Unit 1 Biochemistry
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, typically with a hydrogen-oxygen atom ratio of 2:1. They serve as a major energy source and are important for structure and function in living organisms.
Proteins
Large biomolecules composed of amino acids, essential for various functions including catalyzing reactions, providing structure, and regulating body processes.
Amino Acids
are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins, featuring an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a unique side chain. Have the same base with differing R groups.
Lipids
The fats. Glycerol backbone with fatty acid tails. The longer the tail, the more energy storage there is
Nucleic Acids
RNA, DNA- made up of Nucleotides
Nucleotides
the structural units that make up nucleic acids, consisting of a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
Biological molecules
Essential to life, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Monosaccharide
the simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of a single sugar molecule.
Dehydration
Removing water
Synthesis
the process of combining two or more substances to create a new compound
Triglyceride
An ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids, serving as a major form of stored energy in organisms.
Ester
Chemical compound formed from an alcohol and an acid, often used in the formation of fats and oils.
Polypeptide formation
the process of linking amino acids together through peptide bonds to form a protein or peptide.
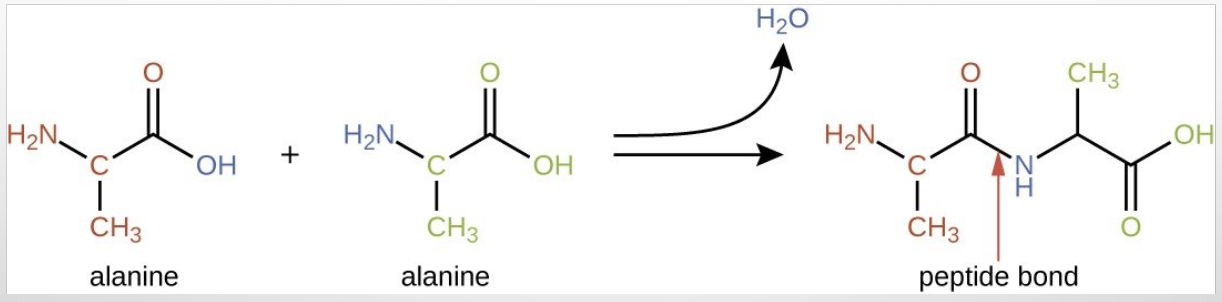
Nucleic acids
biomolecules essential for storing and transmitting genetic information, including DNA and RNA.
dehydration synthesis
is a chemical reaction that involves the removal of water to join two or more molecules, commonly seen in the formation of polymers.
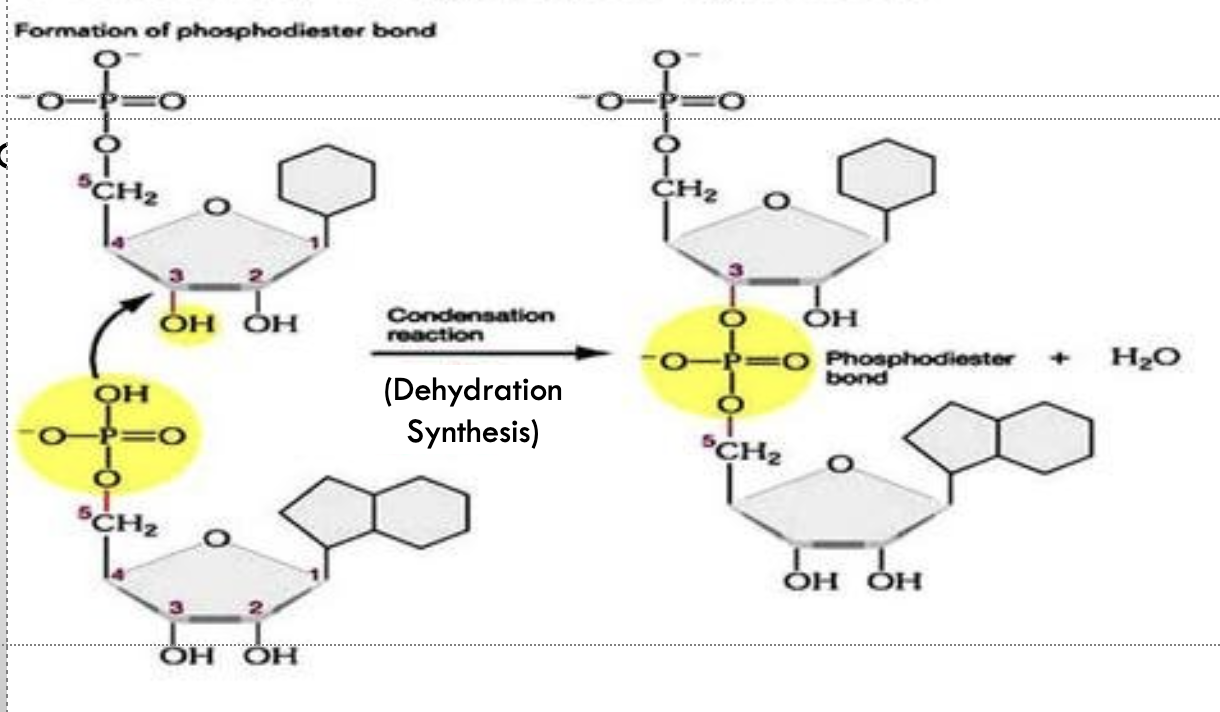
Hydrolysis
is a chemical reaction that involves the breaking of bonds in a molecule through the addition of water, often occurring during the breakdown of polymers.
Why is hydrolysis important
Its essential in digestion and metabolic processes, converting complex molecules into simpler ones.
monosaccharides
are the simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar molecules like glucose and fructose, which serve as building blocks for more complex carbohydrates.
disaccharides
are carbohydrates composed of two monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bonds, such as sucrose and lactose.
polysaccharides
are complex carbohydrates formed by long chains of monosaccharide units, such as starch, glycogen, and cellulose, serving as energy storage or structural elements in organisms.