Circulatory system: Scaling up: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Heart
A hollow and muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, made up of involuntary muscle tissue called cardiac muscle
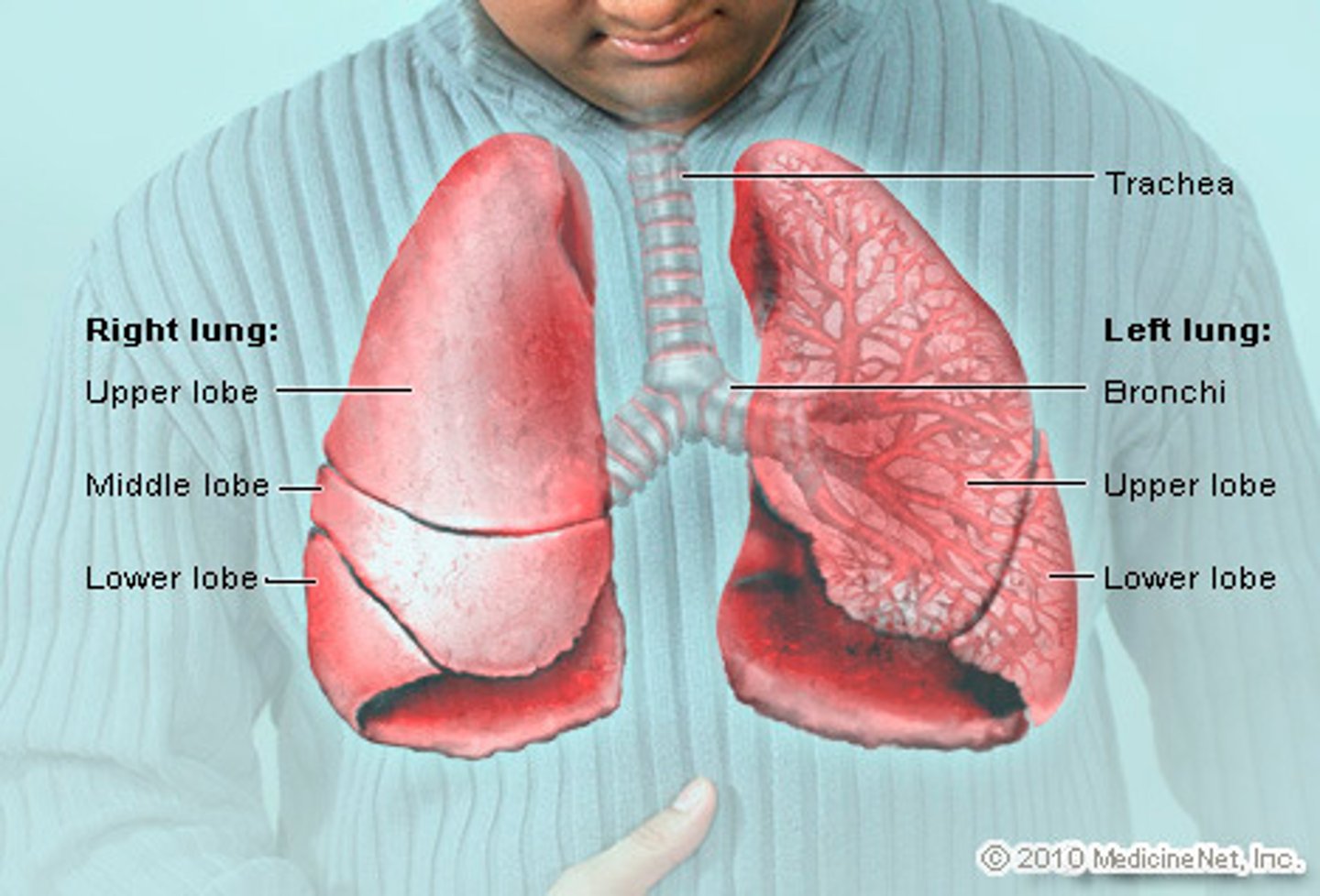
Lungs
The main organs of the respiratory system, responsible for gas exchange where oxygen is exchange with carbon dioxide in the blood
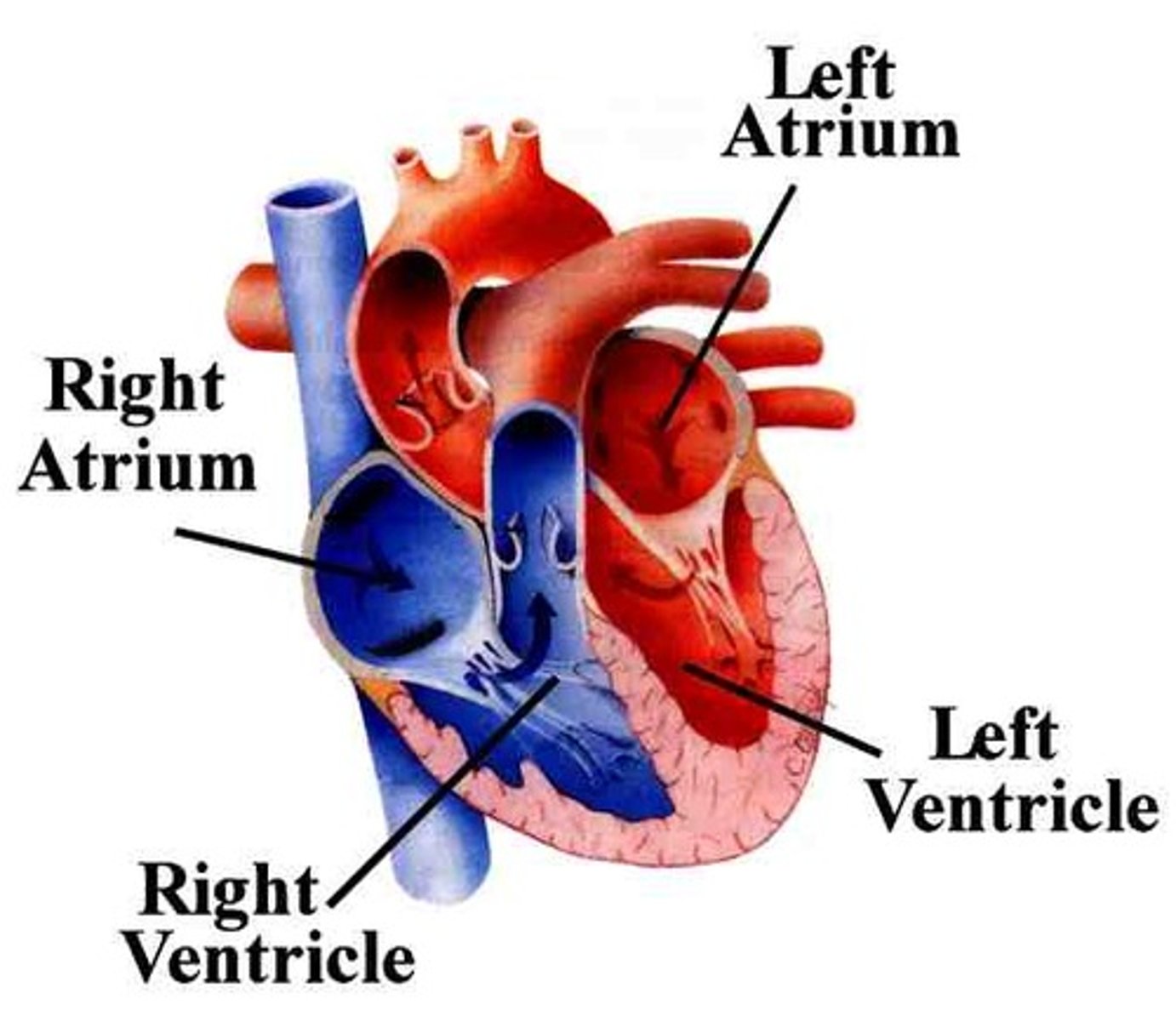
Left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta
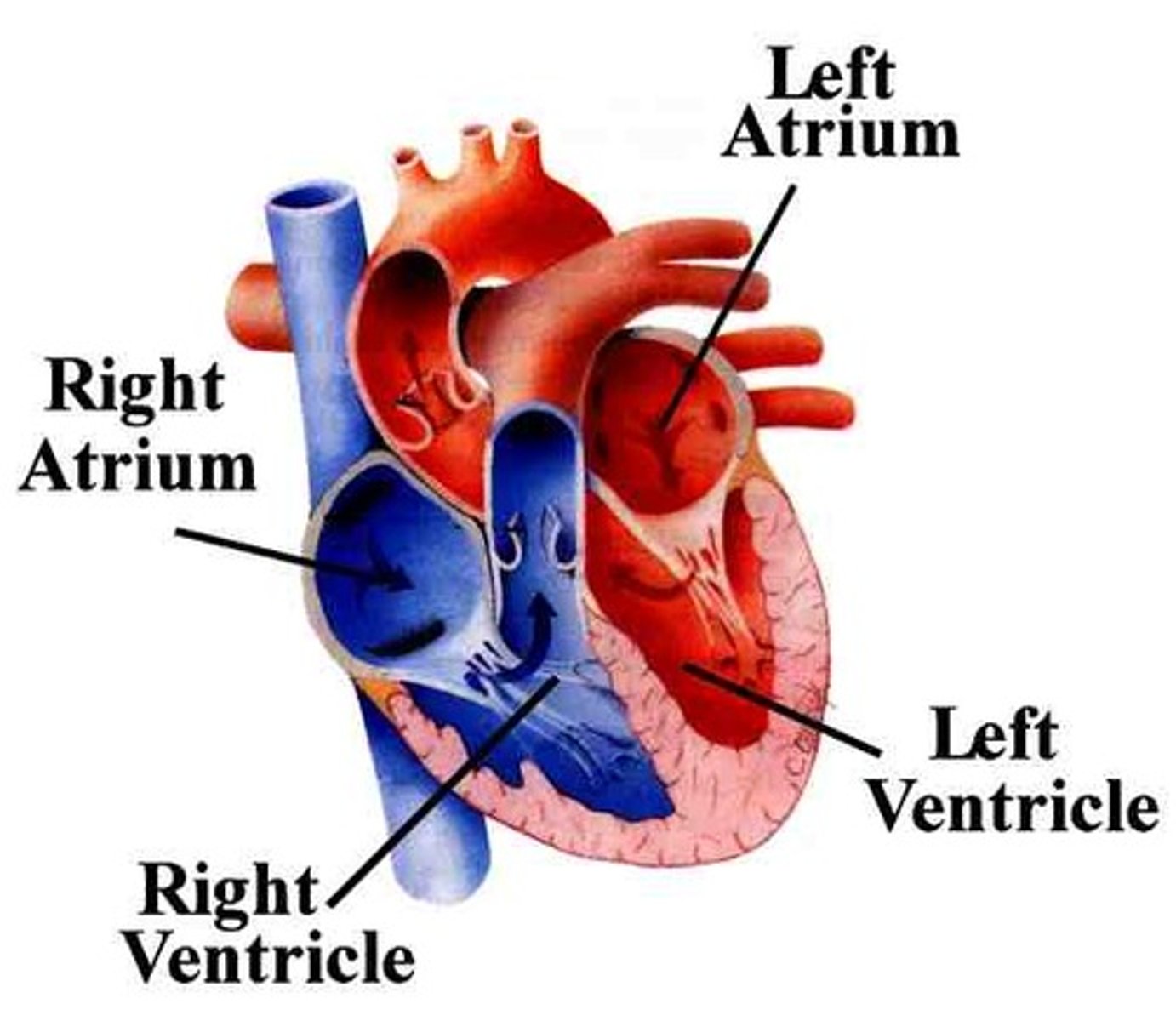
Right ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery
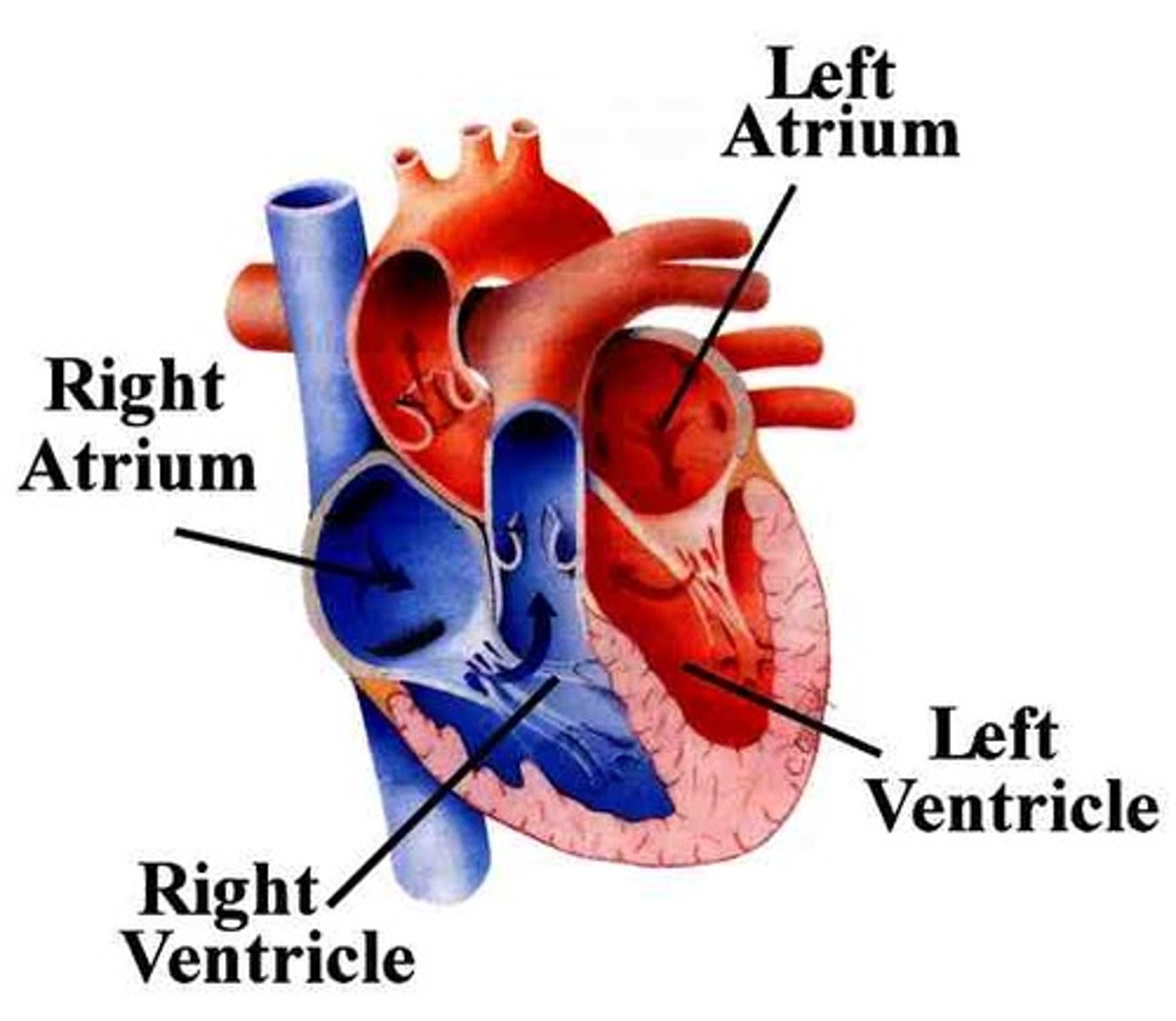
Atria
Upper chambers of the heart that receive blood, the right atrium receives blood from the vena cava and the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary vein
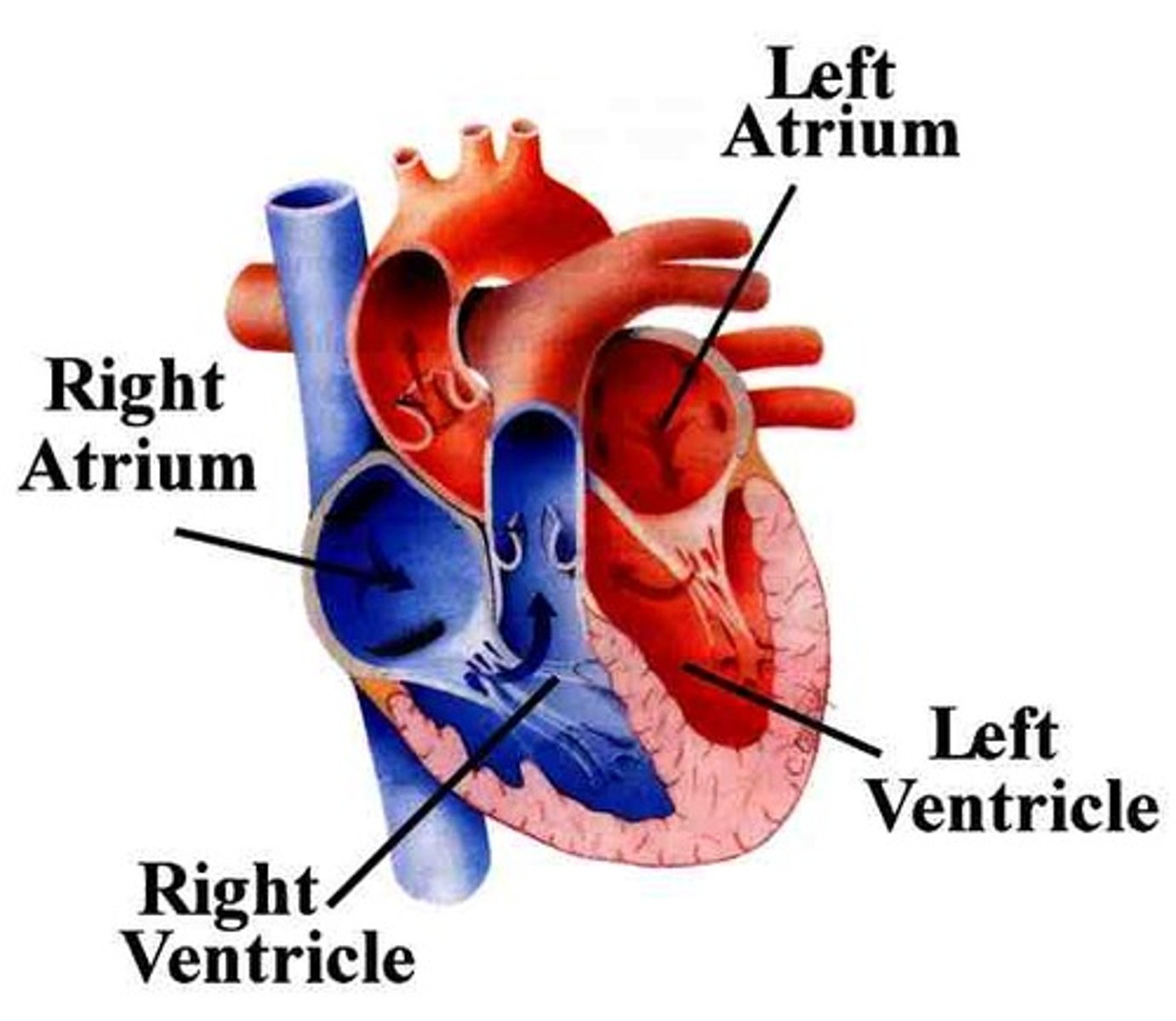
Aorta
The largest artery in the body, carries oxygenated blood to the body from the left ventricle
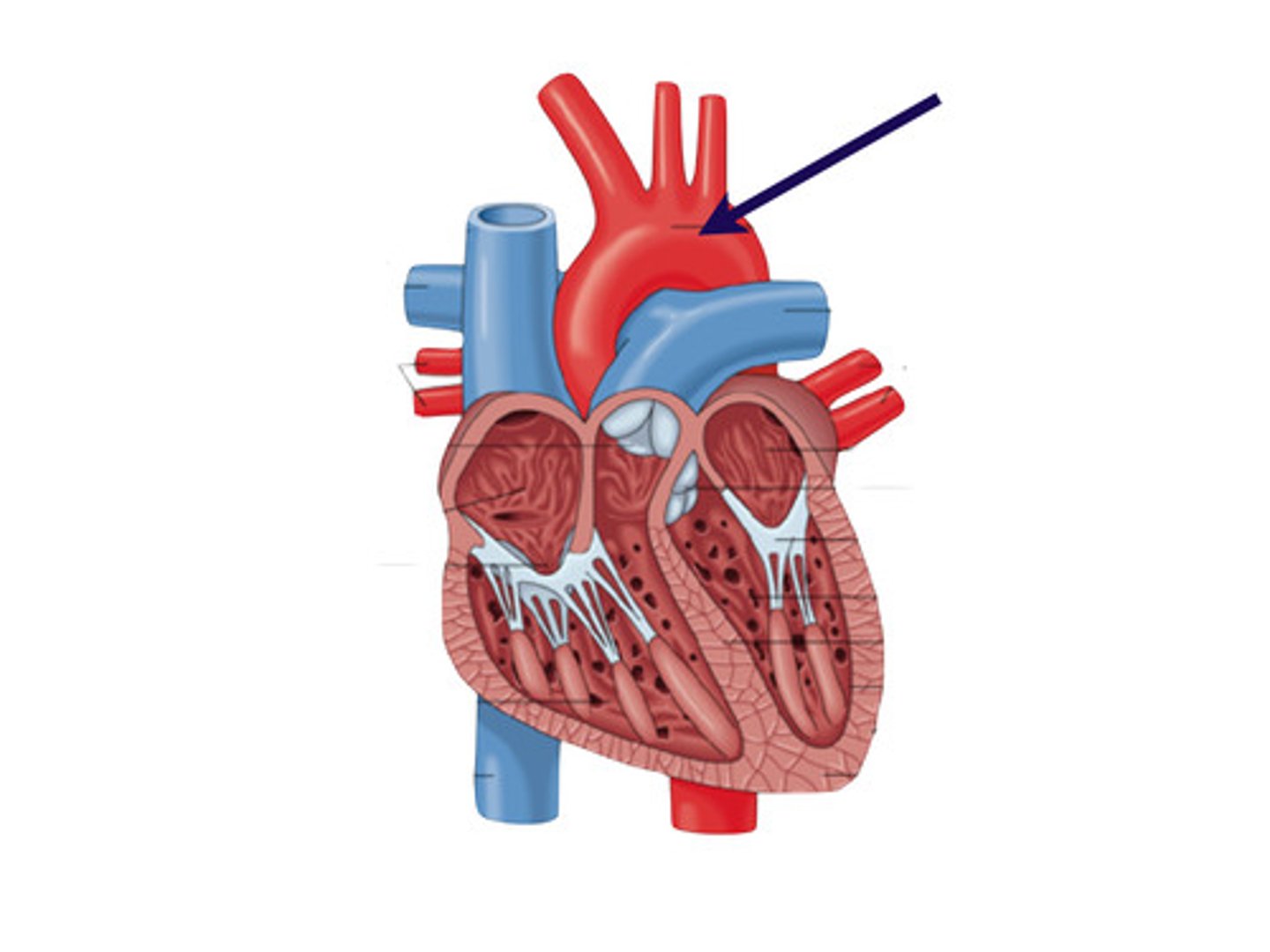
Vena cava
The largest vein in the body, carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart, specifically to the right atrium

Pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
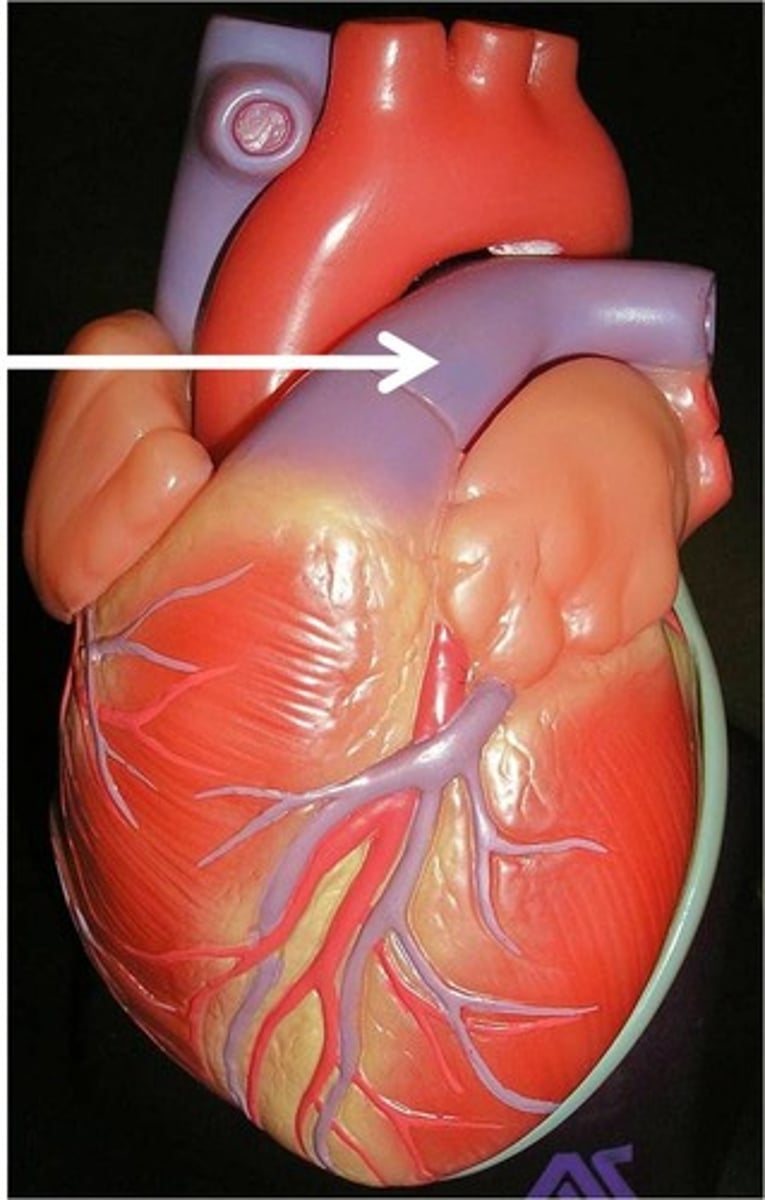
Pulmonary vein
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
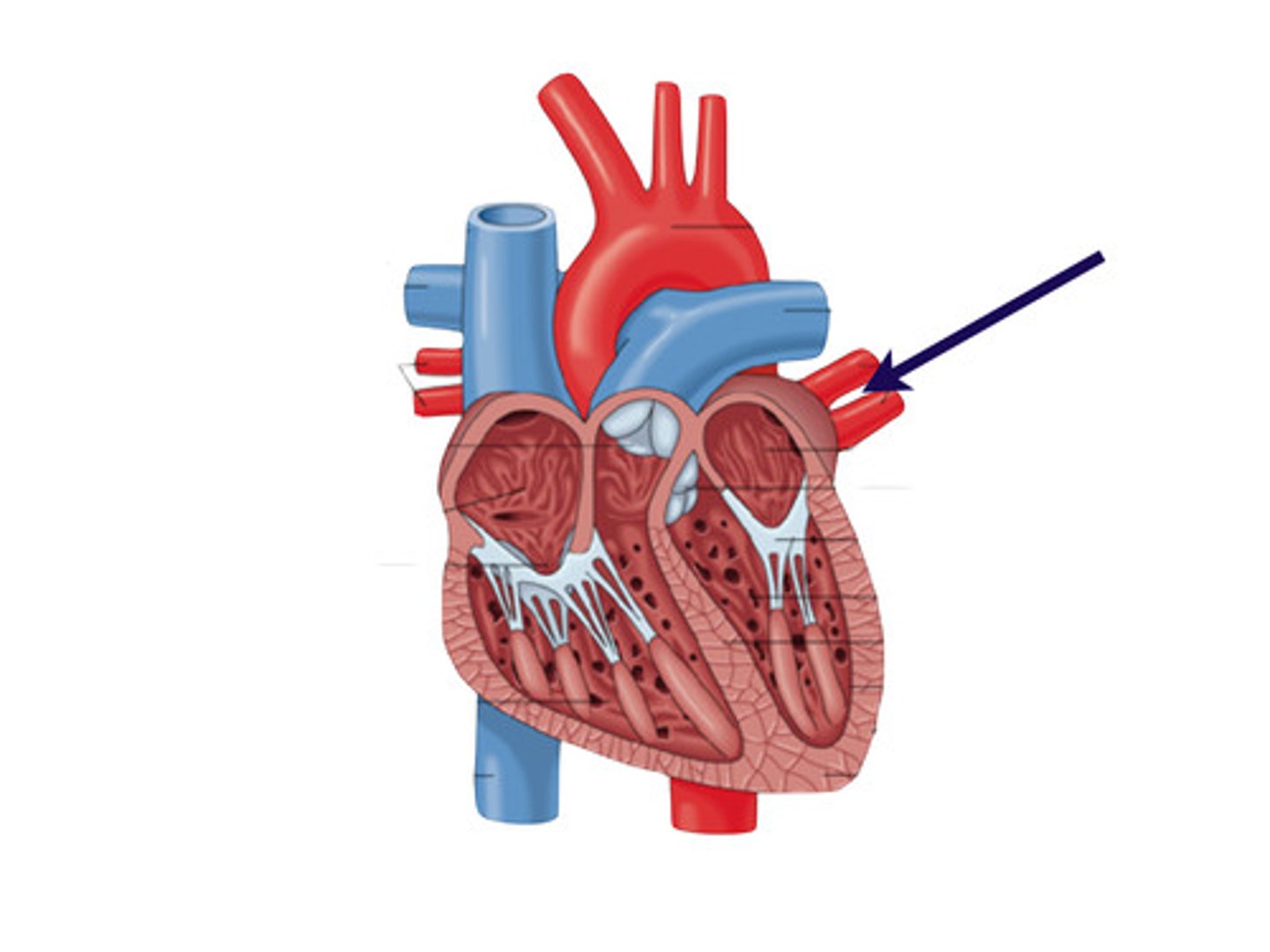
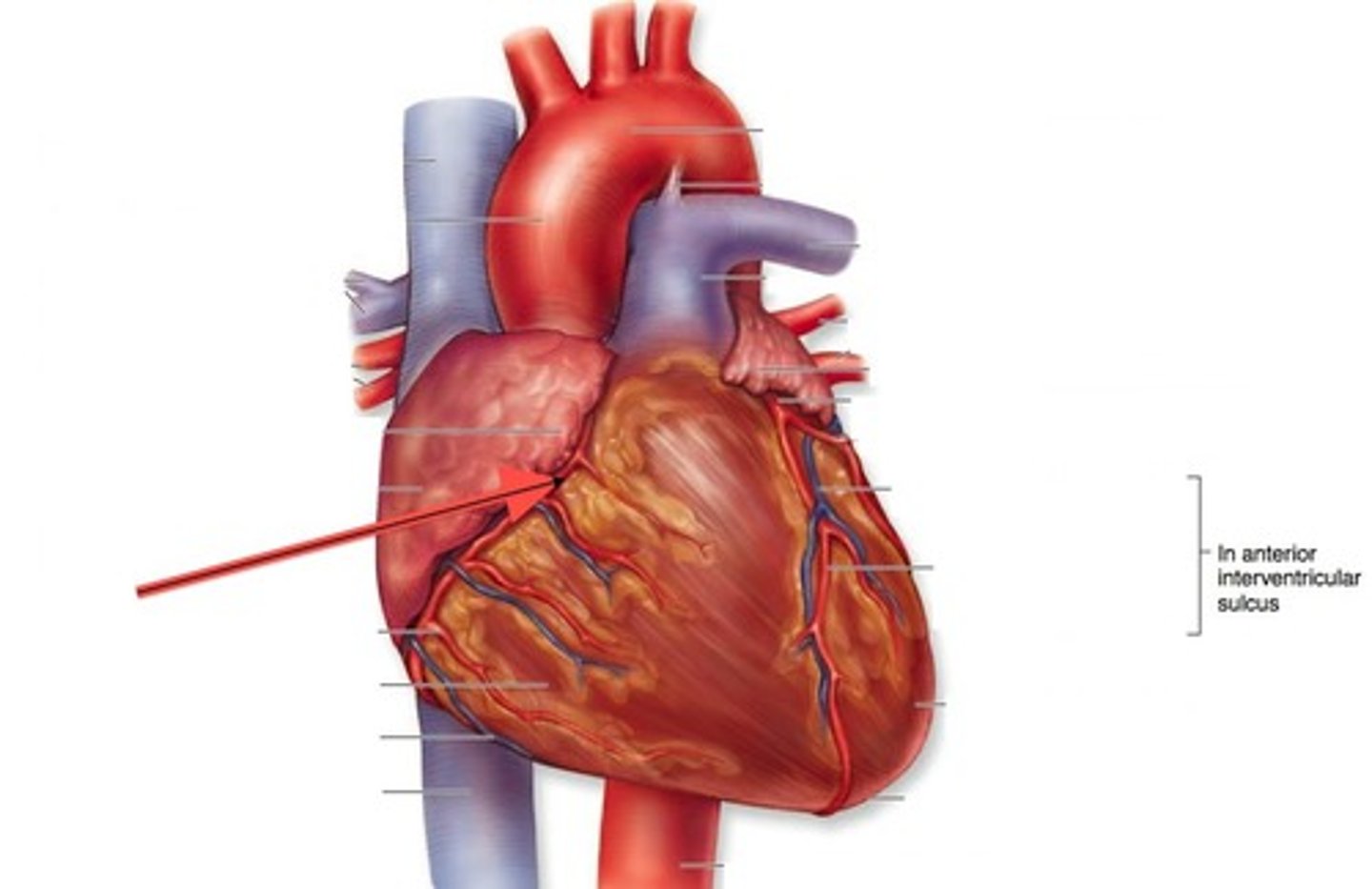
Coronary arteries
Blood vessels that supply the muscle of the heart
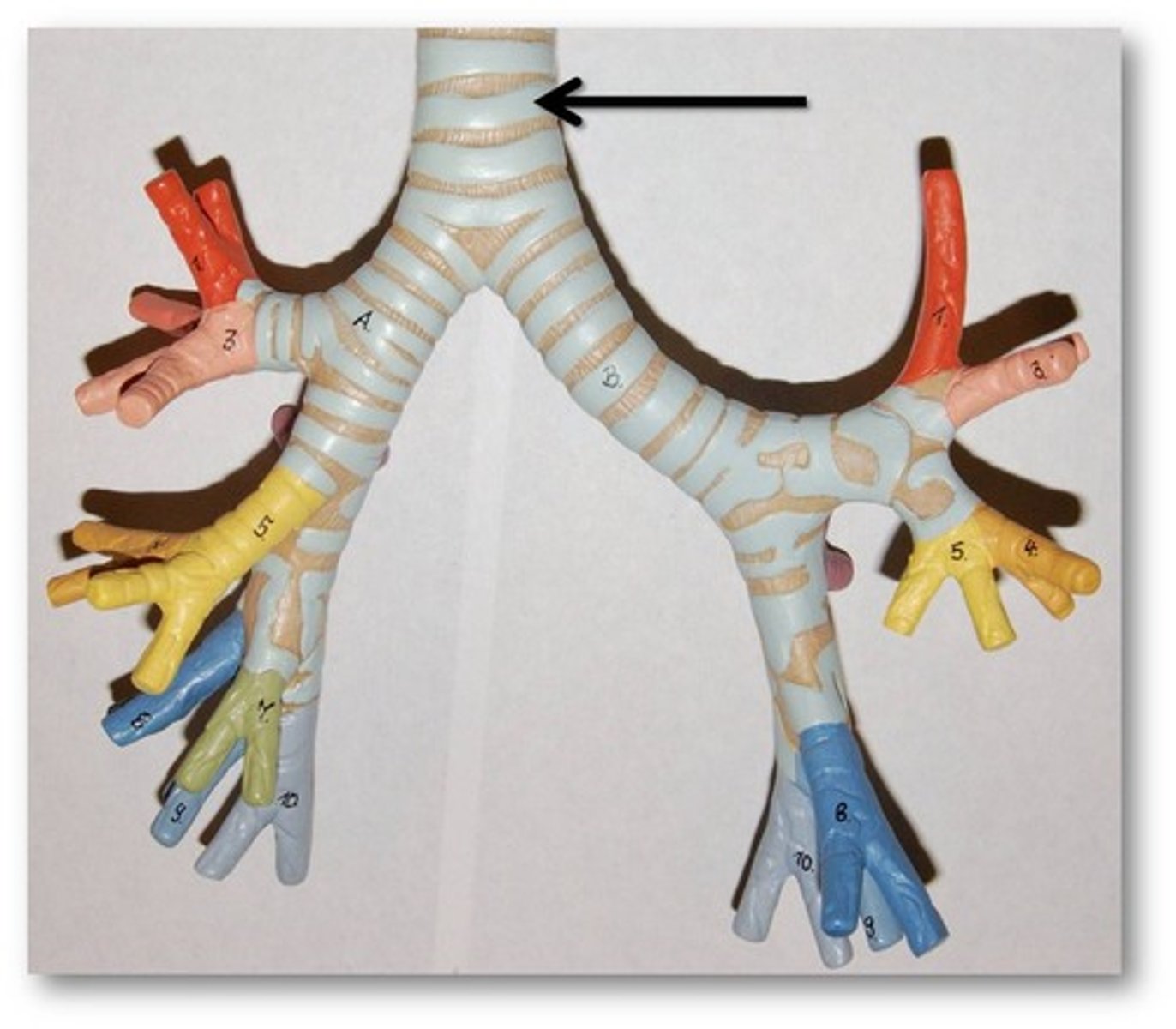
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
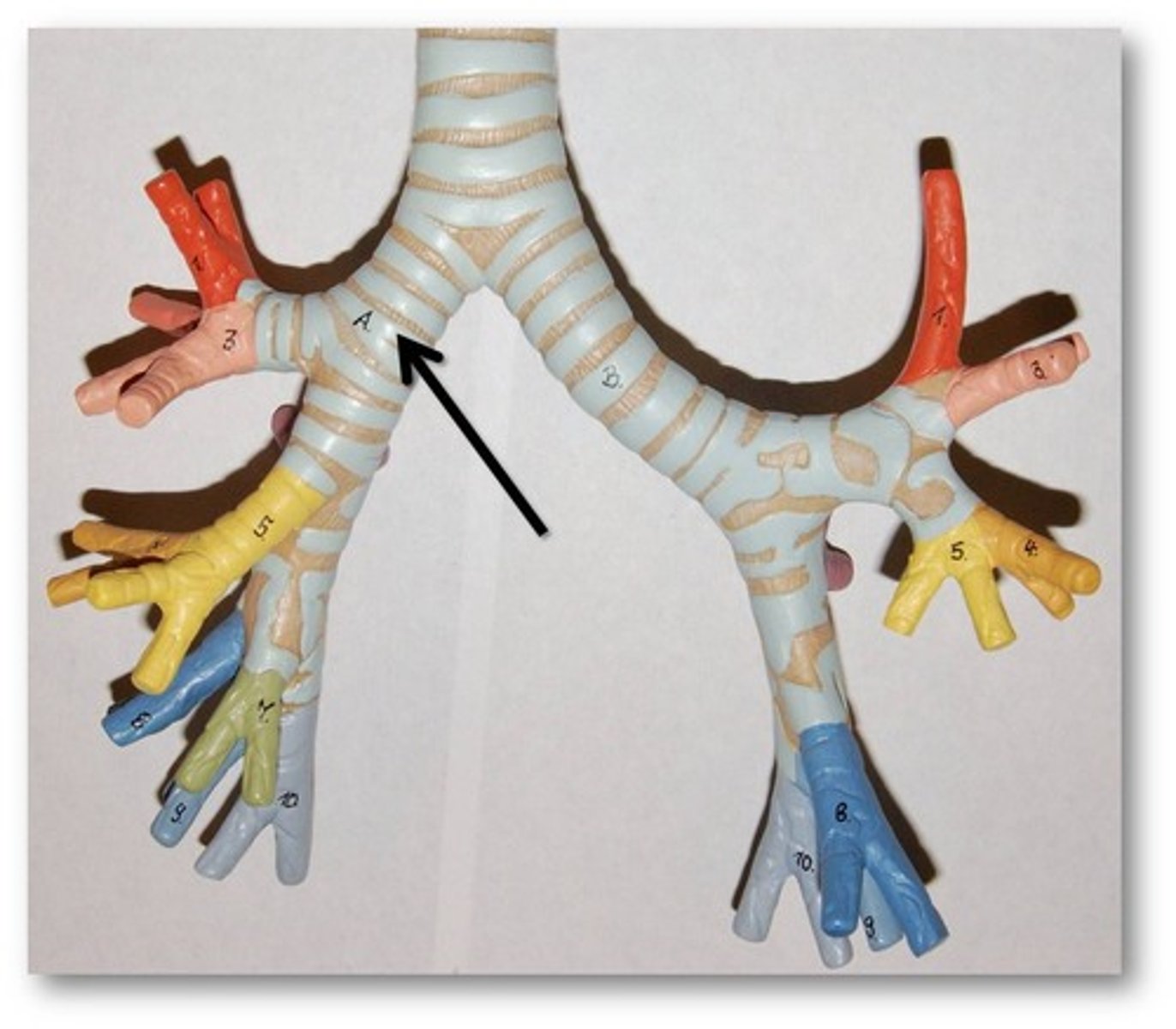
Bronchi
Two short branches at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs
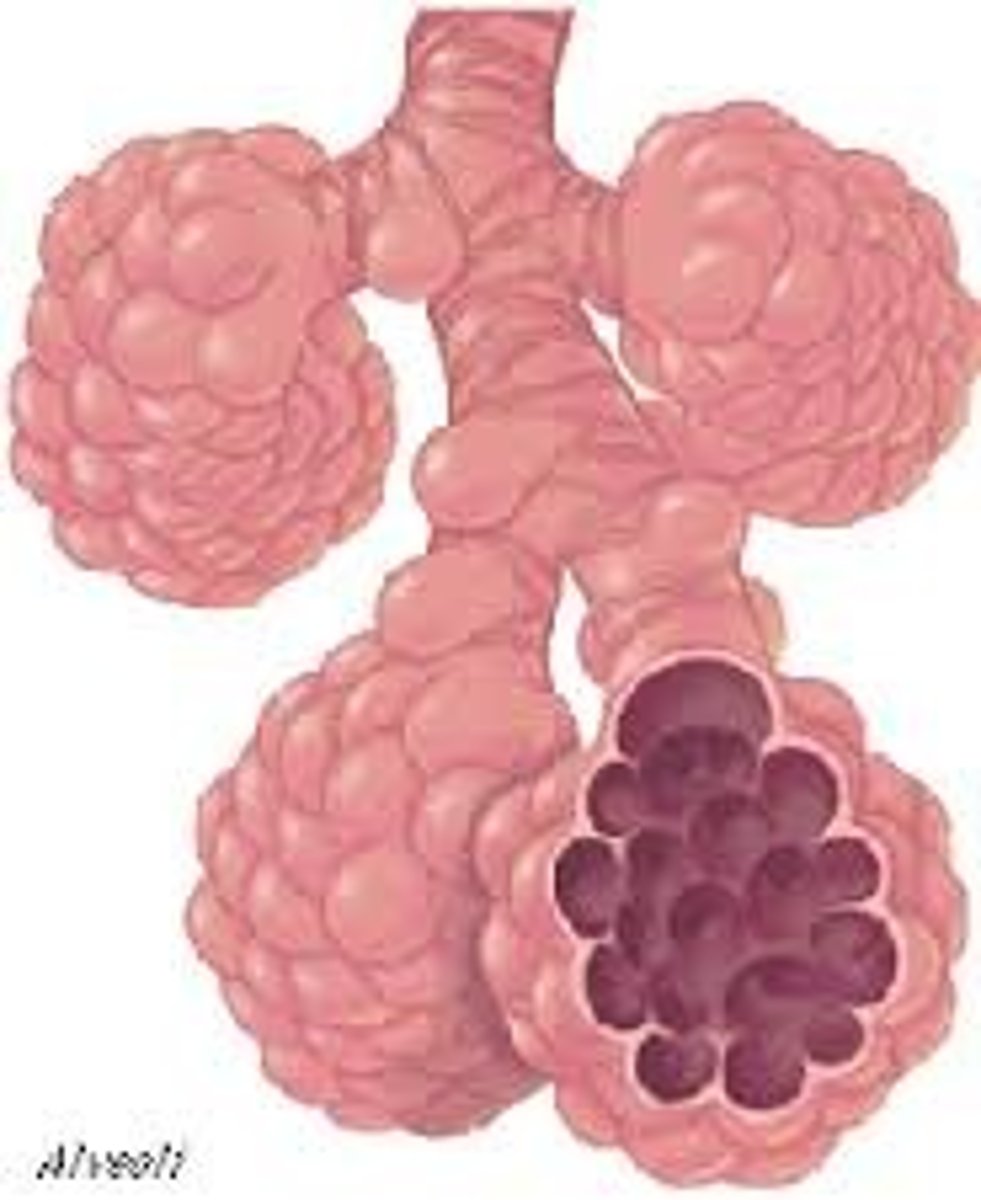
Alveoli
Tiny sacs of lung tissue where gaseous exchange takes place with the blood
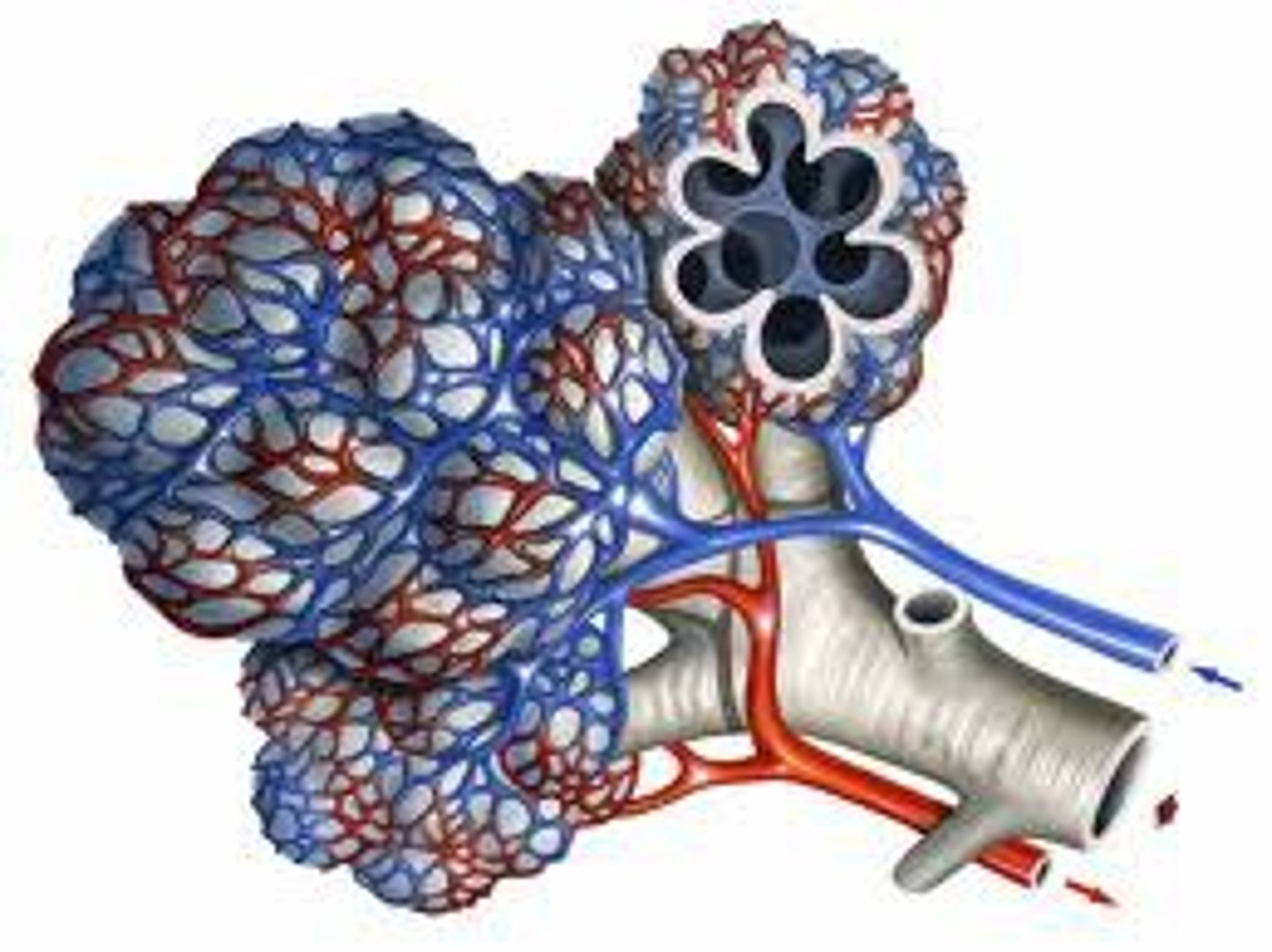
Capillary network
An interconnecting network of capillaries surrounding the alveoli
Arteries
Blood vessels they carry blood away from the heart
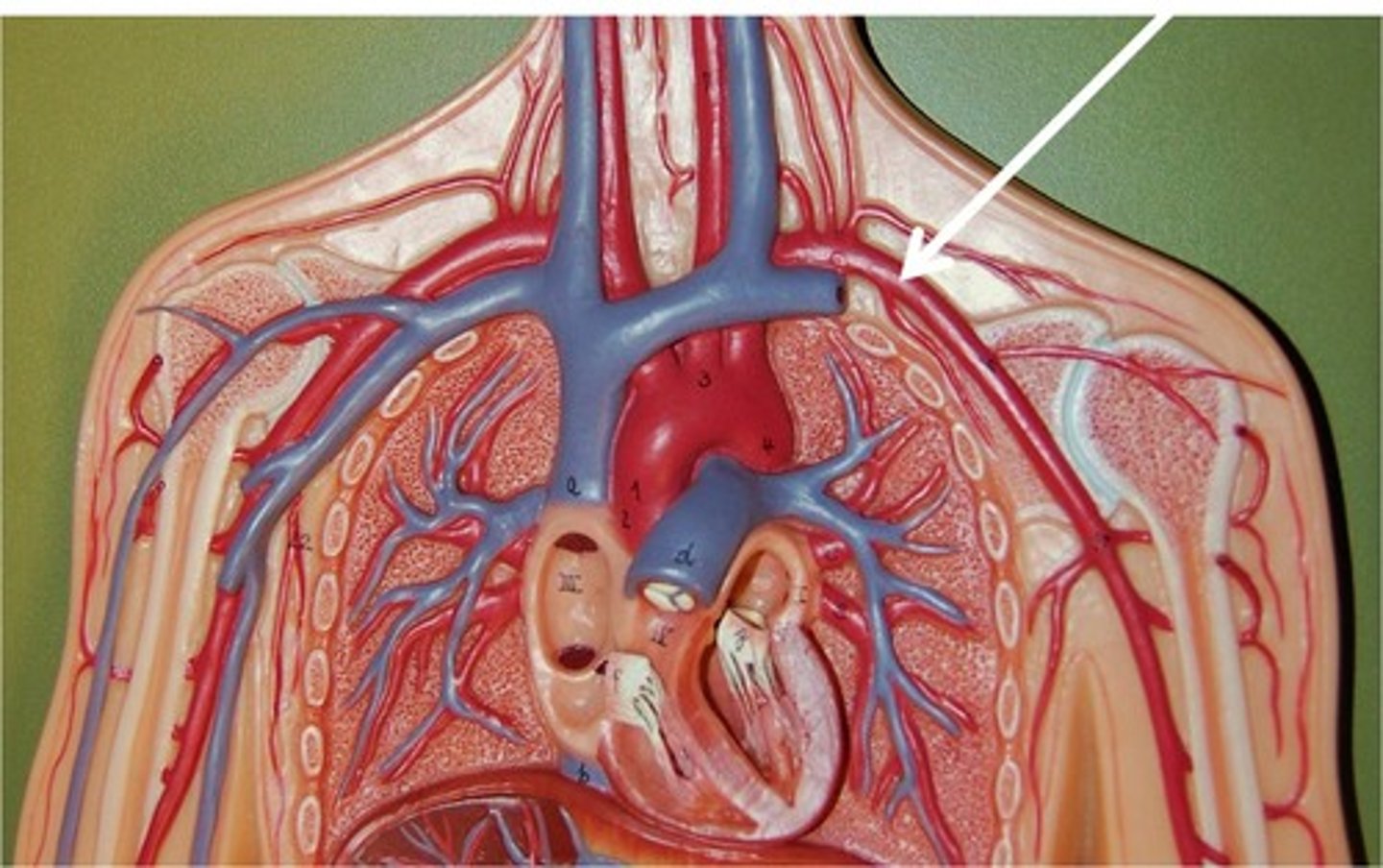
Veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart

Capillaries
Smallest and thinnest blood vessels where the exchange of molecules takes place

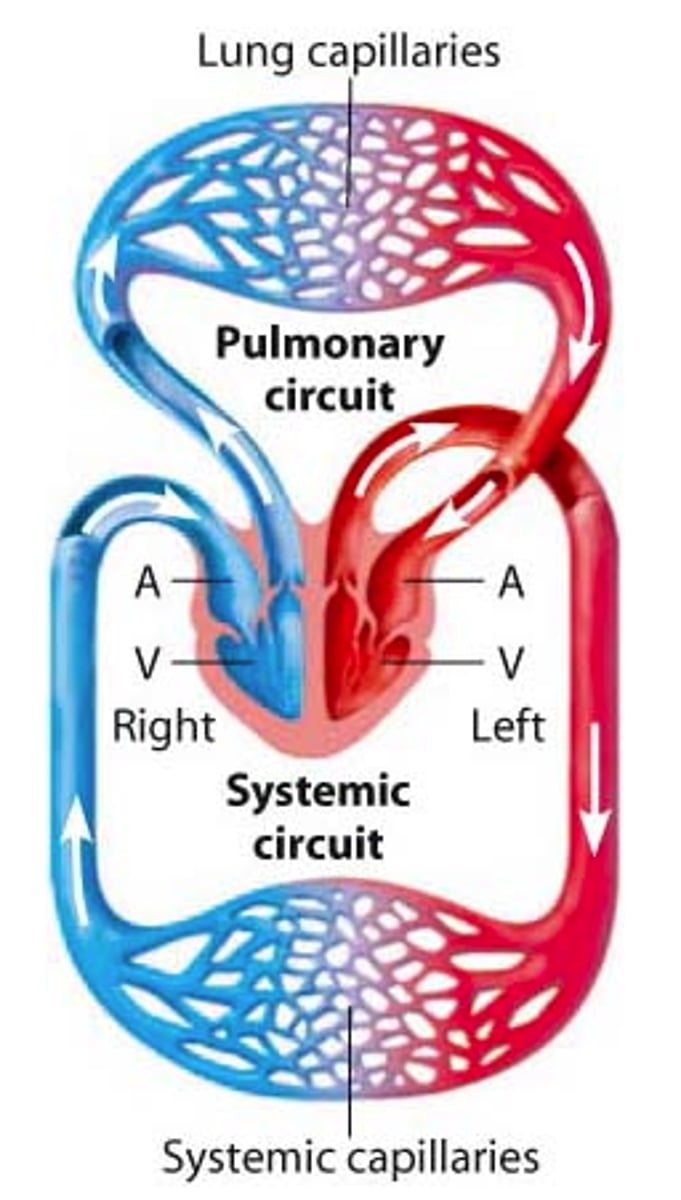
Double circulatory system
The human circulatory system is a double system that has a circuit linking the heart and lungs and a circuit that links the heart to the rest of the body
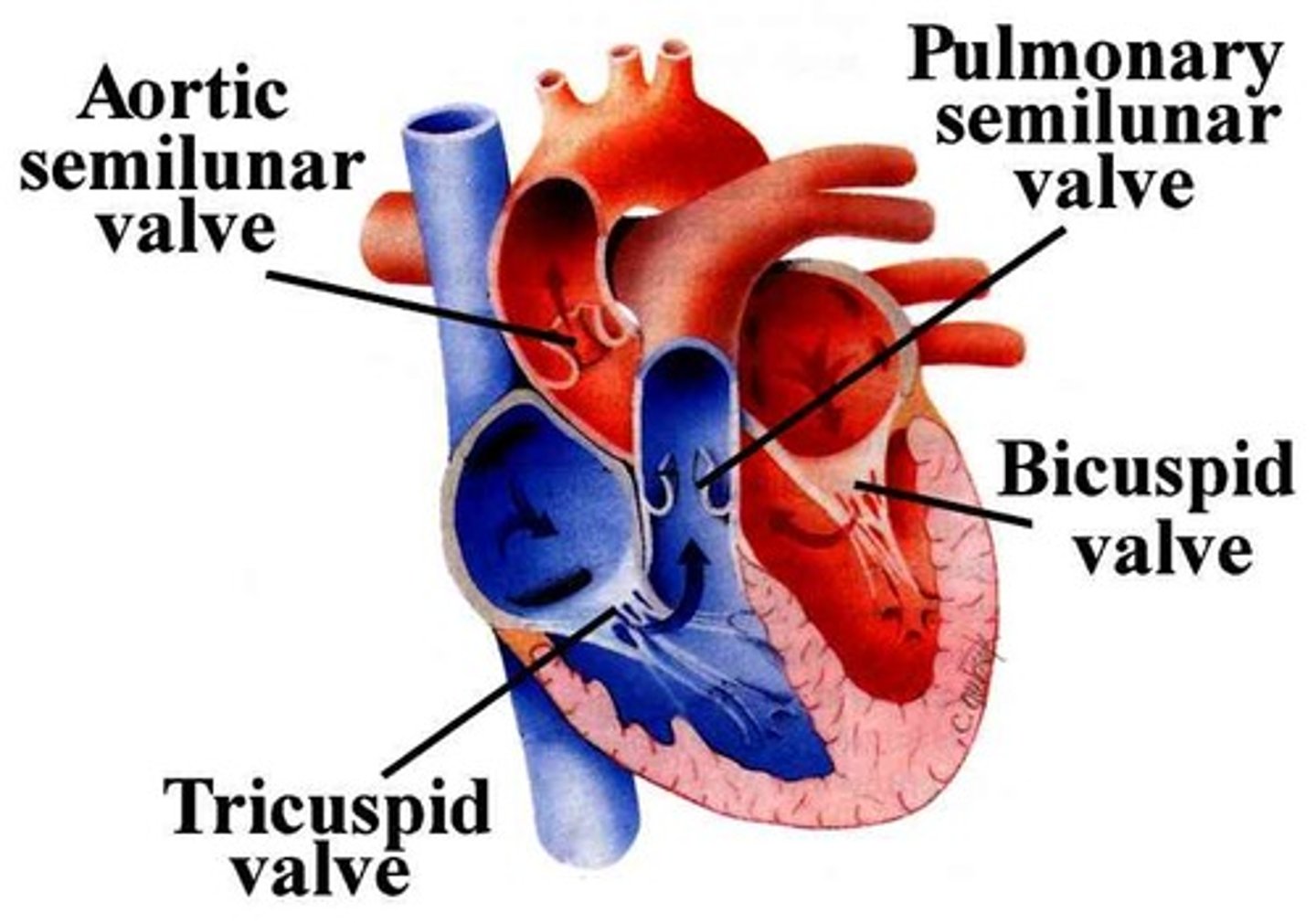
Tricuspid valve
The valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle, its role is to make sure blood flows the correct way through the atrium into the ventricle

Pulmonary valve
The semilunar valve positioned between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, it enables a regular flow of blood from the heart to the pulmonary artery and lungs
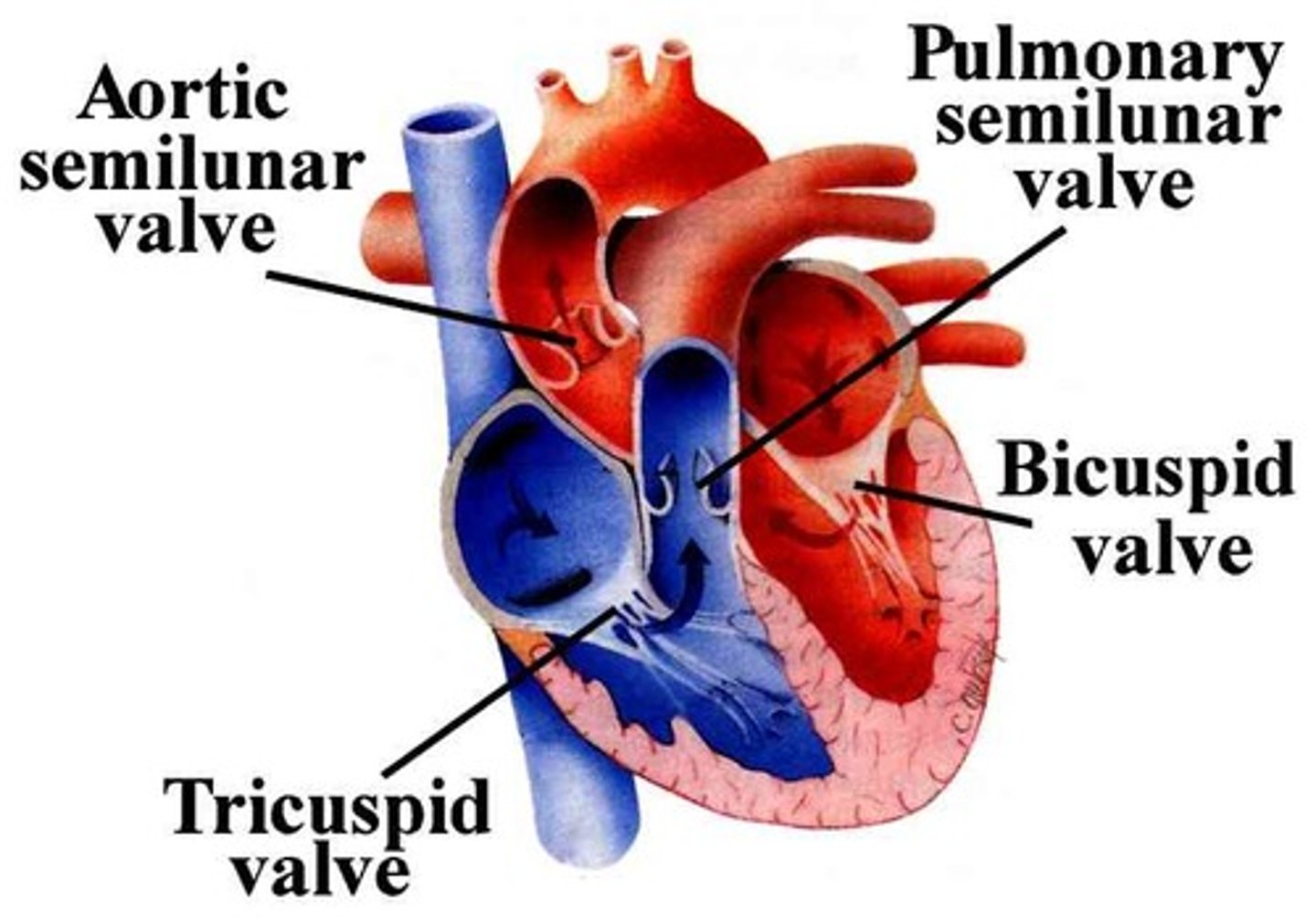
Mitral or bicuspid valve
The bicuspid valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle, its role is to make sure blood flows the correct way through the atrium into the ventricle
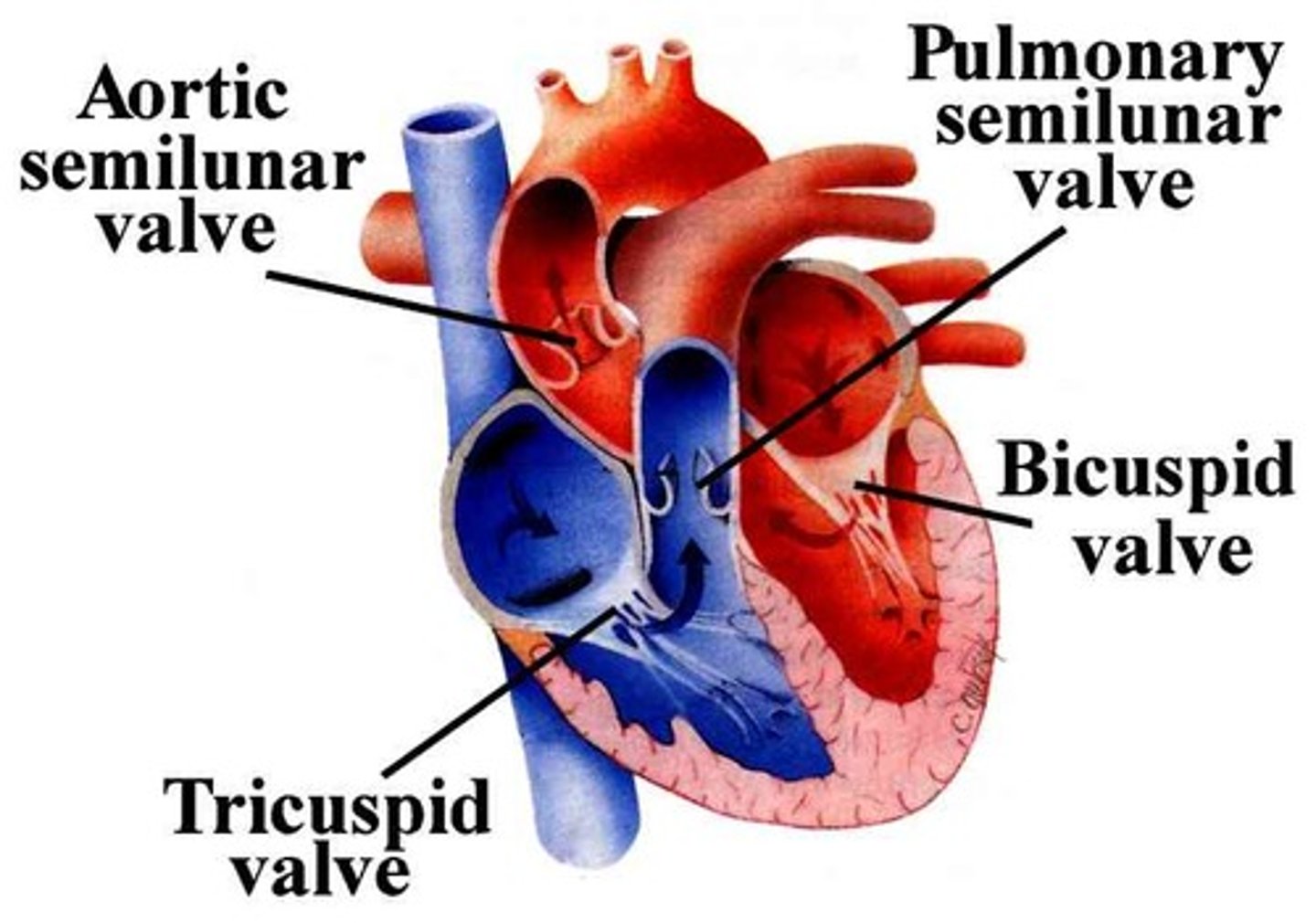
Aortic valve
The semilunar valve separating the aorta from the left ventricle, helps to keep blood flowing in the correct direction so that oxygenated blood can reach the rest of the body via the aorta