oogenesis STUDY MEISOSIS AND GENETICS
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
what happens to one cell in meiosis one in oogenesis
one cell receives half genetic info and majority of the cytoplasm of the parent cell
polar body
receives half of the genetic info and cast away (they die)
during meiosis 2 what does the remaining cell do
divides a second time and forms a polar body that is cast away
a single haploid ovum that contains half the genetic info and nearly all the cytoplasm of the original parent cell
what does the process of oogenesis produce?
2 polar bodies and a single haploid ovum
test cross —
crossing of an organism of unknown dominant genotype with an organism that is homozygous recessive, resulting in offspring with observable phenotypes. Test crosses used to determine the unknown genotype
hypercholesterolemia
recessive disorder (hh) causing cholesterol levels to be many times higher than normal → leads to heart attacks in kids as young as 2yrs.
polygenic traits
traits affected by 1+ gene (eg eye color)
multiple alleles
some traits involving more than 2 alleles
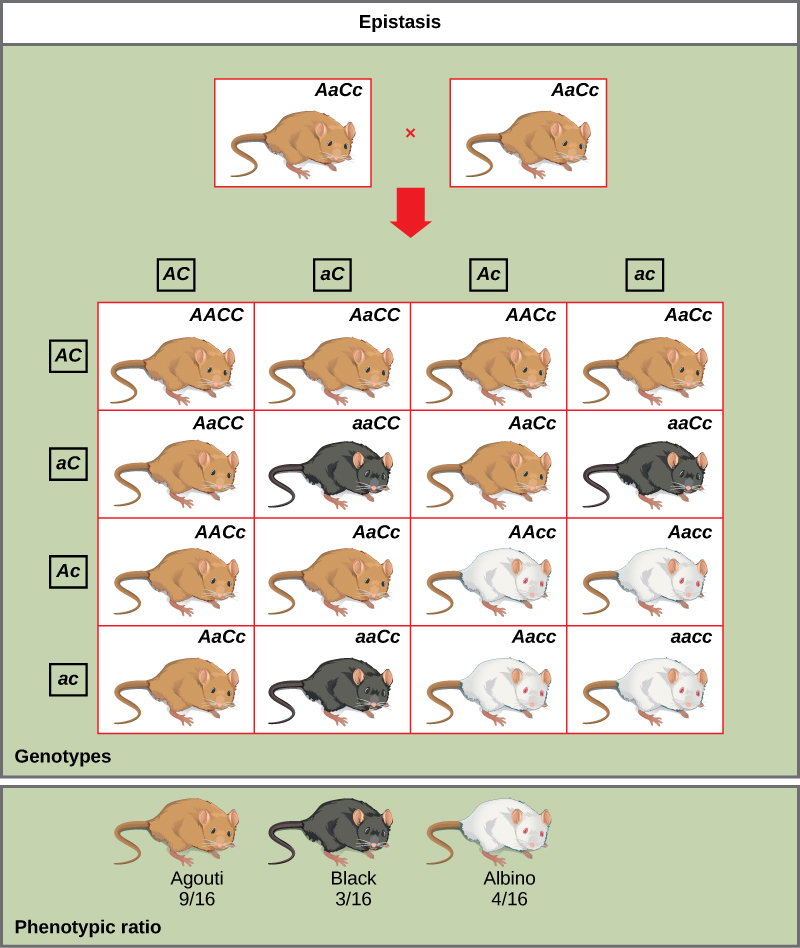
epistasis
expression of 1 gene affects the expression of another gene
eg The wild-type coat color, agouti (AA), is dominant to solid-colored fur (aa). However, a separate gene (C) is necessary for pigment production. A mouse with a recessive c allele at this locus is unable to produce pigment and is albino regardless of the allele present at locus A (Figure 1). Therefore, the genotypes AAcc, Aacc, and aacc all produce the same albino phenotype. A cross between heterozygotes for both genes (AaCc x AaCc) would generate offspring with a phenotypic ratio of 9 agouti:3 solid color:4 albino (Figure 1). In this case, the C gene is epistatic to the A gene.
gene locus
A locus is the specific physical location of a gene or other DNA sequence on a chromosome, like a genetic street address
epistasis ratio
9 : 4 : 3
pleitropy
a single gene has multiple effects on an organism
eg. sickle cell anemia → the gene mutation “sickles” the blood cells, leading to systemic symptoms like heart, lung, and kidney damage
Duchenne’s muscular dystrophy
sex-linked disorder caused by the absence of an essential muscle protein
symptoms: progressive loss of muscle strength & coordination
hemophilia
caused by an absence of a protein vital to the clotting process
symptoms: difficulty clotting blood after even the smallest wounds
red-green color blindness
condition primarily found in males
symptoms: cant tell between red & green
Barr body
inactivated genes on X chromosomes that’s coiled (one of them)
why are all cells in a female not identical?
cell expresses the alleles only of the X chromosome (not Barr body). Occurs separately in each cell & involved random activation of one of a female’s X chromosomes
holandric traits
traits inherited from Y chromosome. eg ear hair distribution
linked genes
lie on the same chromosome → don’t follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment
the less often crossing over happens, how far/close are the genes
closer the genes must be on the chromosome
linkage map
genetic map put together using crossover frequencies, does not provide exact location of genes, only relative location
map unit
aka centigram → used to geographically relate the genes on the basis of these frequencies
how can pedigrees be used?
determine risk of parents passing certain conditions to offspring
tay-sachs
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE — renders the body unable to break down a particular type of lipid that accumulates the brain and eventually causes blindness and brain damage.
Carriers of this disease don’t show any of the effects of the disease. Usually eastern European Jewish descent
cystic fibrosis (CF)
AUTOSOMAL RECESSSIVE — located on chromosome 7. Deletion mutation, so incorrect shape. Excessive secretion of a thick mucus that accumulates in the lungs & digestive tract. 1 in 25 Caucasians is a carrier for this disease
sickle cell anemia
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE — improper amino acid substitution during translation of hemoglobin. Results in hemoglobin that’s less efficient in carrying oxygen → leads to pain, muscle weakness, and fatigue
common among African Americans (1 in 10) heterozygous condition protects against malaria
phenylketonuria (PKU)
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE — cause by single gene defect. Unable to digest phenylalanine (amino acid) → accumulation of a by-product in blood that can cause mental retardation. Avoid that amino acid early on
Huntington disease
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT — repeat expansion in HTT gene. Breakdown of nervous system. Doesn’t show itself until in the 30s-40s. 50% of passing to offspring.
Patau syndrome
trisomy 13. Causes brain & circulatory defects
Edwards syndrome
trisomy 18. Can affect all organs
Klinefelter syndrome
male receives extra X (XXY). Infertile, has male sex organs but show feminine body characetristics
turner syndrome
sterile females that have sex organs that don’t mature at puberty (XO)
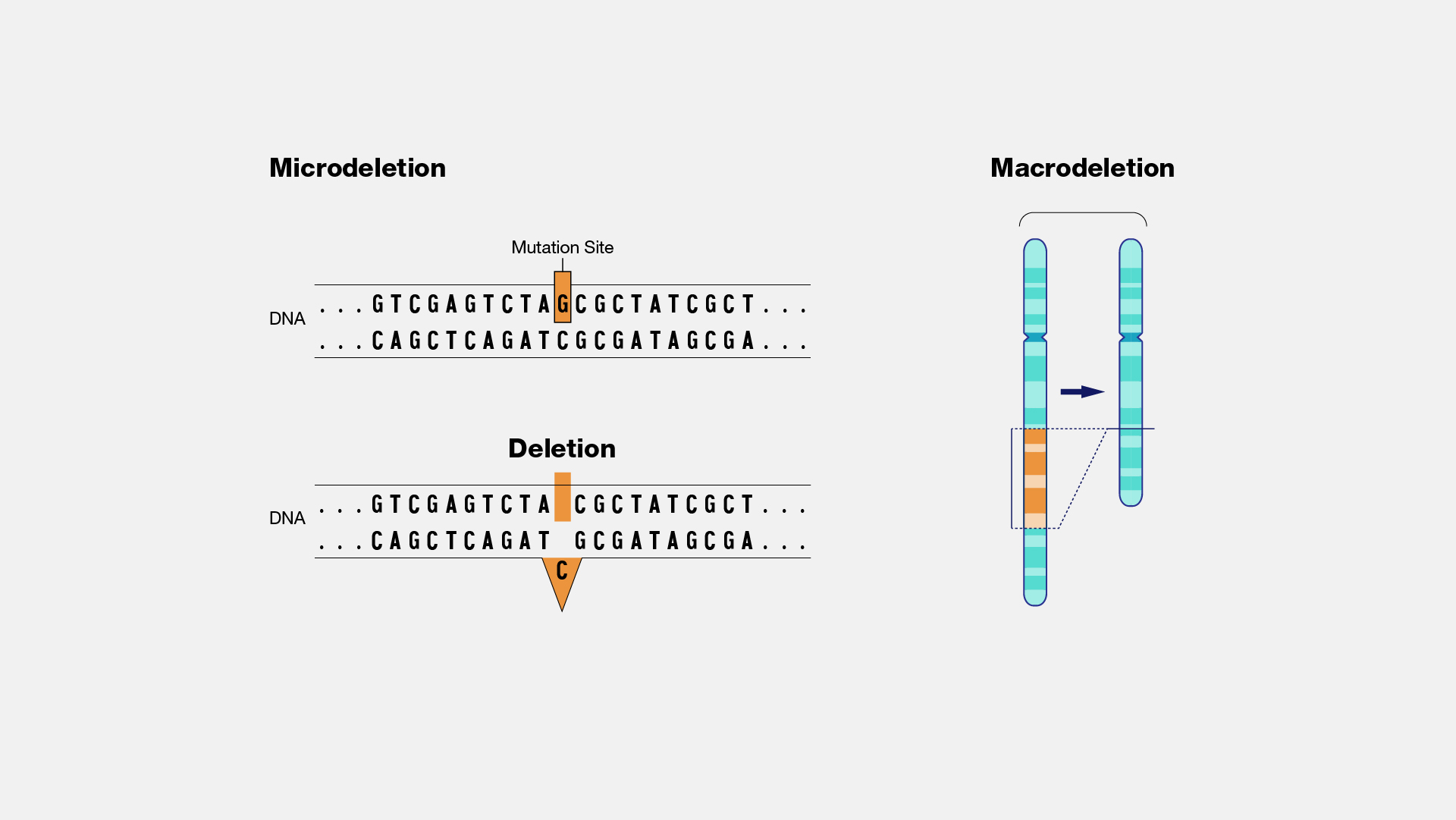
deletion —
a piece of the chromosome is lost in the developmental process
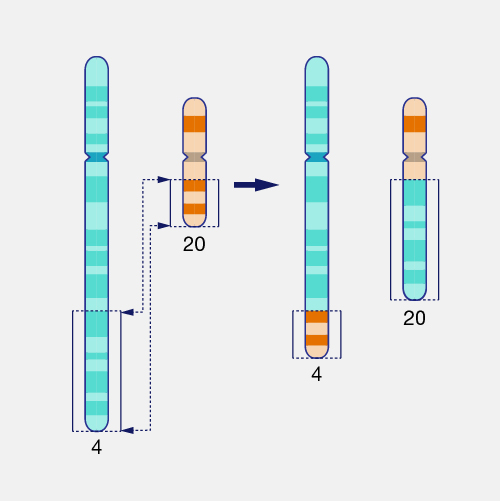
cri-du-chat syndrome
result of deletion in chromosome 5. Mental retardation, abnormal facial features, and small head
chromosomal translocation
piece of 1 chromosome is attached to another, nonhomologous chromosome
chronic myelogenous leukemia
cancer affecting white blood cell precursor cells. A portion of chromosome 22 has been swapped with a piece of chromosome 9
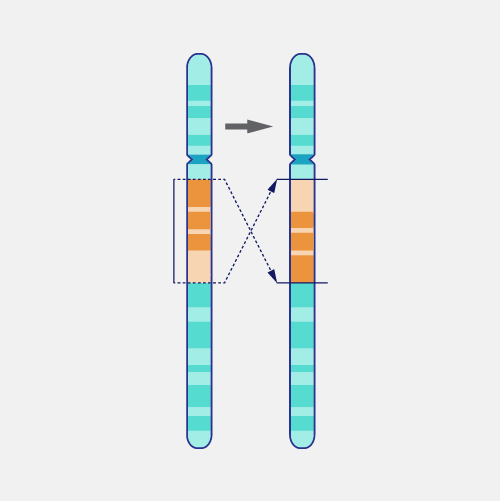
chromosome inversion
portion of a chromosome separates and reattached in the opposite direction
can have no effect or have a gene nonfunctional if it occurs in the middle of a sequence
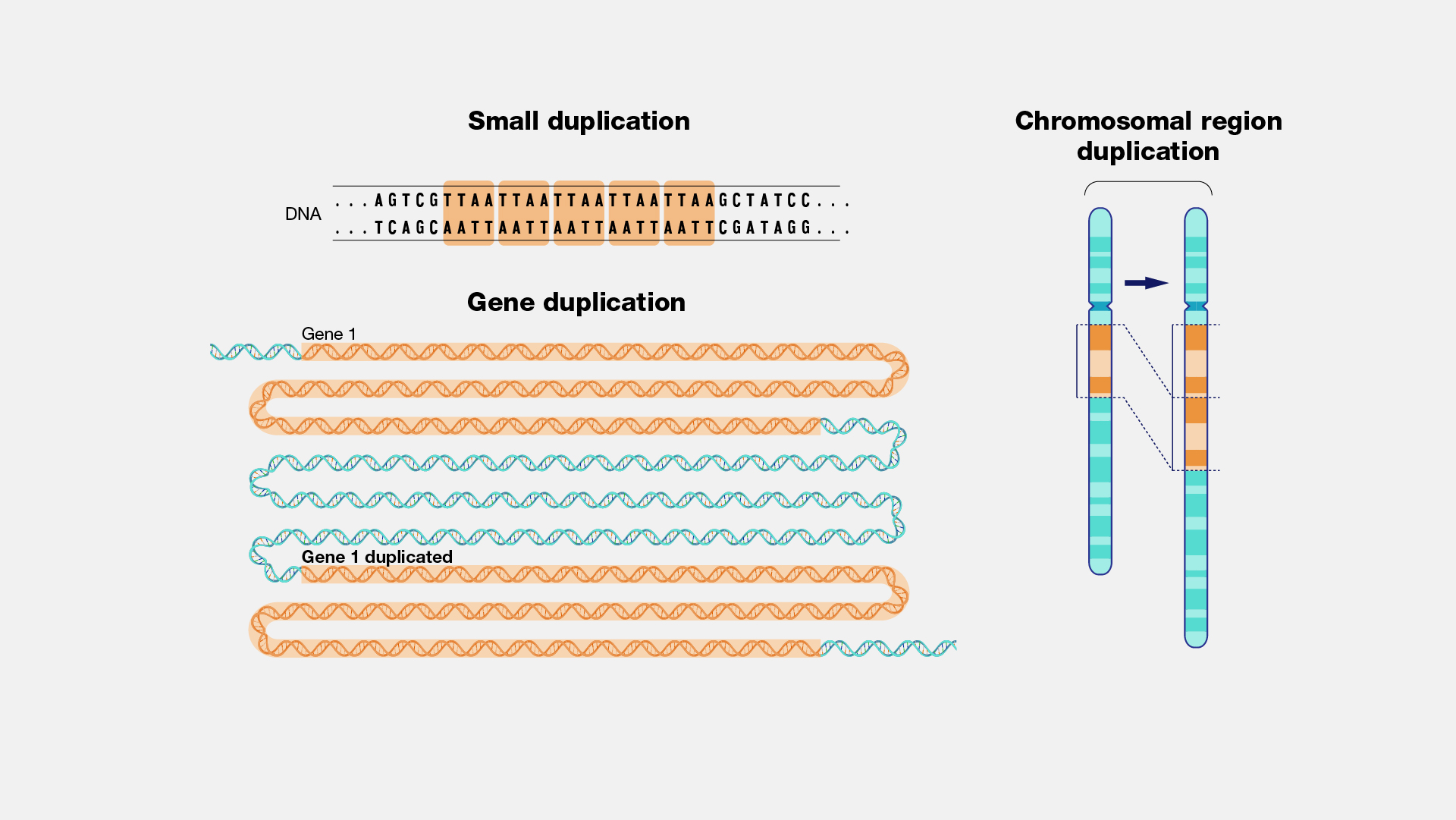
chromosome duplication
repetition of a genetic segment.
often have serious effects on an organism
phenotype plasticity
environmental factors influence gene expression
individuals with the same genotype exhibit different phenotypes in different environments