Water Supply Week 14
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
sedimentation type determination
determines how particle settling velocity may be computed
Type I Sedimentation
particles settle discretely and do not flocculate (without interaction)
settle with a constant velocity
e.g., sand, grit
normal, “dropping” down, no interaction
Type II Sedimentation (flocculant settling)
particles flocculate while settling
size and velocity varying ➔ typically settling velocity increases with flocculation
e.g., particles formed during alum or iron coagulation, trickling filtration
reality, flocculation
Type III Sedimentation (zone settling)
settling of high concentration particles (i.e., > 1000 mgsolids/L)
particles settling as a mass
with a distinct clear zone and sludge zone
e.g., lime softening sedimentation, activated sludge sedimentation, sludge thickeners
very dense presence of solids
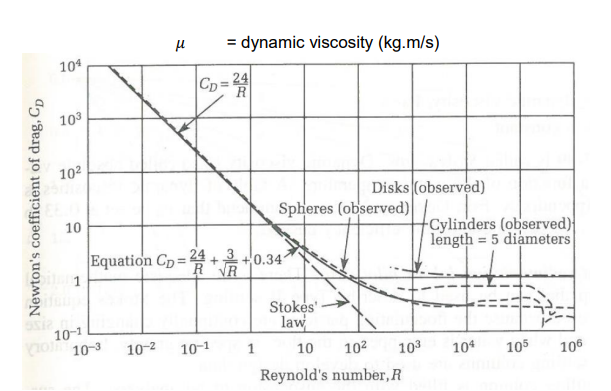
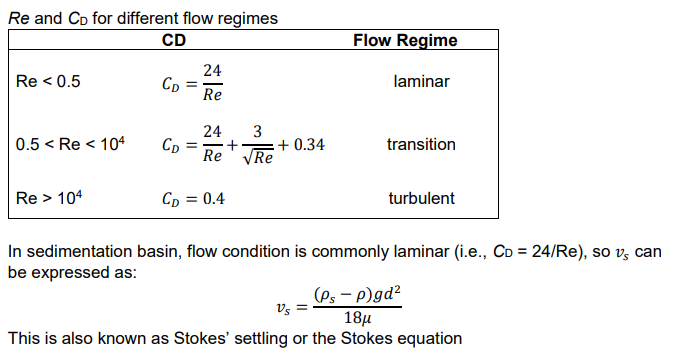
Particle Settling Velocity 𝒗s
dissolved or suspended matters (inorganics, organics) + algae
spectrophotometric measurements against standard solution
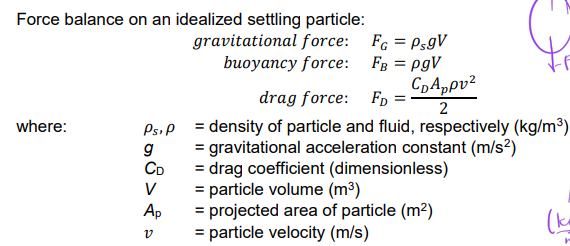

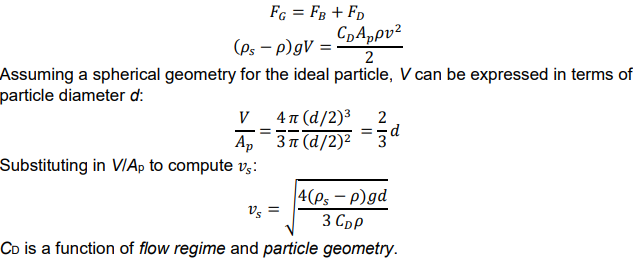
terminal particle settling velocity
At force equilibrium, the gravitational force is balanced by the sum of the buoyancy force and the drag force, so 𝑣 → vs
Reynolds’ number, Re
dimensionless number that evaluate a fluid’s inertial force to its viscous force
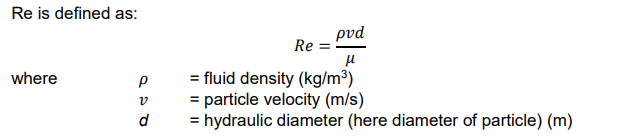
CD vs Re
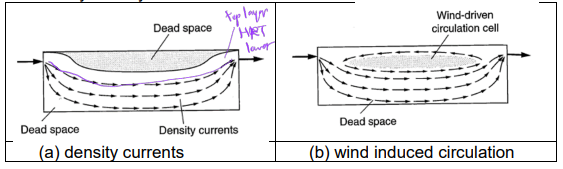
Non-Idealities in Settling: short circuiting of flow
(plug flow unrealistic)
a portion of the flow leaves the reactor before the bulk of the flow arrive at the exit
i.e., 𝑡̅ 𝑠𝑐 < 𝑡̅(or reduced effective volume)
induced by density difference or external force
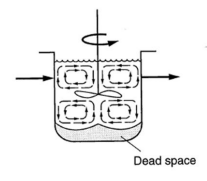
Non-Idealities in Settling: dead zone / space
regions in tank with poor flow condition
originated from reactor geometry (i.e., poor aspect ratio)
Non-Idealities in Settling: inlet position & baffle
- can alter and complicate velocity profiles
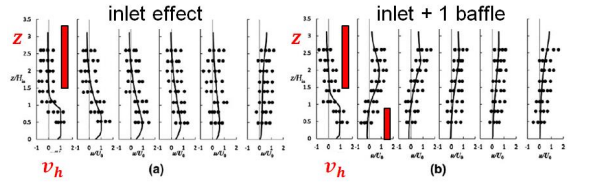
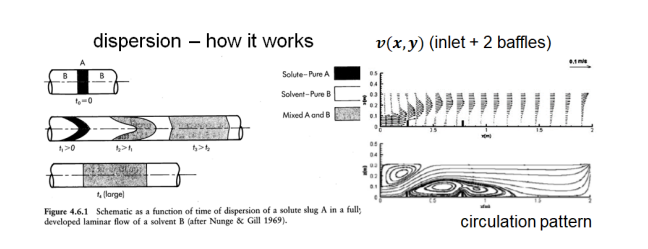
Non-Idealities in Settling: axial dispersion
axial spreading of particles (or chemicals) down concentration gradient
caused by velocity differences, turbulent eddies, and molecular diffusion
disinfection
reduce pathogens / microorganism in water to an acceptable level; not all organisms are destroyed during the process
sterilization
destruction of all organisms
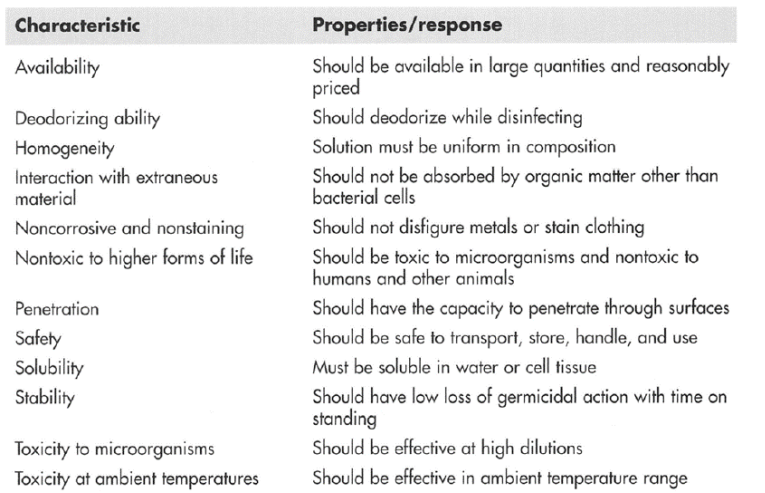
Characteristics of an Ideal Disinfectant
Disinfection Processes
a) Chemical agents
- mostly oxidizing chemicals - chlorine, bromine, iodine
- ozone, phenol and phenolic compounds, alcohols
- soaps, synthetic detergents, hydrogen peroxide
b) physical agents
- heat
- light
- sound wave (i.e., sonication)
c) mechanical means
- pathogens / microbes removed together with particles / colloids
d) radiation
- electromagnetic and acoustic radiation
- radioisotopes (e.g., Cobalt-60, 60Co) emit Gamma rays; used for sterilization because of their penetration power
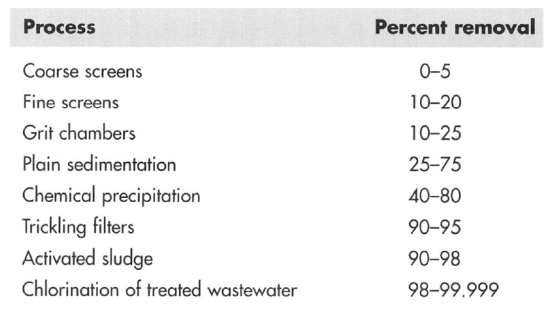
Bacterial Removal / Destruction Efficiency
Mechanisms of Disinfection
1) damage to cell wall
- cell lysis - materials within cell leak out - cell death
2) alteration of cell permeability
- chemicals such as phenolic compounds and detergents can alter permeability of cytoplasmic membrane - selective permeability of the membrane is destroyed - vital nutrients (e.g., N, P) leak out of the cell
3) alteration of colloidal nature of protoplasm
- heat, radiation, strong acids/alkalines can alter colloidal nature of the protoplasm - heat will coagulate cell proteins - acids/bases will denature proteins - proteins cannot function properly
4) alteration of organism DNA or RNA
- UV radiation can cause formation of double bonds in microorganisms as well as rupturing some DNA strands - when UV photons are absorbed by DNA in bacteria and protozoa, DNA and RNA in viruses, covalent dimers can be formed from adjacent thymines in DNA or uracils in RNA - formation of double bonds disrupts the replication process - consequently, the organism can no longer reproduce and is thus inactivated
5) inhibition of enzyme activity
- oxidizing agents (e.g., chlorine) can alter chemical arrangement enzymes and inactivate the enzymes - enzymes cannot perform required functions
Factors Influencing Disinfection Efficiency
1) type of disinfectant
2) contact time
3) concentration of disinfectant
4) temperature
5) type of organism / microbe
6) nature of solution (i.e., dissolved organic matter, suspended particles, chemistry of solution)
Disinfection Kinetics - Chick’s Law
- when microbe contains a single site vulnerable to a single unit of disinfectant, the rate of die-off follows Chick’s law:
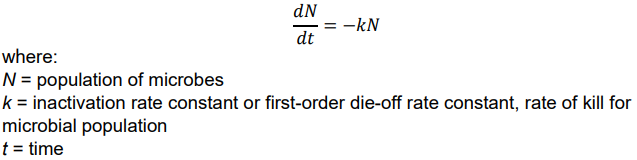
let N0 be initial microbe population (i.e., at t = 0), then
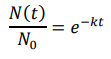
Role of Disinfectant Concentration
Herbert Watson observed inactivation rate related to disinfectant concentration:
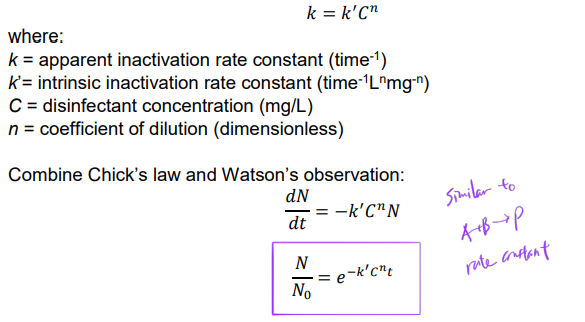
Assumptions
1) concentration C is constant with respect to time
2) well-mixed condition for both microbes and disinfectants (i.e., instantaneous well-mixed + homogeneous)
3) no time lag for disinfectant to reach vulnerable sites in microbes
Inactivation
- depicts the extent of microbial inactivation (or kill-off)
- fraction microbial population remain:


Ex. Determination the extent of inactivation (in log-inactivation) for a water undergoing a disinfection process with a k of 0.2 h-1 for 1 h.
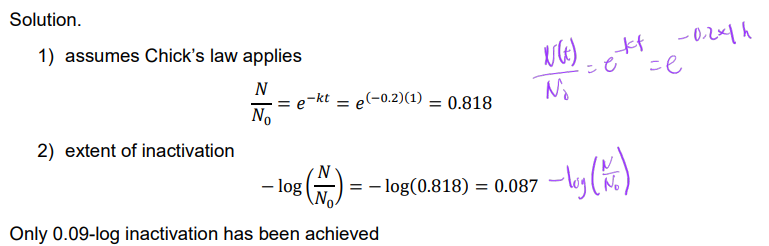
Disinfection Temperature
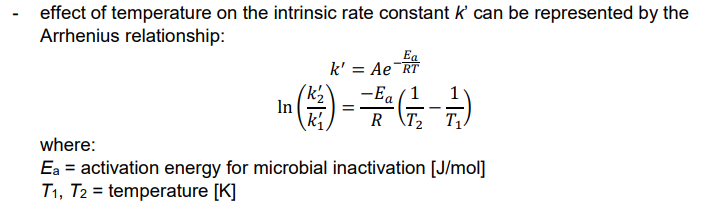

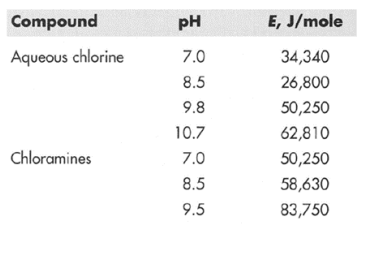
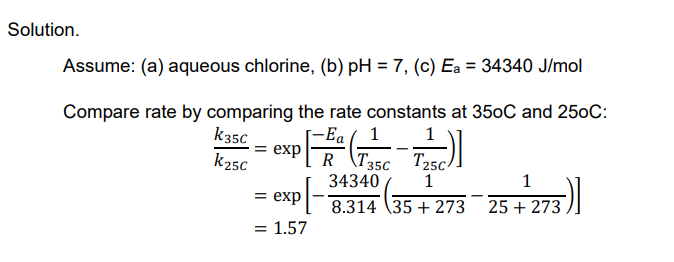
Ex. Compare the inactivation rates of chlorine disinfection at 35oC and 25oC. Assume that the treated water has a pH of 7.0.
C-T Curve
can achieve extent of inactivation by controlling 1) concentration of disinfectant residual and 2 contact time

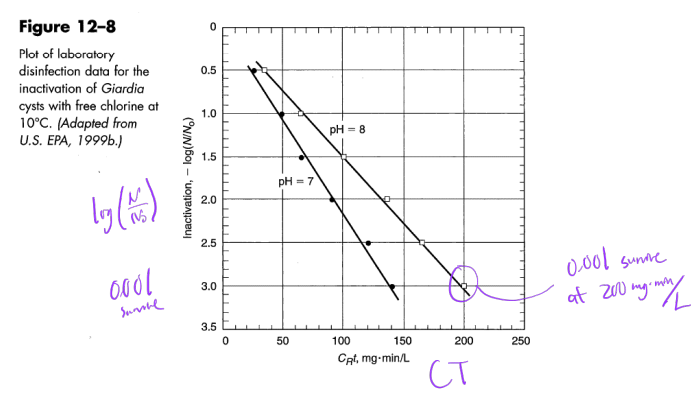
Ex. Determine the contact time needed to achieve a 1 log-inactivation of Giardia cysts using 5 mg/L free chlorine at 10oC and pH 7
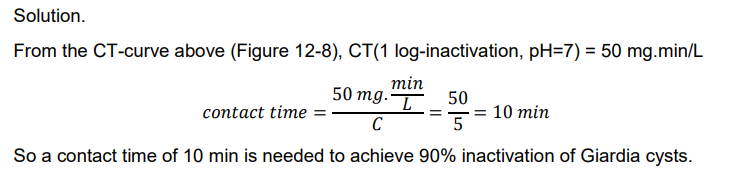

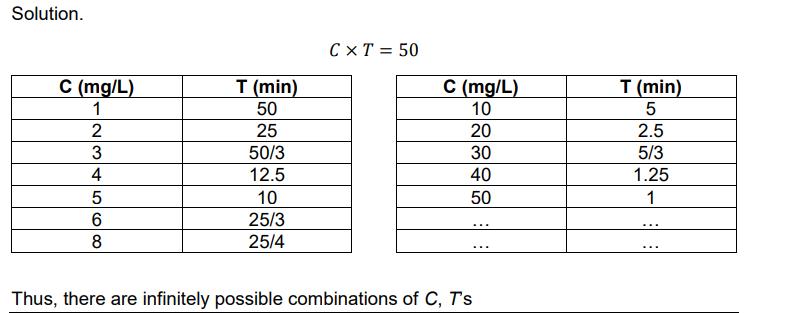
Ex. What are the combinations of C and T for a CT value of 50 mg.min/L?
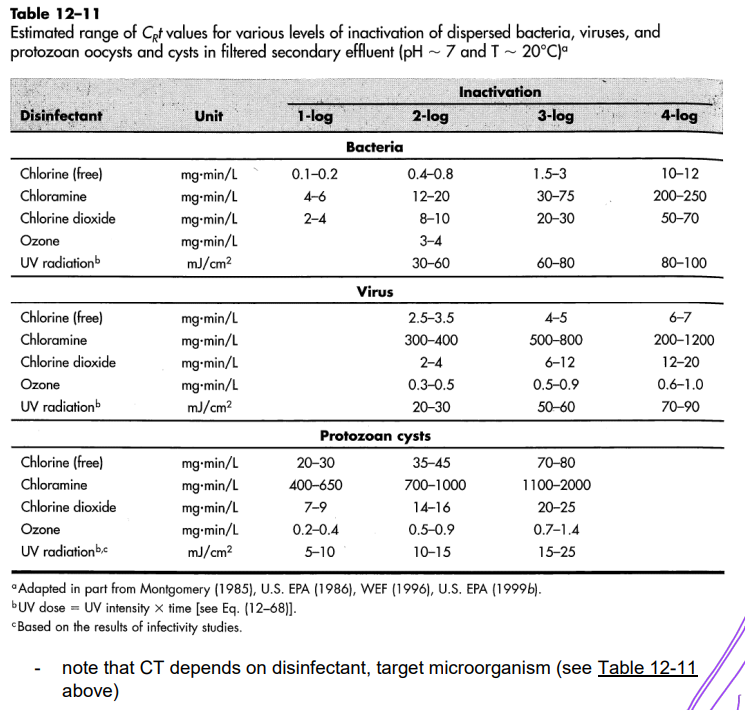
Estimated range of CRt values