between populations
→ exchange of alleles
new genes into population → increased genetic variation
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Describes+Predicts allele frequencies in nonevolving population
5 Conditions of Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
large population- no genetic drift (Bottleneck+Founder Effect)
no migration
no net mutation- no genes modified, deleted, duplicated
random mating- no sexual selection
no natural selection
Hardy-Weinberg Equation

Evidence for Evolution
Geographical- characteristics of habitat
Geological- environmental features of Earth over time (Fossils)
Physical- phenotypes
Biochemical- chemical composition (DNA+proteins)
Mathematical
Fossils
Dated by:
-age of rocks
-decay of isotopes
Provide info: Earth’s history
Morphological Homologies
Features shared by common ancestry
-variation in structure present in common ancestry
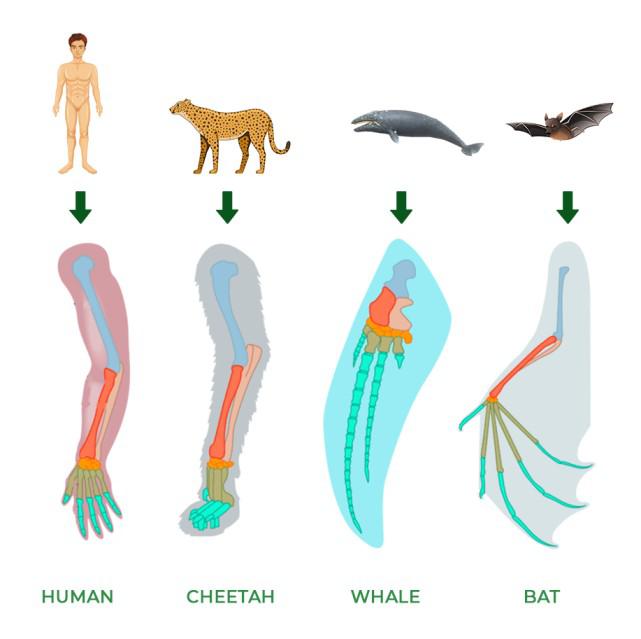
Vestigial Structures
-features serve little purpose for organism
ex. human tailbone
Biochemical evidence
-similar genetic code
-similar process of gene expression
Common Ancestry Evidence
-membrane-bound organelles
-endosymbiotic theory
-linear chromosomes in eukaryotes
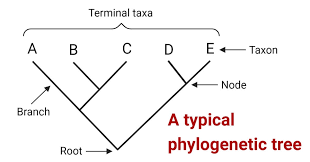
Phylogenetic Tree
-evolutionary relationship among species
-shows changes over time through fossils/molecular evidence
-shows extinct lineages
-shows evolutionary timescale+degree of change through length of lines
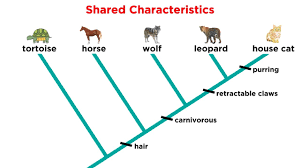
Cladogram
evolutionary relationships among species
-clade indicates common ancestor
-lacks info
-DOES NOT show duration of lineage+amt. of evolutionary change
Out-group
Lineage least related to particular organisms
Speciation
-Populations reproductively isolated from each other
→ creation of new species
-diversity of life forms
Reproductive isolation
-no interbreeding
-cannot produce fertile offspring
-no gene flow between pop.
-prezygotic vs. postzygotic barriers
Prezygotic Barriers
Prevents production of fertilized egg
-habitat isolation
-temporal isolation: species breed at dif times
-behavioral isolation: mate preferences
-gamete isolation: sperm cannot fertilize egg of another species
Postzygotic Barriers
Prevents zygote from developing into a viable offspring
-hybrid inviability
-hybrid sterility
-hybrid breakdown: only first generation hybrids are viable are fertile
Allopatric Speciation
Evolution of new species due to population being geographically isolated over period of time
-no gene flow
-separation→ dif selective pressures
Sympatric Speciation
Reproductive isolation from surviving ancestral pop. →Evolution of new species
-no geographic barrier
-result of genetic mutations
-sexual selection
-habitat differentiation
→ high species biodiversity
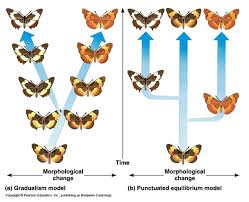
Punctuated Equilibrium Model
-Evolution occurs after period of little/no change
changing ecological conditions→ evolution
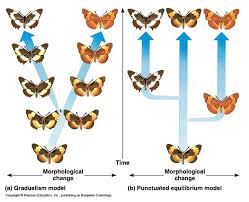
Gradualism Model
Evolution over millions of years
-ecological conditions gradually change over long period of time
Divergent Evolution
Adaptation to new habitat→ phenotypic diversification
Adaptive Radiation
evolution of new species → empty ecological niches filled
Extinction
Human activity causes:
-habitat loss, climate change, habitat degradation, pollution, invasive species
Niche
Role of organism within env.
-producer, consumer, decomposer
when species goes extinct→ open niche for another species to occupy
→ adaptive radiation+ speciation
ex. after dinosaurs extinct→ mammals occupied niche
Genetically Diverse Populations
more resilient to environmental change
Environmental Pressures
-climate change
-catastrophic geological events
-habitat loss
-predation
Antibiotic Resistance
-population resilience
-resistance passed to offspring
-bacteria can give drug resistance to other bacteria (Conjugation)
Deleterious Traits
-reduce chance of survival
Adaptive Traits
Increase chance of survival
Selective pressures in env. determine if traits is advantageous/disadvantageousGe
Geological evd. of life on Earth
Earth formed: 4.6 bya
-Env. too hostile until 3.9 bya
-earliest fossil evidence for life 3.5 bya
Origin of Life on Earth
Primitive Earth: inorganic precursors for the synthesis of organic molecules
-Presence of free energy
-no O2 (atmos. oxygen)
-org. molecules could have come to earth by celestial event
Theory of formation of organic molecules
-shows organic molecules can be formed from inorganic molecules in the absence of life
-monomers building blocks of complex molecules
→ ability to replicate, store, + transfer info
RNA World Hypothesis
Proposes RNA could have been earliest genetic molecule
-stores info and carries out biological processes
unlike DNA/Protein which need each other